3.1 - 3.3 Biology - Cell Theory + Eukaryotic Cells
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
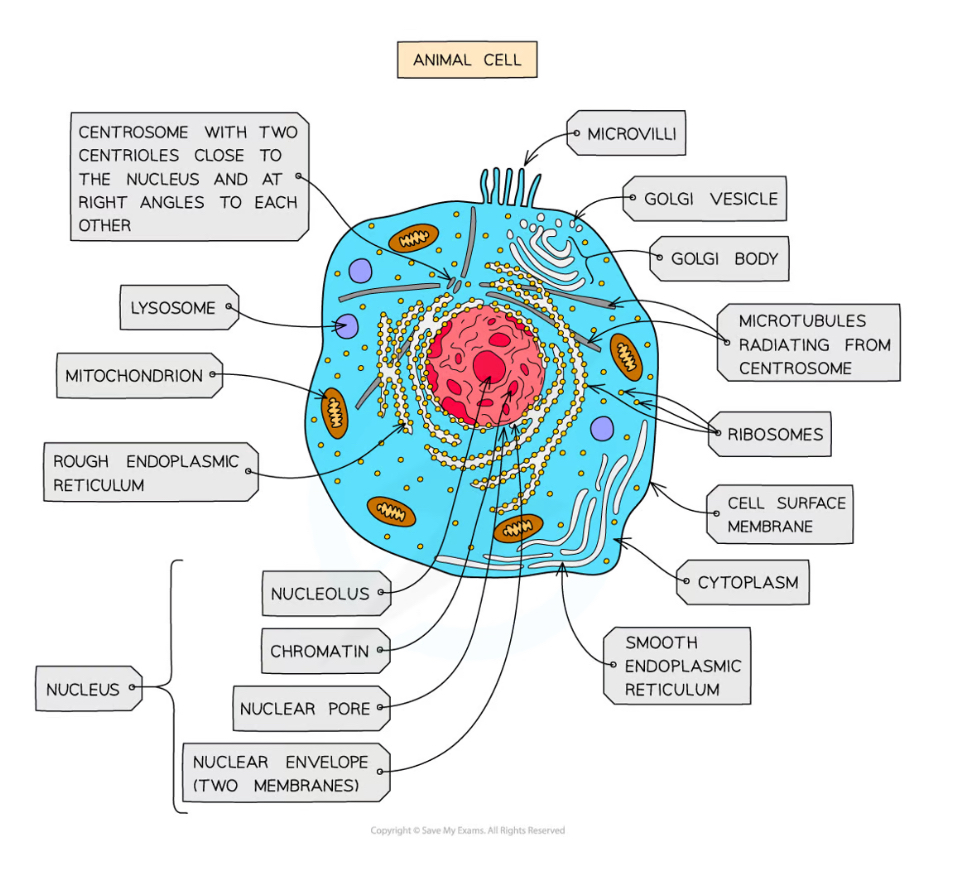
Organelles in all living organisms
Cytoplasm
Ribosome
Cell membrane
DNA
Ultrastructure
The internal structure of cells
Animal cells only organelles
Microvilli
Centrioles
Plant Cells ONLY Organelles
Chloroplasts
Vacuole
