PSY 101: Exam 1 Study Guide
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
When was the first psychosocial clinic opened?
1896
What is psychology?
the scientific study of the mind, brain, and behavior
How can psychology be studied from different levels of analysis?
Psychology can be studied from a societal level, behavioral level, mental level, neurochemical level, and molecular level.
What are the current debates of psychology?
NATURE vs NURTURE: What determines our behavior? Our genetics (Nature) or our environments (Nurture) ?
FREE WILL CONTROVERSY: Do we have free will? Does it exist?
Which discipline did psychology originate from?
Philosophy! (Many philosophers wrote about human development!)
When did William Wundt reestablish psych as a laboratory science?
1879
When did the Stanley Halls open?
1883
When was the first text of psychology written?
1890
What was the first professional association funded in 1892?
APA (American Psychological Association)
Who wrote "The Interpretation of Dreams" and when was it written?
Sigmund Freund and 1899
Who was Mary Whiton Calkins?
First female president of the APA in 1904
Who are Kenneth and Mamie Clark?
Psychologists who studied segregation studies; Why do black kids choose a white doll even with black dolls present??
What is structuralism?
an early school of psychology that used introspection to explore the structural elements of the human mind
"What?"
Key Figures: Titchener, Wundt
What is functionalism?
the study of the structure and function of each part of society.
"Why? What does it serve someone to do something?"
Key Figures: William James
What is behaviorism?
the scientific study of the relationship between behavior and reinforcement
"How? How have we learned to behave differently in different settings?"
Key Figures: Watson & Skinner
What is cognitive psychology?
scientific study of mental processes
"How did we learn to think the way we do? How do our thoughts dictate how we experience something?"
Key Figures: Piaget
What is psychoanalysis?
an idea that human behavior is influenced by unconscious memories
"How does our subconscious experience effect us?"
Key Figures: Freund (not a surprise)
What is the humanistic perspective?
stresses the human ability for self fulfillment and the importance of consciousness, self awareness, and the ability to make choices
"How do people find fulfillment and meaning in life?"
Key Figures: Moslow & Rogers
What type of education do you need to become a psychologist?
Graduate school and advanced training in psychology (typically at a doctorate level)
What are the different types of psychological specialties?
Clinical, Counseling, School, Forensic, and Industrial-Organizational
What is a clinical specialty?
a branch of psychology that studies, assesses, and treats people with psychological disorders
What is a counseling specialty?
a branch of psychology that assists people with common problems in living (often related to school, work, or marriage) and in achieving greater well-being
What is a school specialty?
school psychologists work with educators to help meet the intellectual, social and emotional needs of school aged children
What is a forensic specialty?
a branch of psychology that deals with the law and legal issues relevant to all ages of clients in all types of settings.
What is an industrial/organizational specialty?
the application of psychological concepts and methods to optimizing human behavior in workplaces
EX: How to motivate employees?
How do psychologist study behavior?
By using the scientific method
What are characteristics of psychology and the scientific method?
Empiricism (objective observation of the world), Replication (demonstrating & observing a phenomenon more than once), and Publication (making observations available to everyone so that others can evaluate the claim)
What are ways psychologist get fooled into believing what's NOT true?
Repetition of false information, desire for easy answers or quick fixes, selective perception or memory, inferring causation from correlation, and exaggeration of truth
What is the difference between causation and correlation?
CAUSation means one variable directly causes the other
CORRELAtion means both variables have a relationship (they correlate)
What are some goals of the scientific study of behavior?
1.) Describe behavior
2.) Predict behavior
3.) Identify causes of behavior
4.) Explain behavior
What are the types of research? Define them.
Observational: objectively observe and record behavior
Correlational: measure two variables and determine the presence of a relationship
Experimental: manipulate the independent variable and determine causation to dependent variable
What is a scientific theory?
A systematic body of ideas that organizes what is known about a topic from past observations and makes predictions about future observations
What is a hypothesis?
