Biology Semester 2 Freshman Year - Unit 9: Protein Synthesis
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
this is for the protein synthesis unit
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
True or False: The instructions in DNA are used to build proteins
True
What is the organelle in a cell that builds proteins?
Ribosomes
Can ribosomes “read” DNA?
No. That is why, using the Central Dogma, DNA is transcribed into RNA, which enables the ribosomes to actually “read” the RNA and use it to make proteins.
What is the monomer of a protein?
amino acid
True or False: Amino acids have unique properties that affects how the protein folds.
True
What does the amino acid sequence determine?
protein shape
What does protein shape determine?
protein function
What is the difference between DNA & RNA?
DNA:
Double strand
sugar = deoxyribose (DNA)
Nitrogenous Bases: A, T, C, G
Base Pairing Rules: A = T, C = G
RNA:
Single strand
sugar = ribose (RNA)
Nitrogenous Bases - A, C, G, U (Uracil) - There is no Thymine
Base Pairing rules: A = U, C = G
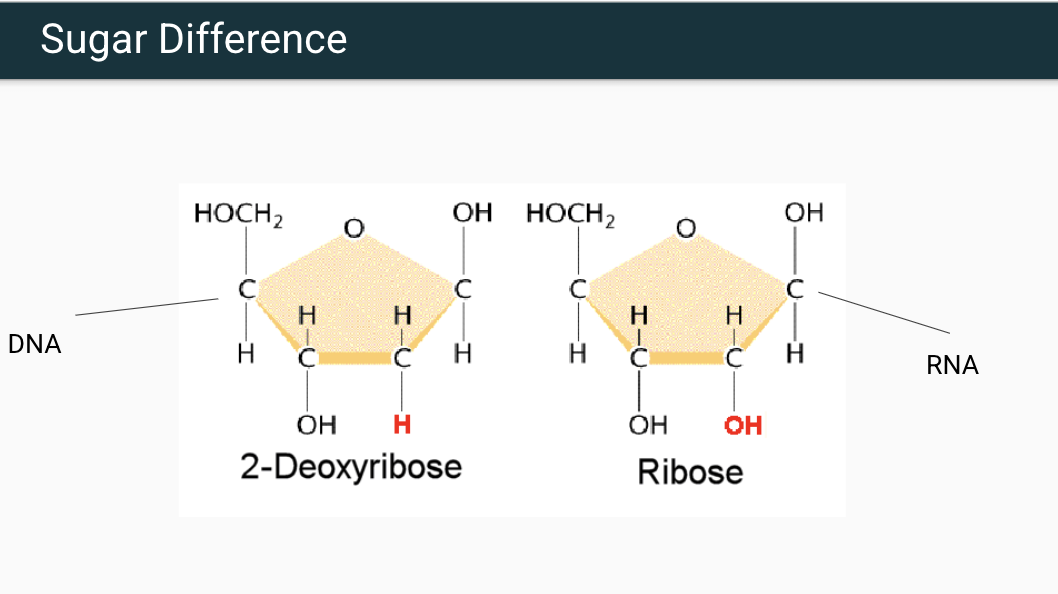
What is the Sugar Difference between DNA and RNA?
Deoxyribose: lacks an oxygen atom on the 2’ carbon hence the “deoxy”
Ribose: Has a hydroxyl group (-OH) on the 2’ carbon
What are the three main types of RNA?
mRNA (messenger RNA) - carries instructions from the nucleus to the ribosomes to make proteins
rRNA (ribosomal RNA) - makes up the ribosomes
tRNA (transfer RNA) - brings amino acids to the ribosomes to help make proteins
What is mRNA?
Its full form is messenger RNA and it carries instructions from the nucleus to the ribosomes in order to make proteins.
What is rRNA?
Its full form is ribosomal RNA and it makes up the ribosomes.
What is tRNA?
Its full form is transfer RNA and it brings amino acids to the ribosomes to help make proteins.