Cellulose Cell Wall
Microvilli
Folded regions of the cell surface membrane that increase cell surface area for absorption
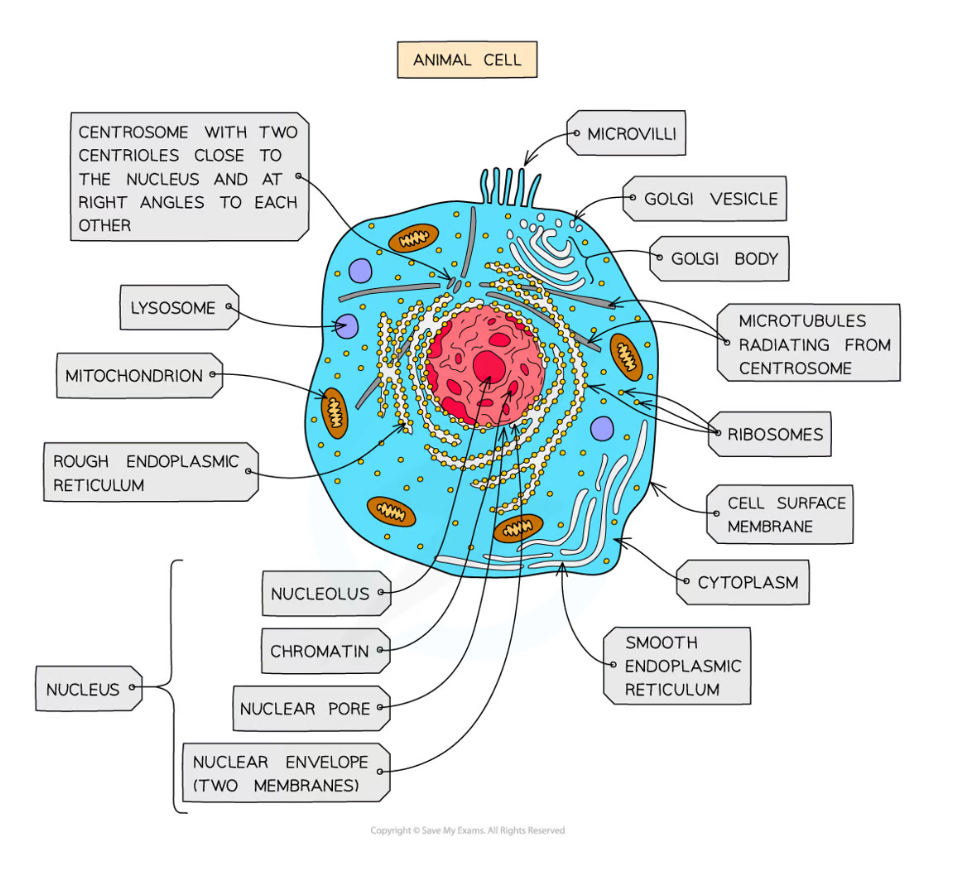
Cell Surface Membrane Function
Controls the exchange of materials between the internal cell environment and the external environment
- ALWAYS say cell SURFACE membrane
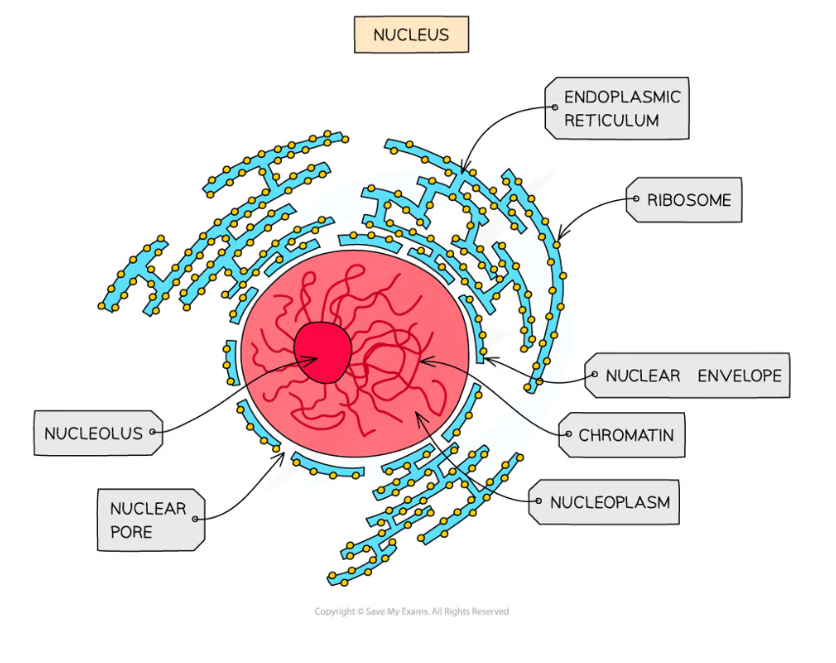
