Chapter 9 - Polymers
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Polymers
Termed as plastics
cheap
easy to manufacture
versatile
Polymer structure
Made up of many monomers, covalently bonded
Plastic
Ability to be molded into different shapes readily
Addition Polymerisation
C=C double bonds break and go to the side, to attach with other molecules
Naming For Polymer (In addtion reaction)
poly + name (e.g. polyethene)
Empirical formula of monomer
same as polymer
Properties Of Polymers
dispersion forces increase as molecule increases in size
lightweight
non-conductors of electricity
durable
versatile
acid-resistant
flammable
Low Density Polyethene (LDPE)
polymer is formed too fast for neat and symmetrical formation - goes off in branches
branches caused distance between chains, and cannot pack closely together
dispersion force becomes weaker
made in high temp (300 degrees), high pressure
Properties Of LDPE
non crystalline
more branching
low density
transparent
low dispersion forces
low melting point (e.g. cling wrap)
soft
non-conductor of electricity
High Density Polyethene
plastics made in:
low pressure, low temp
has fewer branches - molecules pack closer
more crystalline and ordered
allowed to form well, warm slowly and cool slowly - therefore stronger
Properties Of HDPE
high density
hard
relatively high melting point
crystalline sections
non-conductor of electricity
opaque (not clear) (e.g. milk bottles)
Vinyl Group
Inclusion of more electronegative atoms to increase the melting point (inclusion of chlorine instead of hydrogen)
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
Inclusion of Chlorine so it is more durable
used in:
floors
pipes, plumbing
electrical wire insulation
medical tubing and blood bags
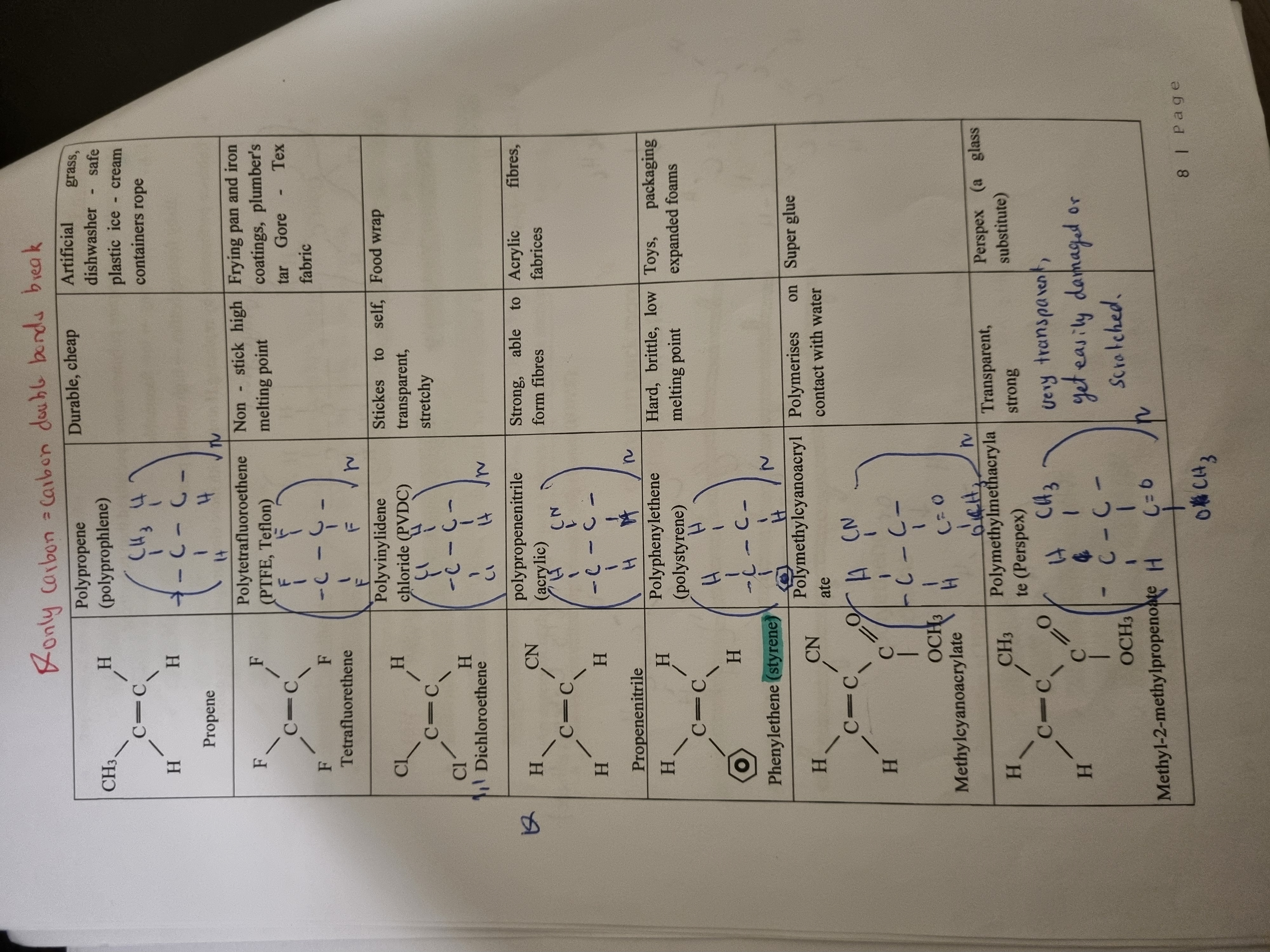
Common Polymers
Polypropene - artificial grass, dishwasher (durable and cheap)
Polytetrafluoroethylene (Teflon) - frying pan, iron coatings (non-stick high melting point)
Polyvinylidene (2 chlorines) - sticks to self, stretchy (food wrap)
polypropenenitrile - fabrics (strong, able to form fibres)
polyphenylethene (has benzene) - toys, packaging (hard, brittle, low melting point)
Polymethylcyanoacrylate - super glue - polymerises on contact with water
Perspex - glass substitute - transparent and strong
Three types of thermosetting polymers are
thermoplastic polymers - (i.e. PVC)
thermosetting polymers
elastomers
Thermosetting polymers (hard)
very hard and rigid (cannot be remoulded or reshaped once hardened)
have covalent cross links that form a rigid structure
are so strong that when tried to heat, monomer-monomer covalent bonds will also break
Char
used to make shatterproof crockery and saucepans
Thermoplastic Polymer (soft)
weak bonds between chains
can easily be remolded or reshaped
easily melts
has low melting point
Elastomers (In-between)
have occasional cross links, but are also soft
can “stretch” and elongate but return to original position.
