Hematology/Body Fluids Week 6
1/243
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
244 Terms
Differentiate qualitative and quantitative disorders of granulocytes
-Qualitative = A change in structure or function of the granulocytes.
-Quantitative = an increase or decrease in the number of granulocytes
Give examples of quanitative disorders
CML
LR
Give examples of qualitative disorders
Pelger Huet
May Hegglin
Chediak Higashi
Alder Reilly
Describe a shift to the left. What disorders cause it?
Increase in immature granulocytes (ex. LR and CML)
Describe a right shift. What disorders cause it?
Increase in more mature cells, characterized by hypersegmented neutrophils (ex. pernicious anemia and other megaloblastic anemias)
Define a hypersegmented neutrophil
Greater than 5 lobes
What are Auer rods?
Fused primary granules
What is toxic granulation?
prominent purplish to bluish-black granules in the cytoplasm of segs; probably made of left-over primary granules
What are Dohle bodies?
Light blue/blue-gray inclusions in the cytoplasm of segs (made of RNA remnants/endoplasmic reticulum)
What are vacuoles?
phagocytic, colorless, hole-like inclusions in the cytoplasm of segs (and monocytes) that indicate degenerative changes
When are toxic granulation, vasuoles, and Dohle bodies seen?
In patients with bacterial infection, inflammation, burns, chemotherapy, and other toxic states
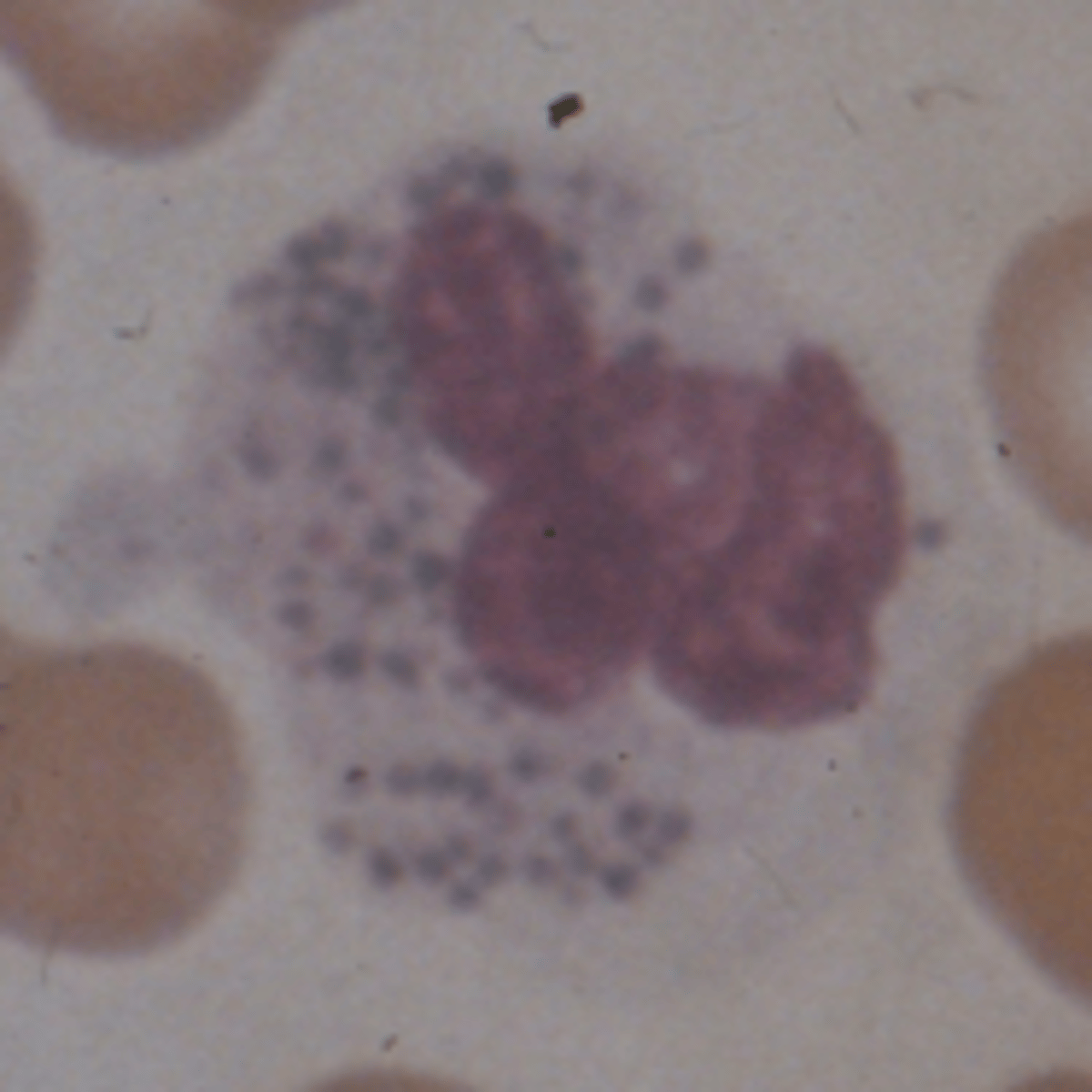
What are the causes of Alder-Reilly
Automsomal recessive causing lysosomal enzyme deficiency that metabolizes mucopolysaccharides, which accumulate in tissue
What are the clinical findings in Alder Reilly?
-Skeletal deformity (gargoylism)
-Associated with Hurler's/Hunter's syndromes
-Shortened lifespan
What are the blood/lab findings in Alder Reilly?
Large deep purple to lilac granules in segs, basos and eos
What is often confused with Alder Reilly granules? How can the two be differentiated?
Toxic granulation; Alder Reilley granules are larger, more uniform and more evenly distributed in cells and among cells in same patient
What is the cause of May Hegglin?
Autosomal dominant causing abnormal platelet function and shortened platelet life span
What are the clinical findings in May Hegglin?
-Mild to severe bleeding
-Increased risk of infection
What are the lab/blood findings in May Hegglin?
-Abnormal/Giant platelets
-Thrombocytopenia
-Dohle-like bodies in segs, basos, eos, monos
What is the cause of Pelger Huet?
Autosomal dominant causing defective DNA metabolism
What are the clinical findings in Pelger Huet?
Benign condition, so far as we know; the main problem is if a tech miscalls the segs as being immature or a shift to the left
What are the blood/lab findings in Pelger Huet?
-Hyposegmented neutrophils (1-2 lobes)
-Round dumbell/peanut/pince-nez shape nucleus
-Chromatin darker, clumpier than normal segs
What causes pseudo Pelger Huet?
Burns, toxic drugs, certain leukemias
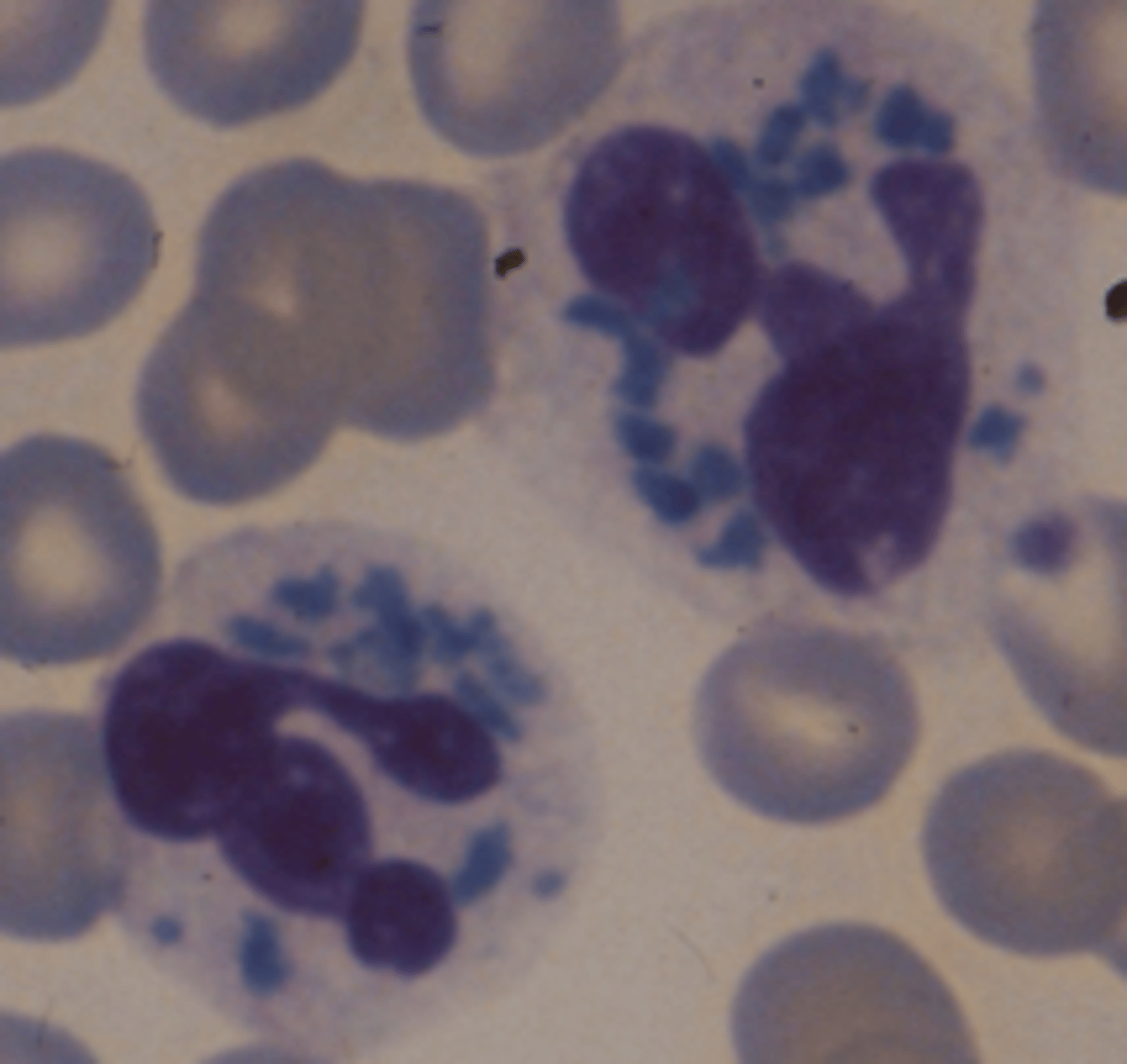
What causes Cediak-Hiagshi?
Autosomal recessive that causes defective lysosomes that destroy phagocytized bacteria and other material during bacterial infections
Clinical findings in Chediak Higashi
-Albinism
-Light sensitivity
-Mild bleeding
-Thrombocytopenia
-Neutropenia
-Recurrent bacterial infections
-Shortened life span
Lab/blood findings in Chediak Higashi
-Large fused oval/round/elongated granules (gray-blue in segs and red-purple in lymphs or monos)
How can CML be differentiated from LR?
CML
-WBC count 50,000-500,000
-Increased eos and basos
-No toxic granules/Dohle bodies/vacuoles (unless in treatment)
-Anemia
-LAP <20
-Philadelphia chromosome t(9;22)
LR
-WBC 5,000-30,000
-Band predominant cell
-Segs do have toxic granulation/Dohle bodies/vacuoles
-No anemia
-Lap >100
-No Philadelpha chromose
Describe the Philadelphia chromosome
t(9;22)
Sudan Black (SBB) positive cell line, substance stained, and diagnostic value
-Stains lipids in Myeloblasts
-positive in AML M1-M4
Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) positive cell line, substance stained, and diagnostic value
-Stains glycogen
-Positive in Erythroleukemia (AEL/M6) and ALL (Block)
Peroxidase (MPO) postive cell line, substance stained, and diagnostic value
-Stains myeloperoxidase in the granules of myeloblasts
-Positive in AML M1-M4
Tartrate-Resistant Acid Phosphatase (TRAP) positive cell line, substance stained, and diagnostic value
-Stains tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase in hairy cell lymphs
-Positive in hairy cell leukemia
Specific esterase chemical name
Napthol AS-D chlorocacetate
Specific esterase positive cell line, substance stained, and diagnostic value
-Stains esterase in granulocyte precursors in cytoplasm
-Positive in AML M1-M4 and M6
Nonspecific esterase chemical name
a-napthol acetate or butyrate
Nonspecific esterase positive cell line, substance stained, and diagnostic value
-Stains non-specific esterase in monocyte precursors in cytoplasm
-Positive in AML M4 and very positive in AML M5
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase (LAP) positive cell line, substance stained, and diagnostic value
-Stains lekocyte alkaline phosphatase in specific granules of more mature cells
-<20 in CML and >100 in LR
What are two outstanding characteristics of most leukemias?