What contains the nucleus?
a double membrane called the nuclear envelope
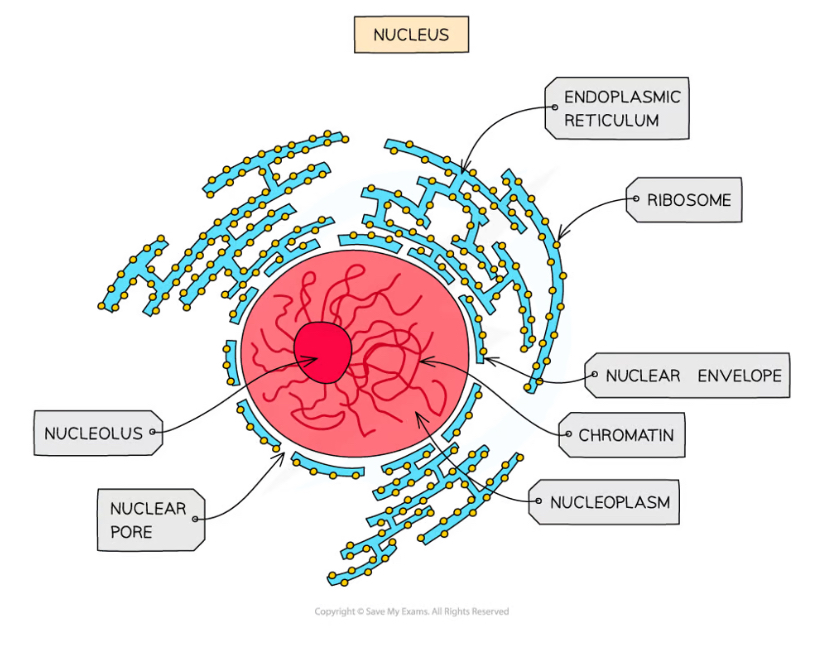
Nuclear pores - Function
Allows mRNA and ribosomes to travel out of the nucleus
Allows enzymes and signalling molecules to travel into the nucleus
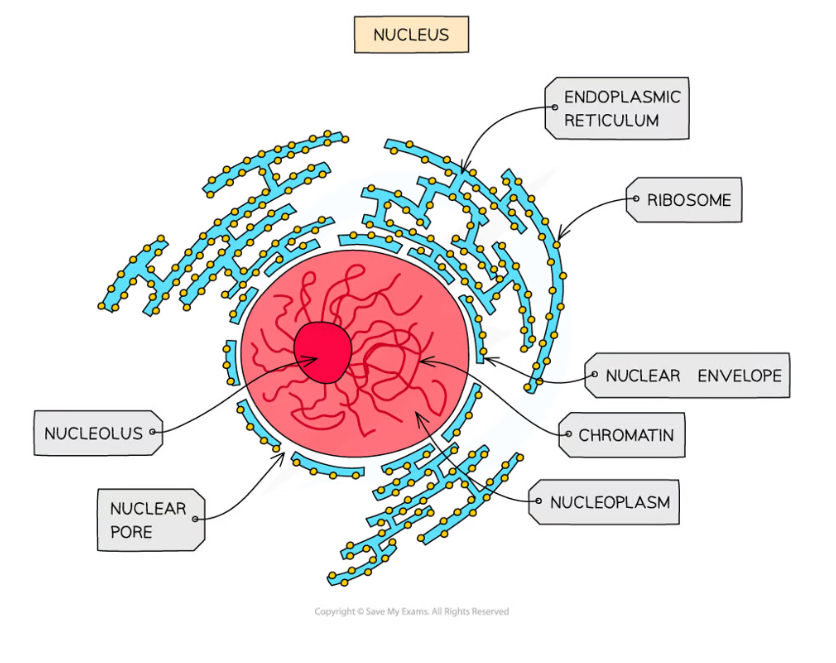
What are chromosomes made from?
chromatin
Sections of linear DNA tightly wound around proteins called histones
