BNUR1017 Nursing Review: Infection Control, Bed Making, Positioning, and Patient Safety
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Asepsis
Asepsis is the absence of pathogenic (disease-producing) microorganisms.
Medical asepsis
Medical asepsis (clean technique) reduces organisms and prevents transfer.
Surgical asepsis
Surgical asepsis (sterile technique) destroys microorganisms and their spores.
4 Moments of hand hygiene
The specific times when hand hygiene should be performed to prevent infection.
Alcohol-based disinfectant
A method of hand hygiene appropriate when hands are visibly dirty.
Soap
Removes visible soiling but is ineffective at killing microorganisms.
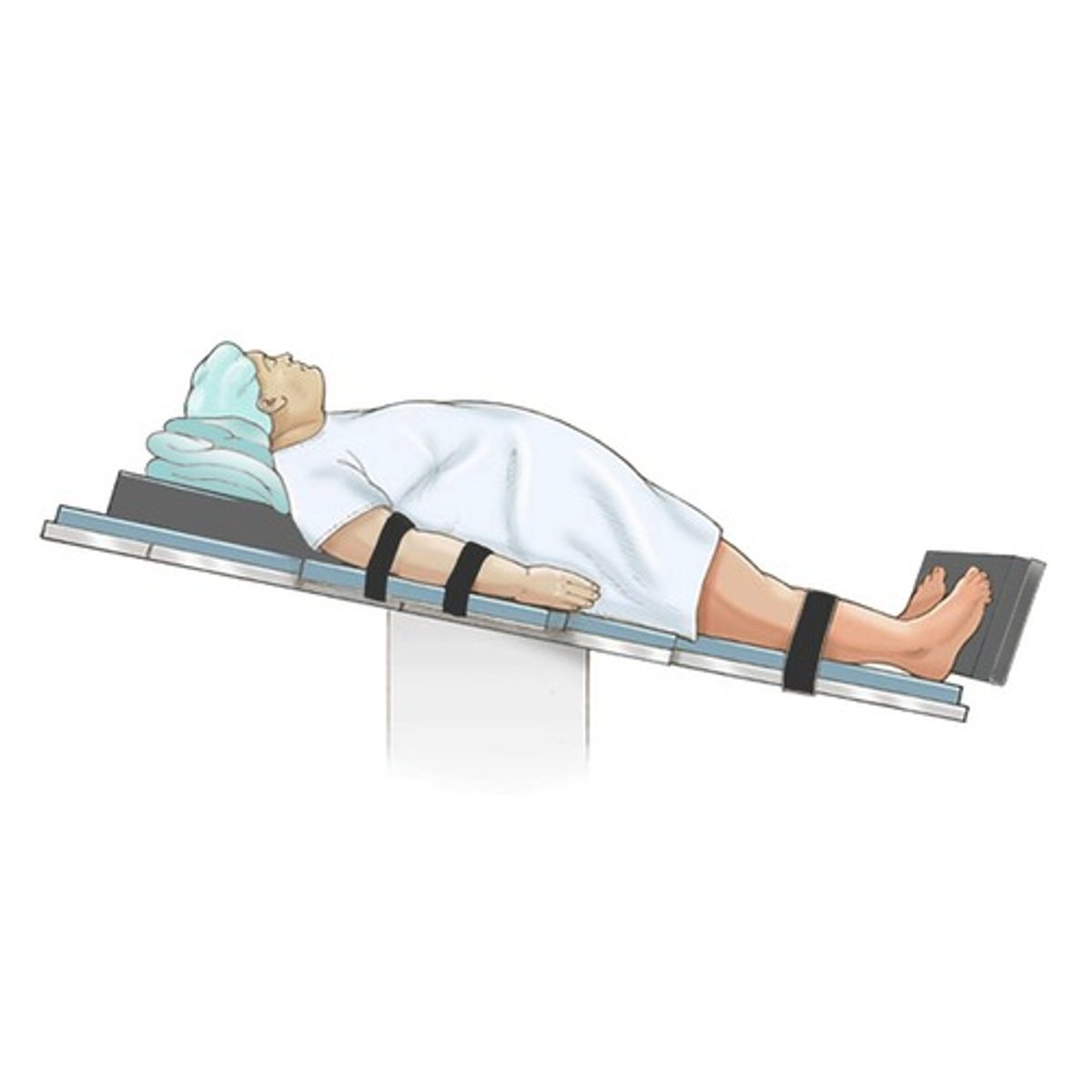
Trendelenburg position
Bedframe tilted with head of bed down.