-it is a malignant, unregulated proliferation of cells in bone marrow that may infiltrate other organs (liver, spleen, lymph nodes)
-it compromises normal blood cell production
What are six predisposing factors of leukemia?
-radiation
-certain chemicals
-viruses (HTLV, EBV)
-hereditary factors (Down's syndrome)
-primitive immune defects
-myeloproliferative disorders
What are the symptoms of leukemia?
-fever
-night sweats
-fatigue
-weakness
-pallor
-petechiae
-bleeding
-weight loss
What are the major types of leukemia based on cell line?
-Myelogenous (granulocytes, monocytes, erythrocytes, megakaryocytes)
-Lymphocytic (lymphocytes and plasmacytes)
List the traits of acute leukemia
-all ages
-sudden onset
-lasts weeks to months
-Predominant cell is blast
-mild to severe anemia
-mild to severe thrombocytopenia
-variable WBC count
-Mild organomegaly
List the traits of chronic leukemia
-Adult age
-Gradual onset
-Lasts months to years
-Predominant cell is mature cells
-Mild anemia
-Mild thrombocytopenia
-Increased WBC
-Prominent organomegaly
What is FAB classification based on?
-cellular morphology in PBS and BM
-Requires >30% blasts to diagnose acute leukemias
-now uses cytochemical staining
What is the WHO classification based on?
-cell lineage (immunophenotyping)
-cellular morphology in PBS and BM
-Requires >20% blasts to diagnose acute
-Genetic features
-Clinical syndrome/prognosis/treatment
How does FAB distinguish acute myelocytic leukemia from acute lymphatic leukemia?
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)- stains intranuclear enzyme; positive in immature lymphoblasts (L1 and L2 positive)
Acute myelocytic anemia (AML) PBS
-5,000-30,000 (may be anywhere from 1,000 to 200,000)
-Triad: neutropenia, erythrocytopenia, and thrombocytopenia
-15-95% blasts, which may have azurophilic granules
-auer rods in myeloblasts
AML other lab findings
-increased uric acid and LDH from cell turnover
-increased calcium from bone resorption
-serum and urine miramidase is elevated in monocytic leukemias (M4-5)
M1 description, PBS, staining, and characteristics
-AML without maturation past blast stage
-Predominant cell is myeloblast
-Myeloblasts have auer rods in 50% of patients
-SBB, MPO, and Specific esterase positive
M2 description, PBS, staining, and characteristics
-Most common AML
-AML with maturation
-Predominant cell is myeloblast
-Auer rods in myeloblasts in 70% of patients
-Maturation past blasts often seen
-Increased eos and basos