Nucleolus function
ribosome production
Mitochondria Function
Site of aerobic respiration
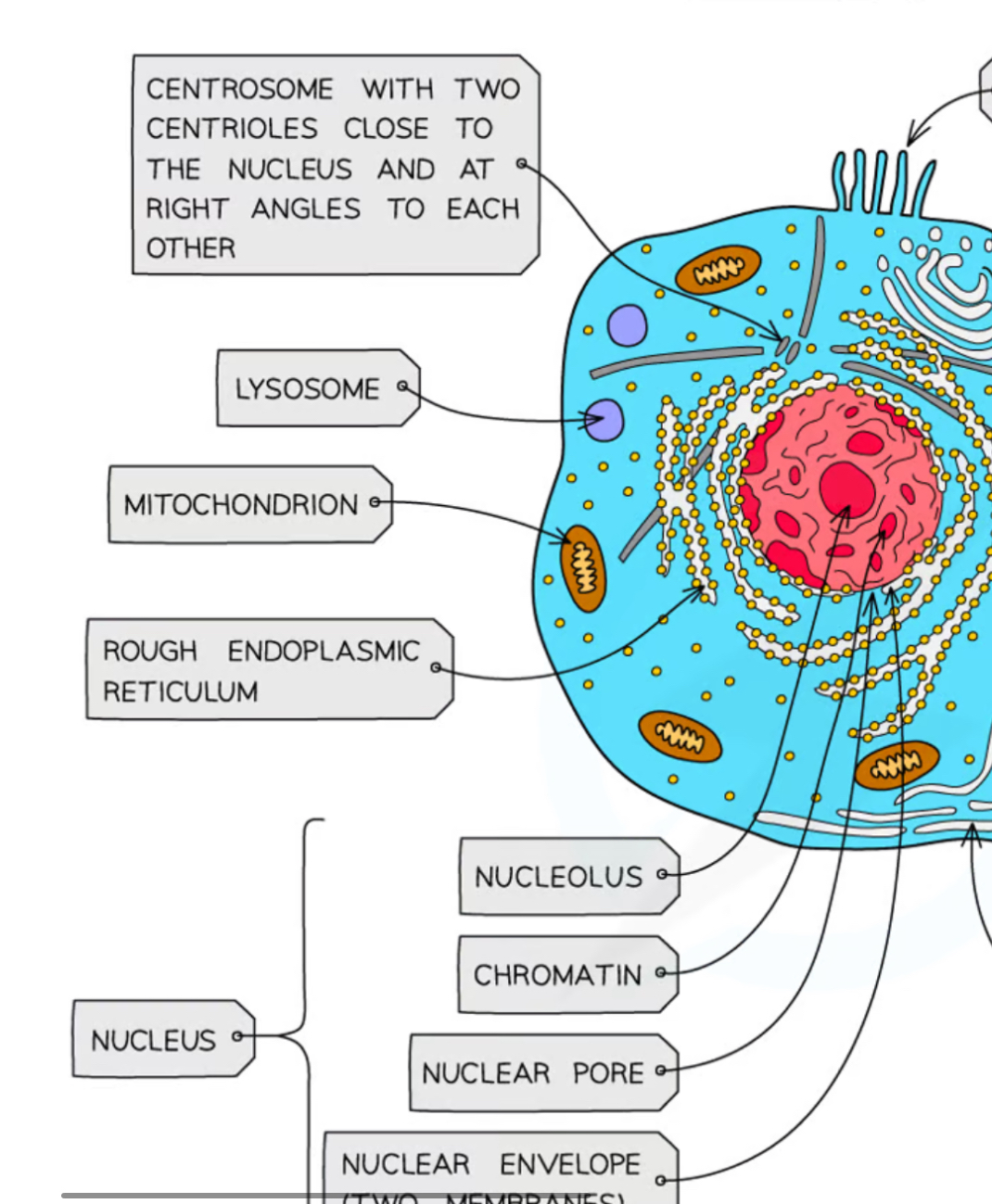
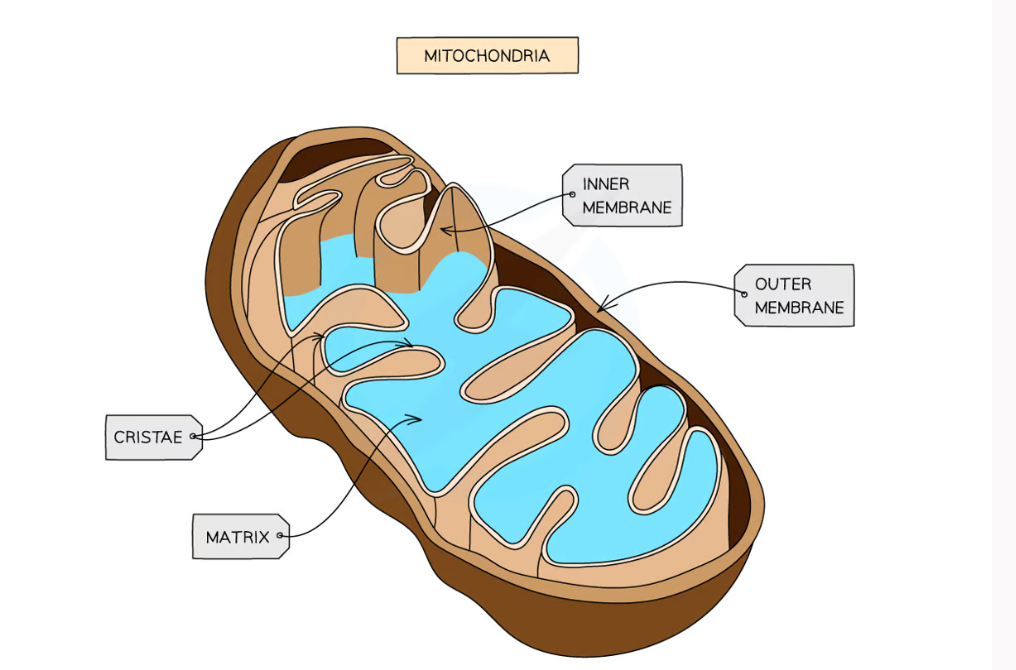
What surrounds the mitochondria?
A double membrane
Inner membrane folded to form cristae
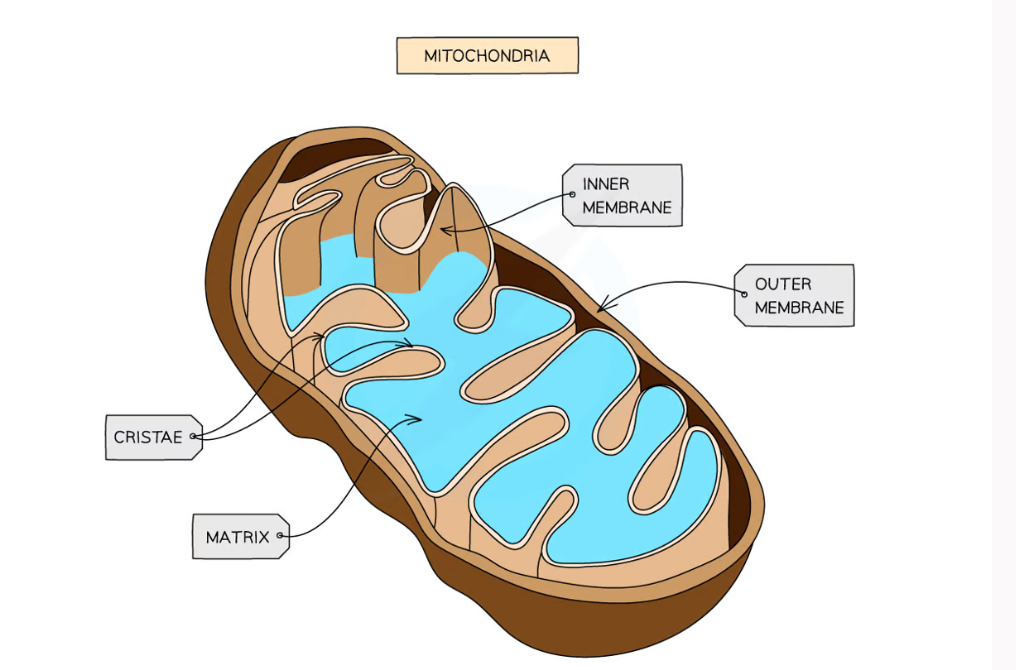
What does the matrix of mitochondria contain?
