Exam 1 part 1 (lectures 1-3)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/166
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:03 PM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
1
New cards
biochemistry
application of chemistry to understand biological processes of cells and living organisms at the molecular level
2
New cards
core concepts of biochemistry
1. energy + metabolism
2. structure + function
3. information storage + transfer
4. Homeostasis
5. Evolution
3
New cards
Organic molecules that biochemistry focuses on
1. carbohydrates
2. lipids
3. proteins
4. nucleic acids
5. high-energy compounds (ATP)
4
New cards
(T/F) ALL of the organic molecules listed before are polymers
FALSE - lipids are NOT polymers
5
New cards
Why care about biochemistry?
provides underlying principles that govern life in all its diverse forms, helps understand mechanisms of disease, drug + vaccine development
6
New cards
Definition of life
1. ability to acquire, store and transport energy
2. organization in membrane-bound compartments (cells)
3. self-contained genetic information (nucleic acids)
4. ability to replice
1. evolves/changes over time - growth and response to stimuli
7
New cards
3 domains of life
bacteria, eukaryotes, archaea
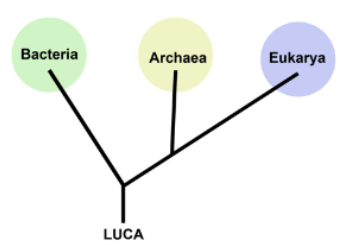
8
New cards
LUCA
last universal common ancestor - most recent form from which all surviving life on Earth is descended
9
New cards
(T/F) LUCA is the first life on Earth
FALSE
10
New cards
which rRNA genes are most used for making phylogenetic trees?
16S or 18S
11
New cards
Why is 16S or 18S rRNA genes most used for making phylogenetic genes?
because they are the most conserved between species
12
New cards
Prokaryotes are unicellular
Eukaryotes can be unicellular OR multicellular
13
New cards
prokaryotic cell vs eukaryotic cell
prokaryotic
1. nucleoid
2. no membrane-bound organelles
eukaryotic
1. nucleus
2. membrane-bound organelles
1. nucleoid
2. no membrane-bound organelles
eukaryotic
1. nucleus
2. membrane-bound organelles
14
New cards
what determines a cellular size LOWER limit?
size of genetic information, cell structure, biomolecules
15
New cards
what determines a cell UPPER limit?
efficiency of nutrient uptake, transport, and metabolism
16
New cards
source of chemical elements of life
big bang → star formation → star lifecycles
17
New cards
What are the most common elements making up life?
CHNOPS (over 97% of the mass of cells)
18
New cards
Why is carbon so well suited for life?
1. widespread abundance
2. ability to form stable bonds with numerous elements
3. ability to form polymers at common Earth temperatures
19
New cards
methyl
RCH3
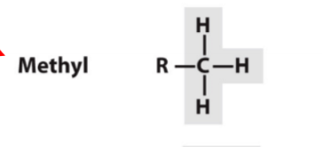
20
New cards
phenyl
aromatic carbon group
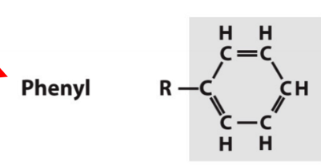
21
New cards
carbonyl (aldehyde)
RHC=O
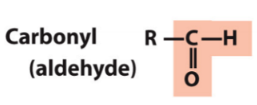
22
New cards
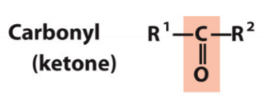
carbonyl (ketone)
RRC=O
23
New cards
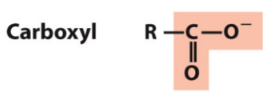
carboxyl
ROC=O
24
New cards
hydroxyl
ROH

