Axial Skeleton-Skull
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
supports and protects body organs like the brain, heart and lungs
protects special sense organs like eyes, nerves for smell, and auditory and balance structures
attachment sites for muscles such as back muscles, intercostal muscles for breathing, and facial expressive muscles.
what are the functions of the axial skeleton
head; neck; and main trunk structures
remember what makes up the axial skeleton which is:
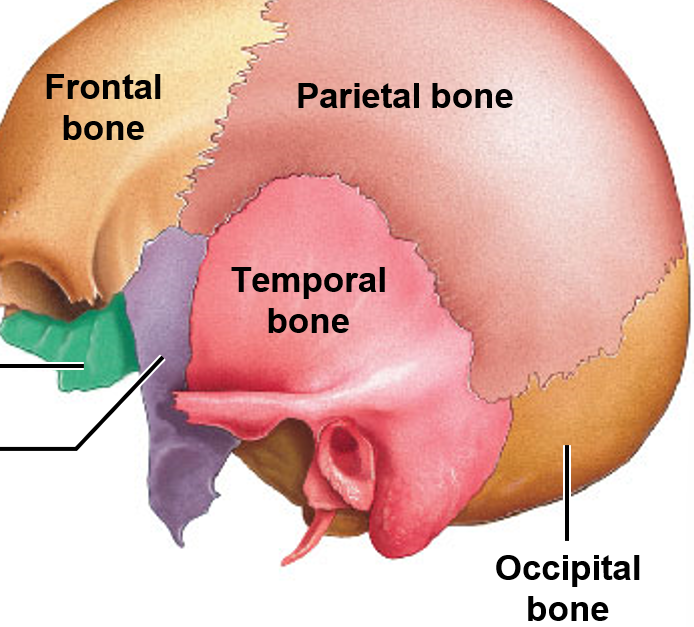
Frontal bone
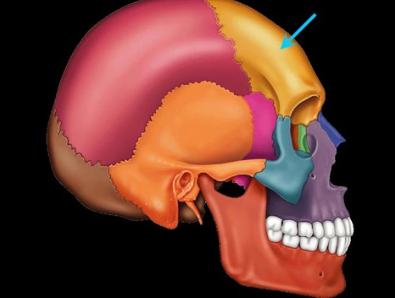
Mandible
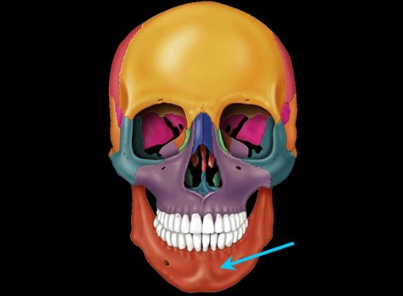
temporal bone
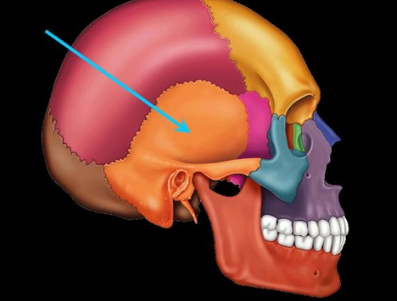
occipital bone
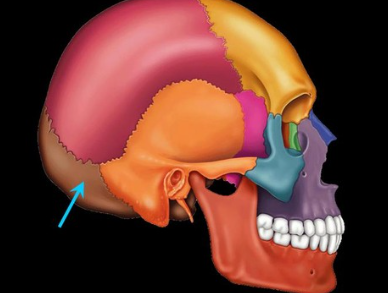
sphenoid bone