Enzyms needed for aerobic respiration
mitochondrial DNA
replication of mitochondria before cell division
Where can ribosomes be found?
rough endoplasmic reticulum
Cytoplasm
What are ribosomes?
Complex of ribosomal RNA and proteins
Riboosome function
Site of translation
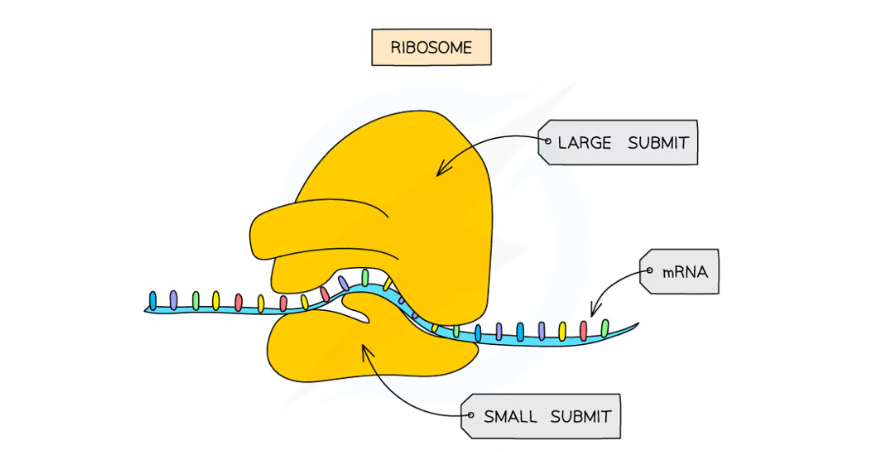
Size of ribosomes in eukaryotic cells
80s ribosomes
Size of ribosomes in prokaryotes
70s ribosomes
What organelles contain 70s ribosomes?
mitochondria
chloroplasts
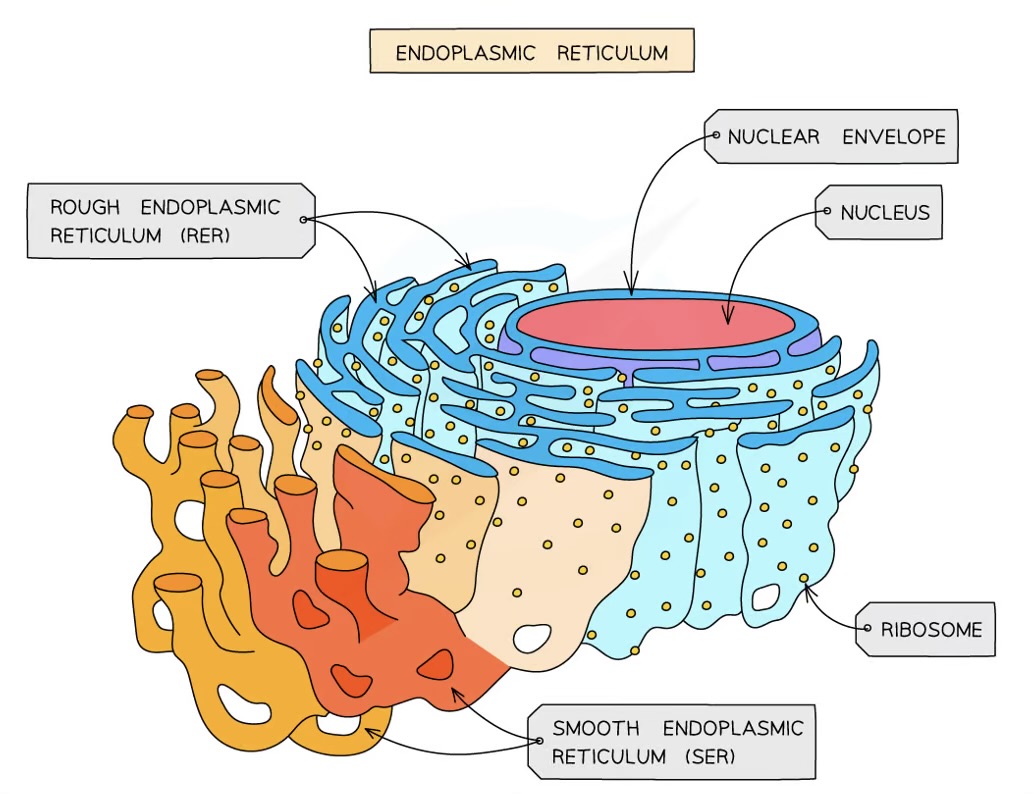
Rough endoplasmic reticulum - what is it made of?
