chapter 19- HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:56 PM on 4/30/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
1
New cards
HIV selectively infects…. cells
T-helper
2
New cards
what is the genus of HIV
*Lentivirus*
3
New cards
what type of virus is HIV
retrovirus
4
New cards
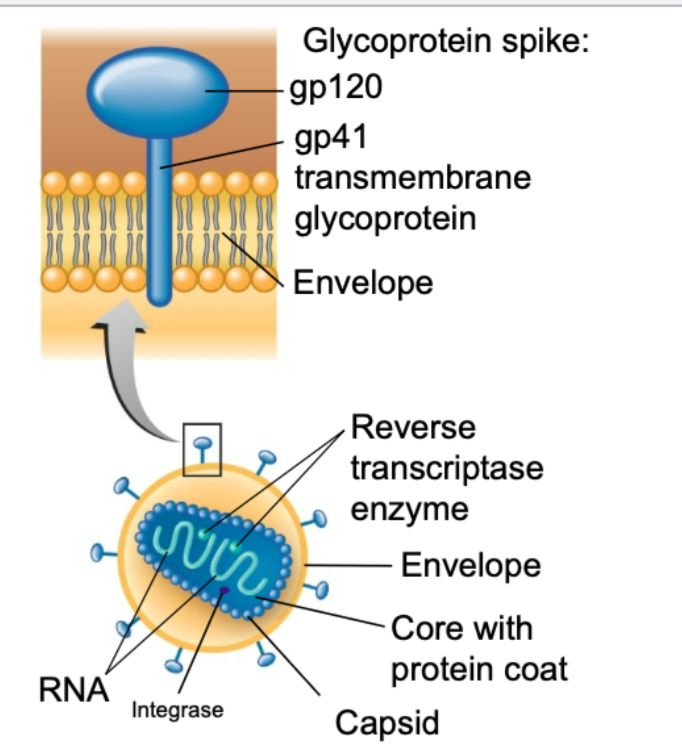
what is contained with the capsid of HIV
2 identical strands of RNA
5
New cards
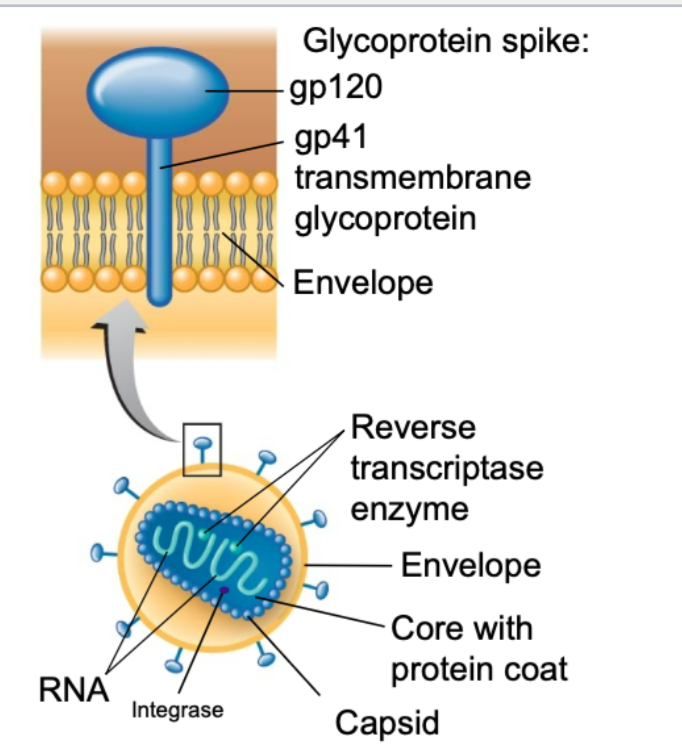
what are two important enzymes that HIV contain
reverse transcriptase
integrase
integrase
6
New cards
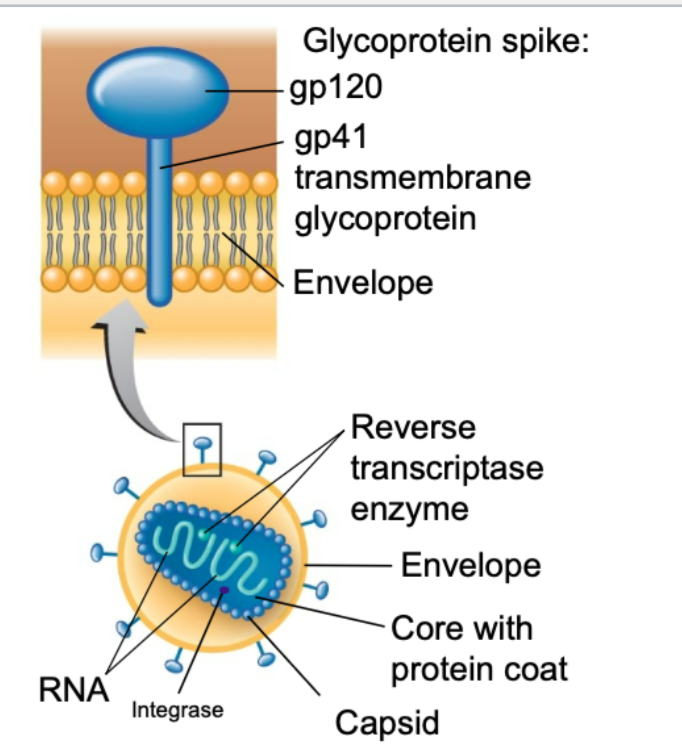
cell plasma membrane of HIV is … (phospholipid)
enveloped
7
New cards
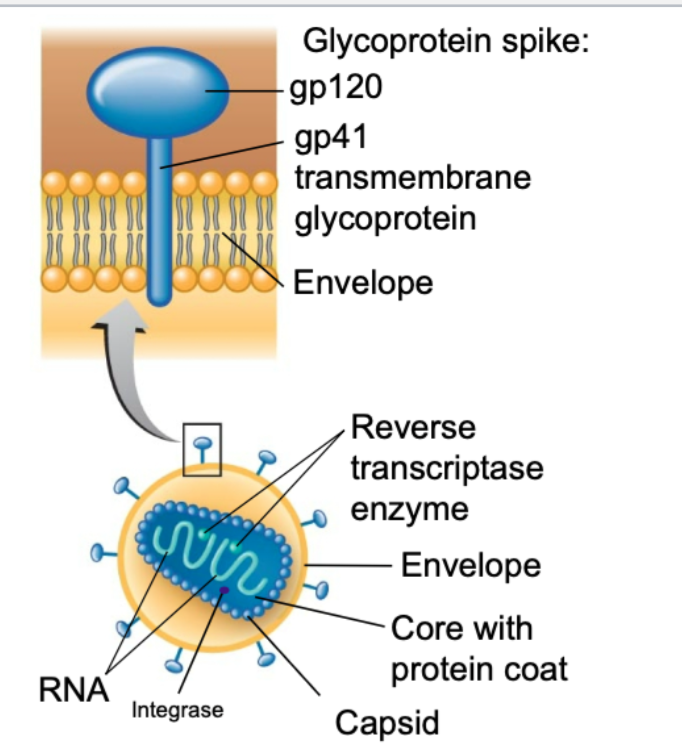
what are found on the other surface of HIV
spike proteins
8
New cards
what are two specific regions of the spike proteins
gp120
gp41
gp41
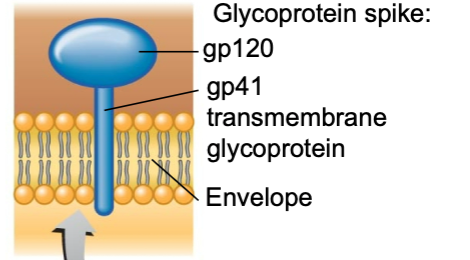
9
New cards
gp120 combine with … receptors
CD4+
10
New cards