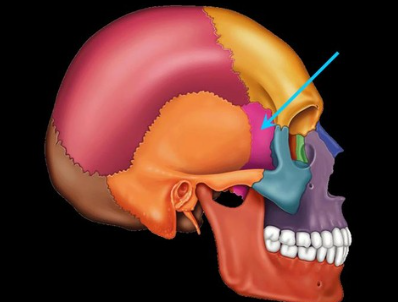
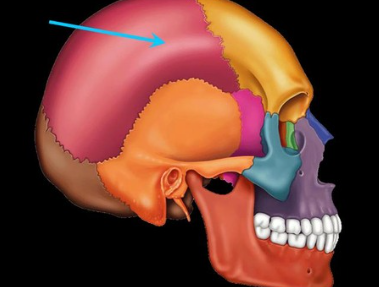
parietal bone
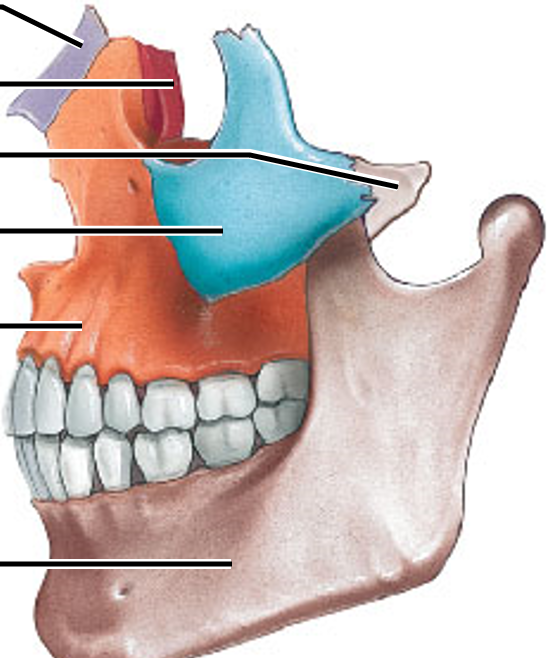
ethmoid bone
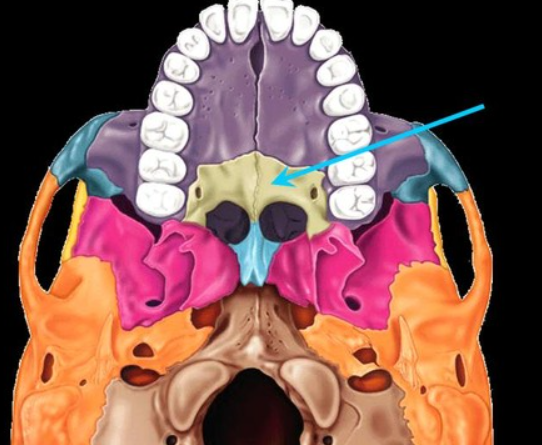
what is the green
vomer bone
what is right behind the blue
hyoid bone
sits high up in the neck. It is mobile and suspended by or held up by the stylohyoid ligaments. This bone has a horseshoe shape (U shape)

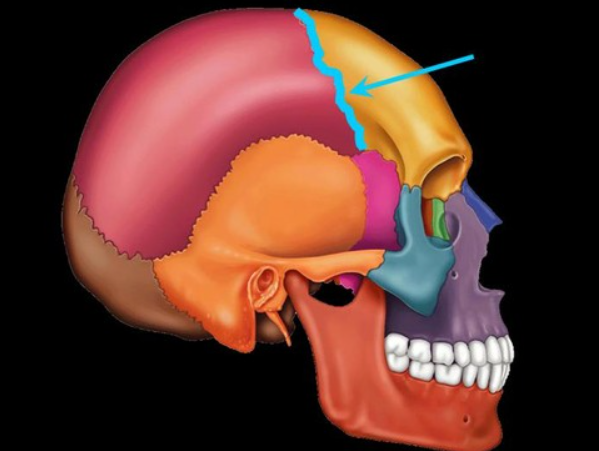
coronal suture
sits between the frontal lobe and parietal lobe
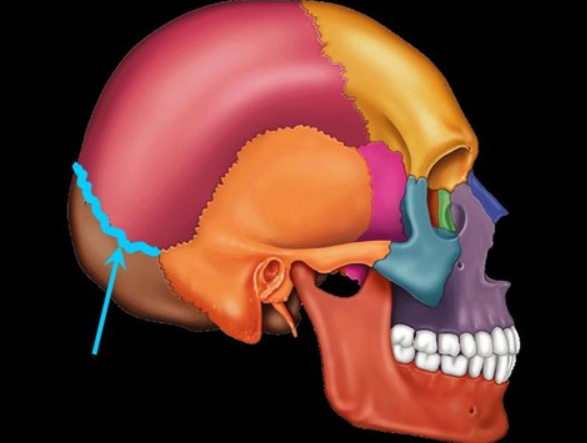
lamboid suture
sits between the occipital and parietal lobe
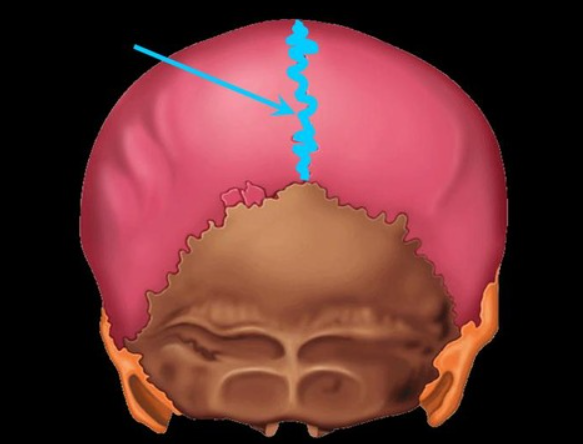
sagittal suture
sits between the right and left parietal bone
Synarthrotic joints. No, there is no movement.