-Psuedo Pelger-Huet
-MPO, SBB, specific esterase positive
M3 description, PBS, staining, and characteristics
-APL, PML
-Predominant cell is promyelocyte
-Multiple bundles of auer rods
-t(15;17)
-SBB and MPO positive
-DIC often seen
M4 description, PBS, staining, and characteristics
-Second most common AML
-AMMOL
-Gum infiltration and bleeding
-Predominant cells are myeloblasts and monoblasts
-M4Eo hasmoderate eosiniphilia
-M4Eo = inv(16) or del (16)
-M4 = del(11)
-Myeloblasts are MPO, SBB, specific esterate positive
-Monoblats are non-specific esterase positive and inhibited by fluoride
-Incerased urine/serum muramidase
M5 description, PBS, staining, characteristics
-AMOL, Schilling's leukemia
-M5a: >80% monoblasts
-M5b: >80% are promonocytes and monocytes
-Infiltration of gums and skin rash common
-Serum/urine muramidase
-Nonspecific esterase positive and fluoride inhibited
-M5a: t(9;11)
-M5b: t(8:16)
-DIC prevalence second to M3
M6 description, PBS, staining, characteristics
-AEL (acute erythroleukemia)
-DiGuglielmo's leukemia
-more common in adults over 50
-very rare
-Erythroblasts and bizzare/large nRBCs
-Myeloblasts
-BM: 50% erythroblasts, 30% myeloblasts
-PAS and specific esterase positive
-Increased LAP score
M7 description, PBS, staining, characteristics
-AMEGL
-rarest
-middle aged men
-Pancytopenia and megakaryoblasts and atypical megakaryocytes
-BM: >30 megakaryoblasts and "dry" tap bone marrow (fibrotic)
-Platelet peroxidase positive and factor VIII positive
What four chromosomal abnormalities are useful for diagnosis?
M2: t(8;21)
M3: t(15;17) diagnostic
M4a: del(11)
M4Eo: inv(16) or del(16)
CML age affected, clinical findings, lab findings
-Middle aged adults (40-59)
-Anemia N/N
-Splenomegaly sommon
-50% have hepatomegaly
-Bone tenderness
-Fatigue, fever, night sweats, weight loss
-50,000-500,000 WBC
-Severe left shift
-Increased eos and basos
-Normal to greatly increased platelets
-<20 LAP
Two main causes of death in leukemia patients
-hemorrhage
-overwhelming infections
Name three types of treatment for leukemia
-Radiation
-Chemotherapy
-Bone marrow transplant (most successful)
Myeloblast
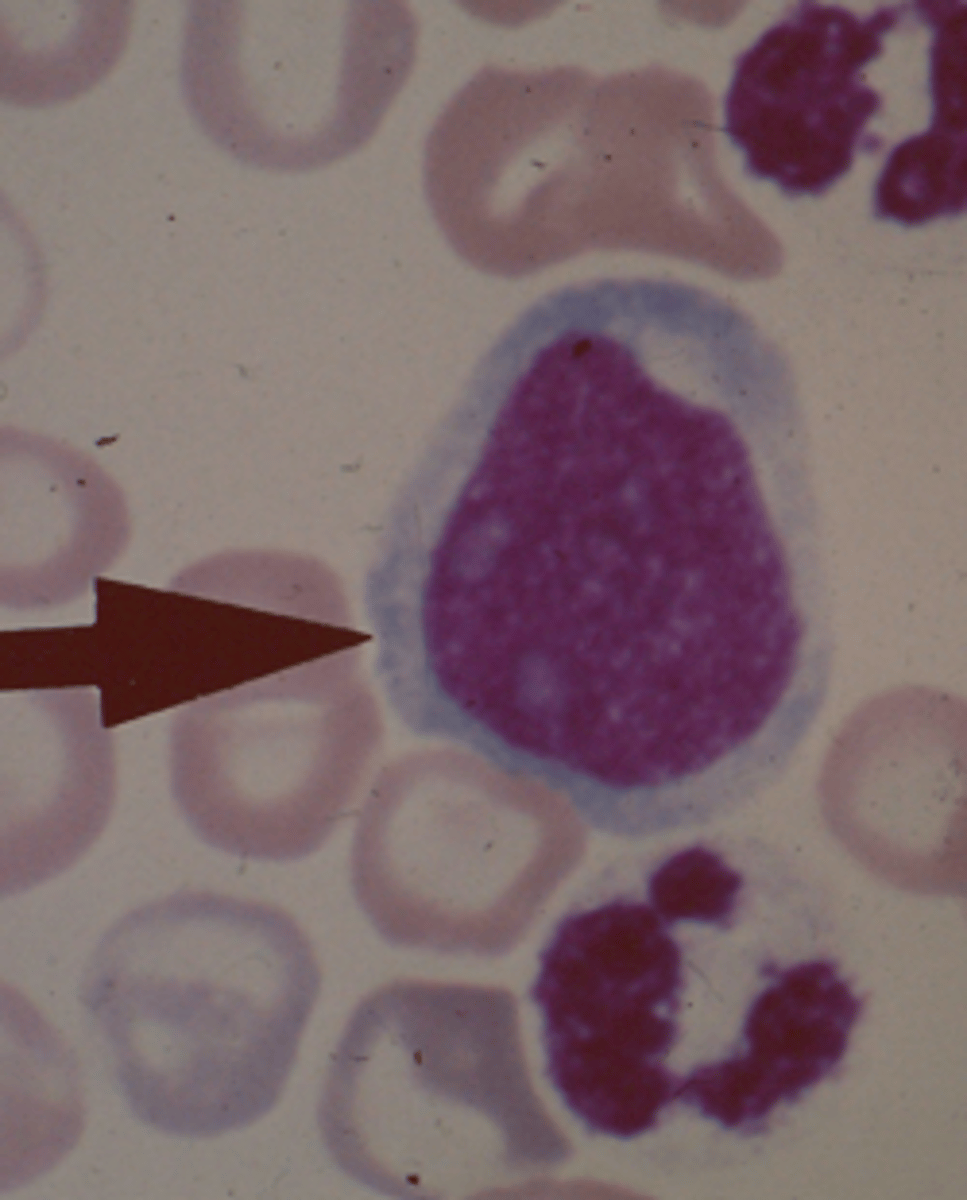
Promyelocyte
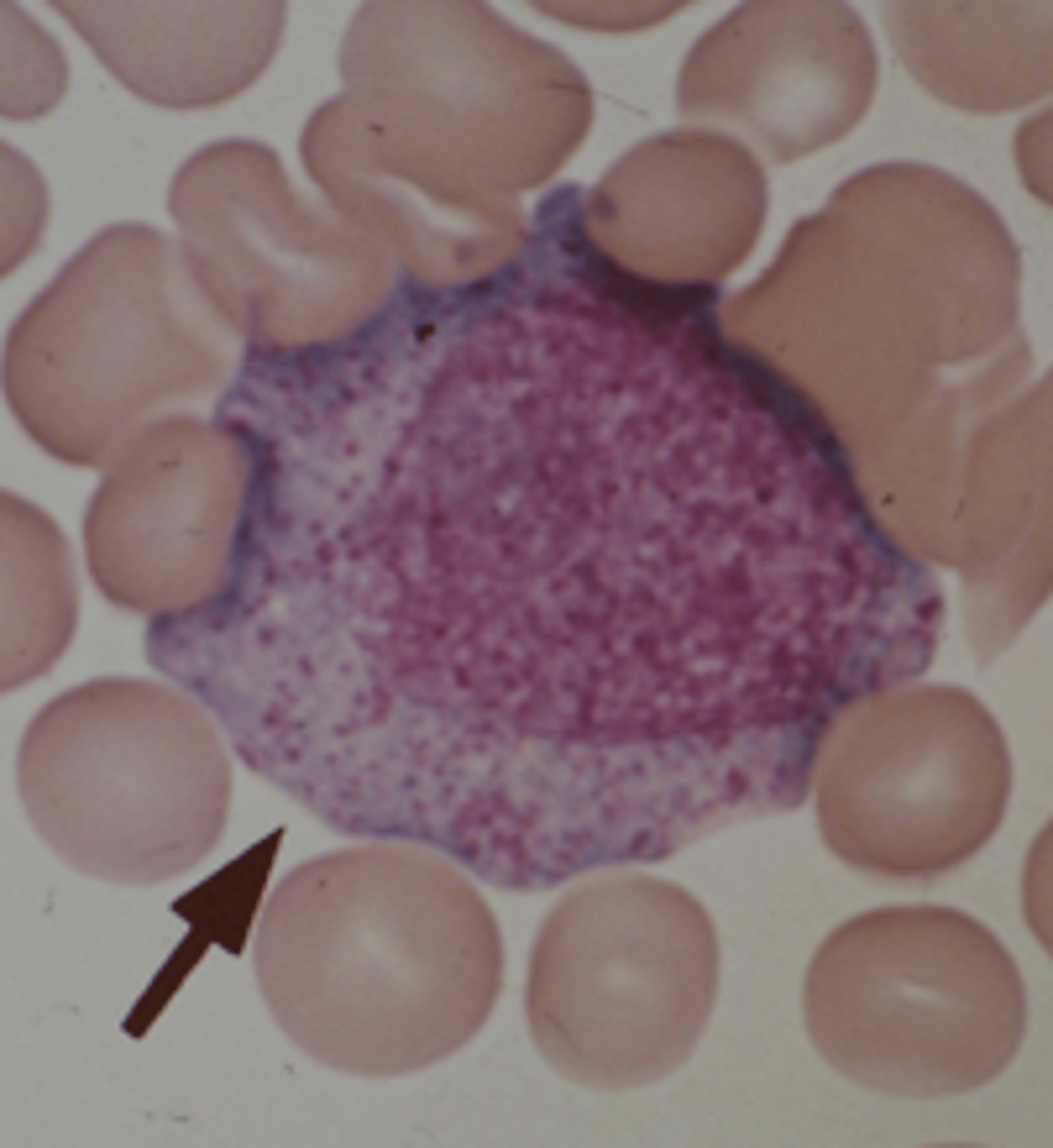
Myelocyte
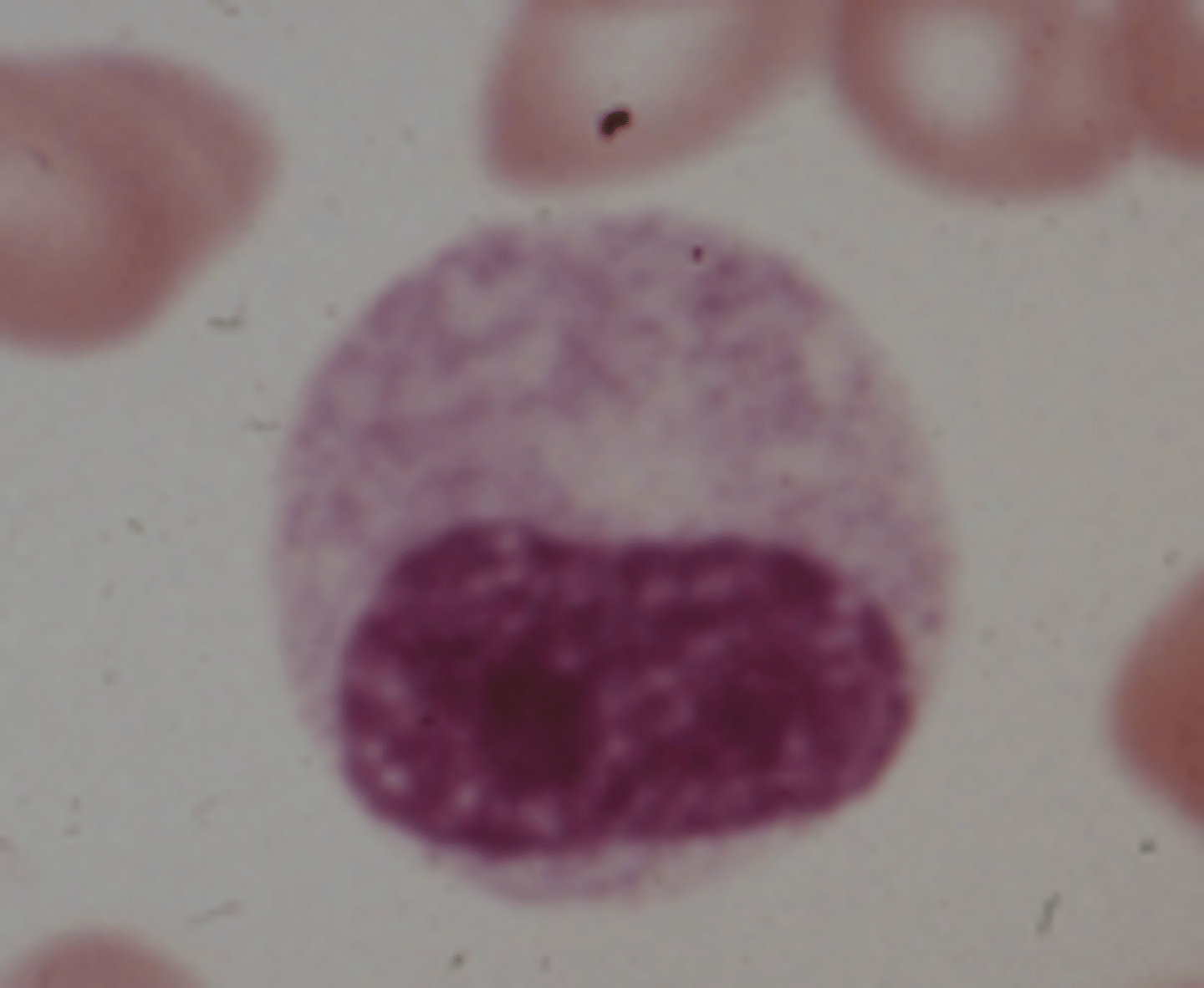
Metamyelocyte
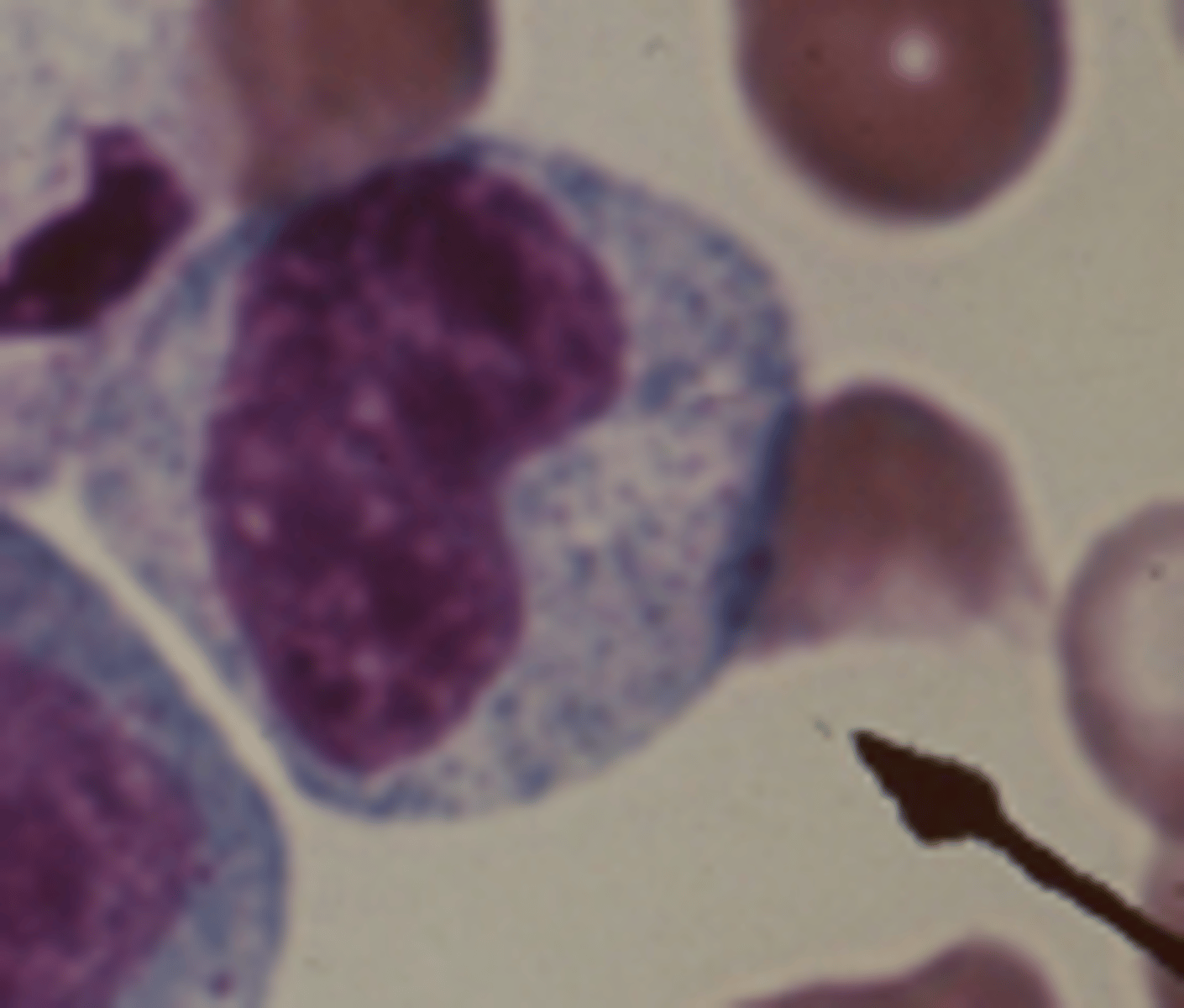
Band
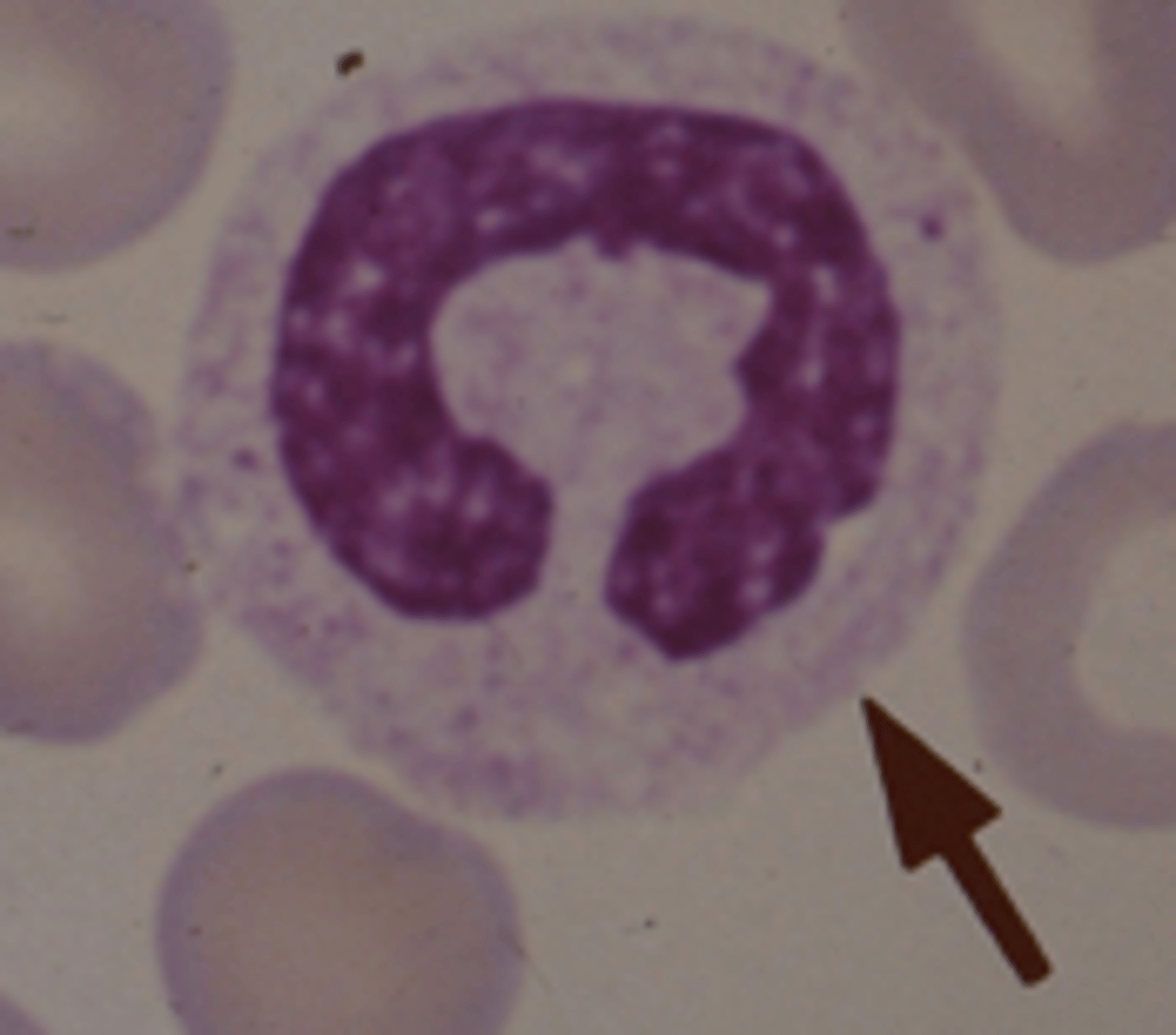
Neutrophil
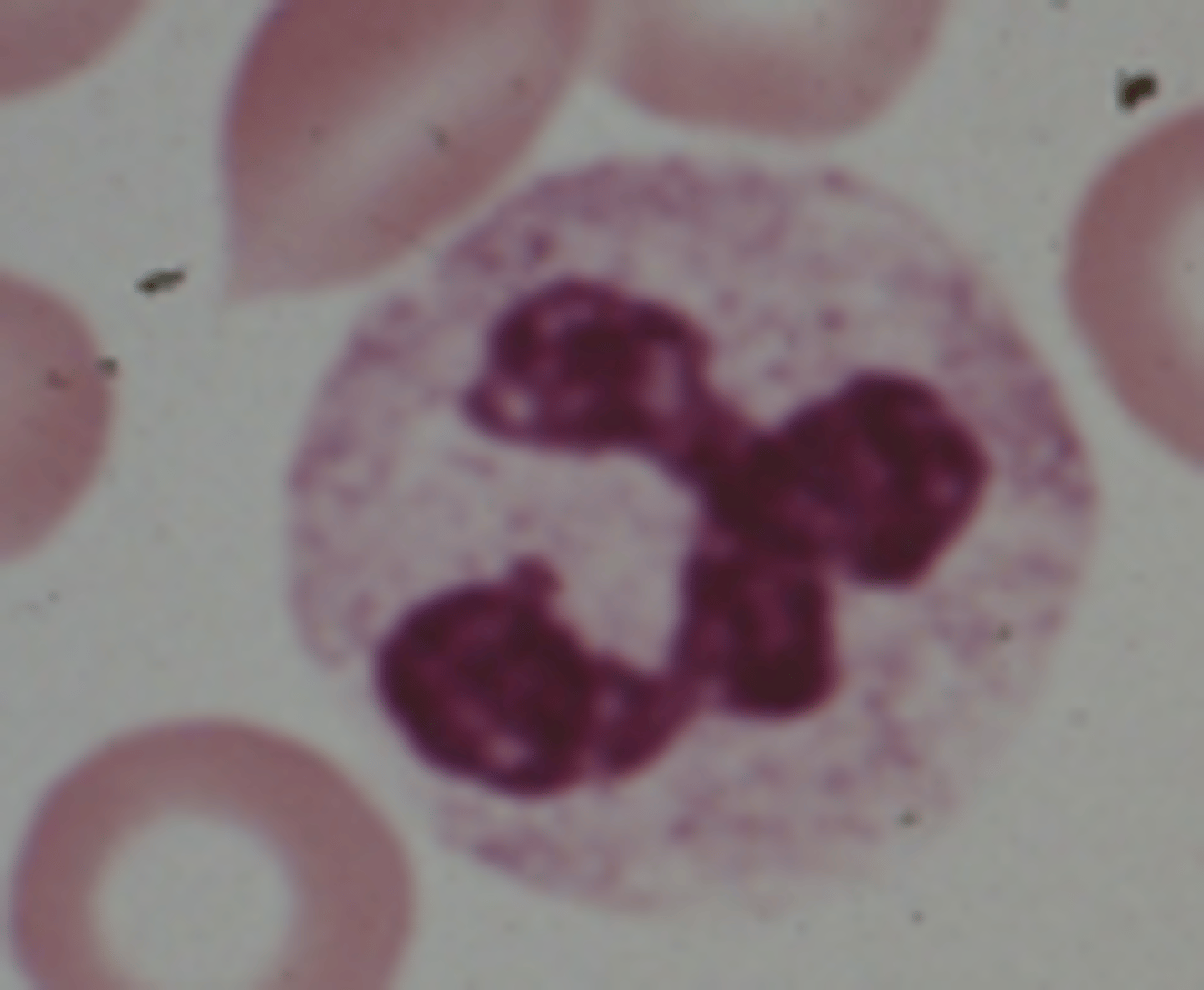
Acute
Acute or Chronic Leukemia?