25
New cards
amino
CNH3

26
New cards
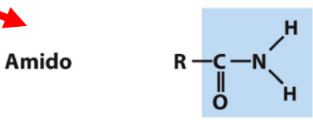
amide
O=CNH2
27
New cards
sulfhydryl
RSH

28
New cards
disulfide
RSSR

29
New cards
thioester
RC=OSR

30
New cards
purposes of functional groups
1. structure + stability
2. molecular interactions with water or other biomolecules
3. activity (enzymes)
1. energy storage/transfer
31
New cards
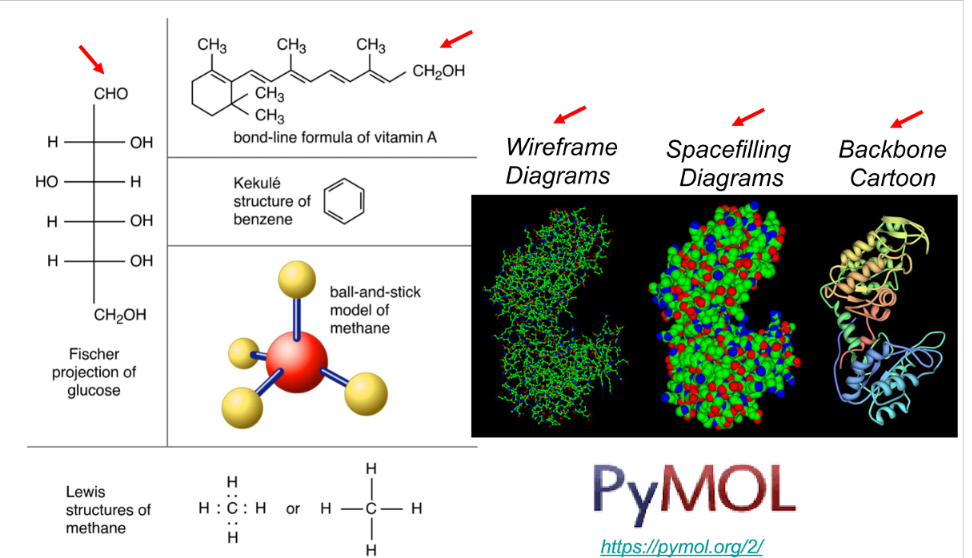
different ways to visualize biomolecules
fischer projection, Lewis strucures, bond-line formation, ball-and-stick, wireframe, backbone
32
New cards
stereoisomers (spatial isomers)
same molecular formula, unique 3D orientations of atoms in space
33
New cards
structural/constitutional isomers
same molecular formula, differ in the way that the atoms are connnected
34
New cards
enantiomers
mirror images, identical physical configuration (type of stereoisomer)
35
New cards
diastereomers
non-mirror images, can have unique chemical properties (type of stereoisomer)
36
New cards
most biomolecules are ___ and __
chiral, have a few chiral centers, and are a single type enantiomer
37
New cards
Cells primarily synthesize _ amino acids and _ sugars
L-amino acids, D-sugars
38
New cards
(T/F) biomolecules are static
FALSE - undergo conformational changes where stereochemistry is importanta
39
New cards
thermodynamics
energetics of chemical reactions and molecular interactions in cells
40
New cards
first law of thermodynamics
cells absorb/release energy and convert it into different forms
41
New cards
second law of thermodynamics
overall randomness (entropy) in the universive tends to increase over time
* cells release energy as heat which increases S(surr)
* cells release energy as heat which increases S(surr)
42
New cards
Gibbs free energy equation
delta G = delta H - T(delta S)
43
New cards
delta G in the Gibbs equation
Gibbs free energy, change in energy available for work (units: kJ/mol)
44
New cards
delta H in Gibbs equation
enthalpy, change in heat content (units: kJ/mol)
45
New cards
delta S in the Gibbs equation
entropy, change in degree of disorder (units: kJ/Kelvin\*mol)
46
New cards
T in Gibbs equation
temperature (units: Kelvin)
47
New cards
delta G degree in Gibbs equation
standard free-energy change - G at “standard conditions”
48
New cards
reactions where delta G are < 0 are ___
spontaneous
49
New cards
reactions where delta H < 0
reaction releases heat
50
New cards
when delta S < 0
reaction is more ordered
51
New cards
Reactions in cells need to be __ or become coupled with other favorable ones
spontaneous
52
New cards
what signs should delta H and delta S be for a spontaneous reaction
negative delta H and a positive delta S
53
New cards
endergonic reaction
energy is absorbed, delta G > 0, not spontaneouse
54
New cards
exergonic
energy is released, G < 0, spontaneous
55
New cards
kinetics
speed/rate that chemical reactions and molecular interactions occur in cells
56
New cards
equilibilrium
occurs when the rate of product formation is equal to the rate of reactant formation
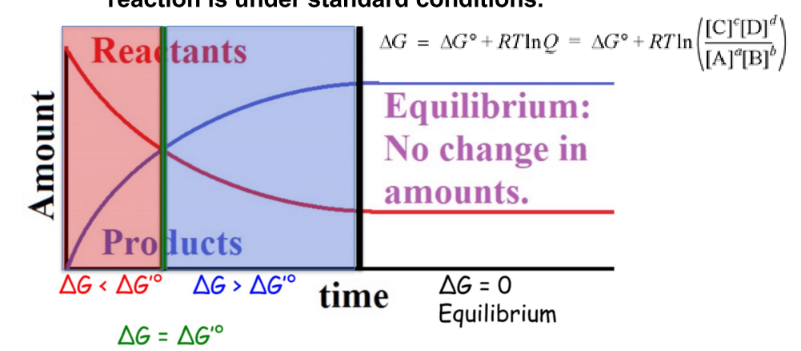
57
New cards
Q
reaction quotient