A prediction about the outcome of a research
What happens to theories with different levels of support?
Theories with ample support get accepted! Theories with little support either get modified or rejected.
What are variables?
Characteristics that can take on different values for different observations
What is the difference between an independent variable and a dependent variable?
Independent: controlled and manipulated
Dependent: recorded and measured
The independent variable's effects on the dependent variable is being tested in an experiment.
What are operational definitions?
re-define concepts and constructs as specific, observable, and measurable events (functional re-definition)
EX: memory capacity (# of words recalled from a list of 50)
What is a sample? What is a population?
Sample: Small group that we measure
Population: Large group of interest
What is a biased sample?
A sample that doesn't accurately represent the population.
What is random sampling?
a sample that fairly represents a population because each member has an equal chance of inclusion
How do naturalistic observational studies work?
Researcher makes observations of people/animals in their normal environments
What is the case study approach?
a descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
How can we use correlational research to predict behavior?
If two variables have been known in the past to correlate, then we can assume they will continue to correlate in the future. We can use the value of one variable that is known now to predict the value that the other variable will take on in the future.
What are correlational coefficients?
A number that shows the strength of the relationship between two factors.
1 or -1= very strong
0= no strength
How can we interpret the strength and direction of a correlation coefficient?
The closer to 1 or -1, the stronger
The closer to 0, the weaker
Negatives mean the direction is titled down
Positives mean the direction is titled up
0= no direction and no strength
What does experimental research allow researchers to do?
It allows researcher to identify causal relationships between
variables
What are the differences between experimental and correlational research?
Correlational research: utilizes two measured variables
Experimental research: manipulate one variable, measure another
What is random assignment?
participants have an equal chance of being in every experimental group
How is random assignment different from random sampling?
Random assignment is creating groups that are statistically equivalent. Random sampling is a sample from a population at random so that the sample is similar to the
population.
What is a confound?
Factors that are plausible alternative explanations and might have also affected the DV results.
What is validity?
accuracy
What is external validity?
Can we generalize the results of our experiment to the population from which our sample was drawn? Do the results apply to everyone?
What is internal validity?
Can we draw correct conclusions about the causal relationship between the IV and DV? Is our experimental design free of confounds that provide plausible alternative explanations of the results?
What is a construct?
An abstract psychological concept that we cannot observe
or measure directly (memory, happiness, etc.)
What is construct validity?
Is our operational definition of a construct a good way to measure the construct? When we measure the construct operationally, are we really measuring the underlying construct of interest?
Why do we need statistics in behavioral research?
different people behave differently in identical situations
What is p-value (probability values)?***
Refers to the probability that a condition or circumstance would happen just by chance without experimental intervention
What is meant by statistical significance?
Because the p-value is very small (
What are the core ethical principles of research with humans?
Beneficence, Autonomy, and Justice
Core Ethical Principles: What is beneficence?
Maximize the benefits to society while minimizing harm to research participants
Core Ethical Principles: What is autonomy?
Allow research participants to give consent to participate in research. Don't force or coerce people to participate.
Core Ethical Principles: What is justice?
Don't conduct research on a small segment of the population (one type of person). Be sure that the people who are bearing the burden of participating are representative of those who can benefit from the research.
What are the measures of central tendency?
mean, median, mode
What are descriptive statistics?
Descriptive statistics are summary statistics that allow the researcher to organize data in ways that give meaning and facilitate insight. They are calculated to describe the sample (ie. demographic statistics) and key study variables.
What are inferential statistics?
Inferential statistics are designed to address objectives, questions, and hypotheses in studies to allow inference from the study sample to the target population. They help us to: identify relationships examine predictions determine differences among groups
What is reliability?
the consistency with which the same event is repeatedly measured. scores are consistent across repeated testing.
What are our five main senses?
1. Vision
2. Hearing
3. Touch
4. Smell
5. Taste
Plus...
vestibular system (balance)
proprioception (info about body and limb position)
What does "Sensation and Perception" examine?