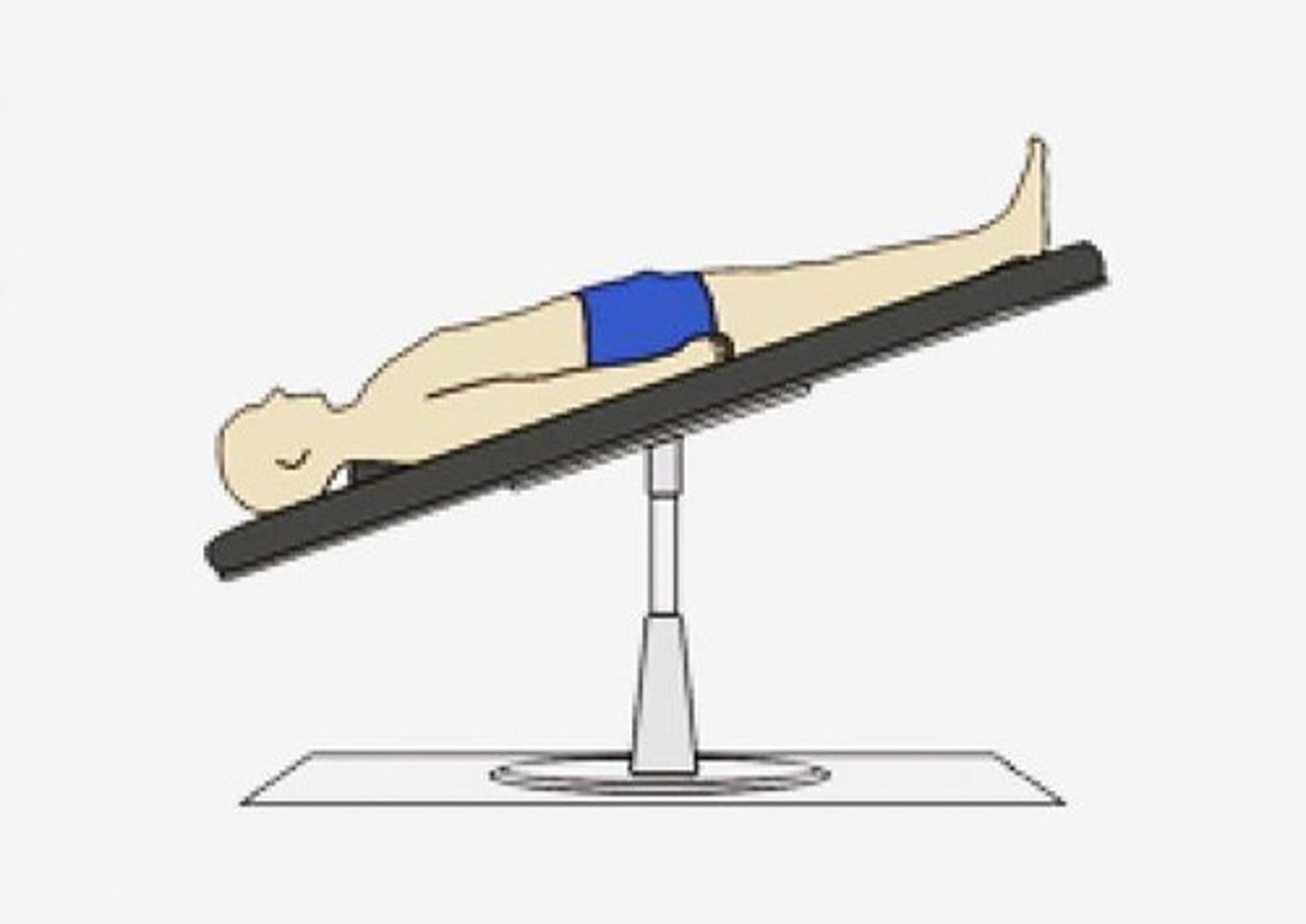
Reverse Trendelenburg position
Bedframe tilted with foot of bed down.
Supine position
Bed horizontal with floor.
Semi-fowler's position
Head of bed (HOB) elevated 30-45 degrees.
Fowler's position
Head of bed (HOB) elevated 45-90 degrees.
Bathing Safety Guidelines
Adapt to level of dependence, personal hygiene accessibility, contact with bodily fluids, and evaluate before and after care.
Risk Factors For Skin Breakdown
Includes immobilization, reduced sensation, nutrition and hydration alterations, secretions and excretions on the skin, vascular insufficiency, external devices, and age.