What is step 1 of the Central Dogma?
Transcription (DNA to RNA)
What is the purpose of the first step in the Central Dogma (transcription)?
Segments of DNA (genes) are used as a template to create a complementary single stranded RNA molecule. This allows the instructions to build proteins to leave the nucleus.
Where does transcription occur in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes: happens in the nucleus
Prokaryotes: happens in the cytoplasm
What is step one of transcription?
RNA polymerase binds to a promoter
promoter = region of DNA that represents the start of a gene
this causes the DNA to unwind and expose a template
What happens in step two of transcription?
RNA nucleotides pair with one strand of DNA and RNA polymerase bonds the nucleotides together
the DNA helix winds again as the gene is transcribed
What happens in step three of transcription?
The RNA strand detaches from the DNA once the gene is transcribed
RNA then needs to be processed before it can leave the nucleus
If the DNA template strand is CGTA, then what would be the complementary RNA strand?
GCAU
Remember: There is no Thymine in RNA, instead there is Uracil
What happens in the step four of transcription?
Pre-mRNA molecules require editing before they are ready to be read by ribosomes
Introns - portions that are cut out and discarded (noncoding portions)
Exons - remaining pieces that are sliced together to form spliced together to form final mRNA
What happens in transcription?
1) RNA polymerase binds to DNA at the start of a gene (promoter)
2) Complementary mRNA strand is made from DNA template strand
3) mRNA detaches from DNA and is processed to remove introns and splice (join) exons together
What is the second step of the Central Dogma?
Translation (RNA to Protein)
What is the purpose of translation (RNA to Protein)?
It converts mRNA messages into polypeptides (proteins)
Where does translation occur?
cytoplasm / ribosomes
Amino acids are coded by what?
mRNA base sequences through codons that specify each amino acid
What is a codon?
It is a sequence of three nucleotides that codes for an amino acid.
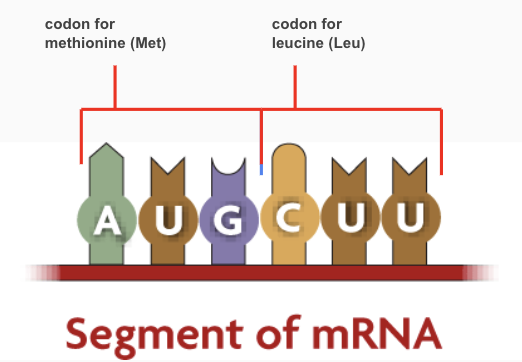
If the DNA template strand showed “CGTA”, what would be the complementary RNA strand
GCAU
What is the universal code for all organisms?
the genetic code
it matches each codon to its amino acid or function
And since it is the universal code for all organisms
There are three stop codons
one start codon (AUG) codes for methionine
Translate this DNA strand “TAC CGT ACT” into its complementary RNA strand
AUG GCA UGA
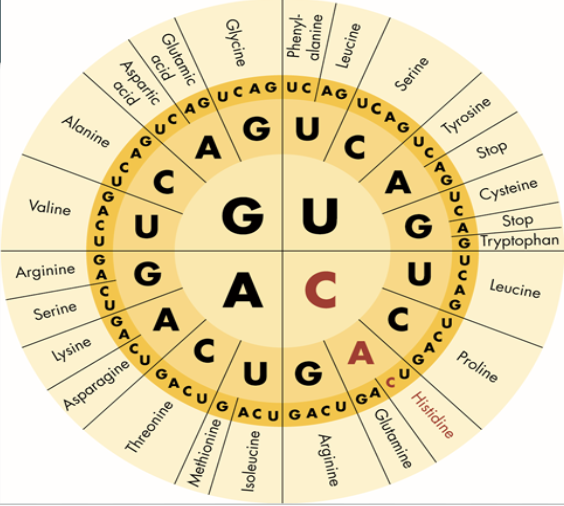
Translate this RNA strand “AUG GCA UGA” into an amino acid sequence
Met-Ala-Stop
What are the major players of translation?
mRNA: carries the instructions of the protein to be built
Ribosome: pulls the mRNA one codon at a time
tRNA: brings amino acid to the ribosome
What happens in step one of translation?
