Content Category 2B: The structure, growth, physiology, and genetics of prokaryotes and viruses
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
archaea and bacteria
§ 1-celled organisms visually similar to bacteria
§ single circular chromosome,
§ divide by binary fission or budding,
§ share a similar structure to bacteria.
Interestingly, Archaea are resistant to many antibiotics.
archaea and eukarya
§ hypothesized that eukaryotes and domain Archaea share a common origin.
§ Both start translation with Met,
§ similar RNA polymerases
§ associate their DNA with histones.
bacteria and eukarya
bacteria and eukaryotes have analogous structures→ difficult to develop medicines target only bacteria.
no spindles and asters (eukaryotic mitotic apparatus) → prokaryotic cytoskeleton pulls replicated DNA apart.
Bacteria don’t have Golgi, ER, mitochondria, chloroplasts
Bacterial cell wall = PG vs plant cell wall=cellulose and fungi cell wall is made of chitin.
• Flagellar propulsion, mechanism for bac
o Bacterial flagella is made of flagellin. eukaryotic flagella made of microtubules (9+2)
o MOA bacterial flagella is rotation. A rotor at the base of the flagella drives the rotation, powered by a proton or sodium gradient. (eukaryotic flagella is powered directly by ATP)
archaea
genes and several metabolic pathways like eukaryotes
Considered extremophiles; harsh environments with extremely high temperatures, high salinity, or no light.
some are photosynthetic, many chemosynthetic ( make energy from inorganic compounds, including S- and N-based compounds, like ammonia/NH3
hfr or high frequency genetic recombination
bacterial cell in where F plasmid has integrated into the chromosome (through transformation)
During conjugation with F⁻ cell, Hfr cell transfers chromosomal genes starting from F plasmid’s origin.
full transfer is rarely completed, recipient stays F⁻ but gains some new genes.
Hfr strains are used to map bacterial genes based on transfer timing.
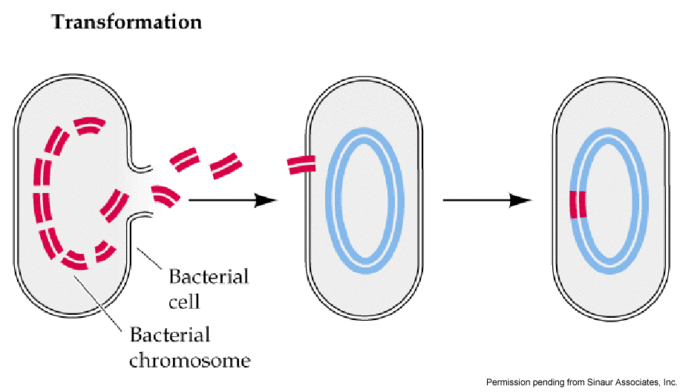
transformation
incorporation into bacterial genome of DNA fragments from external medium
o When a bacterium dies, it lyses and spills many DNA fragments into the environment
o Another bacteria encounters these DNA fragments, takes them in, and integrates them into its own genome
o If the DNA fragments contained an antibiotic resistant gene, then the transformation just made the bacteria antibiotic resistant

conjugation

o Transfers genetic material between bacteria via conjugation bridge (made of sex pilli on donor male+)
o Recipient female (-)
o E.coli can make pillus (F+) if it has fertility factor(plasmid that contains conjugation/pillus genes)
o F+ bacteria can transfers plasmid to F-bacteria
o Conjugation can also transfer some genomic DNA (because F+ plasmid can integrate into the chromosome)