Sensation and perception processes of identifying objects and events in the world so we can move in environment
Why study sensation and perception?
Helps understand behavior and mental activity.
Helps understand how sensory systems work
Helps design better and more effective ways of presenting info to people
What is sensation?
Occurs in organism when physical energy produces a change in specialized elements of the nervous system called receptors
"I see a spot of light" "I hear a buzz"
What is perception?
The results of psychology processes in which sensations are interpreted and organized to give meaning to objects or events that produce sensations attributed to specific object in the world
"I see the moon" "I hear fire alarm"
What is transduction?
Conversion of physical energy into electrical energy in nervous system
What are the different ways to measure perception?
Phenomenological methods: present stimulus ask the person to describe it (limited)
Yellow circle ( works ok for simple stimuli, less useful for complex, not precise, does not work for animals)
What is psychophysics?
The study of the relationship between physical stimuli and the resulting psychological experiences
What is the difference between detection and discrimination?
Detection: what is weakest stimulus we can detect
Discrimination: what is smallest different between stimuli that we can discriminate
What is an absolute threshold?
the minimum stimulation needed to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time
When do neurons fire action potentials?
When they are stimulated by an all-or-nothing response
What are response biases?
The brain receives info from sensory neurons and decides whether stimulus is present
What are the two types of response bias in psychology?