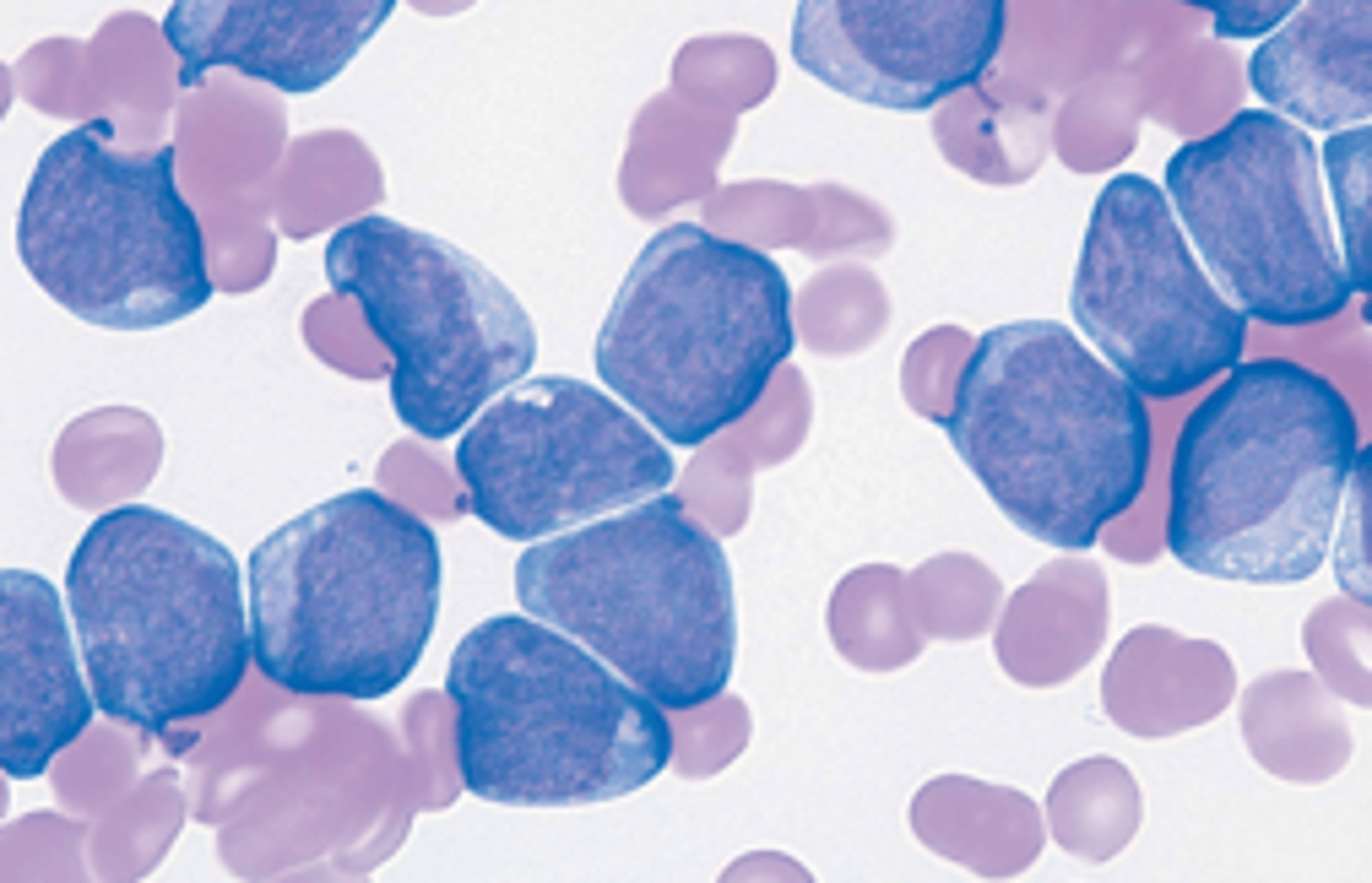
Chronic
Acute or Chronic leukemia?
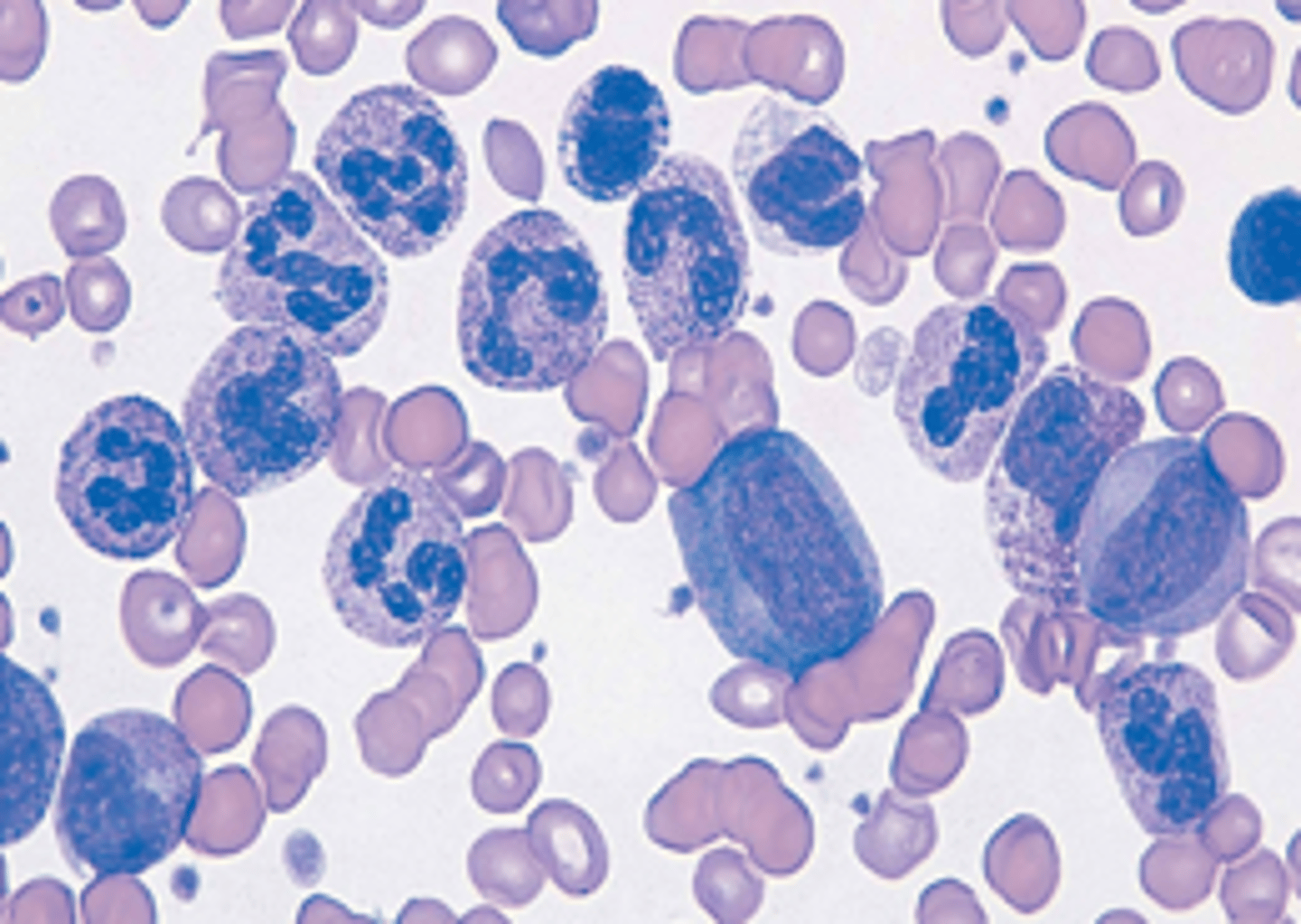
Hypersegmented neutrophil
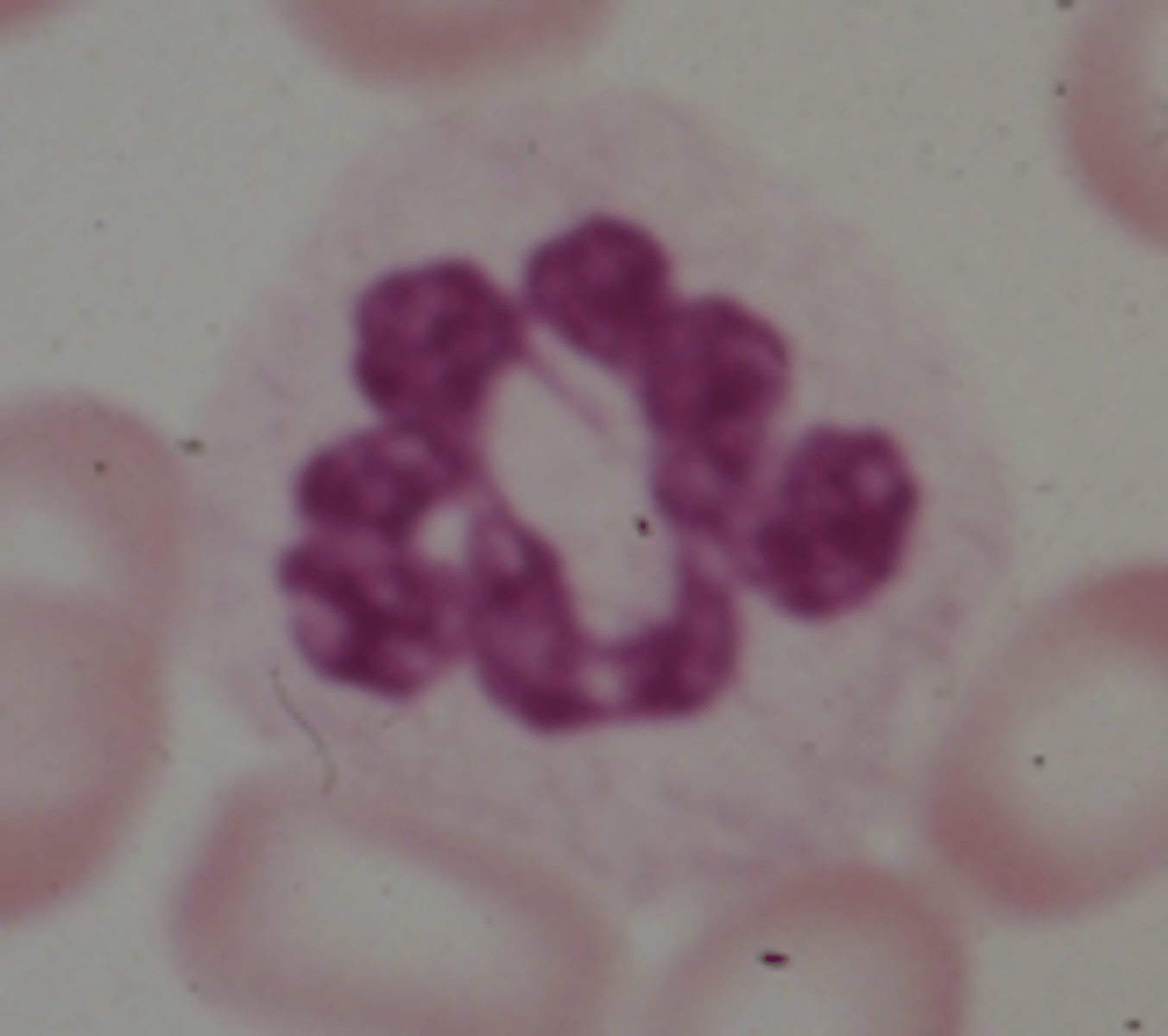
Toxic granulation
What inclusion?