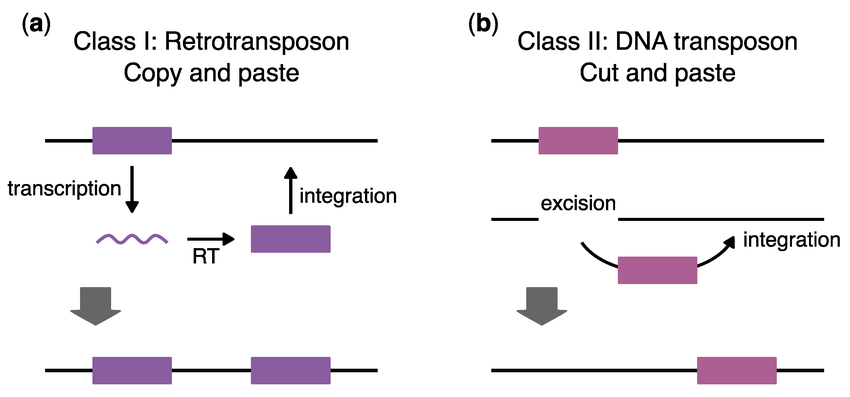
transposons
· (present in prok + euk cells)
o heterogeneous class genetic elements can insert at new locations on chromosomes. 3 groups:
§ Class I, retrotransposons; Class II, DNA transposons; Class III, miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements
o direct repeat flanking sequences = not part of transposons,
o terminal inverted repeats = part of the transposons.
o DNA transposons translocate via cut-and-paste mechanism, retrotransposons translocate via a copy-and-paste mechanism.
o Transposons cause significant changes in genome organization and gene sequence. insertion/deletion mutants and chromosomal inversion mutants.
o tools in gene delivery or targeted mutation.

bacteriophage structure
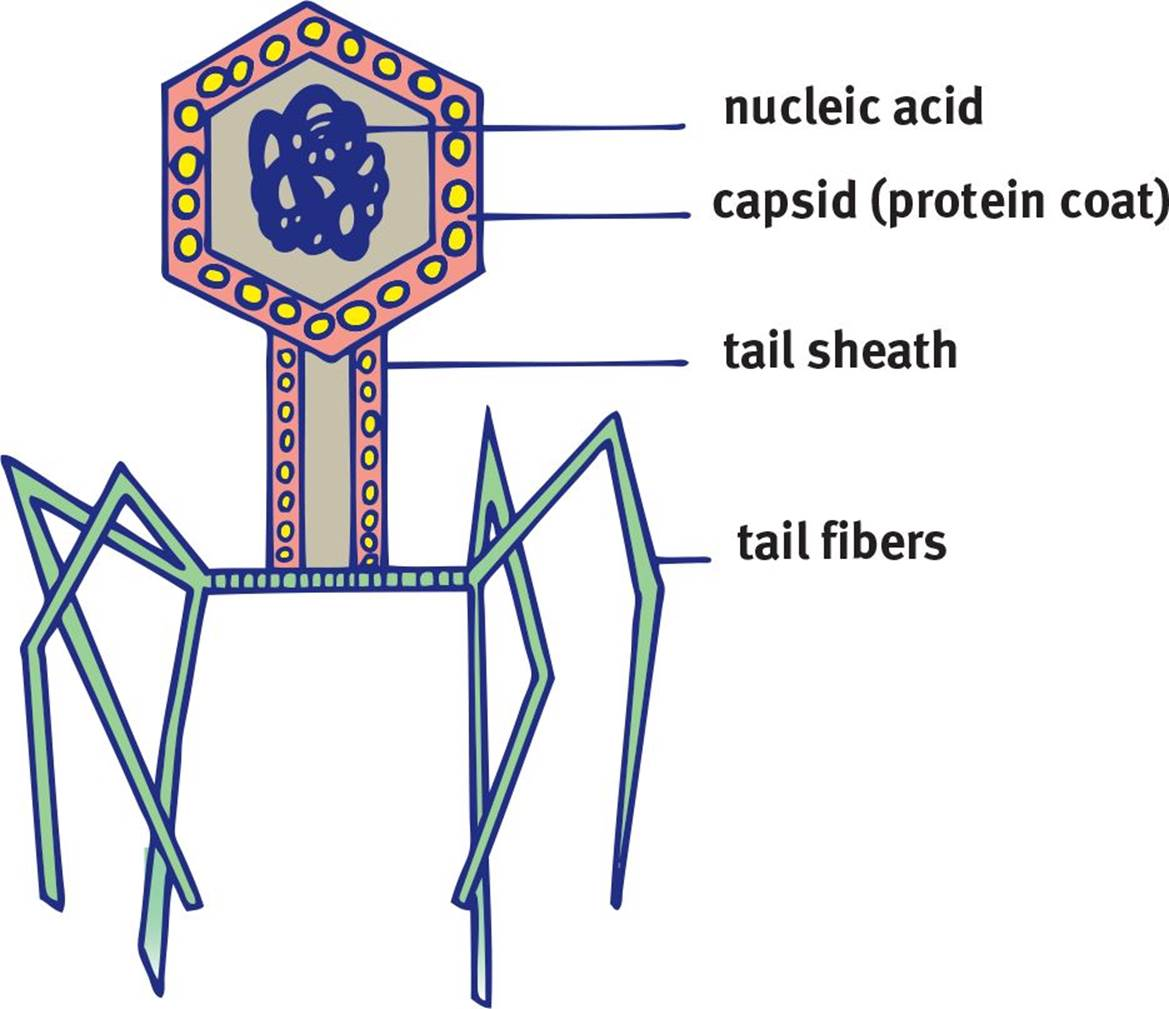
o Head stores genetic material
o Sheath provides a passageway for genetic material to be injected into the host bacteria
o Tail fibers attach to the host bacteria