Initiation: the ribosome comes together at the start codon of the mRNA and tRNA brings over a methionine
What happens in step two of translation?
Elongation: Ribosome “reads’’ the mRNA messages one codon at a time to help form a growing chain of amino acids
What happens in step 3 of translation?
Termination: Ribosome disassembles when it reaches a stop codon and polypeptide chain is released
then, the polypeptide chain is folded into its functional shape
REMEMBER: Protein shape/fold determines protein function
and sent to the Golgi to be modified and packaged
Then transported to its final destination.
What organelle in the cell makes ribosomes?
nucleolus
Where are ribosomes found?
cytoplasm and rough endoplasmic reticulum
What does the Golgi do?
it modifies and packages proteins
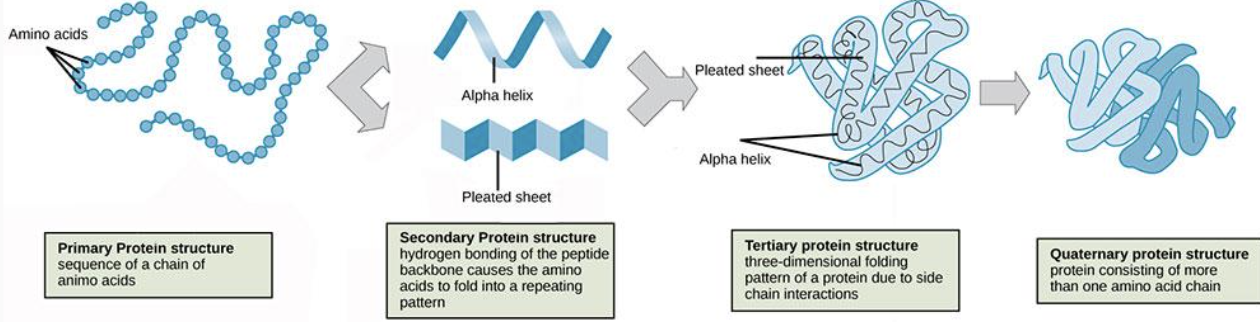
What are the four types of protein folding?
What are examples of proteins carrying out cellular functions?
Enzymes: Speed up reactions
Antibodies: Fight disease
Form structures such as hair and muscle
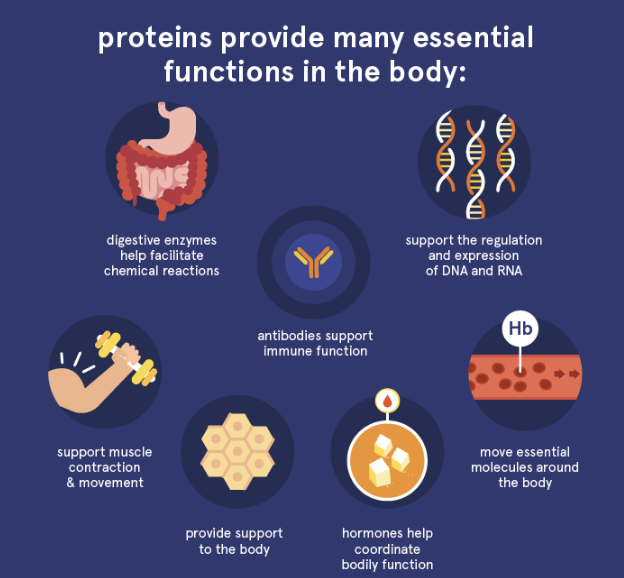
What happens in translation?
