Quantum Theory and Electronic Structure of Atoms
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Emission Series | Dual Nature of the Electron | Quantum Mechanics | Quantum Numbers | Atomic Orbitals
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Lyman Series
Emission Series in the H Atom:
n = 1
Balmer Series
Emission Series in the H Atom:
n = 2
Paschen Series
Emission Series in the H Atom:
n = 3
Brackett Series
Emission Series in the H Atom:
n = 4
Ultraviolet
What is the Spectrum Region of the Series:
Lyman
Visible and Ultraviolet
What is the Spectrum Region of the Series:
Balmer
Infrared
What is the Spectrum Region of the Series:
Paschen
Infrared
What is the Spectrum Region of the Series:
Brackett
Standing Waves
Electrons, when considered as waves, can be described as (answer) within the atom, specifically around the nucleus.
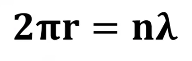
Equation for the Dual Nature of the Electron
De Broglie
Stated that waves can behave like particles and particles can behave like waves.
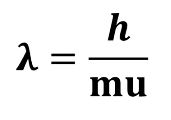
De Broglie’s Equation
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
There's a limit to how precisely certain pairs of physical properties of a particle, like position and momentum, can be known simultaneously.
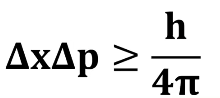
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Equation
Change in Position
What does the Δx in the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Equation stand for?
Change in Momentum
(mass x velocity)
What does the Δp in the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle Equation stand for?
Orbitals
In Quantum Mechanics, what do you call the orbits?
Electron Density
In Quantum Mechanics, what do you call the Electron?
solid particle; NOT solid particles
With Bohr, Electrons are treated like a (answer). In Quantum Mechanics, particles are (answer).
Schrödinger Equation
A fundamental equation in quantum mechanics that describes how the quantum state of a physical system changes over time.
Psi (𝚿)
Symbol for Wave Function
Electron Density
If you get the 𝚿2, you will get the…?
Quantum Numbers
Describes the distribution of Electrons in an atom; they are derived from solving the Schrödinger Equation for the Hydrogen atom.
Principal Quantum Number (n)
Points to which orbital is occupied by an electron; n = 1, 2, 3,….
Angular Momentum Quantum Number (l)
Tells us the shape of an orbital located in n; l = 0 to (n-1)
Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
Describes an orientation in space of the orbital in space (which orbital); -l, (-l + 1),…, 0 , (+l - 1), +l
Electron Spin Quantum Number (ms)
Points to one of the two electrons that can occupy an orbital in a specific subshell in a specific shell; ms = -1/2, +1/2
Node
A region within a quantum mechanical system, such as an atom, where the probability of finding an electron is zero.