o Out of the RNA viruses, those that convert their genome into DNA inside their host are called _________
retroviruses
o Retroviruses contain their own reverse polymerase to convert RNA to DNA before the host’s polymerases take over
viruses
• General structural traits (nucleic acid and protein, enveloped and non-enveloped)
o Protein coat covers nucleic acid
o cant replicate by themselves. depend on host’s replication organelles
o host’s ribosomes makes necessary protein coats and polymerases that replicate viral genetic material.
o Some have envelope derived from the host’s cell membrane, others lack it (non-enveloped)
Enveloped viruses bud off host’s membrane
Non-enveloped viruses cause host to burst to release viral particles
o Viruses don’t have any organelles or a nucleus. genetic material is simply packed inside a protein coat.
o Viruses are roughly 100 times smaller than bacteria, and 1000 times smaller than eukaryotic cells
Generalized phage and animal virus life cycles
o Attachment to host, penetration of cell membrane or cell wall, and entry of viral genetic material
o Use of host synthetic mechanism to replicate viral components
§ Host’s ribosomes synthesize necessary enzymes. Host’s ATP provides necessary energy. The host also provides the raw materials such as nucleotides and amino acids.
o Self-assembly and release of new viral particles
§ The coat proteins and viral genetic material will assemble into viral particles by themselves
Transduction
• transfer of genetic material by viruses
o 1. Virus infects cell: host DNA degraded into fragments, viral DNA takes over control
o 2. Host DNA fragment gets packed into virus progeny by accident
o 3. Virus progeny infects another cell, injects previous host’s DNA fragment
o 4. Fragment enters cell, finds its homologous counterpart, and crossover
Retrovirus life cycle
• : integration into host DNA, reverse transcriptase, HIV
o 1. Retrovirus enters the host
o 2. Viral reverse transcriptase converts viral RNA genome into double-stranded DNA
o 3. Virally encoded enzyme, called integrase, adds in viral DNA into the host’s genome at a random place
o 4. When the host replicates, the viral DNA gets replicated also
viroids
· Prions and viroids: subviral particles
o smaller than viruses because only made circular ssRNA.
o Before, they were only found to infect plants. Today, they have been found in humans, in the case of Hepatitis D.
catalytic RNA can make or break covalent bonds, self-cleave to create more viroids. NOT the same as virions (whole viruses)