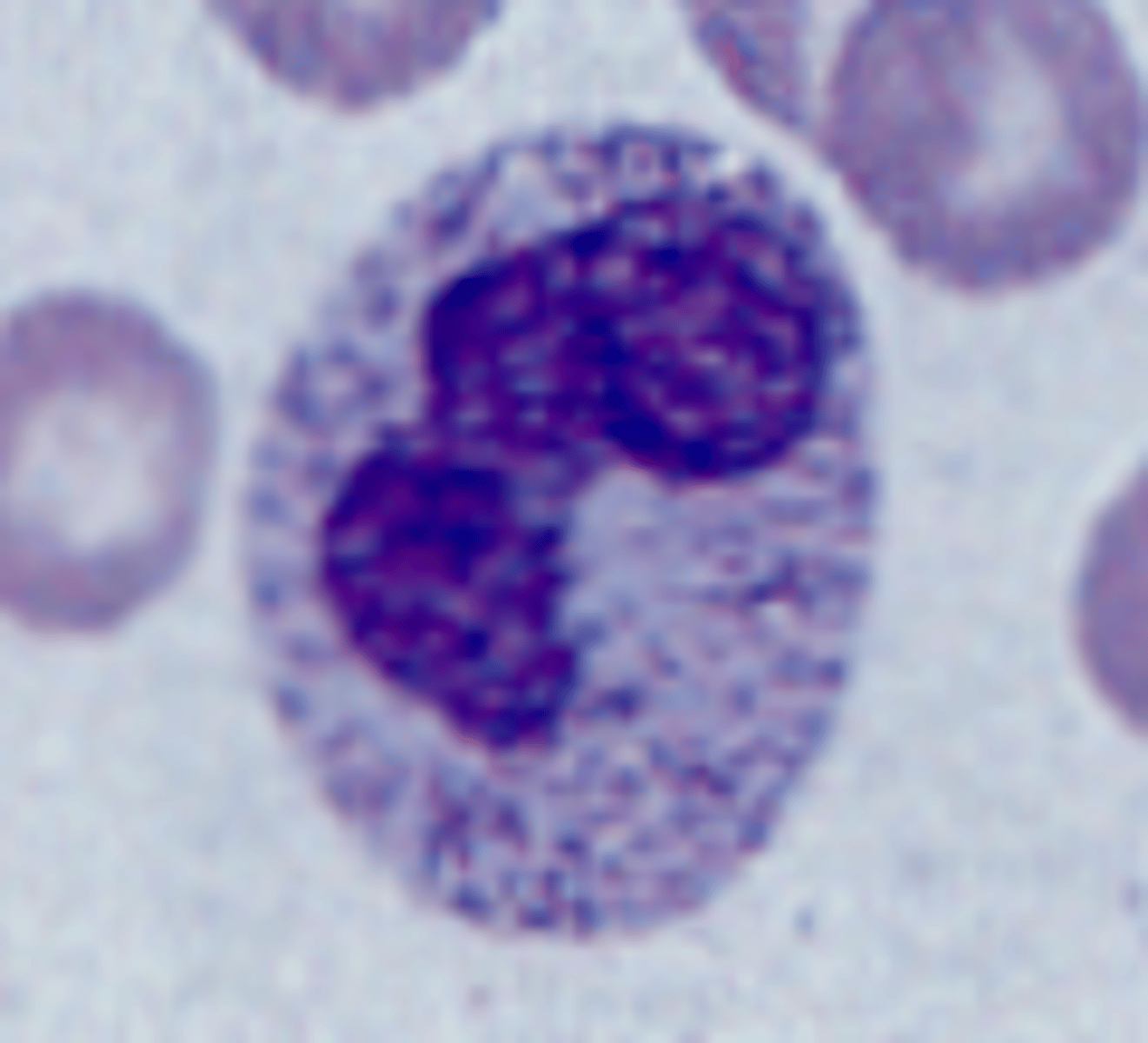
Vacuoles
What inclusion?
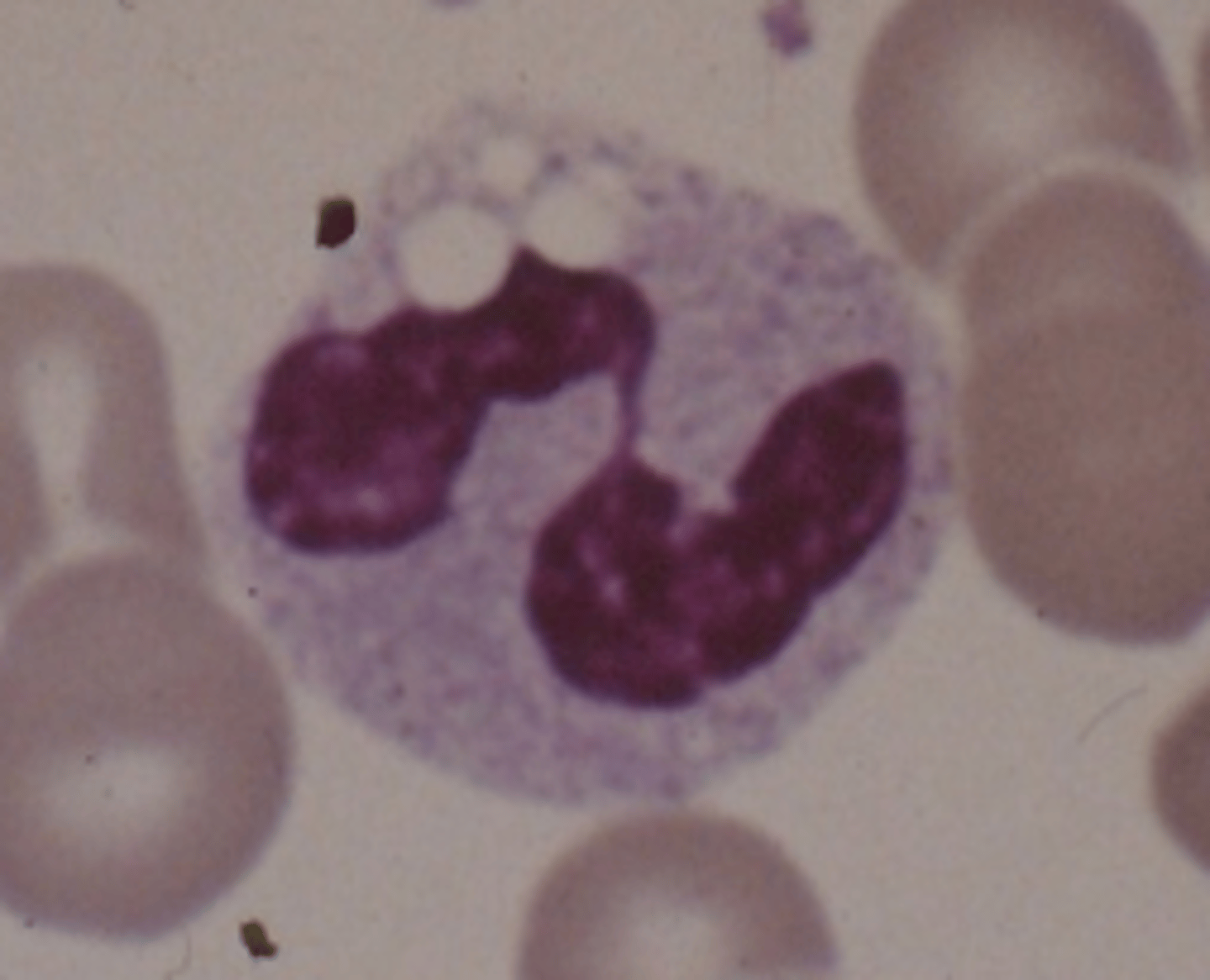
Dohle body
What inclusion?
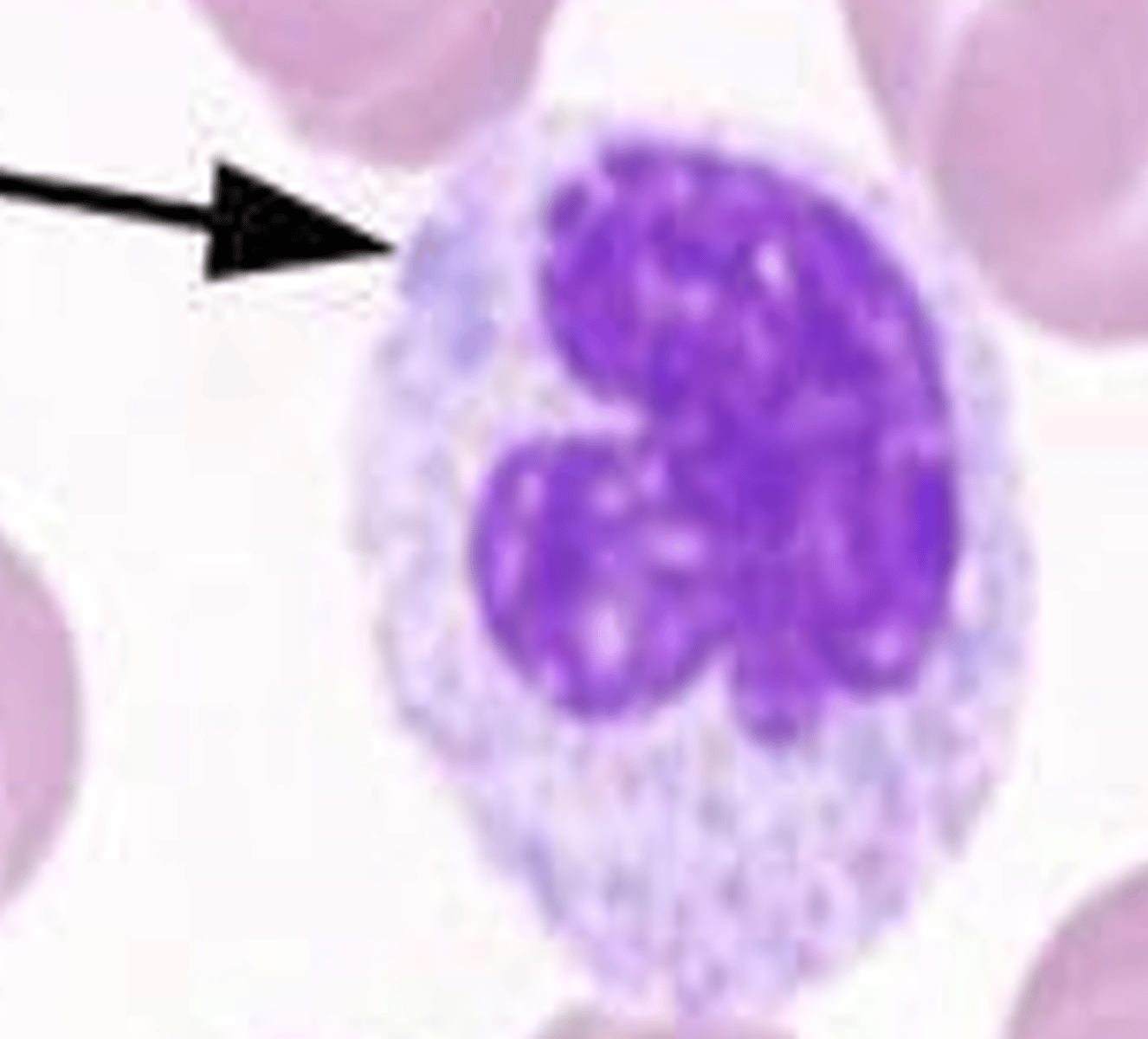
Pyknotic neutrophil
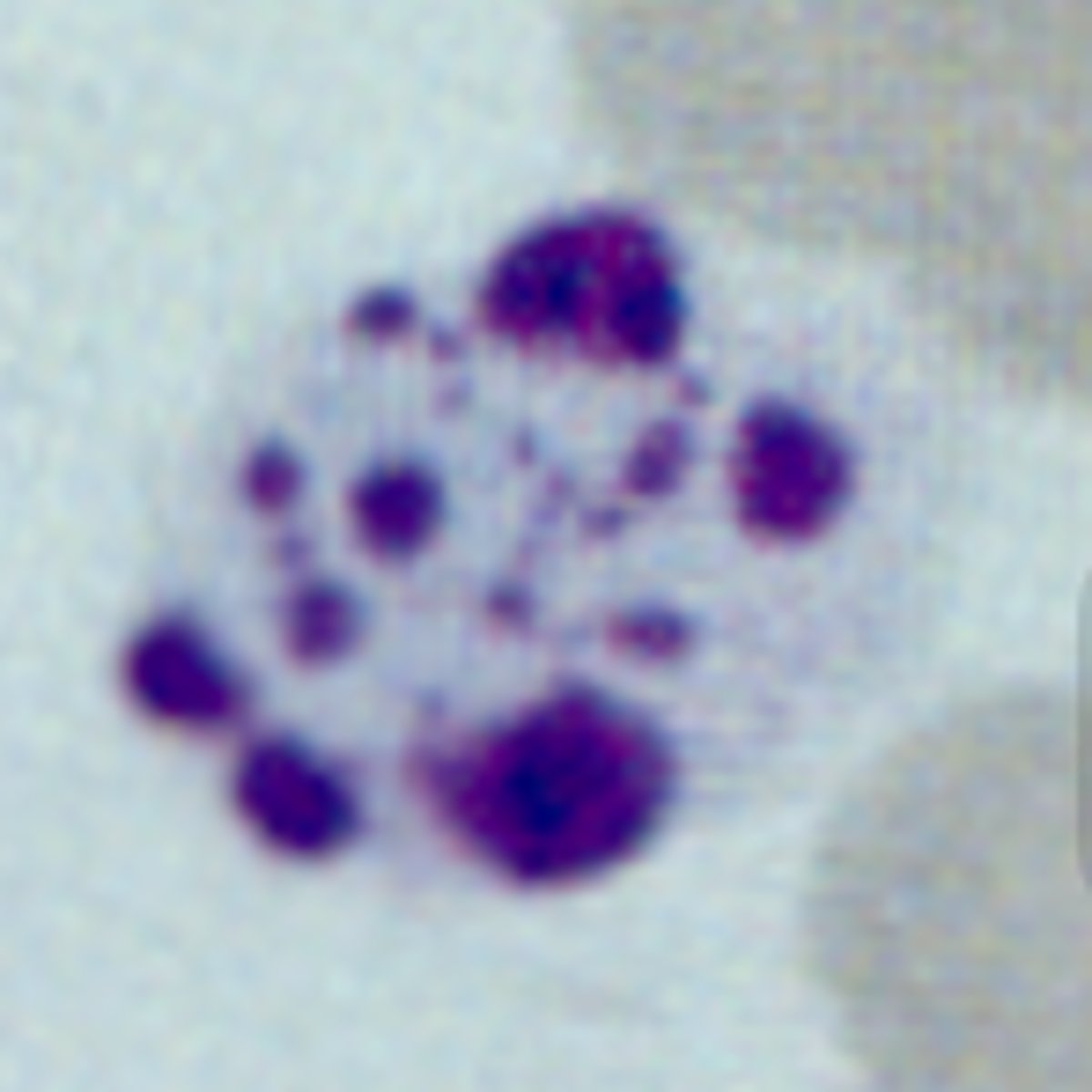
Pelger-Huet