folds of membrane continuous with the nuclear envelope
surface covered in ribosomes
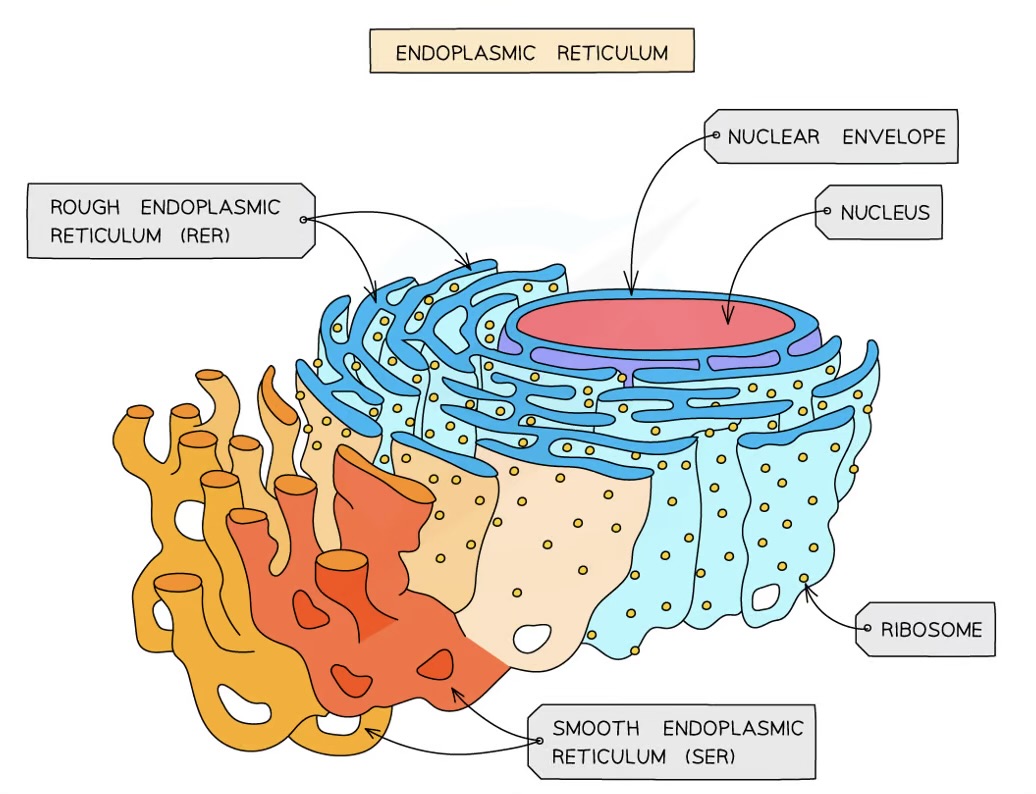
RER Function
folds and processes proteins in the lumen, made on the ribosomes
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Function
the production, processing and storage of lipids, carbohydrates and steroids
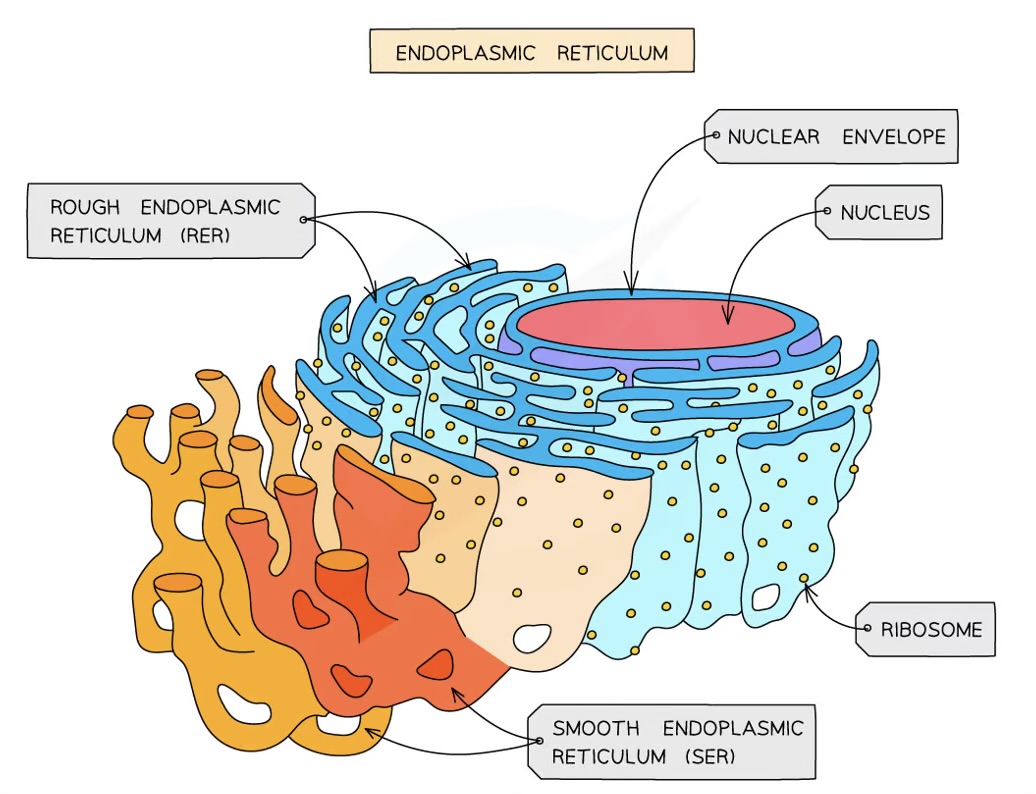