A conservative bias and a liberal bias.
What is a liberal bias?
A person who wants to appear sensitive will be more likely to say "yes"
This leads to fewer misses, fewer correct rejections, more hits, and more false alarms.
What is a conservative bias?
A person who wants to appear insensitive will be more likely to say "no"
This leads to more misses, more correct rejections, fewer hits, and fewer false alarms
What is signal detection theory?
a theory predicting how and when we detect the presence of a faint stimulus (signal) amid background stimulation (noise). Assumes there is no single absolute threshold and that detection depends partly on a person's experience, expectations, motivation, and alertness.
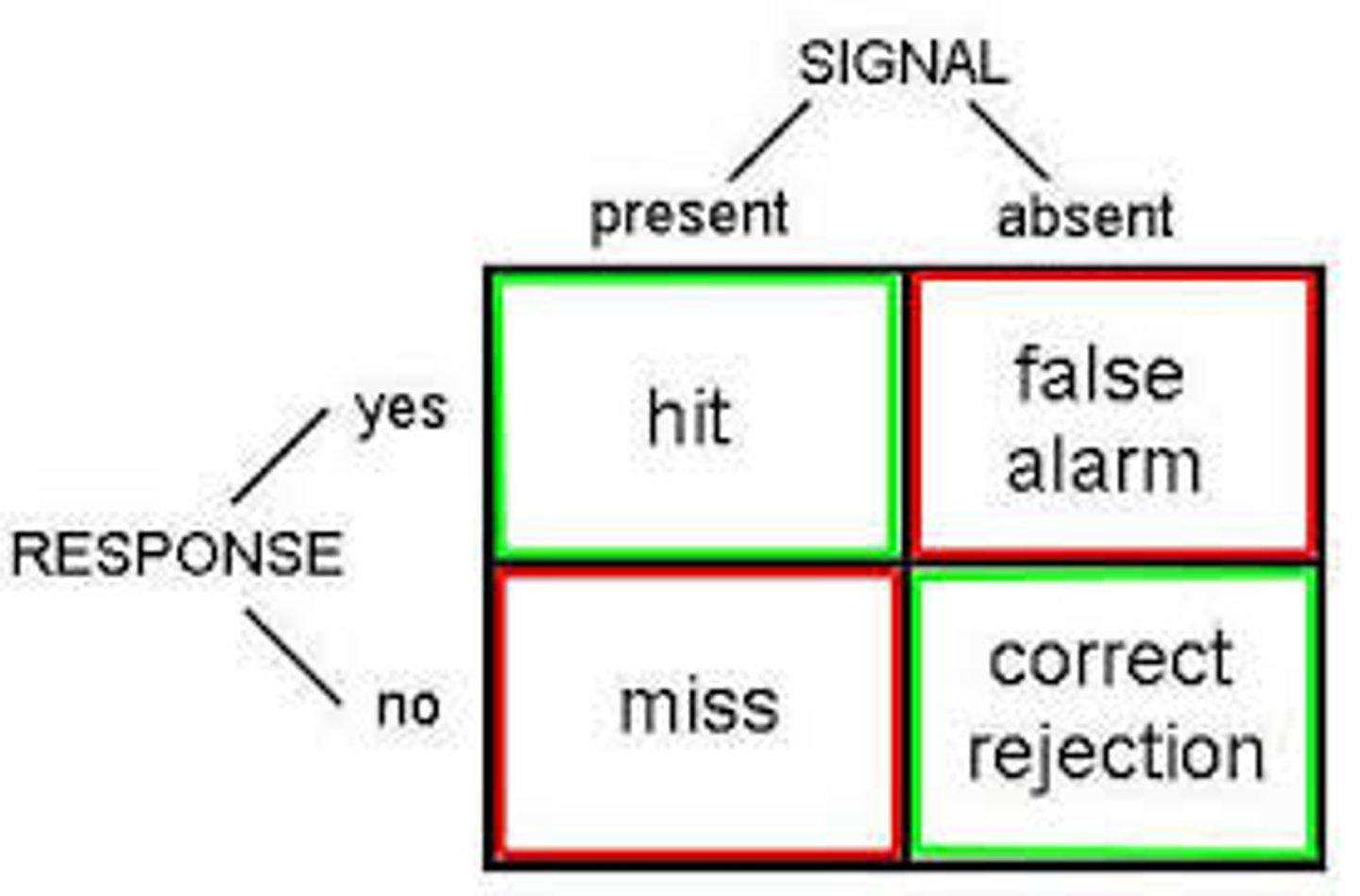
SIGNAL DETECTION THEORY: What is the term for when there is a signal present and a person responds "no"
A miss.
SIGNAL DETECTION THEORY: What is the term for when there is no signal present and a person responds "no"
A correct rejection.
SIGNAL DETECTION THEORY: What is the term for when there is a signal present and a person responds "yes"
A hit.
SIGNAL DETECTION THEORY: What is the term for when there is no signal present and a person responds "yes"
A false alarm.
What is Weber's Law?
the principle that, to be perceived as different, two stimuli must differ by a constant minimum percentage (rather than a constant amount)
The larger the original stimulus, the larger the just noticeable difference (JND) needs to be for it to be detected
What is adaptation?
The ability to adjust to new information and experiences.
What is the visual stimulus?
Electromagnetic energy is the stimuli that enter your eye: energy emitted or reflected from objects in the form of electrical or magnetic waves
What are the properties of waves?