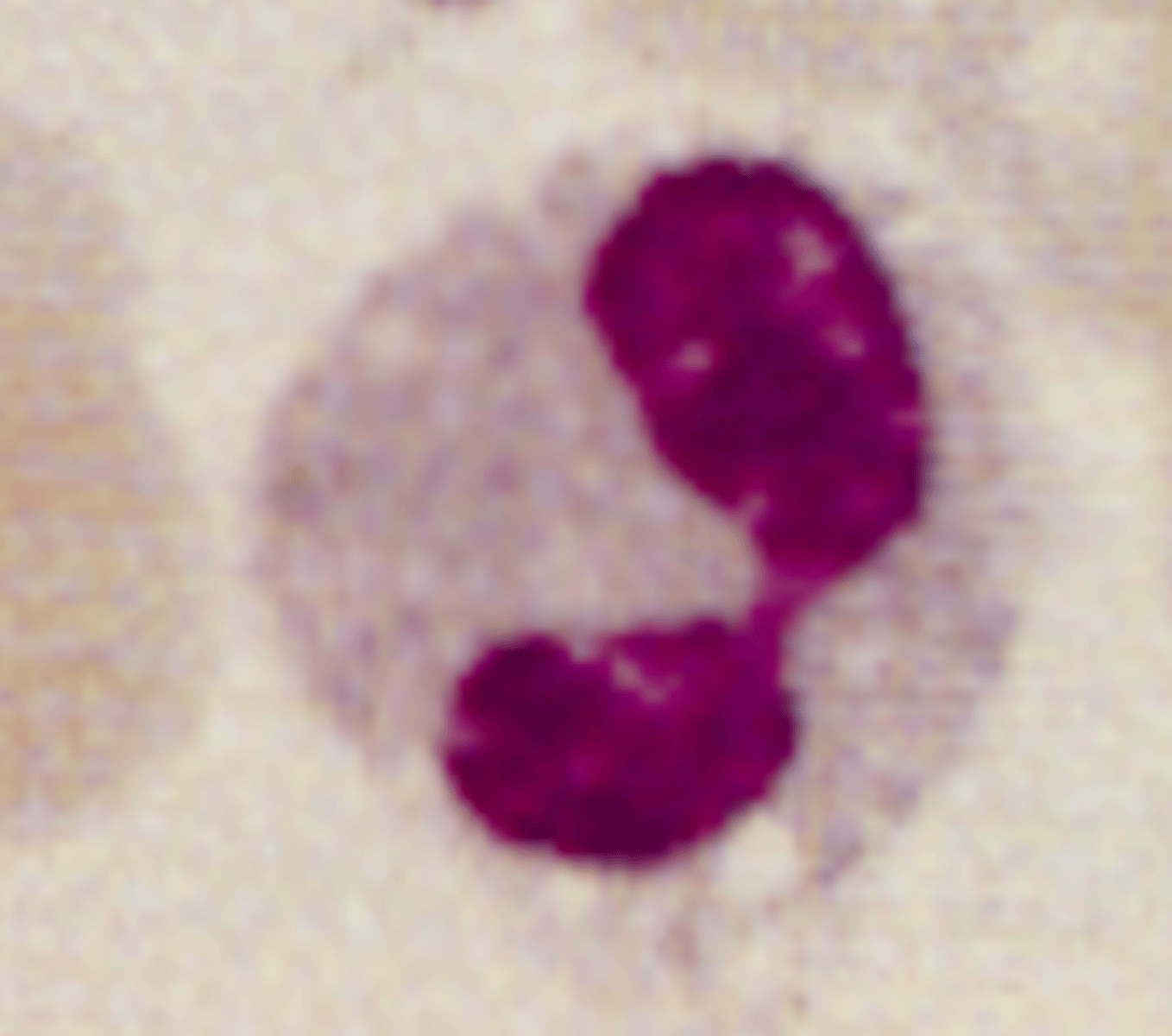
May-Hegglin

Chediak-Higashi
Alder-Reilly
M1 (AML without maturation)
What AML would you expect to see this PBS in?
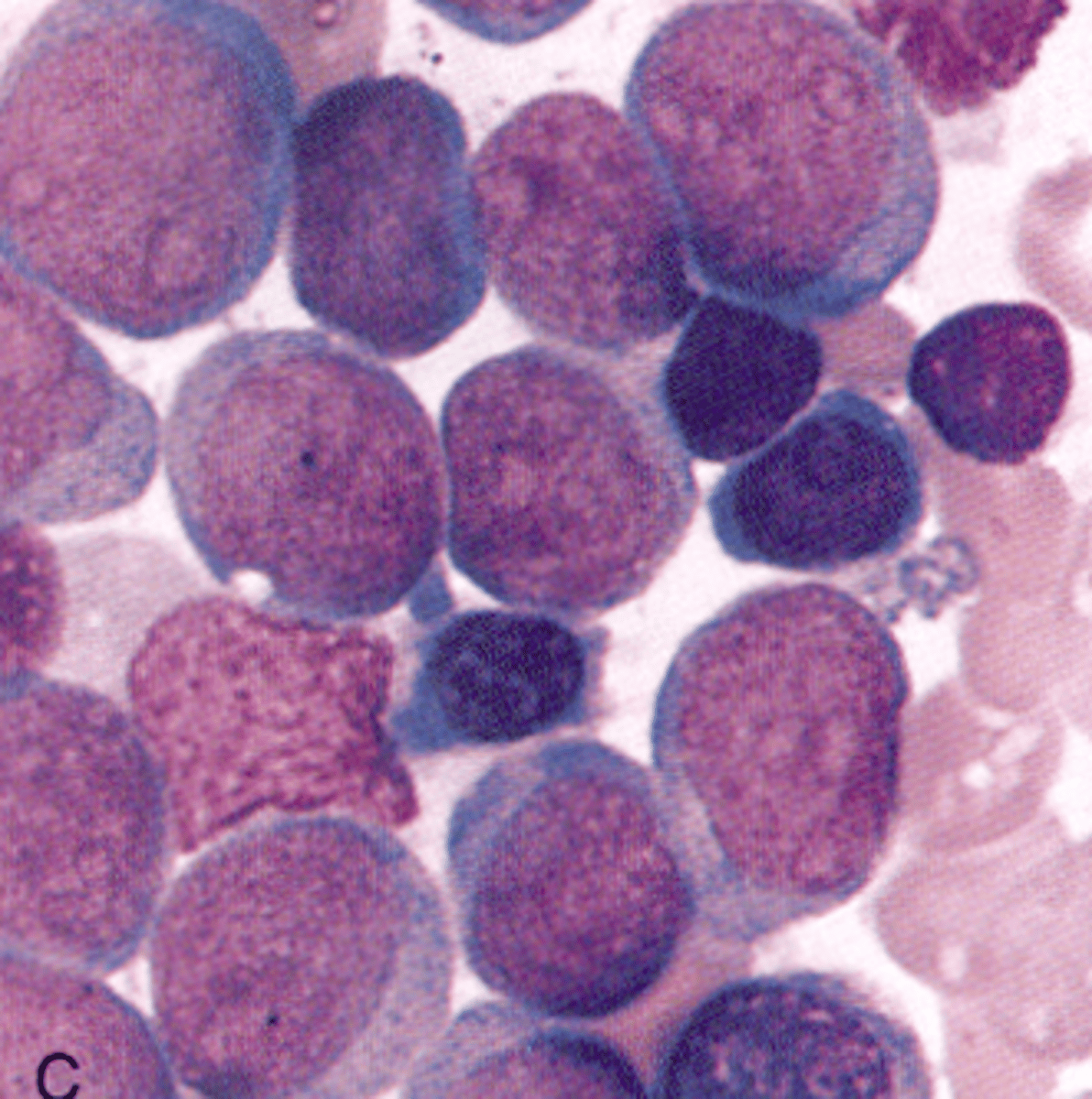
M2 (AML with maturation)
What AML would you expect to see this PBS in?