what three types of cells are CD4 molecules are carried on
T helper cells
macrophages
dendritic cells
macrophages
dendritic cells
11
New cards
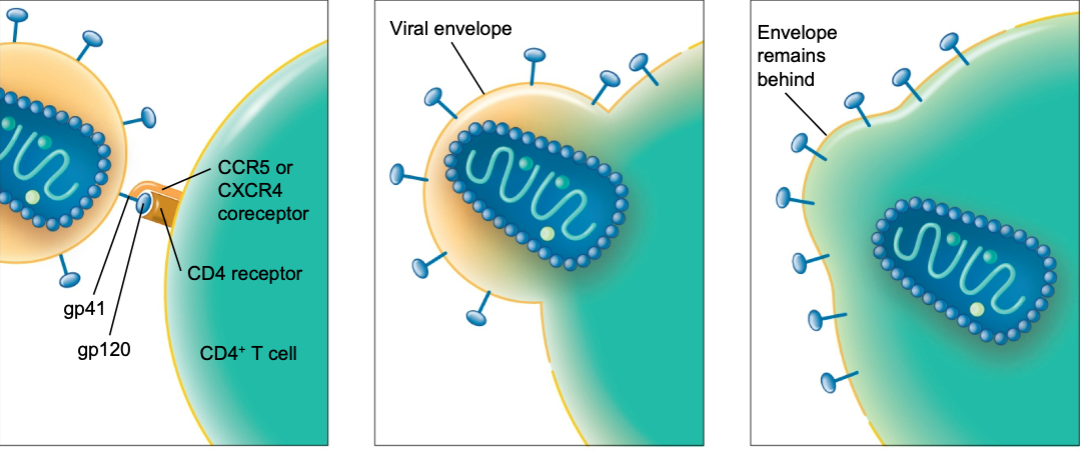
basic three stages of HIV attachment to receptors on target T cell
1. attachment
2. fusion
3. entry
12
New cards
explain the attachment stage of HIV attachment to receptors on target T cell
the gp120 spike attaches to a receptor and to a CCR5 or CXCR4 receptor on the cell
13
New cards
explain the fusion stage of HIV attachment to receptors on target T cell
the gp41 participates in fusion of the HIV with the cell
14
New cards
explain the entry stage of HIV attachment to receptors on target T cell
entry pore is created
after entry, the viral envelope remains behind and the HIV un-coats, releasing the RNA core for directing synthesis of new viruses
after entry, the viral envelope remains behind and the HIV un-coats, releasing the RNA core for directing synthesis of new viruses