58
New cards
Keq - equilibrium constant
relative amounts of products vs reactants at equilibrium

59
New cards
when Keq>1
more products at equilibrium, delta G < 0
60
New cards
when Keq
more reactants at equilibrium, delta G > 0
61
New cards
when Keq = 1
equal amounts of products and reactants at equilibrium, delta G = 0
62
New cards
equation relating delta G to Keq
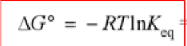
63
New cards
Le’Chateliers principle
passive process - when equilibrium is disturbed the equilibrium shifts to counteract and reestablish equilibrium
64
New cards
homeostasis
dynamic steady state at cellular level, active process requiring biomolecules
65
New cards
Le-Chatelier vs homeostasis
both resist changes to a system, Le’Chatlier is passive while homeostasis is active
66
New cards
steady state vs equilibrium
equilibrium is a reversible process A→B AND B→A
steady state requires more steps A→B→C
steady state requires more steps A→B→C
67
New cards
metabolism
set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in a cell
68
New cards
metabolite
an intermediate or end product of metabolism
69
New cards
metabolic pathway
coordinated series of chemical reactions (product of one reaction becomes the substrate for the next reaction)
70
New cards
anabolic
the building up (synthesis) of metabolites and biomolecules
* usually consumes/requires energy
* usually consumes/requires energy
71
New cards
catabolic
breaking down of compounds
* energy is either stored or released as heat
* energy is either stored or released as heat
72
New cards
chemical oxidation is to _ as sunlight is to _
cellular respiration, photosynthesis
73
New cards
cellular respiration
glucose is oxidized with oxygen to release ATP (spontaneous)
74
New cards
photosynthesis
light drives synthesis of glucose and oxygen from CO2 and H20
75
New cards
are humans aerobic or anaerobic?
aerobic
76
New cards
ATP
energy currency of the cell, hydrolyzed to release ADP and energy
77
New cards
reaction coupling
pairing a energetically favorable reaction with an energetically unfavorable reaction (add the delta Gs of both reactions)
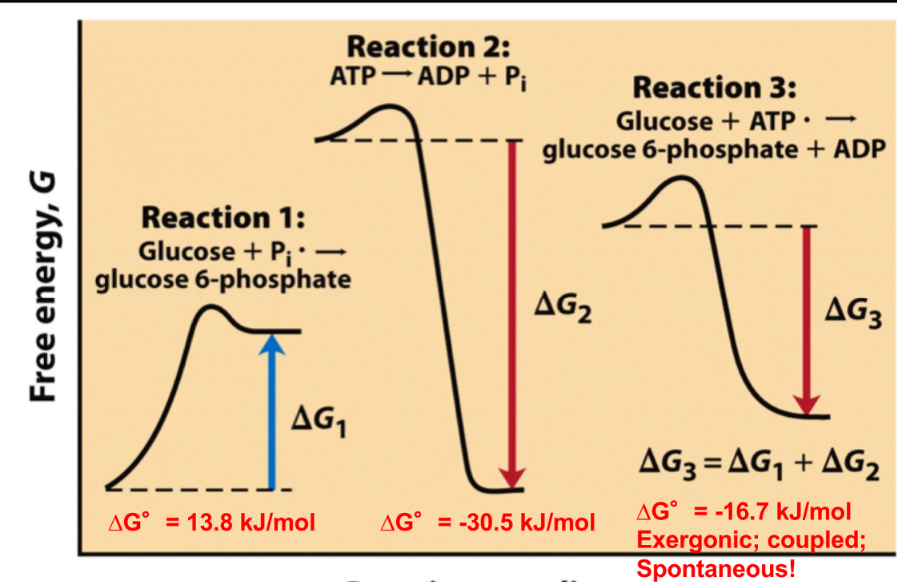
78
New cards
activation energy (Ea)
minimum energy required to cause a process to occur
79
New cards
what is the source for activation energy needed to push reactions forward
catalysts or heat energy from the surroundings
80
New cards
catalysts
enzyme or RNA that increases the rate of a chemical reaction
81
New cards
G++
activation free energy - catalysts lower this
82
New cards
(T/F) Catalysts alter delta G\*
FALSE - enzymes lower the activation free energy G++
83
New cards
gene
region of DNA that encodes cellular function
84
New cards
genome