What joint category do the skull sutures fall into? Would there be movement at these joints?
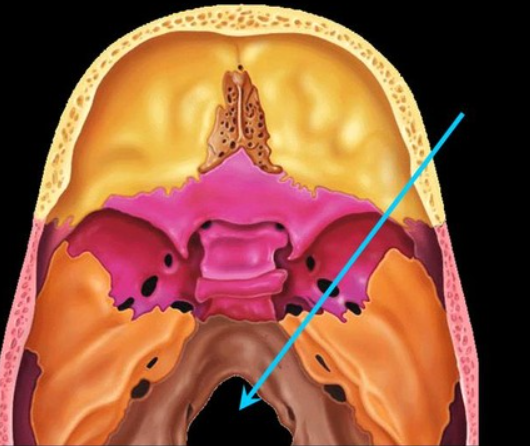
foramen magnum
the big circular hole in the middle of the skull
palatine bone
that is the maxilla as well as the palatine process of the maxilla near the palatine bone
what is the orange near the teeth
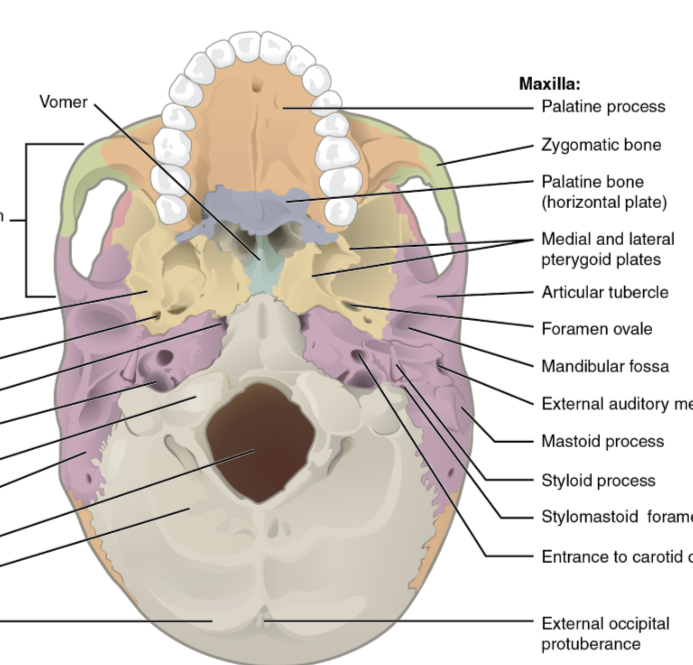
chewing muscle
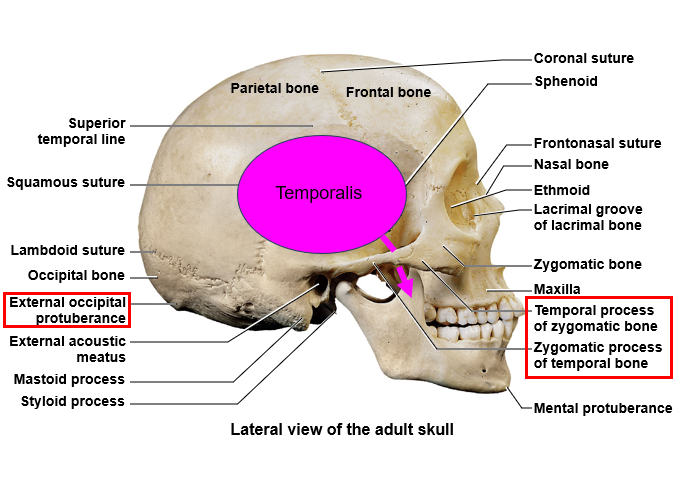
what is the red thing?