15
New cards
what is used to convert single-stranded RNA to DNA
reverse transcriptase
16
New cards
Viral DNA integrates into the … chromosome as a …
host
provirus
provirus
17
New cards
SHORT ANSWER QUESTION… stages of multiplication of HIV
1. enters by fusion between attachment spikes and the host cell receptors
2. un-coating releases the RNA strands and enzymes
3. reverse transcriptase copies viral RNA to produce double-stranded DNA
4. the new viral DNA goes into the host cell’s nucleus and is integrated into the host cell chromosome, using integrase
5. virus matures and eventually leaves the host cell after acquiring everything it needs such as an envelope and attachment spikes
18
New cards
an active infection is when new viruses bud from …
host cells
19
New cards
a latent infection is when DNA is … in the chromosome as a …
hidden
provirus
provirus
20
New cards
HIV normally attacks … first and the goes onto the … … and then finally reaches the … cells
macrophages
lymph nodes
T-helper cells
lymph nodes
T-helper cells
21
New cards
what are the two subtypes of HIV
HIV-1
HIV-2
HIV-2
22
New cards
what type of HIV is more prevalent
HIV-1
23
New cards
HIV-1 is related to viruses that infect … and …
chimpanzees and gorillas
24
New cards
HIV-2 is not often encountered outside of…
West Africa
25
New cards
which of the two subtypes are less pathogenic
HIV-2
26
New cards
which of the two subtypes has a longer asymptomatic period and a lower viral load and morality rate
HIV-2
27
New cards
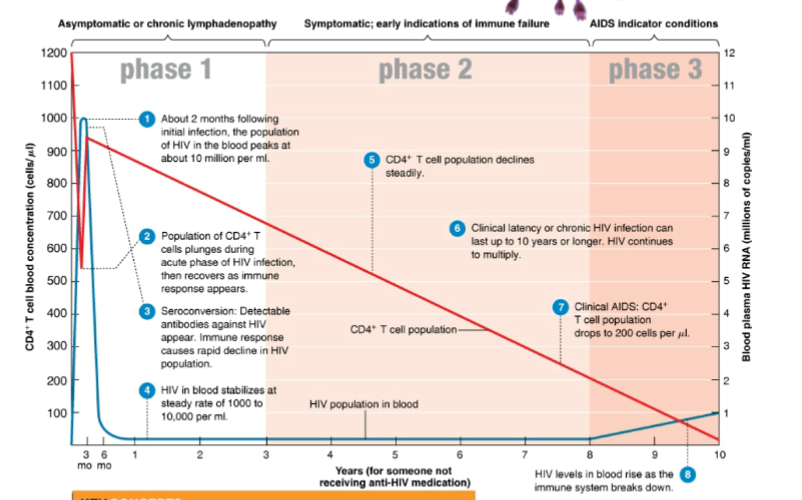
what is the main character of phase 1 of HIV infection
asymptomatic
28
New cards
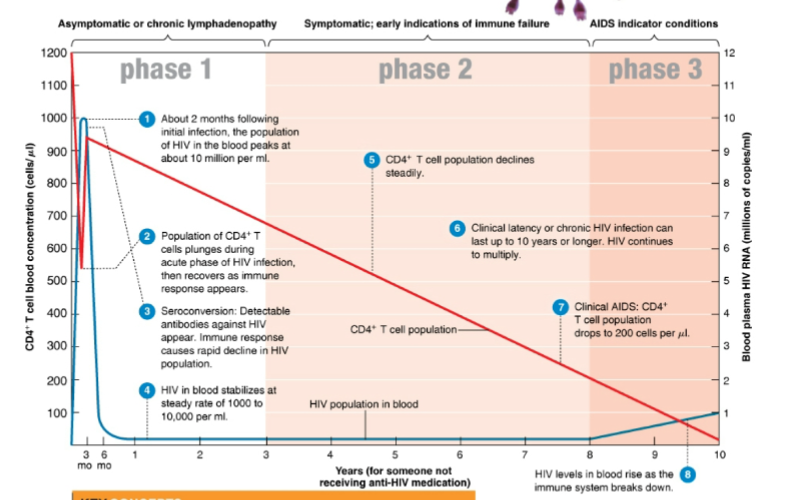
in phase 2 of HIV infection, what steadily declines
CD4+ T cells
29
New cards
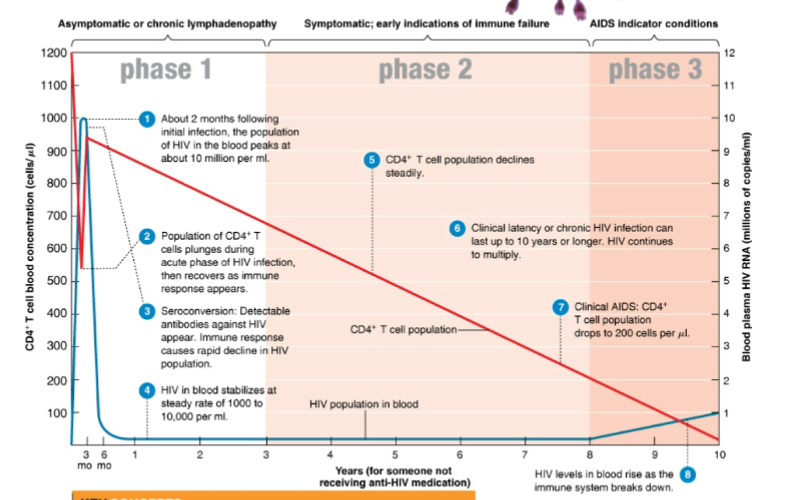
in phase 2 of HIV infection only a few … cells release the virus and there are few serious … ….