High Fowlers Position
Position where the patient is seated upright to assist with oral nutrition.
Aspiration precautions
Place a patient in a position that minimizes the risk of aspiration.
Patient diet orders
Includes clear fluids, full liquid, pureed, mechanical/dental soft, soft, and regular diets.
Body mechanics
Keep back, neck, pelvis, and feet in alignment; tighten stomach muscles; face direction of movement.
Bed making importance
Important for safety, comfort, and emotional well-being.
Evaluation after care
Assess the patient's condition before and after providing care.
Correctly position patient
Maintain body alignment, comfort, circulation, and balance.
Aids for patient positioning
Pillows, trochanter rolls, rolled towels, splints, various foam boots/wedges/hand splints.
Range of Motion (ROM)
ROM can be active, passive or active assisted.
Posterior
Dorsal.
Anterior
Ventral.
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment.
Distal
Farther from the point of attachment.
Medial
Closer to the midline of the body.
Lateral
Farther from the midline of the body.
Superior
Above or higher than another part of the body.
Inferior
Below or lower than another part of the body.
Flexion
Decreasing the angle between two body parts.
Extension
Increasing the angle between two body parts.
Hyperextension
Movement of a body part beyond its normal resting position.
Dorsiflexion
Movement of the foot upwards.
Plantar flexion
Movement of the foot downwards.
Abduction
Movement of a limb away from the body.
Adduction
Movement of a limb towards the body.
Eversion
Turning the sole of the foot outward.
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward.
Circumduction
Circular movement of a limb.
Stage 1 Pressure Ulcer
Non-blanchable erythema of intact skin; skin is intact.
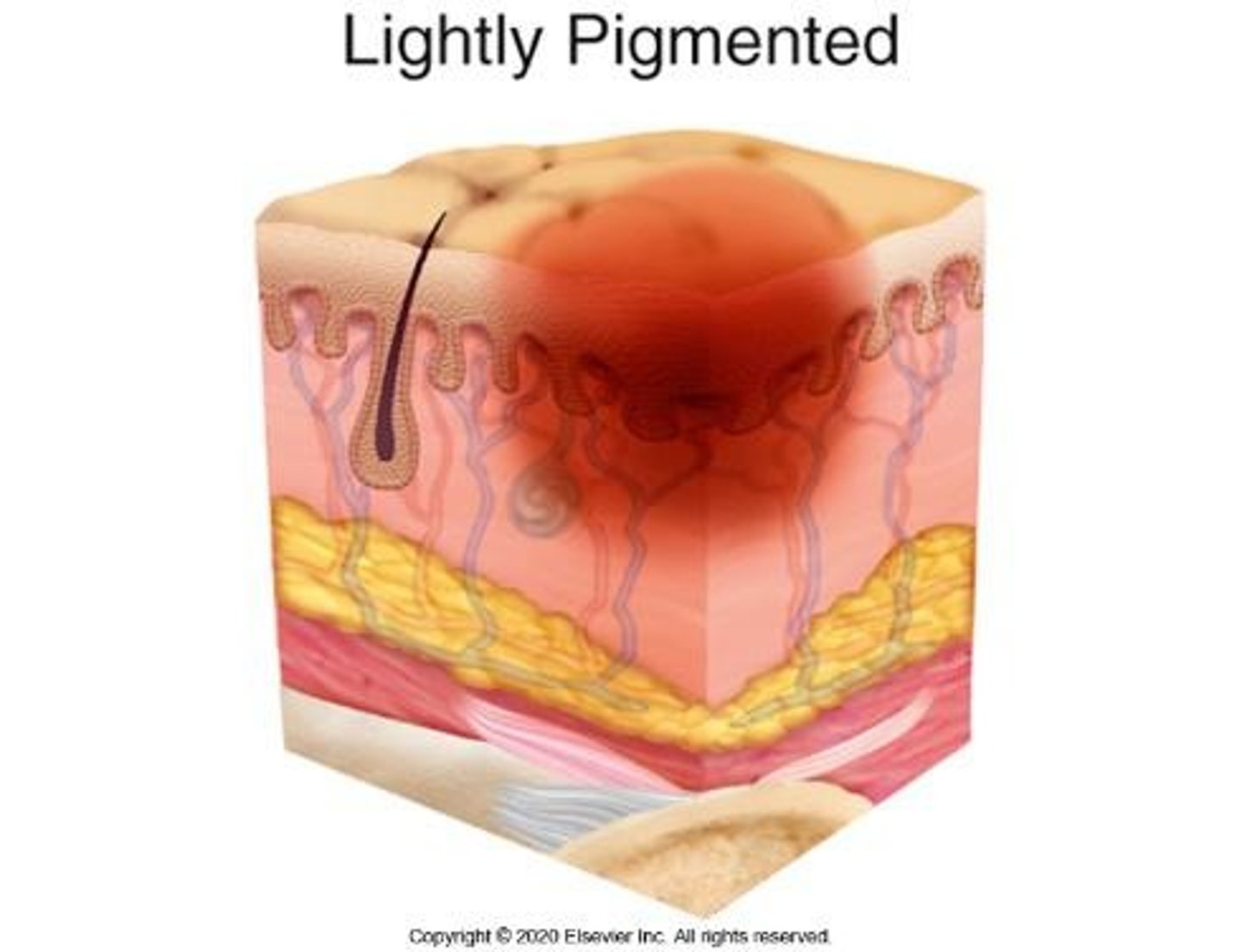
Stage 2 Pressure Ulcer
Partial-thickness skin loss with exposed dermis; wound bed is viable, pink or red and moist.
