Lecture 11 - Epigenome: Chromatin Marks
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
How is a necklace an analogy for DNA?
string - DNA
Beads - Histone octomers
areas with more beads = heterochromatin
areas with less beads = euchromatin
Describe what a nucleosome is
Nucleosome
involves hisones, thier tails, and DNA
Assembly
DNA strands can have histone octomers around folded regions
contain 2x each of H2A, H2B, H3, H4
Histone tails are AA strings not assmebled
Describe how we decode histone marks like H3K27me3
H3 = Histone 3
K27 = Lysine 27
me3 = 3 methyl groups
All added post-translationally , after translation and assembly of histone protein
What are different ways the post-translational modification (PTMs) can interact with DNA throughout he histone protein?
Case 1: Loose
Loosen interaction between DNA + protein (histone)
DNA less associated (connected) with nucleosome → opening chromatin
facilitate interaction with transcription machinery → euchromatin
Case 2: Strengthen
Strengthen interaction between DNA + protein
DNA will become strongly associated with nucleosome → closing chromatin
Less interaction with transcription machinery → heterochromatin’
PTMs can change accessibility of the promoter region of genes
What facilitates moving of nucleosomes?
DNA methylation → transposons inhibits
Histone PTMs (histone tails) → can either inhibit or promote
Other protein → use energy
What are differnet types fo epigenetic variation?
Cytosine DNA methylation
Histone modifications and variants
Nucleosome position and 3D structure
What are features of Histone PTMs?
Many flavors
ex: phosphorylation, methylation, acetylation
Function often unknown
Combinations matter
Histone “Code”
different PTMs are identified at specific histone proteins each with different functions
PTMs work in combinations, not isolated
Describe the process of immunopurification with histone PTMs
1) Crosslink DNA to protein
2) fragment chromatin with sonicator or fragmentase
3) Immunopurify
4) Reverse crosslink chromatin → DNA no longer attached to protein
5) Elute DNA
6) Add Illumina adapters and seq the DNA
7) Align + count reads → tells you how much DNA associates with a given Histone PTM
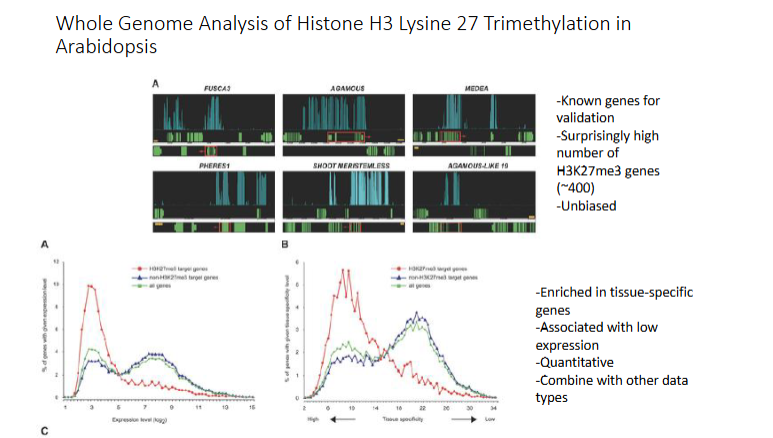
Takeaways fr9om H3K27me3 in Arabidopsis
Top Graph
larger green rectangles - exons
black lines - introns
smaller green rectangles - UTR
Top Graph Takeaways
Genes with HeK27me3 tend to have lower expression than without
Genes with H3K27me# tend to be in highly specific tissues
Bottom Graph
highest proportion of H3K27me3 have low expression
H3K27 have higher tissue specificity
Conclusions on H3K27Ac experiments
H3K27Ac associated with higher gene expression and is not dependent on H3K4me
H3K27Ac in liver associated with increase in expression
What can chromatin marks define
functional states
different combinations of histone PTMs define a functional state
predict functional states depending in data sets
H3.3
RNAPII colocalize with regions on the chromosome with H3.3 and activating HPTMs
likely associated with high expression
The presence of a single histone post-translational modification can determine expression of a gene. True or false?
False; work of combination of different PTMs
Immunopurification was used to identify piwiRNas, to determine sites of DNA methylation and to identify regions of DNA associated with histone post-translational modifications. True or false?
True
There are multiple ways in which lysine 27 of the Histone 3 protein can be post-translationally modified. True or false?
True; ex: me3 or Ac
H3K27me3 is associated with gene repression in both plants and animals. True or false?
true
Determining if a histone protein co-localizes with RNA Polymerase II can provide a clue that a histone protein may be associated with transcription. True or false?
True