prions
· Prions and viroids: subviral particles
o no genetic material
o only made of proteins.
o prion protein in beta-sheet conformation (normal protein generally in shape of an alpha helix).
o prion protein and normal protein= same amino acids = same protein but in different shapes.
o When beta-sheet comes in contact with alpha-helix changes α-helix to β-sheet.
o more become β-sheets protein deposits. (somewhere in the brain, normal cleanup still happens, leaves huge holes in your brain as proteins are removed, causing disease)
prokaryotic plasmids
plasmids = extragenomic DNA
o dsDNA
o exist and replicate independently of the genomic DNA, or be integrated into it
o inherited
o not needed for growth and reproduction in wild
bacterial growth
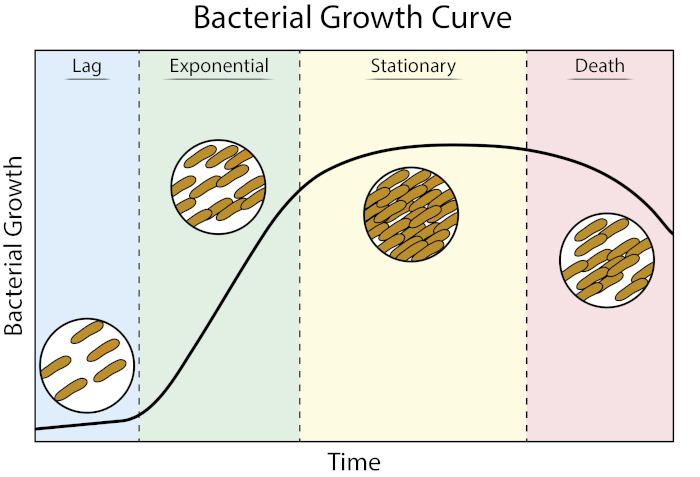
o Exponential growth
o Bacterial growth starts off being exponential because of the nature of binary fission. Later, when food becomes short, and it gets crowded, growth slows and eventually plateaus

facultative anaerobe
o doesn’t need oxygen for growth and metabolism, but grows better with oxygen
o Aerotolerant anaerobes:
don’t use oxygen, but can survive in oxygenated environments
bacterial relationships
o Parasitic = +/- ex disease causing bacteria
o Mutualistic = +/+ ex, E. coli in your gut; the natural flora on your skin
o Commensalistic = +/0
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) enters the human body and remains dormant in the nervous system until it produces an outbreak after exposre to heat, radiation, or other stimuli. Which of the following statements correctly describes HSV?
A.While it remains dormant in the nervous system, the virus is in its lytic cycle.
B.During an outbreak, the virus is in the lysogenic cycle.
C.Herpes simplex virus adds its genetic information to the genetic information of the cell.
D.The herpes simplex virus contains a tail sheath and tail fibers.
C. Lytic cycle: virus’s DNA takes control of host cell genetic machinery to make numerous progeny. Host cell lyses and releases new virions (each capable of infecting other cells)
Lysogenic cycle: viral DNA added to host cell genome → stays dormant for days/yrs
Spontaneously or environmental conditions can reactivate a provirus to join the lytic cycle
matlose
2 glucose molecules linked via α1-4 glycosidic linkage
[R] sugar found in grain
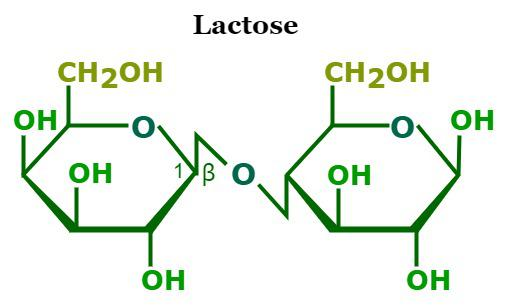
lactose
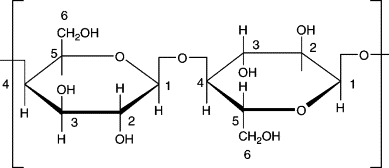
Gal— β1,4—Glucose
[R] sugar found in milk
![<p>Gal— β1,4—Glucose</p><ul><li><p>[R] sugar found in milk</p></li></ul><img src="https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d6cfc33f-609a-4698-98fd-0483d1b608e3.png" data-width="100%" data-align="center" alt="knowt flashcard image"><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d6cfc33f-609a-4698-98fd-0483d1b608e3.png)
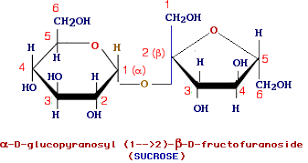
sucrose
Glucose—α1,β2 glycosidic linkage—Sucrose