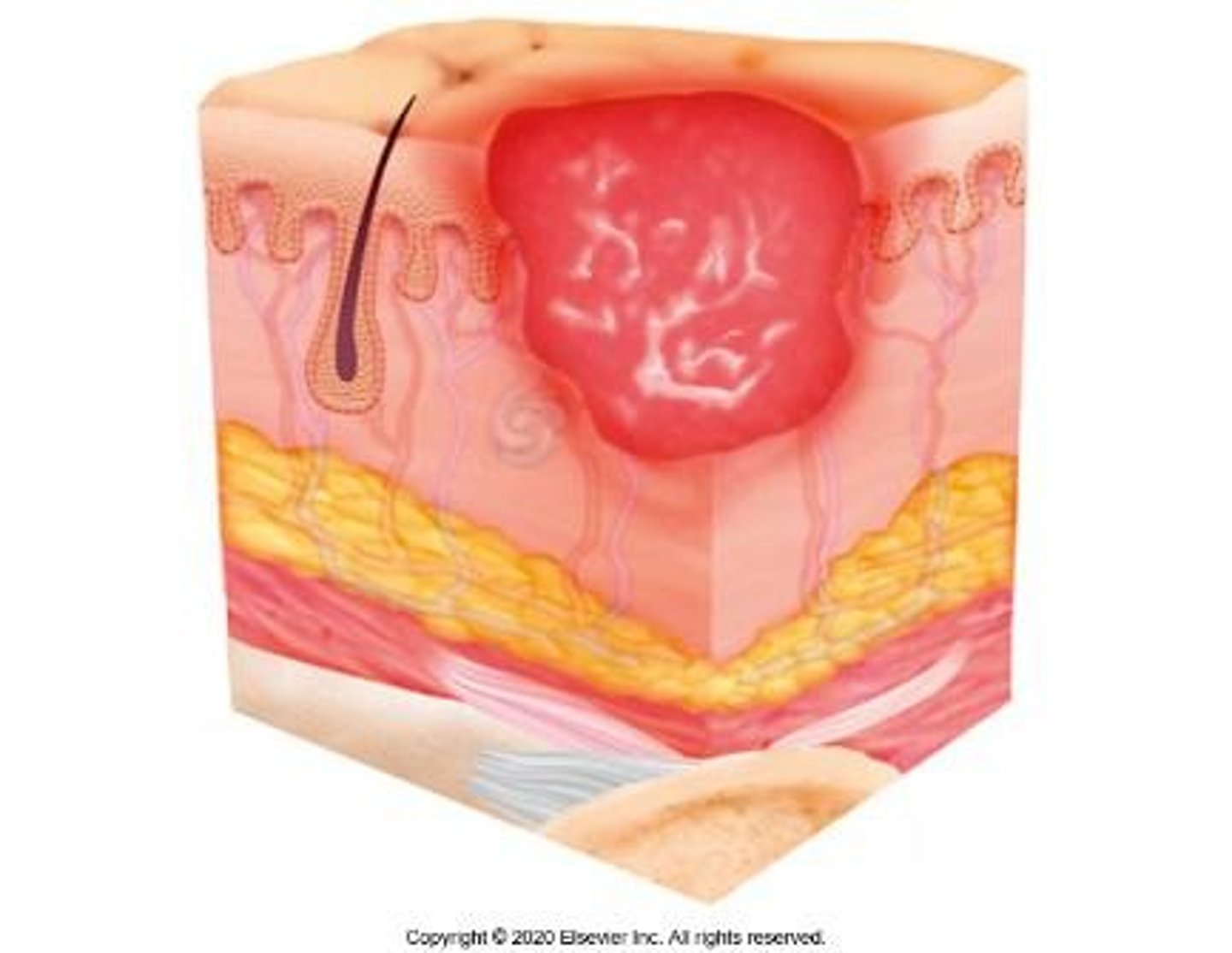
Stage 3 Pressure Ulcer
Full-thickness skin loss; adipose tissue is visible.