entire set of DNA found in a cell
85
New cards
allele
different versions of a gene
86
New cards
central dogma
DNA→RNA→proteins (in reality it goes in many directions)
87
New cards
modern view of central dogma
central dogma + works in the reverse direction/proteins can create more proteins
88
New cards
evolution
change in heritable characteristics of bio populations over successive generations
89
New cards
5 forces of evolution
1. mutation - mistake/change in DNA
2. genetic drift - random small population
3. gene flow - movement of people/migration
4. non-random mating
5. natural selection
90
New cards
homolog
proteins diverged from a common origin
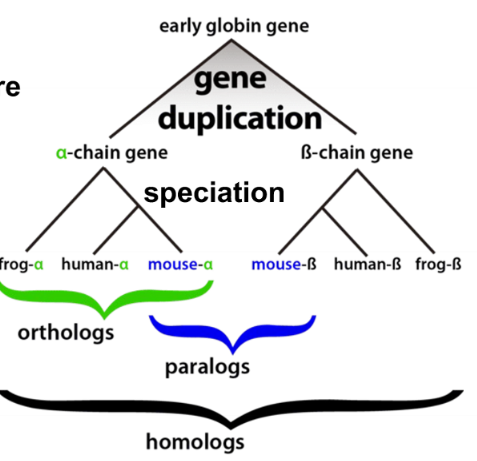
91
New cards
ortholog
genes which evolved from a common ancestral gene by speciation that usually have retained a similar function in different species
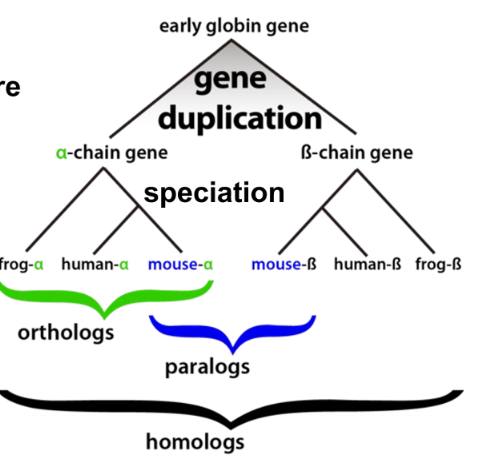
92
New cards
paralog
genes related by duplication within the genome and often they acquire a new function
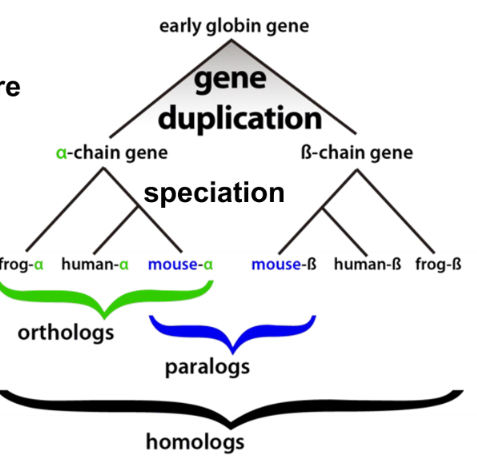
93
New cards
germline mutation
occur in sperm and egg, more important to evolution, can be passed on to offspring
94
New cards
somatic mutations
occur in body cells, NOT passed on to offspring
95
New cards
gene duplications
* source of genetic novelty that can lead to evolutionary innovation w/o deactivating original gene function
* common cause of disease (cancer)
* can occur as the result of an error in recombination or replication
* often immune to selective pressure under which genes normally exist
* common cause of disease (cancer)
* can occur as the result of an error in recombination or replication
* often immune to selective pressure under which genes normally exist
96
New cards
water is some form (liquid, ice, vapor) is necessary for every llife form, which is why
we are looking for water on other planets
97
New cards
role of water in biochemistry
1. water as a solvent - chemical reactions in a cell or btwn a cell and the environment occurs in aqueous solutions
2. water actively participates in many biochemical reactions (30-50% of known biochem reaction involve water consumption or production)
3. biomolecules assume their shapes and function in response to the properties of water
4. the reactivity of the functional groups in many biomolecules depends on the relative concentration of H+ and OH- in solution
5. properties of water shape homeostasis and the evolution of life
98
New cards
(T/F): Water is just a medium/solvent
FALSE - is also an active chemical participant
99
New cards
water dictates almost all of what process?
cellular metabolism
100
New cards
condensation
dehydration synthesis - molecules combined with the loss of a water