e.g. tires, rubber bands
Condensation Polymerisation
When Two molecules with functional groups form, emitting water.
Forms Of Polyethene
UHMWPE - Ultra high Moleculecular Weight Polyethene (bullet proof vest, safety helmets)
LDPE
HDPE
Teflon
Tetraflurorethene
Teflon uses
Frying pans
medical implants
gear
gore-tex clothing (water proof, breatheable fabric)
Properties Of Teflon
Non-stick
Heat resistant
Good mechanical properties
Flame resistant
Chemical resistant
Polar Vs Non-polar Polymers
Polar : strong dipole-dipole forces and weak dispersion forces (stronger)
Non-polar: weak dispersion forces only
Co-polymers
combing two or more different monomers into one polymer
light weight, thermal insulator
allows light and heat to penetrate the glass
allows to get properties of both monomers
ABS
Used to make LEGO blocks
Rigid and strong
Can be melted
popular for 3D printing
Molten ABS is used to build solid objects
Conductive Polymers
Polymer-based circuits that allow electricity to flow as well as being insulative.
Photoconductive Polymers
Create electricity from light
light sensitive monomer - vinyl carbazole
Photoconductive polymer - polyvinyl carabazole
Side Group Of Monomers
Prevent the sliding of chains and stacking closely.
Prevent formation of crystalline structures
Polystyrene
has bulky side group “benzene”
is hard, brittle, but low density
used to make food containers, refrigerator parts and dvd cases
PMMA
large side groups
more malleable, less brittle
Plasticizers
Forcing polymers to form distanced, so that the plastic intentionally is made flexible and soft
Plasticizer in PVC
made more flexible
polymer made softer
normally is room temp
Foamed polymer
Blowing gas through melted polymer
used for “shock absorbing” lightweight, insularity
e.g. takeaway containers or foam
Reasons for Synthetic polymers
easier degradation
fater process
better for environment
Ways to produce biodegradable plastic
make condensation polymer
addign additives (e.g. transaition metals for food wrapping or shopping bags)
Enzyme
biological catalyst
breaks down covalent bonds (hydrolysis)
increases rate of reaction
Bio based
material partly derived from biomass
biodegradable
Organisms in the natural substance, actively breaking it down
compostable
process that distintegrates material leaving no poison in the soil (under 90 days)
PVA (how is it dissolvable)
adding OH group - making it dissolve in water
PETase
Adding of enzyme to PET, and breaks down the covalent bonds for faster degradation
attacks C-O bond.
Mechanical Recycling
Only for thermoplastics (soft)
Polymer structure is unchanged
molded into different products
only physical reshaping
Organic Reaction
Microbial (bacteria) breaks down polymer (hydrolysis)
condensation reaction forms polymers
hydrolysis breaks down polymers into monomers
natural decomposition
Chemical recycling
polymer structure is broken
“cracking” - polr bonds break and changes into smaller molecules
Turned into oils or basic molecules
Used for complex/contaminated plastics
Non compostable bio-polymer
ethene 1,2 diol
to make bioethanol from carbohydrates fermented with yeast
Bio based and compostable
are formed with starch
PLA - polylactic acid
Polyethene
sugar-glucose (ferments) - bioetehanol - biopolyethene
Sugar - bioethanol
sugar (hydrolysis) - glucose (fermentation) - bioethanol
Starch - bioethanol
Starch - sugar - glucose - bioethanol
Common uses of polymers
Why Is Gold Easy To Recycle
Maintains its purity over time
Doesn’t vigorously react with water or other compounds
preserves the energy from mining, and continuous mining for the resource.
What Is Nylon
A thermoplastic - can easily be remolded - covalent bonds are intact, but intermolecualr bonds break