wavelength and amplitude
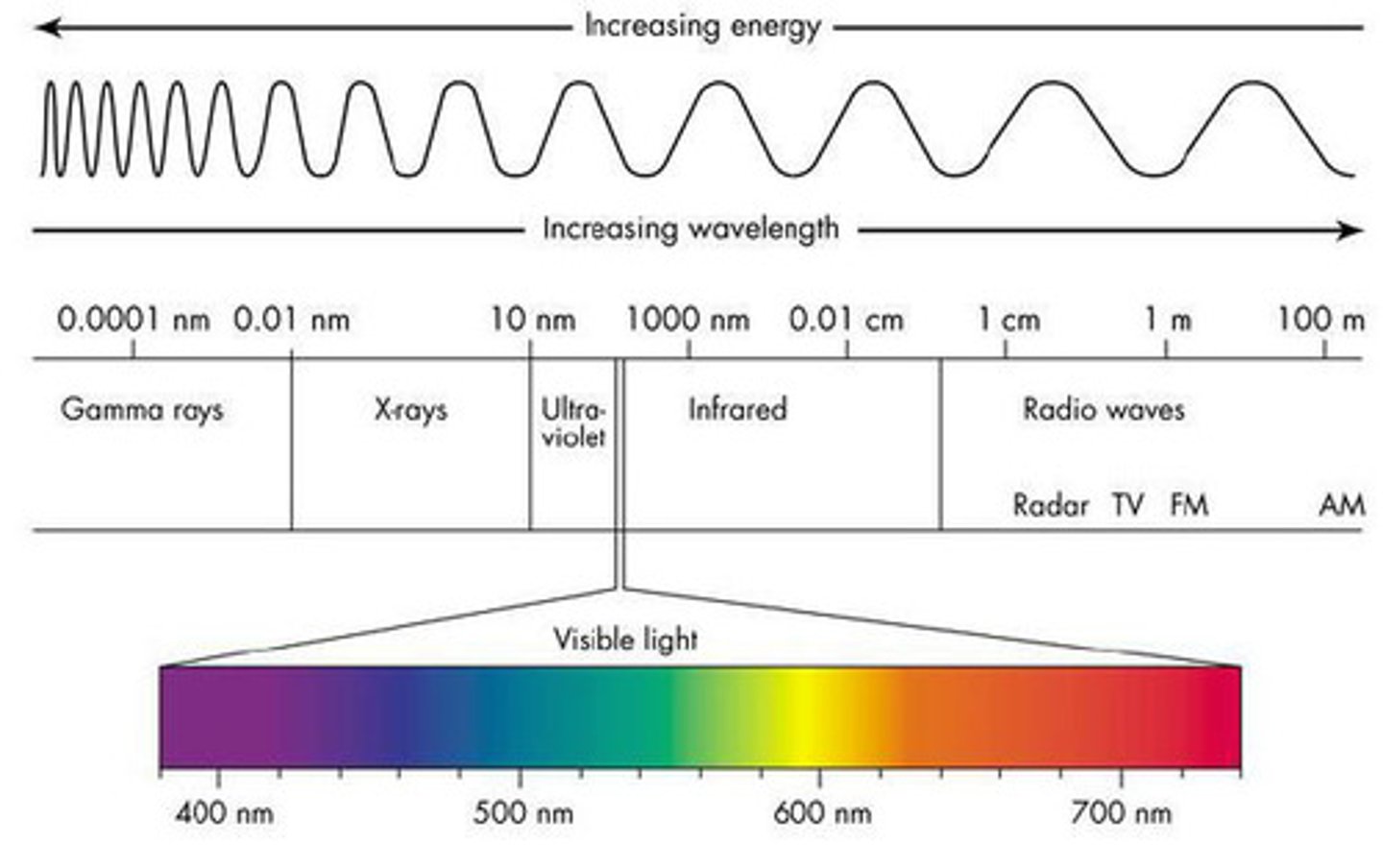
What are human's visual receptors sensitive to?
A small range (400-700 nm) of electrical magnetic waves
What are the stages of visual information processing?
Step 1: Light enters the eye through the cornea.
Step 2: The pupil adjusts in response to the light.
Step 3: The lens focuses the light onto the retina.
Step 4: The light is focused onto the retina.
Step 5: The optic nerve transmits visual information to the brain:
How does transduction occur?
Transduction occurs in rods and cones and those signals pass to ganglion cells and then to brain
What are cones and rods?