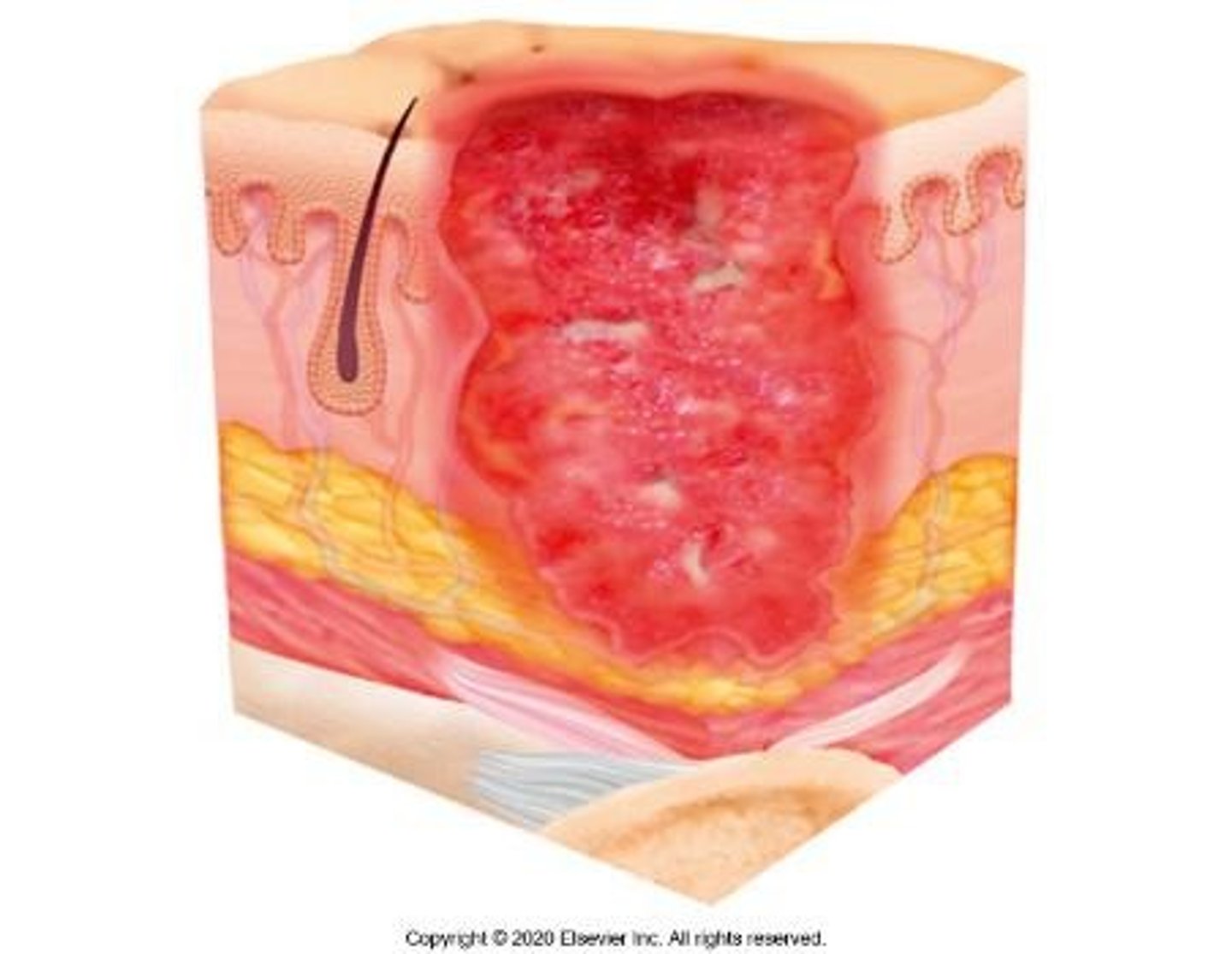
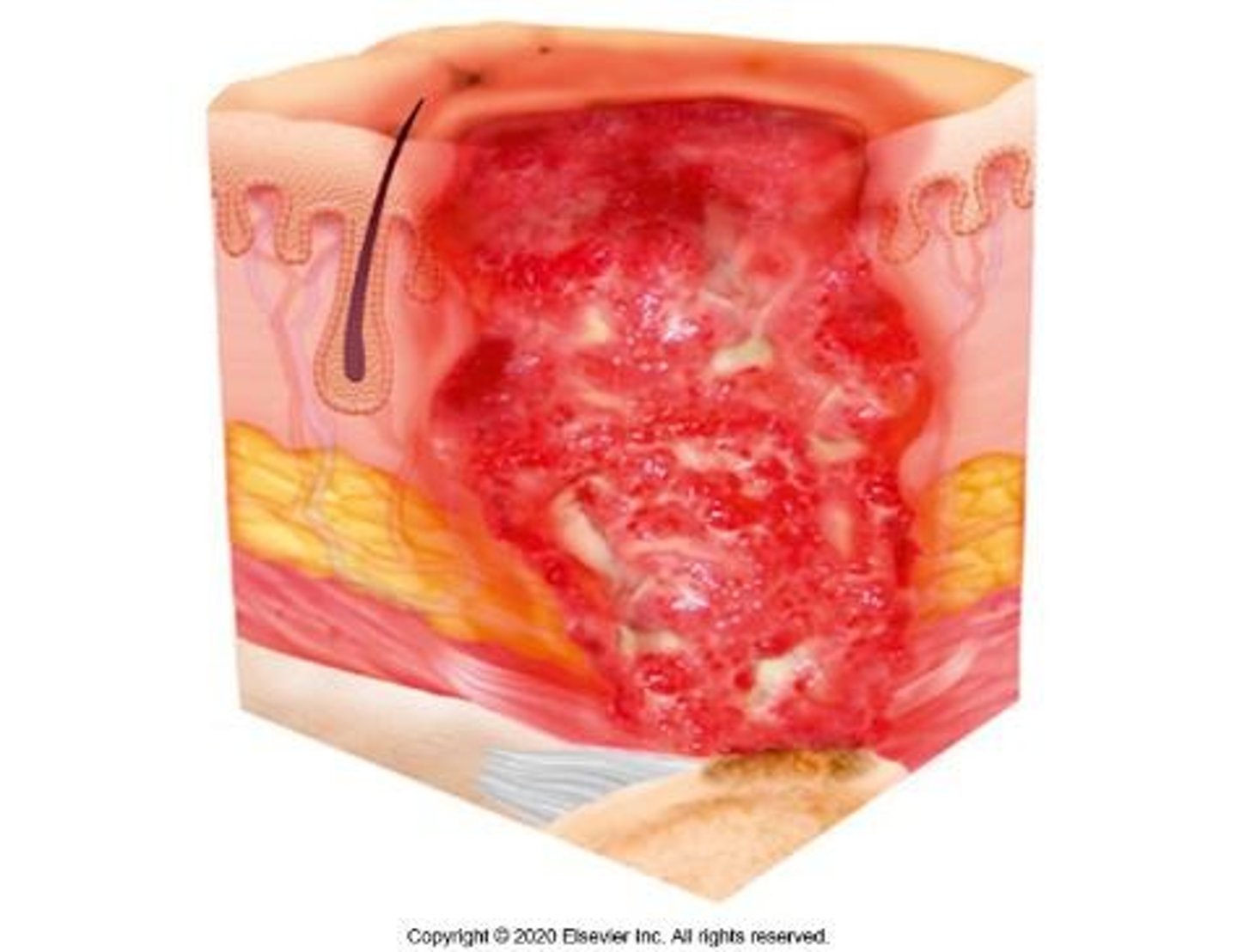
Stage 4 Pressure Ulcer
Full-thickness skin and tissue loss; deep injury with exposed or palpable fascia, muscle, tendon, ligament or cartilage, or bone; slough of eschar may be visible.
Orthostatic hypotension
BP drop >20mm Hg systolic or >10mm Hg diastolic with dizziness, light-headedness, tachycardia, pallor, feeling faint.
Applying Physical Restraints
Use restraints only as a last resort; employed as a temporary measure; associated with serious complications; requires a physician's order.