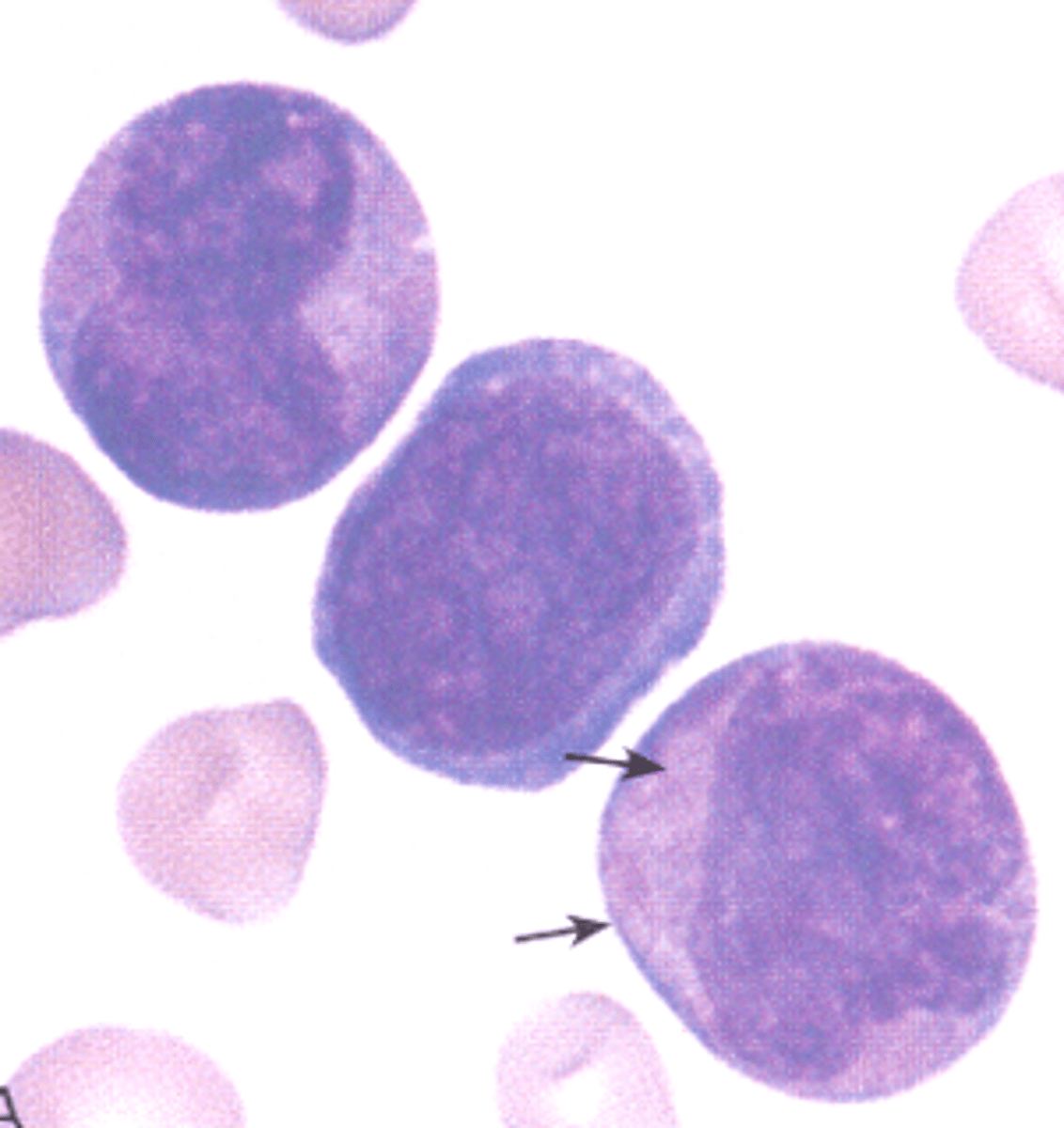
M3 (acute progranulocytic leukemia)
What AML would you expect to see this PBS in?
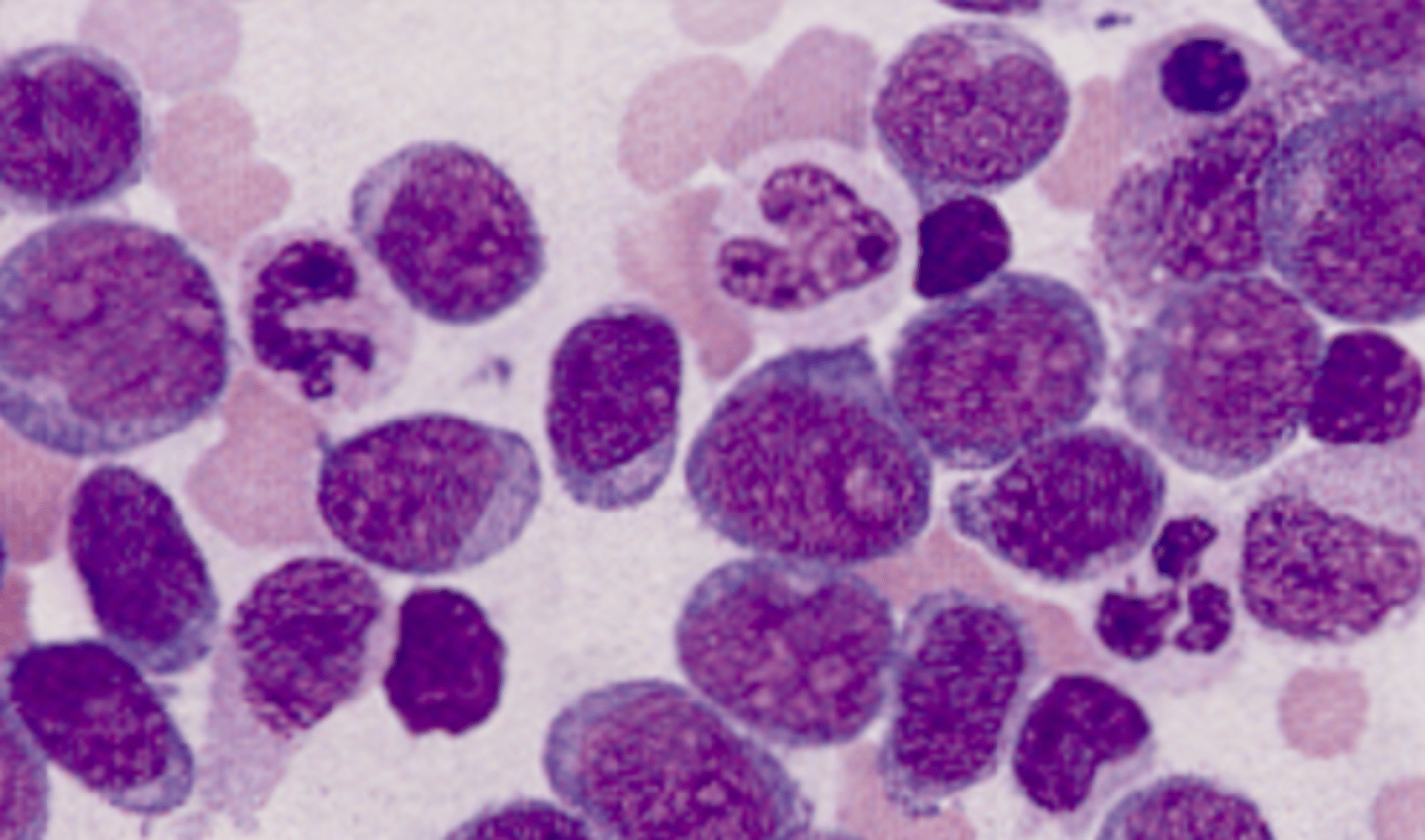
M4 (acute myelomonocytic leukemia)
What AML would you expect to see this PBS in?
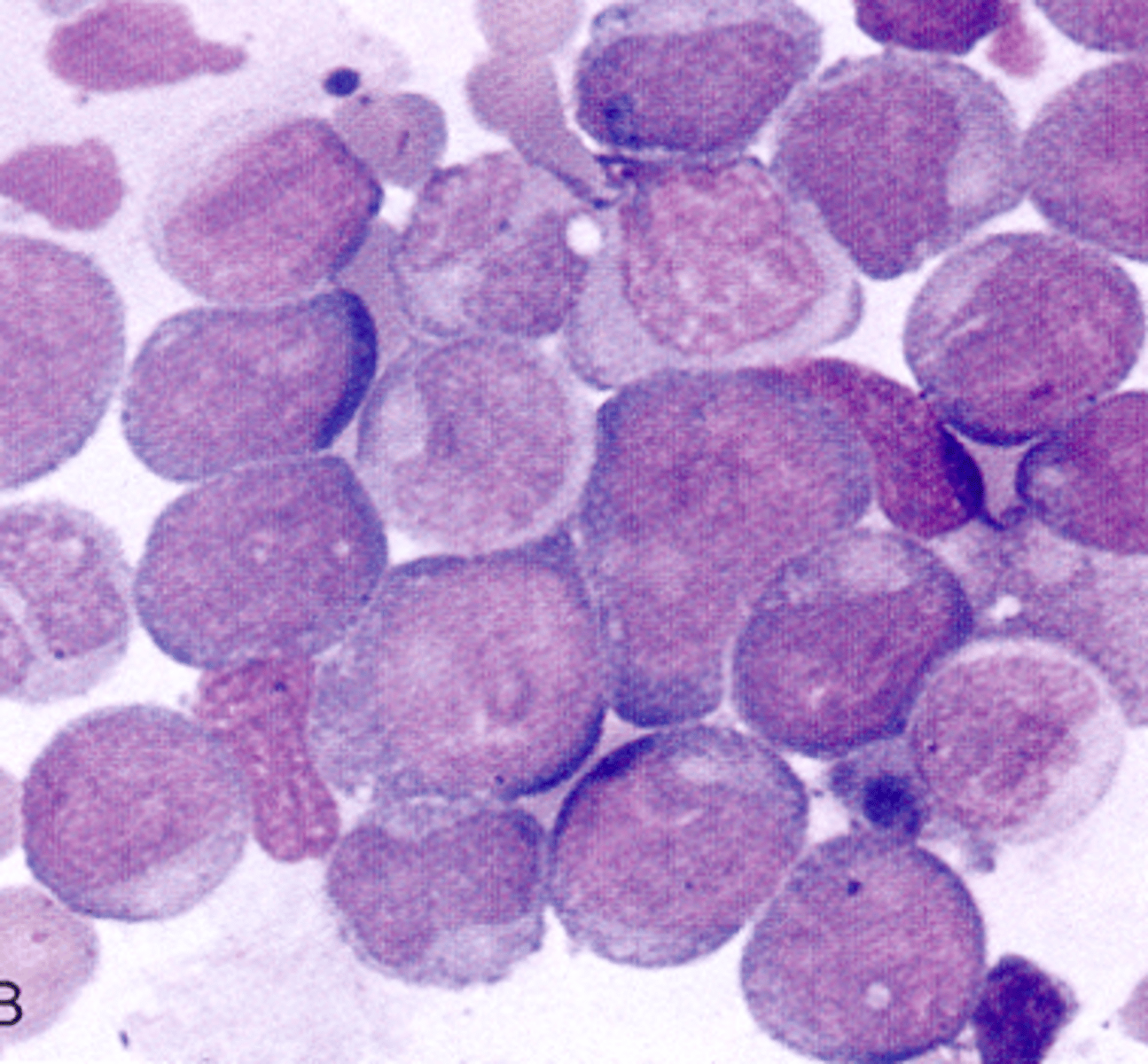
M5 (acute monocytic leukemia)
What AML would you expect to see this PBS in?
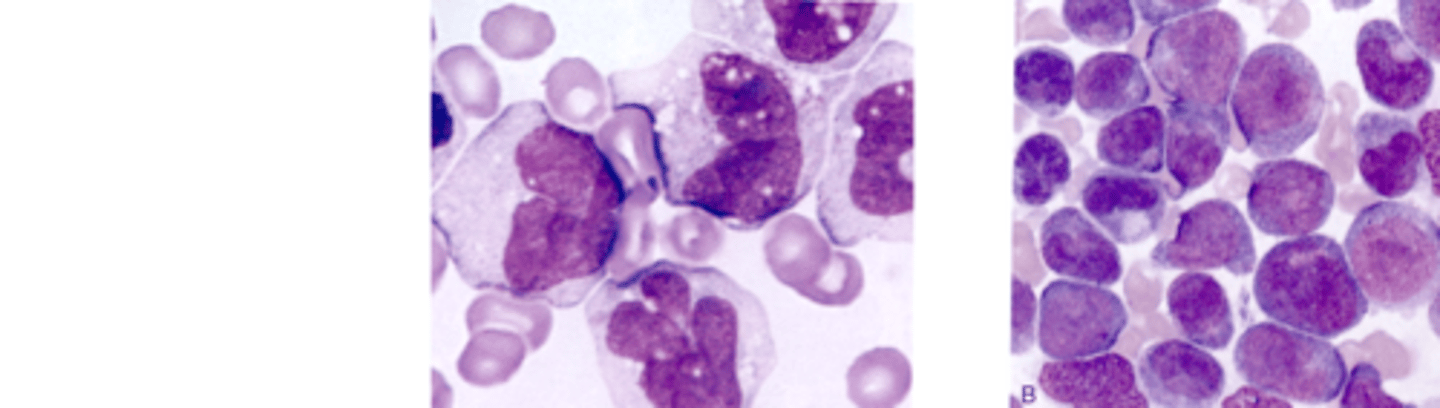
M6 (erythroleukemia)
What AML would you expect to see this PBS in?