photoreceptors in the retina
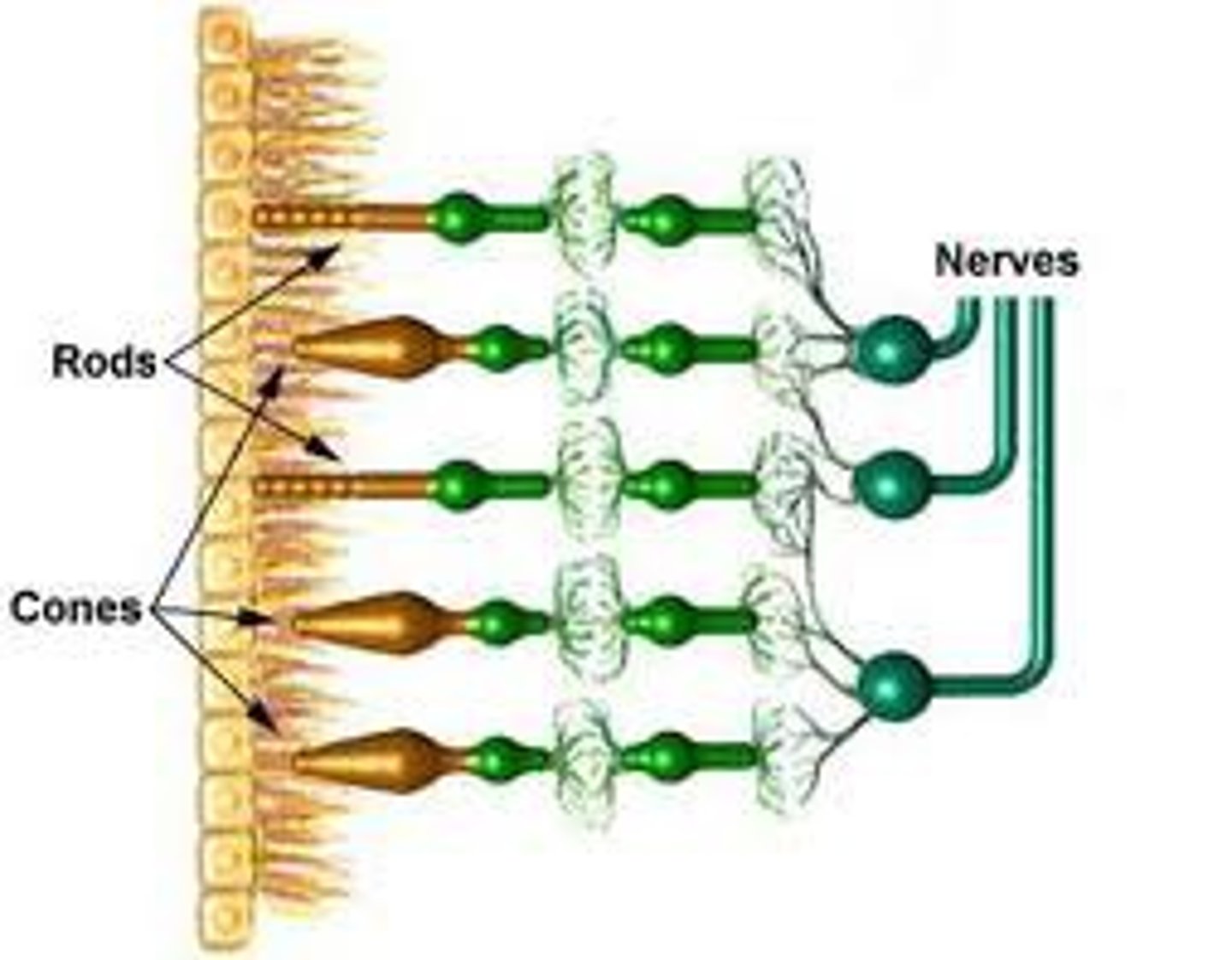
Where are light receptors located?
The retina.