zygomatic arch
what is to the right of the left chewing muscle
temporalis. zygomatic process of temporal bone, temporal process of zygomatic bone. Under lamboid suture and occipital bone there is the external occipital protuberance
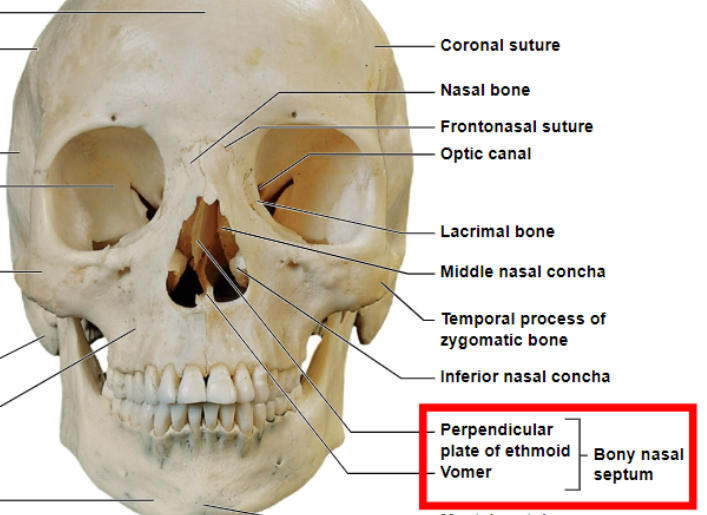
perpendicular plate of ethmoid and the vomer
what makes up the bony nasal septum
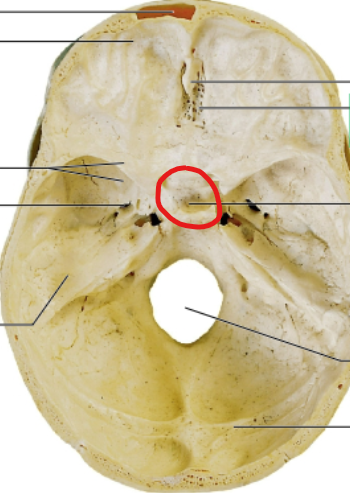
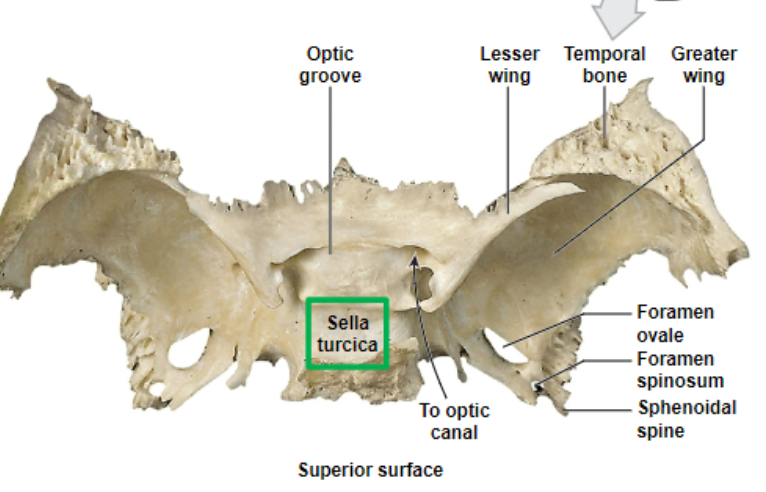
sella turcica
pituitary gland sits here
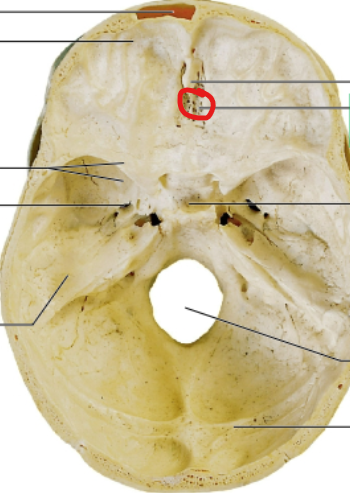
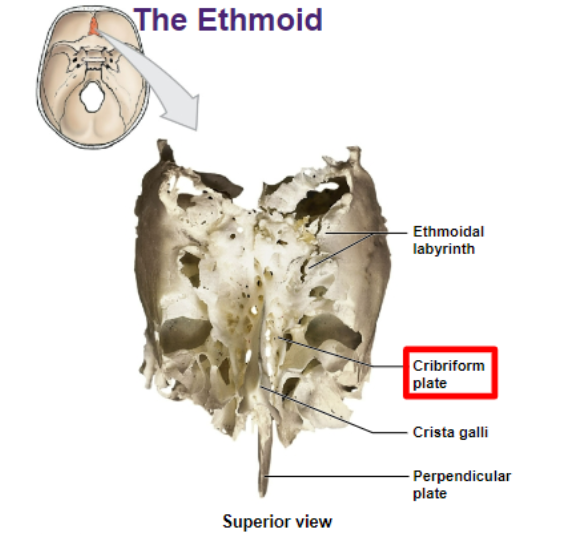
