Functional Anatomy
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Origin
where it comes from
Insertion
where it inserts itself into
Flexion
smaller joint angle
Extension
larger joint angle
Eccentric
force is going onto you (example:going down during bench press)
Isocentric
holding position (example:plank)
Concentric
going against the force (example:going up during squats)
Bi-articulate Muscles
crosses 2 joints; flexion of one and extension of another (example:hamstring muscle-flexes knee and extends hip)
Unilateral
1 leg or 1 arm (unicycle)
Bilateral
2 legs or 2 arms (bicycle)
Open Chain Movement
hands and feet are able to move freely (example:bicep curl and bench press)
Closed Chain Movement
hands and feet are not able to move (example:push-up and squats)
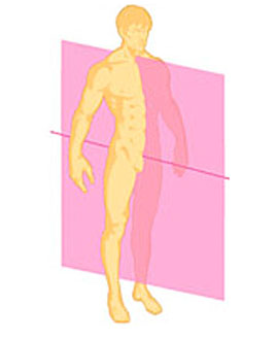
Sagittal
splits you in half vertically
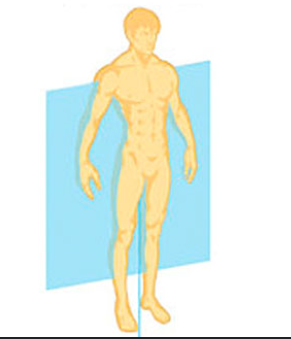
Frontal
splits you from back to front
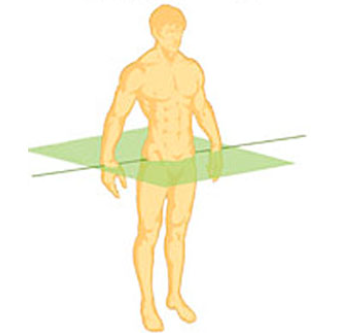
Transverse
splits you in half horizontally
Biceps
Origin:supraglenoid tubercle of scapula, coracoid process of scapula, humerus (shoulder)
Insertion:radial or ulna tuberosity (elbow/forearm)
Function:flexion at the elbow (primary); supination at the elbow,flexion at the shoulder (secondary); biceps brachii long head (bi-articulate)
Triceps
Origin:infraglenoid tubercle of scapula,humerus (shoulder)
Insertion:olecranon of the ulna (elbow)
Function:extension of the forearm at the elbow (primary)
Anterior Deltoid
Origin:lateral third of clavicle
Insertion:deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
Function:flexion at the shoulder (deltoid is shoulder abduction)-primary; abduction and internal rotation at the shoulder (secondary)
Pectoralis Major
Origin:sternum and clavicle
Insertion:humerus
Function:horizontal adduction at the shoulder (primary); internal rotation and flexion at the shoulder (secondary)
Abdominals
Origin:pubis bone, inguinal line, anterior iliac crest (pelvis)
Insertion:xiphoid process of sternum, ribs
Function:trunk flexion (rectus abdominis), trunk rotation (internal and external oblique), and stabilizing torso and pelvis, valsalva maneuver (transverse abdominis)
Rhomboid
Origin:spinous process of T2-T5 vertebra
Insertion:medial boarder of the scapula
Function:scapular retraction (primary); elevate and rotate the scapula (secondary)
Posterior Deltoid
Origin:spine of the scapula
Insertion:deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
Function:shoulder extension w/ latissimus dorsi (primary); external rotation and horizontal abduction at the shoulder (secondary)
Latissimus Dorsi
Origin:illium, spinous processes, ribs, inferior angle of scapula
Insertion:humerus
Function:shoulder adduction (primary); shoulder extension (secondary)
Erector Spinae
Origin:pelvic, vertebral and rib bones in lower to mid back
Insertion:vertebral and rib bones located higher up in back and neck
Function:trunk extension-bilateral (primary); lateral flexion of spine-unilateral, posture (secondary)
Calves (gastronemius,soleus)
Origin:lateral and medial femoral condyle, tibia and fibula
Insertion:calcaneus
Function:ankle plantar flexion (primary); stabilization of the knee/flexion of the knee (secondary); gastrocnemius-knee flexion and ankle plantar flexion (bi-articulate)
Quadriceps
Origin:femur, anterior inferior iliac spine/ilium of pelvis
Insertion:tibial tuberosity via patella/quad tendon
Function:extension of the knee (primary); flexion of the hip-psoas is the primary hip flexor (secondary); rectus femoris-knee extension and hip flexion (bi-articulate)
Hamstrings
Origin:ischial tuberosity of the pelvis
Insertion:medial condyle of tibia, lateral head of fibula
Function:knee flexion (primary); hip extension, tibial stabilization/rotation (secondary); biceps femoris long head, semitendinosus, semimembranosus (bi-articulate)
Gluteus Maximus
Origin:gluetal surface of the illim and posterior inferior surface of sacrum and coccyx
Insertion:greater trochanter of femur, gluteal tuberosity of femur and iliotibial tract (IT Band)
Function:hip extension
Hip Abductors
Origin:gluteal surface of the ilium
Insertion:anterior and lateral surface of the greater trochanter
Function:hip abduction (primary); hip internal rotation (anterior fibers), hip external rotation (posterior fibers), stabilization of pelvis (secondary)
Hip Adductors
Origin:pubis and ischium
Insertion:mainly medial and posterior surface of femur
Function:hip adduction (primary), stabilization of pelvis; hip extension (adductor magnus); gracilis-crosses hip and knee (bi-articulate)