LITARTS_Christianity in the Philippines
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
Iglesia ni Cristo
is a Christian religious organization founded in 1914 in the Philippines, known for its distinctive doctrines, rejection of the Trinity, and emphasis on global evangelism.
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (LDS)
Restored church through Prophet Joseph Smith.
Believes in the restoration of Priesthood keys and the fullness of the Gospel.
Central role of Jesus Christ in beliefs and daily lives.
Mission to invite all to follow Jesus and experience joy through Him.
Considers The Book of Mormon, along with the Bible, as a testament of Jesus Christ.
Belief in these scriptures for a better understanding of God's plan for His children.
Seventh Day Adventist Church
Adventist Protestant Christian denomination.
Distinguished by observing Saturday as the Sabbath.
Emphasis on the imminent Second Coming of Jesus Christ.
Holds annihilationist soteriology, a belief in the ultimate destruction of the wicked.
Victory Church
Evangelical multi-site church based in Taguig, Philippines.
Commonly known as Victory.
Member of Every Nation Churches.
Officially named Victory Christian Fellowship of the Philippines, Inc.
Christian Cross
Traditional symbol representing Christianity.
Widely recognized as the best-known symbol of Christianity.
In use since early Christianity, gaining prominence during the medieval Crusades.
Coexisted with other symbols like Ichthys, Staurogram, Alpha and Omega, Christogram, Labarum, etc.
Originated during times of Christian persecution in the Roman Empire, serving as a discreet means of identification among Christians.

Christian Fish Symbol (Ichthys)
Initially, the symbol of Christianity was a fish.
In Old Greek, "ἰχθύς" (ichthys), corresponding to the Christian postulate abbreviation "ΙΧΘΥΣ" - "Jesus Christ, God's Son, Savior."
The fish symbol served as an inconspicuous representation of Christian identity during times of persecution in the Roman Empire.

Star and Crescent
Used as the flag of the Ottoman Empire from 1844.
Initially not directly associated with Islam but became linked to the faith over time.
Gradual association with Islam due to its widespread use in the decorations of Ottoman mosques in the late 19th century.
Occasionally adopted as an emblem by Islamic organizations, such as the All-India Muslim League in 1940 (later becoming the Flag of Pakistan).
Also adopted by the US American Nation of Islam in the 1970s.

Angel Moroni
Important figure in the theology of the Latter Day Saint movement.
Prominently featured in Mormon architecture and art.
Initially used as a weather vane for the 1844 Nauvoo Temple.
From the 1892 Salt Lake Temple onward, most LDS temples feature a statue of Angel Moroni.
The statue includes an angel with a trumpet.
Notable presence on temples, symbolizing a significant aspect of Latter Day Saint beliefs.

Star of David in Jewish Flags
Jewish flags with hexagrams and other symbols date back to the 14th or 15th century CE.
The use of the Star of David to represent the Jewish community is first recorded in Vienna in the 17th century CE.
Over time, the Star of David has become a widely recognized symbol of Judaism.

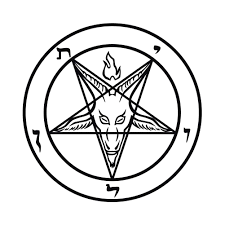
Sigil of Baphomet
Official insignium of LaVeyan Satanism and the Church of Satan.
Derived from an older symbol in the 1897 book "La Clef de la Magie Noire."
Initially used by the Church of Satan during its formative years.
A unique version was created during the writing of The Satanic Bible to exclusively identify with the Church of Satan.
Named the Sigil of Baphomet for the first time in Anton LaVey's The Satanic Rituals.
First appeared on the cover of The Satanic Mass LP in 1968 and later on the cover of The Satanic Bible in 1969.
The symbol is copyrighted by the Church of Satan.
Allah symbol
Strong tradition of aniconism in Islam historically limited the development of symbols for the religion.
Traditionally, Islam lacked a distinct symbol.
Recent developments include the use of single-colored flags (e.g., Green in Islam, Black Standard).
In the 1970s, the desire to create national flags for newly formed Islamist states led to the adoption of written text expressing core concepts:
The shahada is featured in the flag of Saudi Arabia (1973).
The takbir is incorporated into the flags of Iraq (2008) and Iran (1979).

Eye of Horus
Represents protection, royal power, good health, and the god Horus.
Often associated with the Eye of Horus, a powerful and protective symbol in Ancient Egyptian religion.