cribriform plate
olfactory nerves sits here
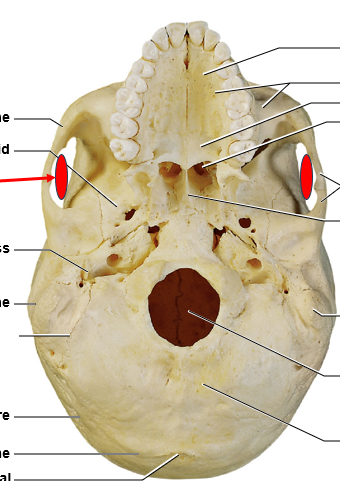
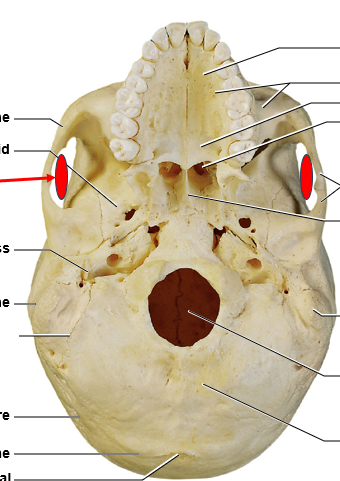
the eyeballs and the muscles that surround them
what would sit under the bone where the red arrows point?
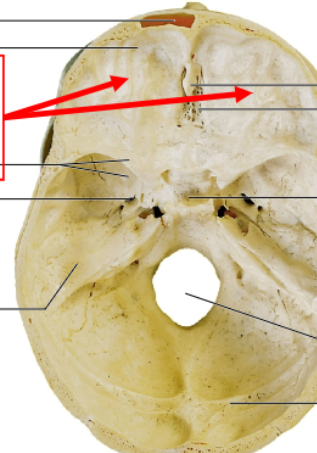
the sphenoid
the most structurally complex and intricate bone of the entire body and is where the sella turcica is
ethmoid
the cribriform plate is in this bone
temporal bone (TMJ = temporo-mandibular joint)
with which bone does the mandible articulate/join?