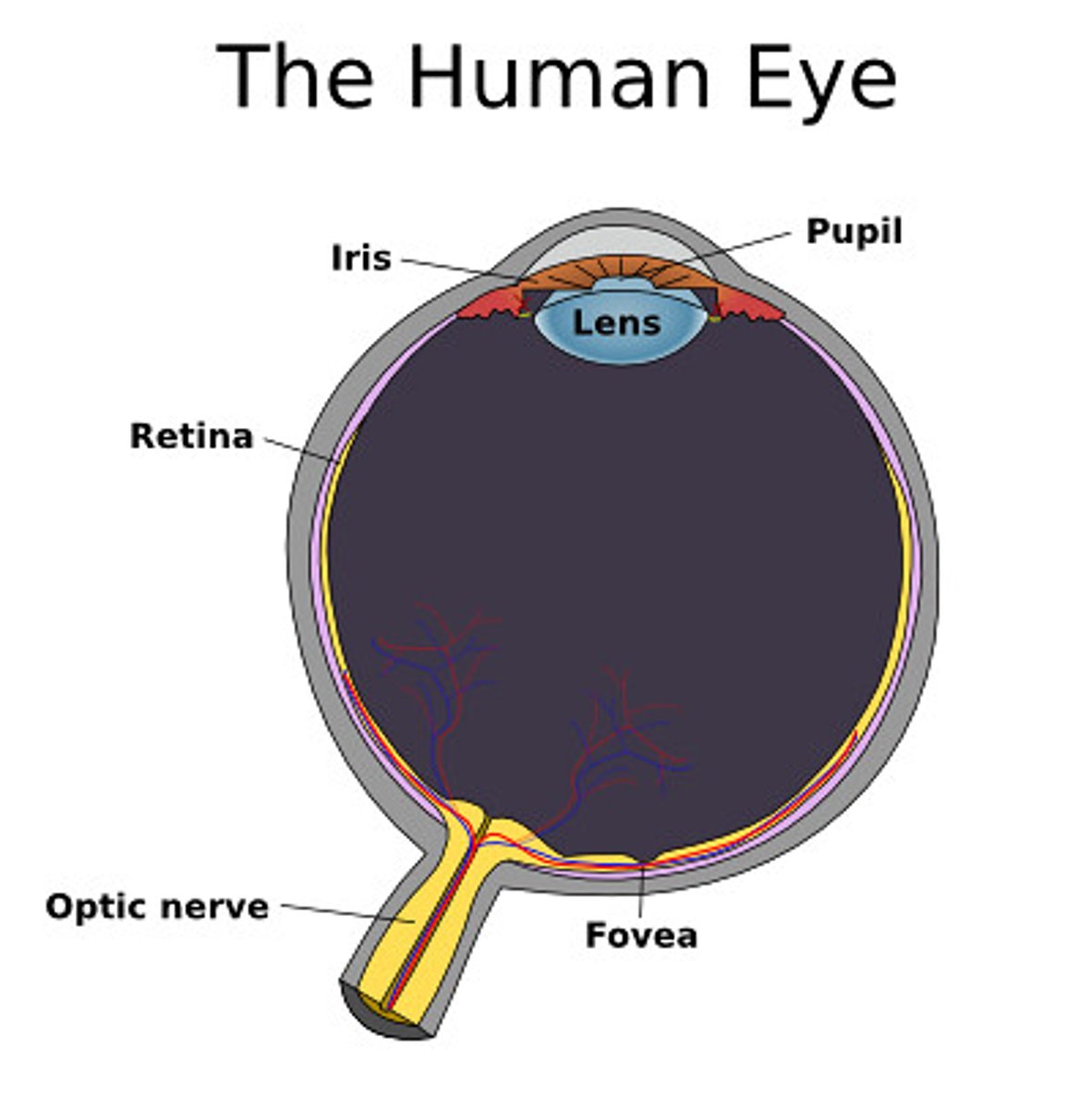
What are the parts of the eye? Where is each one located?
Pupil, cornea, lens, fovea, retina, and optic nerve
How do humans perceive wavelengths?
As colors
What is accommodation of the eye?
The process of changing the shape of the lens to focus on near or distant objects
What is the fovea?