SER - what is it made from?
folds of membrane
no ribosomes on surface
Golgi apparatus
flattened sacs of membrane
regular, stacked
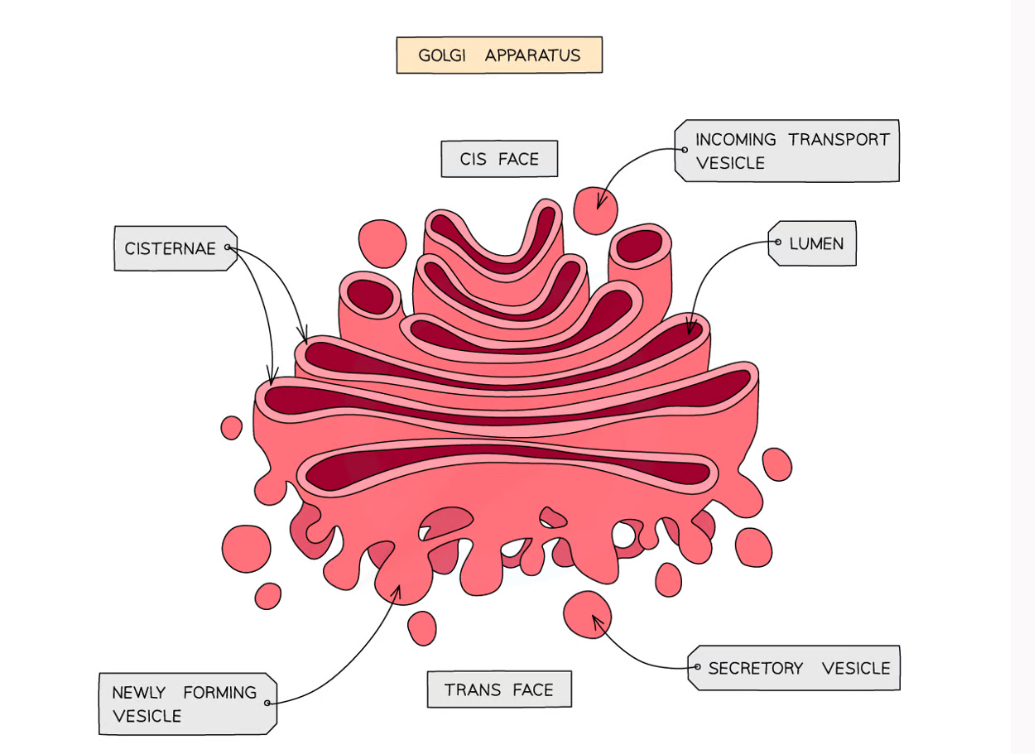
Golgi Apparatus Function
modify proteins and lipids
packaging them into Golgi vesicles
vesicles transport the proteins and lipids to their required destination
What makes up the lysosome?