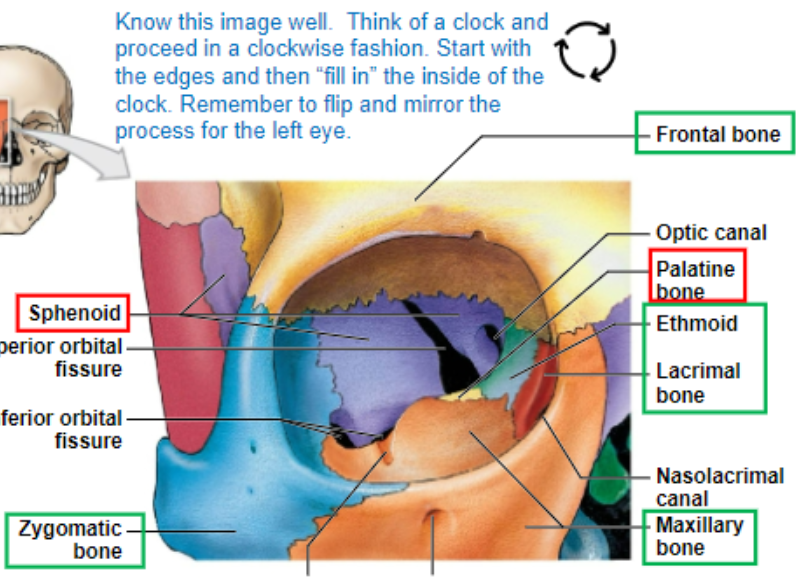
frontal bone, lacrimal bone, ethmoid, sphenoid, palatine bone, maxillary bone, zygomatic bone
know all of this
nasal conchae
churn the air to humidify and warm it
pneumatized bone
The Paranasal Sinuses
-Air-filled chambers that open into the nasal cavity:
• Frontal sinuses
• Sphenoidal sinuses
• Maxillary sinuses
• Ethmoid air cells
What category of bone do these fall into knowing they have hollow spaces in
them?
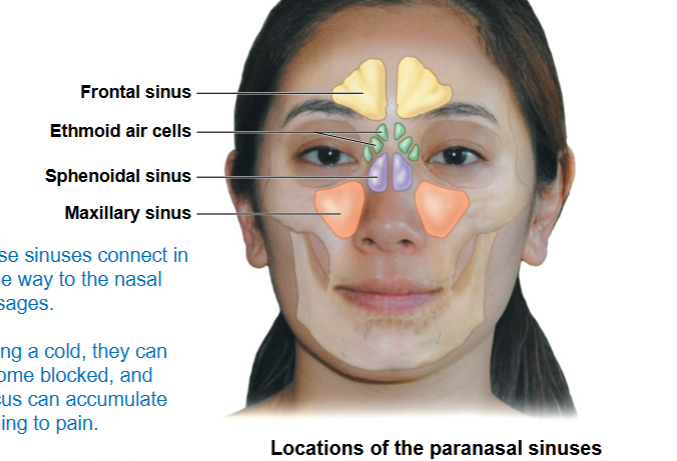
frontal sinus, ethmoid air cells, sphenoidal sinus, maxillary sinus
these connect in some way to the nasal passages. During a cold, they can become blocked, and mucus can accumulate leading to pain
do not
paranasal sinuses (do or do not) lie in the same coronal plane?
hyoid bone
does not articulate with any bones and is therefore extremely mobile
flat bones
what general bone does the sternum fall into?
flat bone
what type of bone is the frontal bone
synovial joint
another name for a diarthrotic joint would be…..
lateral
the ear sits ____ to the mouth
periosteum
outside the bone
endosteum
inside the bone
periosteum
the ____ is the connective tissue layer that wraps directly around a bone
compact
osteons are primarily found in the _____ bone
false; these movements occur at diarthrotic (synovial) joints
True/False:
flexion and extension are movements that can occur at synarthrotic joints
supporting connective tissue. Both bone and cartilage
cartilage falls into which category of connective tissue
palatine bones
the pair of bones that make up the posterior of the hard palate or the roof of the mouth
palatine process of the maxilla
the pair of bones that make up the anterior of the hard palate or the roof of the mouth
False; it is suspended by the stylohyoid ligaments but it is not fixed in place because it is highly mobile
True or false:
the hyoid bone is suspended by the stylohyoid ligaments and fixed in place
mandible, occipital, frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, vomer, hyoid
unpaired bones in the skull (only a single bone in the skull)
parietal bone, temporal bone, zygomatic bone, lacrimal bone, palatine bone, maxillae, nasal bones, inferior nasal conchae
paired bones in the skull (think two of each of that bone; one on the left and one on the right)
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital
main flat bones protecting the brain