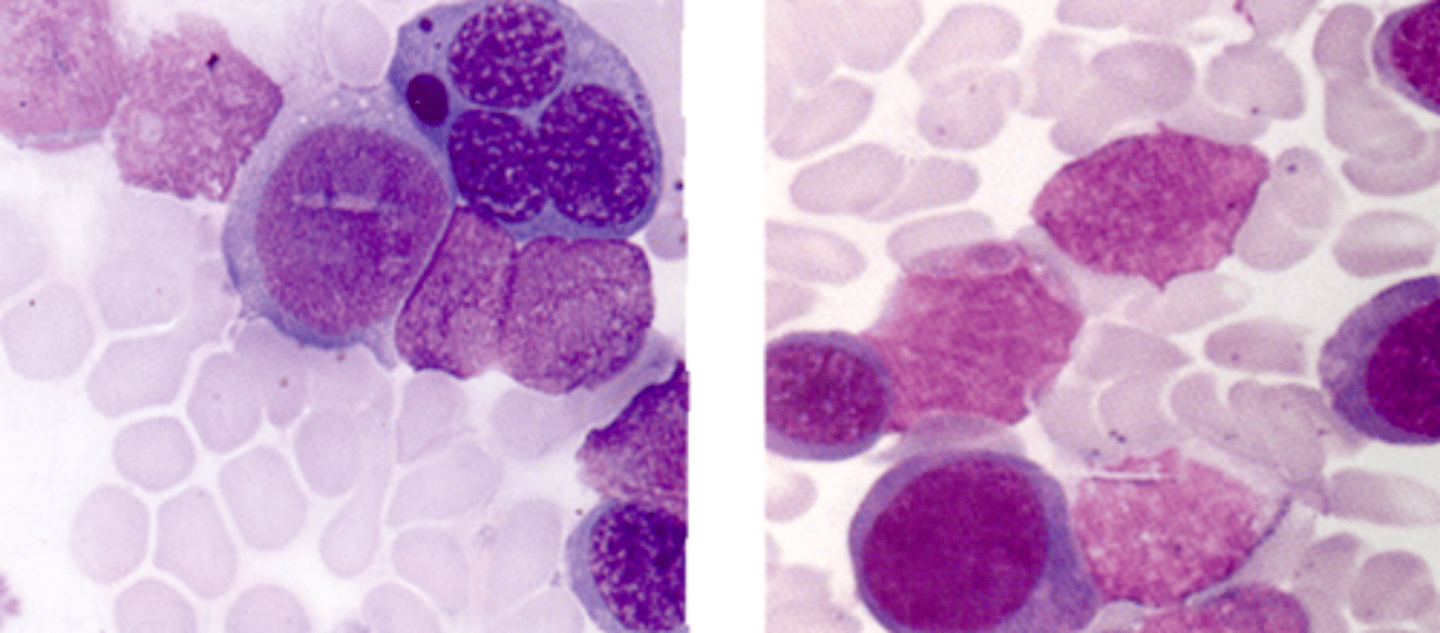
M7 (megakaryocytic leukemia)
What AML would you expect to see this PBS in?
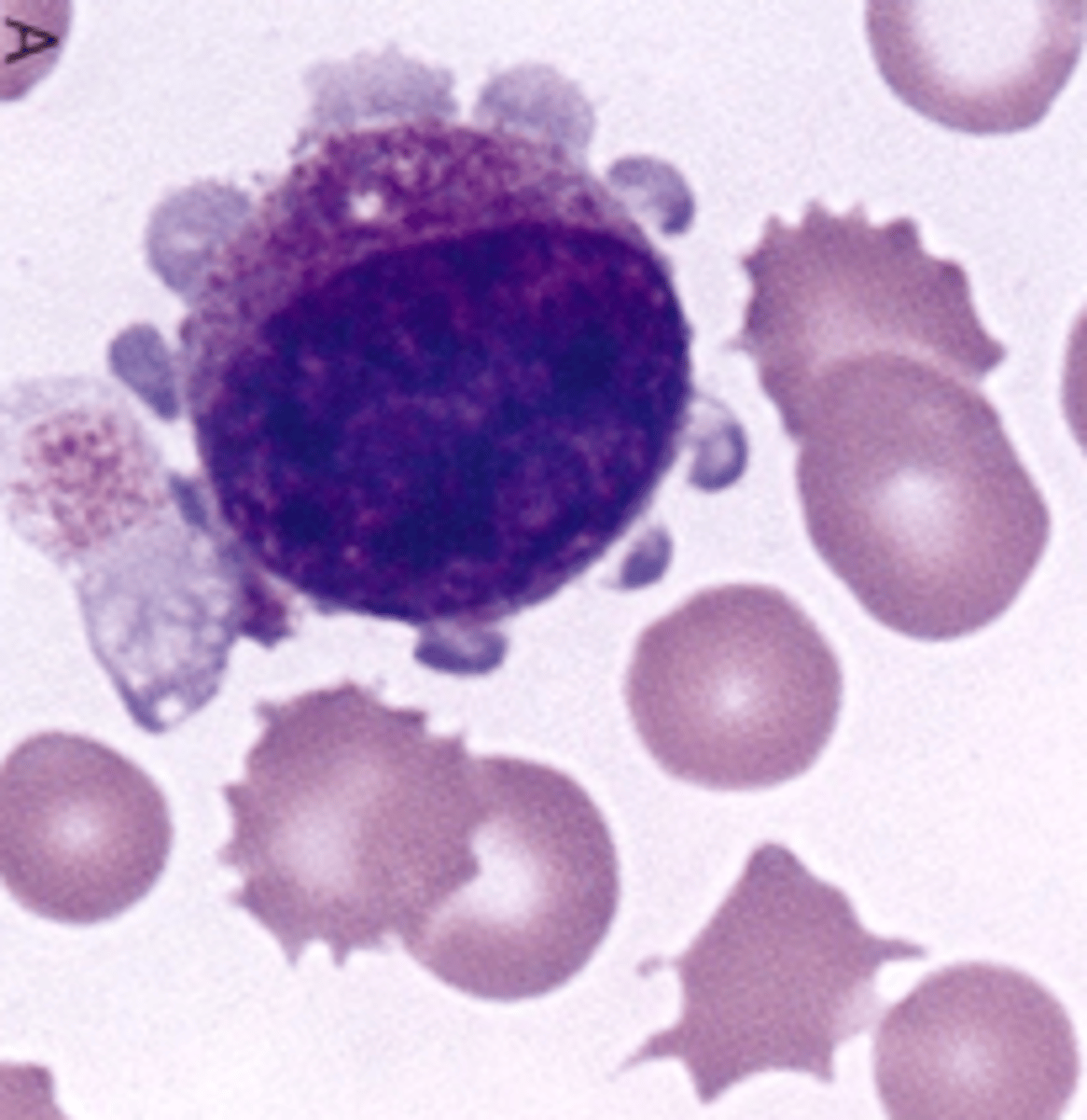
Auer rod
What inclusion?
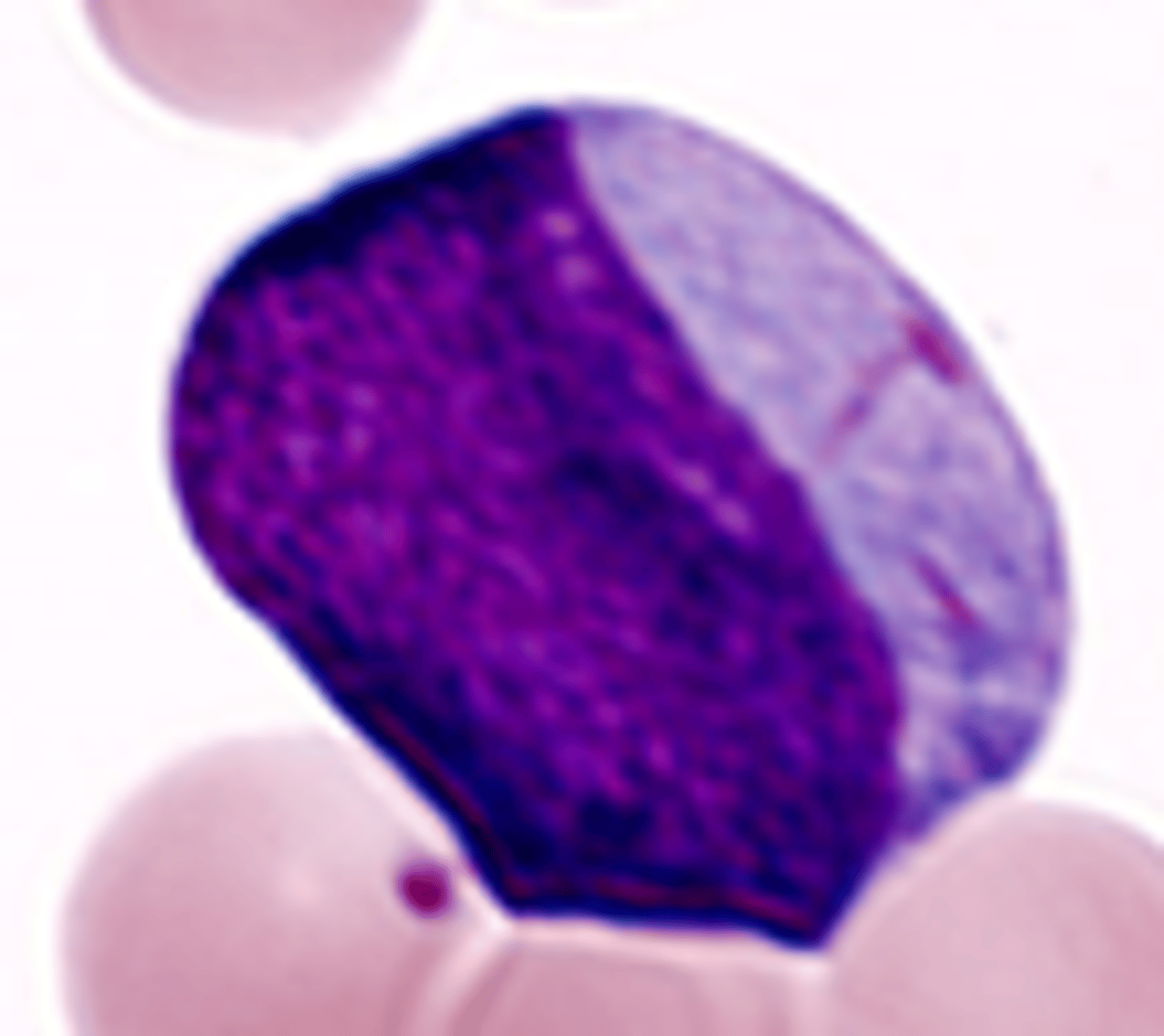
Megakaryocyte
Explain why it is important to determine whether or not a patient has a relative or an absolute lymphocytosis or lymphocytopenia?
Lymphocytosis occurs in viral infections
Lymphocytopenia occurs in heart failure, uremia and malaria
Describe the leukocytosis associated with whooping cough, tuberculosis, cat-scratch disease and mycoplasma pneumonia
relative, but not reactive
Describe the following traits of reactive lymphs seen on a blood smear: Size and N/C ratio
Larger
Smaller N/C
Describe the following traits of reactive lymphs seen on a blood smear: Cytoplasm
Increased amount
Vacuolated
Darker blue or lighter blue
Azurophilic granules
Describe the following traits of reactive lymphs seen on a blood smear: Nucleus
Increased parachromatin and nucleoli
Less mature
Irregular, indented, and immature chromatin
List 5 other names for reactive lymphs.
Atypical lymphs
Stimulated lymph
Activated lymph
Variant lymph
Transformed lymph
Describe the appearance of a plasmacytoid lymph on a blood smear.
Development is somewhere between a lymph and a plasma cell (deep blue cytoplasm, central nucleus)
Describe two common viral conditions that result in leukocytosis, absolute lymphocytosis, and reactive lymph formation
Infectious Mononucleosis (IM)
Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
Name one viral condition that results in leukocytosis, absolute lymphocytosis and, small normal-looking lymph production.
Infectious Lymphocytosis
Differentiate Infectious Mononucleosis (IM) from Infectious Lymphocytosis (IL) for the following: Patient age
IM: 15-25 y.o.
IL: Children
Differentiate Infectious Mononucleosis (IM) from Infectious Lymphocytosis (IL) for the following: Etiologic agent
IM: Epstein-Barr
IL: Coxsackie A, Adenovirus
Differentiate Infectious Mononucleosis (IM) from Infectious Lymphocytosis (IL) for the following: Symptoms
IM: Severe liver disease, fever, lethargy, loss of appetite
IL: Mild diarrhea, vomitting, fever, rash, CNS involvement
Differentiate Infectious Mononucleosis (IM) from Infectious Lymphocytosis (IL) for the following: Lymph morph
IM: Many reactive lymphs
IL: Small normal looking lymphs
Describe the lymphocytosis and the lymphocytes that CMV patients produce.
Absolute lymphocytosis with reactive lymph
How can CMV infection be differentiated from IM by laboratory tests?
Serological titers: anti-CMV
What population is most often afflicted with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)?
Adult males 40+ y.o.