1) mRNA takes information from DNA to the ribosome
2) Ribosome attaches and pulls the mRNA through one codon at a time
3) tRNA brings corresponding amino acid over to the ribosome to form growing polypeptide chain’
4) Process continues until a stop codon is reached and the polypeptide is released to be modified and packaged by the Golgi
What happens in the Central Dogma (including all steps)?
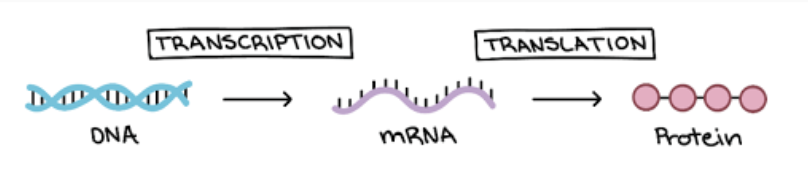
Transcription: Takes a DNA message and turns it into an RNA (mRNA) message in the nucleus
mRNA modification: introns are removed and mature mRNA enters the cytoplasm
Translation: RNA (mRNA) message get read by a ribosome to build a protein
Key players:
mRNA
rRNA
ribosomes
tRNA
What are mutations?
Involve changes to DNA or a chromosome
Changes to the instructions of DN can cause a protein to be made incorrectly
Can be beneficial and Can be harmful
But… Why do most mutations have no effect on an organism?
It is because many amino acids are coded by more than one codon in the DNA, which means that even a change in one codon still ensures that the amino acid is still being produced
True or False: Mutations can only be passed on to offspring if they occur in gametes (sex cells)
True
What are some factors that cause mutations?
Replication errors
DNA polymerase has built-in proofreading function but this is not perfect
Mutagens: environmental or chemical agent that can changes DNA
UV rays
Chemicals
Tobacco
Pesticides
What are Mutagens?
environmental or chemical agents that can cause Mutations/change DNA
UV rays
Chemicals
Tobacco
Pesticides
What are the two types of mutations?
Just a refresher, Mutations are changes in the DNA that may or may not affect the phenotype
Gene Mutations: Changes to the bases in the DNA of one gene
Chromosomal mutations: Affecting whole or part of a chromosome
What is a Gene Mutation?
Changes to the bases in the DNA of one gene
What is a Chromosomal mutation?
Affecting whole or part of a chromosome
What are the two types of gene Mutations?
Point mutation/ substitution
Frameshift mutation
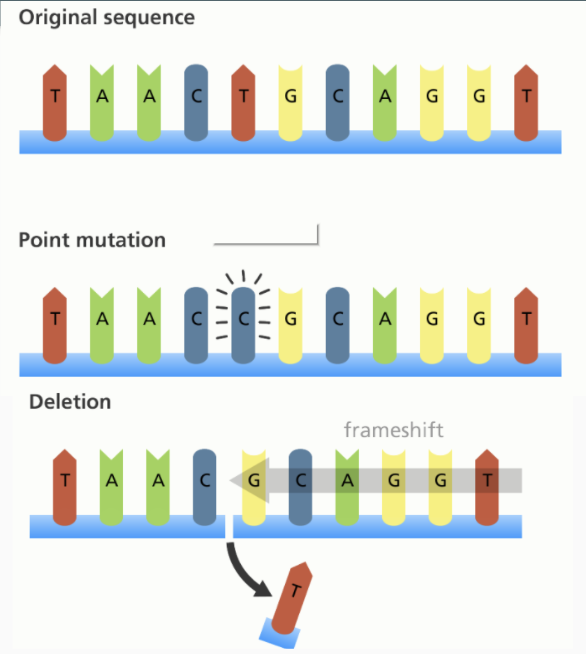
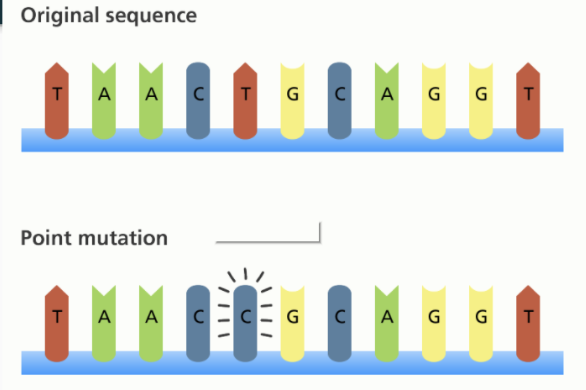
What is point mutation/substitution?