specialist forms of vesicle which contain hydrolytic enzymes
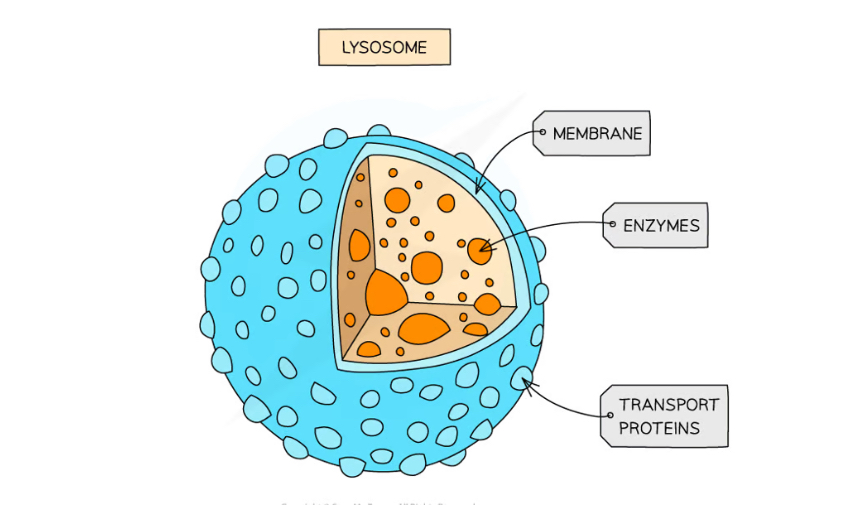
Lysosome Function
break down waste materials such as worn-out organelles
used by cells of the immune system and in apoptosis
Microtubules
filaments of protein
used to move substances around inside a cell
to support the shape of a cell from the inside
Centrioles formed from what?
microtubules
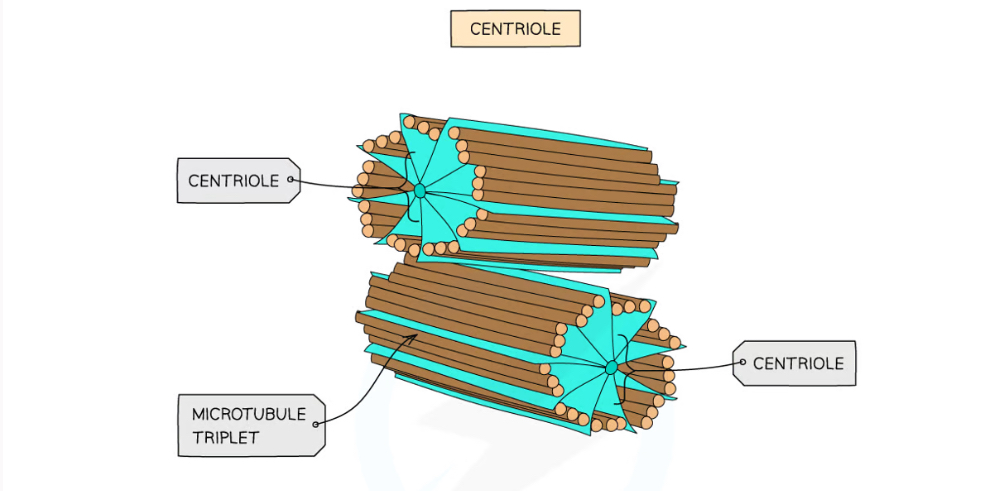
Centriole Function
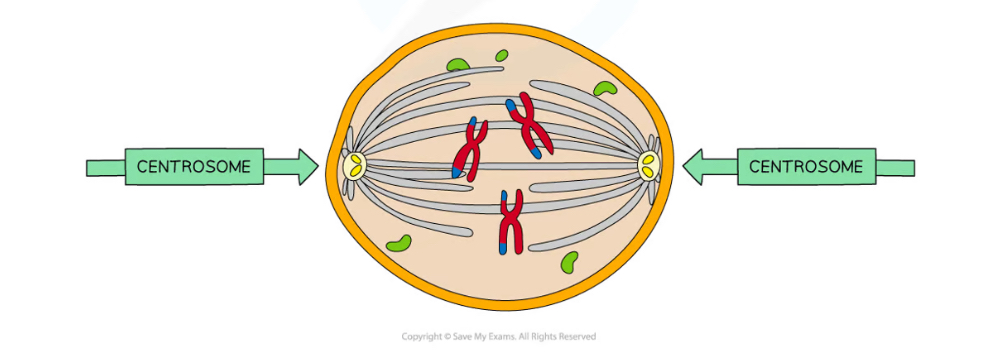
Two centrioles at right angles to each other form a centrosome
Centrosome organises the spindle fibres during cell division
Organelles
specialised parts of a cell that carry out a particular function
Packaging and transporting proteins in a cell
1. The DNA in the nucleus is used to make an mRNA copy of the gene.
2. This leaves the nucleus through a Nuclear pore
3. A ribosome on the RER attaches to the mRNA.
4. Ribosomes synthesise the protein.
Transport vesicles containing the proteins are pinched off from the Rough endoplasmic reticulum
These vesicles fuse with the membrane of the Golgi apparatus, and proteins are released into this organelle.
Inside the Golgi apparatus, the proteins are
processed, modified and packaged for release.
8. Vesicles containing the modified proteins are pinched off from the Golgi apparatus.
9. These travel to the cell surface membrane and fuse with the cell surface membrane.
10. The modified proteins are released to the outside of the cell by exocytosis