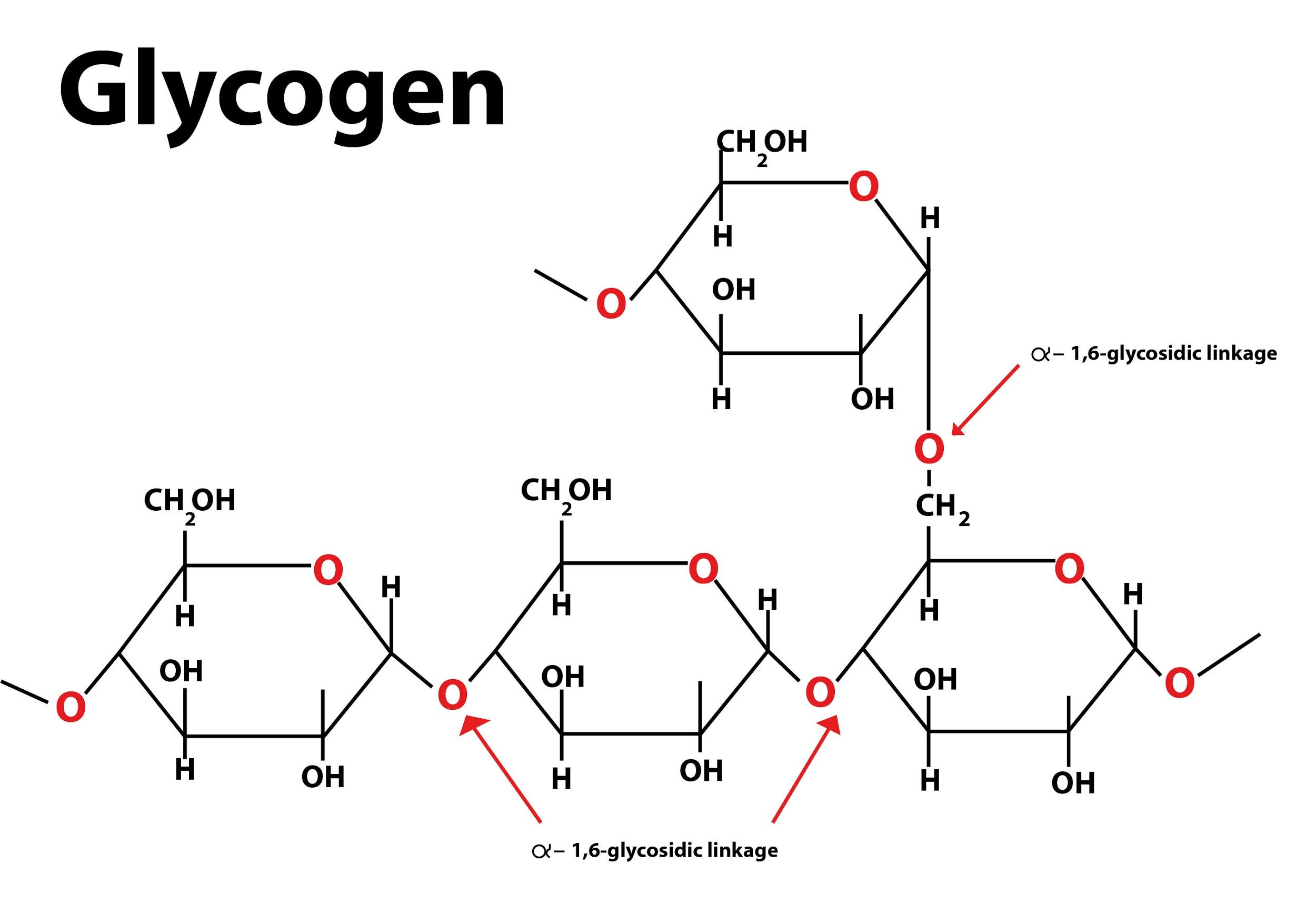
what kind of glycosidic linkages occur in glycogen and starch
α1,4 and α1,6 glycosidic linkages

glycosylation
attaching carbohydrate grp to proteins or lipids
what kind of glycosidic linkages occur in cellulose and chitin
β1,4 glycosidic linkages

gluconeogenesis
making glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors








fetal circulation
diffusion of H20, aa, glucose, O2, inorg salts (needs gradient for diffusion)
HbF has higher O2 affinity than adults
umbilical cord has more umbilical arteries (fetus→placenta) > umbilical veins (placenta→fetus)
foramen ovale connects R and L atria; ductus arteriosus PA→aorta -→ both bypass lungs
ductus venosus - bypass liver, umbilical vein—inferior vena cava