one nucleotide is substituted for another
What is frameshift mutation?
involves insertion or deletion of a nucleotide in the DNA sequence
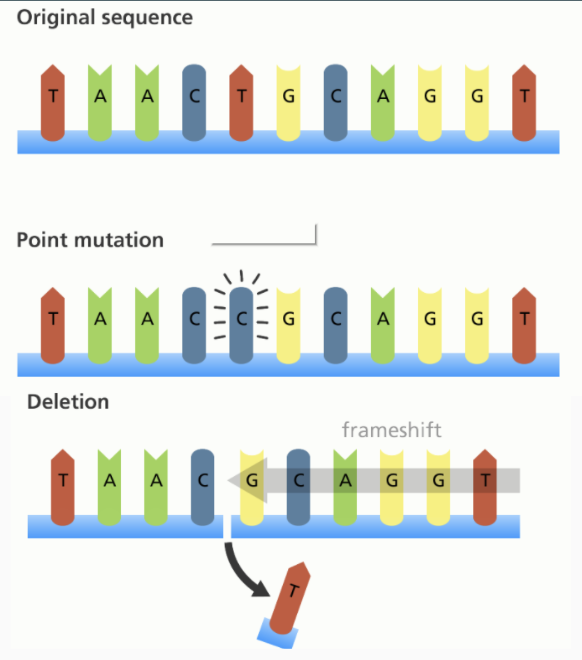
What affects a polypeptide more: a point mutation or a frameshift mutation?
frameshift mutation
If the original mRNA is “THE CAT ATE THE RAT”, what would the mutated RNA be regarding point mutation, if we changed the E in the first “THE” to S?
THS CAT ATE THE RAT
If the original mRNA is “THE CAT ATE THE RAT”, what would the mutated RNA be regarding frameshift mutation if we deleted the E in the first “THE”?
THC ATA TET HER AT
Do chromosomal mutations affect many genes?
Yes
What are the 4 types of chromosomal mutation?
Deletion, duplication, translocation, and inversion
What is deletion (chromosomal mutations)?
part of chromosome is deleted

What is duplication (chromosomal mutations)?
duplicates (copies) part of a chromosome
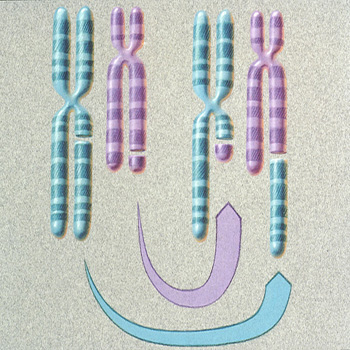
What is translocation (chromosomal mutations)?
results from the exchange of DNA segments between non-homologous chromosomes

What is inversion (chromosomal mutations)?
portion of chromosome is inverted
What are more examples of chromosomal mutations?
aneuploidy and polyploidy
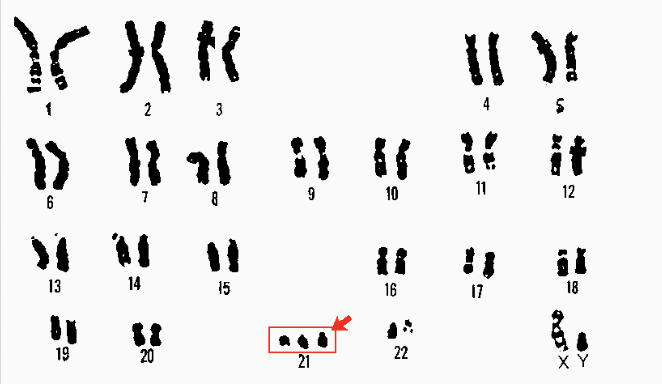
What is aneuploidy?
