Lecture 19: Endocytosis, Autophagy, Cytoskeleton
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
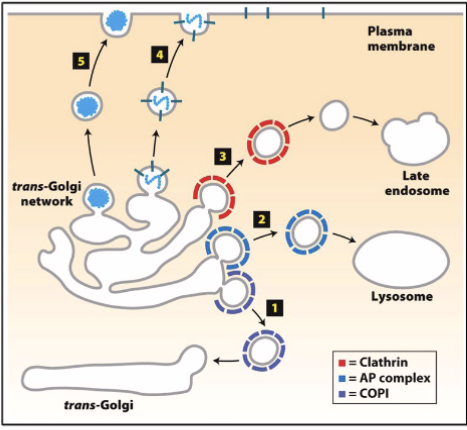
Coatomer: Clathrin and AP complex
AP = Clathrin Adaptor Proteins
AP/Clathrin-coated vesicles:
move from TGN to other vesicles (e.g. lysosomes, endosomes, plant vacuoles)
helps form endocytic vesicles to move vesicles from
plasma membrane to endosomes or lysosomes
Key features of lysosomes
Digestive organelles.
Size: 25 nm to 1 μm.
Internal pH of 4.6 (proton pump or H + -ATPase). Contains hydrolytic enzymes: acid hydrolases.
Lysosomal membrane is composed of glycosylated proteins that act as a protective lining next to acidic lumen
Cytoskeleton
dynamic network of interconnected filaments and tubes that extends
throughout the cytosol (and some organelles) of eukaryotes
structural support
spatial organization within cell
intracellular transport,
contractility and motility
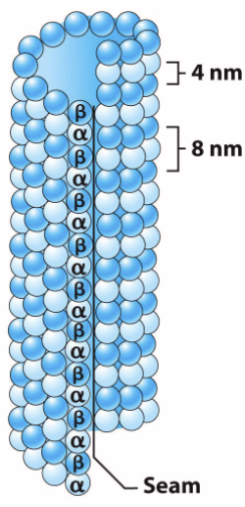
Microtubules (MT)
Largest cytoskeletal element (25 nm diameter).
Polymer of two different proteins (monomers): α-tubulin and β-tubulin.
2 major types:
Axonemal MT:
Highly organized, stable
Part of structures (axoneme) involved in cell movement (e.g cilia, flagella)
Cytoplasmic MT
Loosely organized, very dynamic
Located in cytosol
Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs)
Two classes of MAPs
1. Non-Motor MAPs:
• Control MT organization in cytosol (e.g. Tau protein in neurons).
• Defective Tau protein → neurofibrillary tangles → Alzheimer’s disease (right image, top).
2. Motor MAPs:
• Two main types—kinesin and dynein.
• Use ATP to generate force.
• Can move material along MT track.
• Can generate sliding force between MTs