(point of central focus) most sensitive part where we can see details.
a small depression within the neurosensory retina where visual acuity is the highest
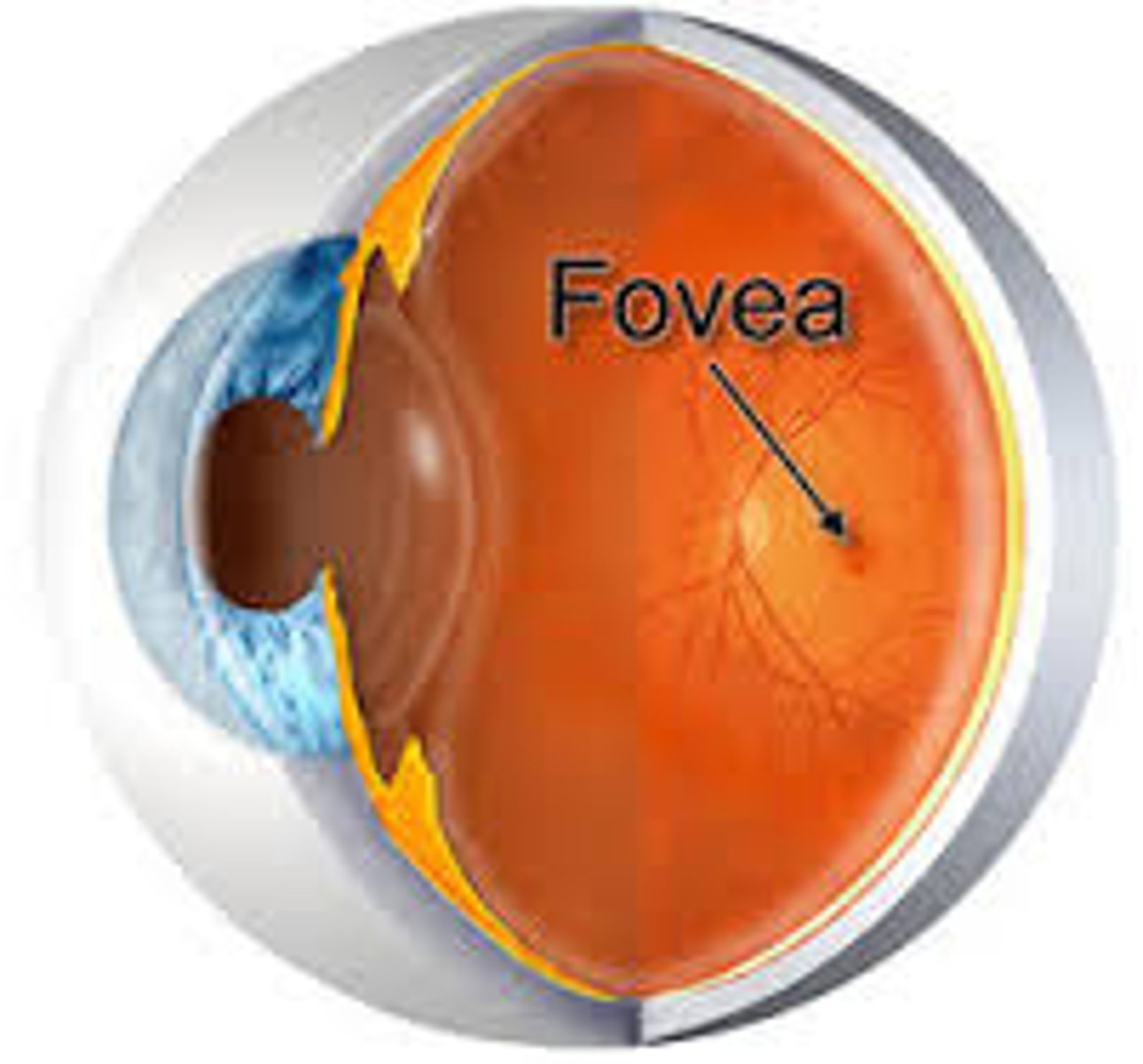
What are the distributions of rods and cones in the retina?
Rods take up the peripheral space which is larger. Cones take up a small area of the retina. There are more rods than cones.