It is a chromosomal mutation where an organism has extra or missing chromosomes
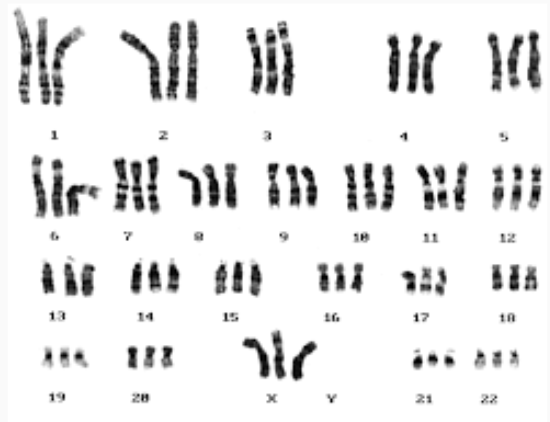
What is polyploidy?
Its is a chromosomal mutation where an organism has an extra set of chromosomes (3n, 4n, etc.)
Why does the DNA have to convert to mRNA to leave the nucleus?
because its too big
How does information flow in the Central Dogma?
DNA to RNA to Protein
Ribosomes link amino acids by forming what bonds between them?
peptide bonds
What polymer is read to make mRNA?
DNA
What is the product of translation?
polypeptide chain (protein)
The synthesis of mRNA in the nucleus, by RNA polymerase, from DNA is called _________?
transcription
Which of the following are mutagens?
tobacco in any form
UV light
man-made chemicals added to water, air, or food
all
Where on DNA, does the RNA polymerase bind to start transcription?
promotor site
What is the output or product of transcription?
mRNA
True or False: tRNA contains a codon
False (it contains an anticodon)
What is the difference between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation?
A point mutation is a single incorrect base in the mRNA sequence.
A frameshift mutation occurs when a base is added or removed causing the remaining mRNA sequence to be shifted.
How many amino acids are coded for by the strand of mRNA below?
AUGGUACGUGGG
4 (why? - remember the codons? each codon is 3 nucleotides and each code for a specific amino acid)