infected
disease symptoms
disease symptoms
30
New cards
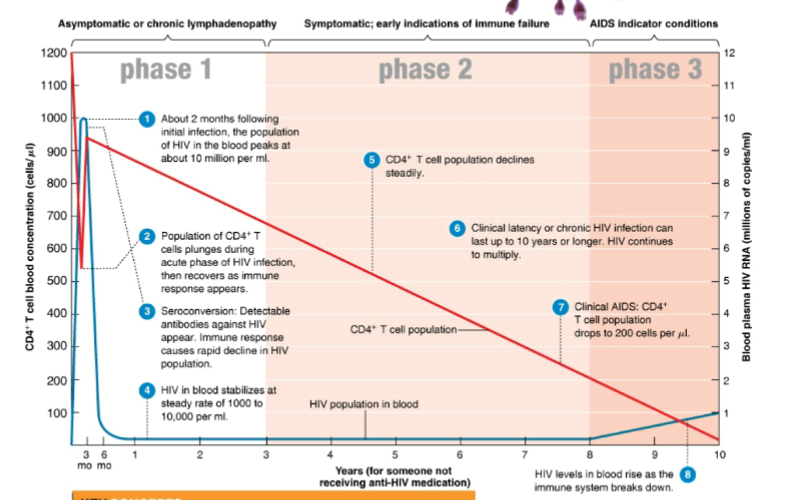
what develops in phase 3 of HIV infection
AIDS develop
31
New cards
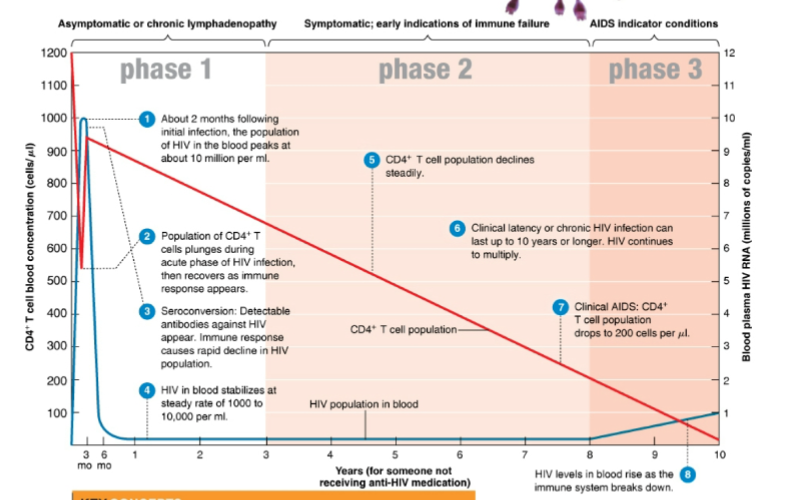
in phase 3 of infection the CD4+ count is below … cell/ ul
200
32
New cards
AIDS is defined as
late stage of HIV infection that occurs when the body’s immune system is badly damaged because of the effect of the virus
33
New cards
HIV infections usually have a … and … initial immune response
strong and effective
34
New cards
… suppress viral numbers
CLTs
35
New cards
why is it impossible to clear the HIV infection
HIV establishes a pool of latently infected CD4+ T cells
36
New cards
what two age groups are more susceptible to HIV infection and lowers their chances of survival due to an underdeveloped immune system
young children
older adults
older adults
37
New cards
what mutation allows individuals to be exposed to HIV virus but never infected from it
CCR5
38
New cards
long term survivors will usually have a… (2 things)
low viral load
effective CLTs
effective CLTs
39
New cards
HIV can survive up to … hours outside a cell
6
40
New cards
HIV can survive more than … days inside a cell
1\.5
41
New cards
what form of sexual contact is the most dangerous in terms of HIV infection
anal-receptive intercourse
42
New cards
there are more than .. million people infected with AIDS worldwide
36
43
New cards
around … % of infected people with AIDS are found in Africa
70
44
New cards
1/3 of AIDs cases in Eastern Europe and Central/ Southeast Asia are from the use of…
infected needles
45
New cards
… transmission is the most common mode of HIV transmission
heterosexual
46
New cards
when gender has a higher rate of HIV transmission
males
47
New cards
what are three types of interventions which are being used to prevent/ treat AIDs
biomedical
behavioral
structural
behavioral
structural
48
New cards
what would happen if a drug was administered for HIV that inhibited fusion/ entry
gp120 receptor will not be able to attach to the CD4+ receptor on the T-helper cell
49
New cards
what would happen if a drug was administered for HIV that inhibited reverse transcriptase
HIV would be not be able to replicate the single stranded RNA stranded into DNA
50
New cards
what would happen if a drug was administered for HIV that inhibited integrase
the new viral DNA will not be able to integrate into the host cell chromosome
51
New cards
what would happen if a drug was administered for HIV that inhibited protease
convert viral precursor proteins into structural and functional proteins