Where does mRNA go after it is created?
ribosomes
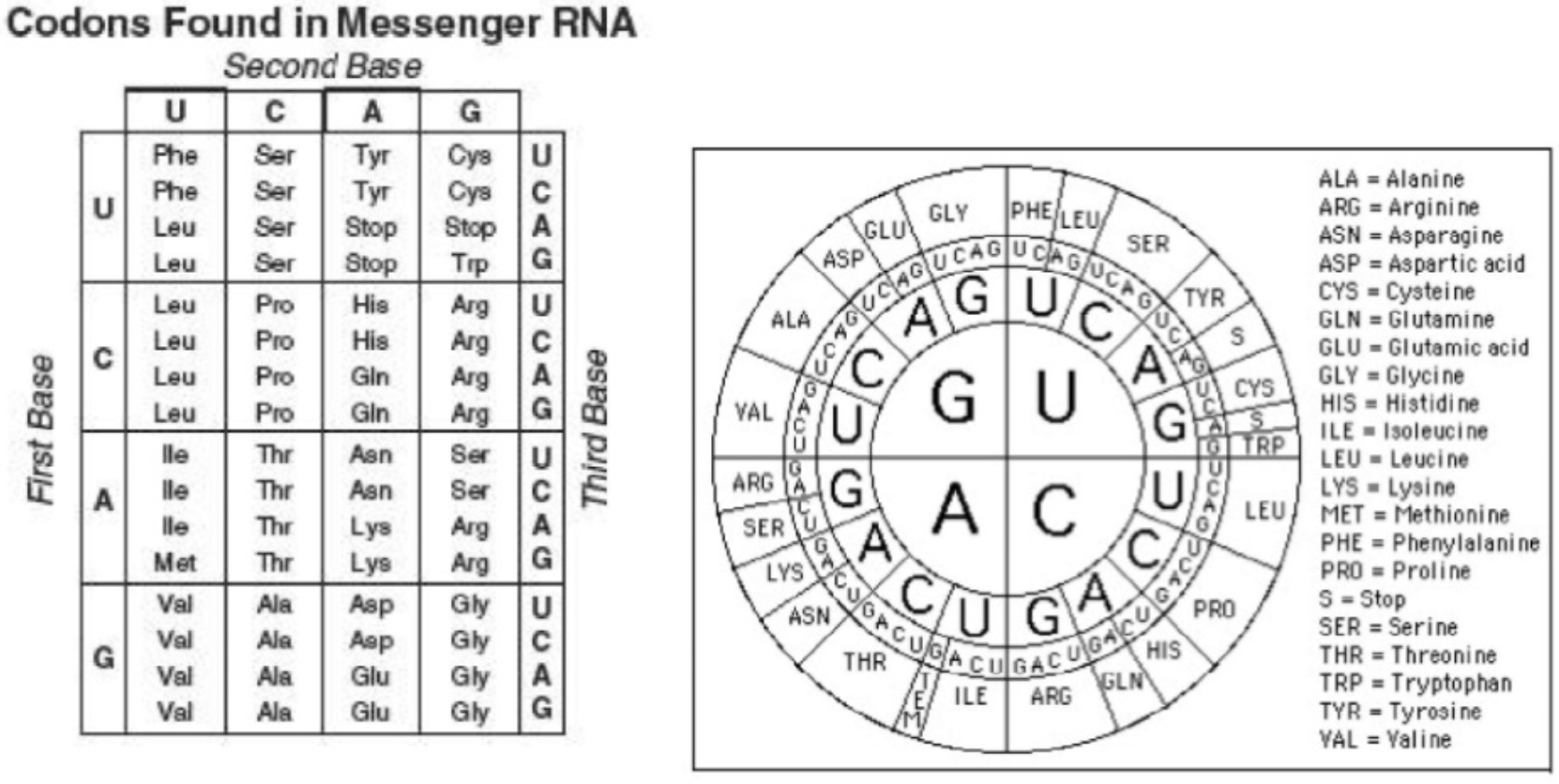
Which amino acid is specified by the mRNA code UGG?
tryptophan (TRP)
Which of the following describes the process of gene expression?
Genes are built by the nucleolus and carried out of the cell by the Golgi body.
DNA is read by an enzyme in the nucleus, then using those instructions, the cell makes polypeptides/proteins.
DNA is copied and then moves to the cytoplasm to make chromatin.
DNA is read by an enzyme in the nucleus, then using those instructions, the cell makes polypeptides/proteins.
Which of the following is another name for the non-coding regions that are removed from pre-mRNA, during editing, before it gets to a ribosome?
introns
The synthesis of polypeptides based on instructions from mRNA, on a ribosome is called_____?
translation
What is the name for the groups of 3 nucleotides found on tRNA?
anticodon
This is a sequence of DNA: TCACGATAC
It is transcribed into an mRNA with this sequence: AGUAGCUAUG
What mutation occurred?
insertion
Where are ribosomes produced?
nucleolus
Where do polypeptides go after being built, to get folded and packaged into proteins?
the Golgi
DNA and RNA use the same nitrogenous (made of nitrogen) bases except for one. Which base is found in RNA but is NOT found in DNA?
Uracil (DNA has Thymine instead of Uracil)
What does the tRNA bring over to the ribosome?
a specific amino acid based on the codon