AP Bio Unit 4 - Cell Communication
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is a Signaling molecule? (or ligand)
Binds to the receptor and can be lots of different things such as hormones or neurotransmitters
What is Signal Transduction?
Receptor gets activated by binding to it’s substrate which often means the receptors will change shape
What is receptor mediated endocytosis?
A process by which cells internalize substances (such as nutrients) by the binding of ligands to specific receptors on the cell surface, leading to the ingestion of materials in a vesicle.
What are some examples of cellular responses?
Types of cellular responses include cell growth, cell division, differentiation, apoptosis (programmed cell death), and changes in gene expression.
What is paracrine signaling?
A form of cell signaling where the target cell is nearby and receives signals through diffusion of signaling molecules in the extracellular fluid.
What is a gap junction?
Connections between two cells that are close together which allow for ions or other small molecules to pass through
What is a ligand-gated ion channel?
A type of ion channel that opens in response to the binding of a ligand, allowing specific ions to flow across the membrane.
What does it mean to ligand to something?
To bind
What is mitosis?
Series of phases that divide one diploid cell into two identical diploid cells
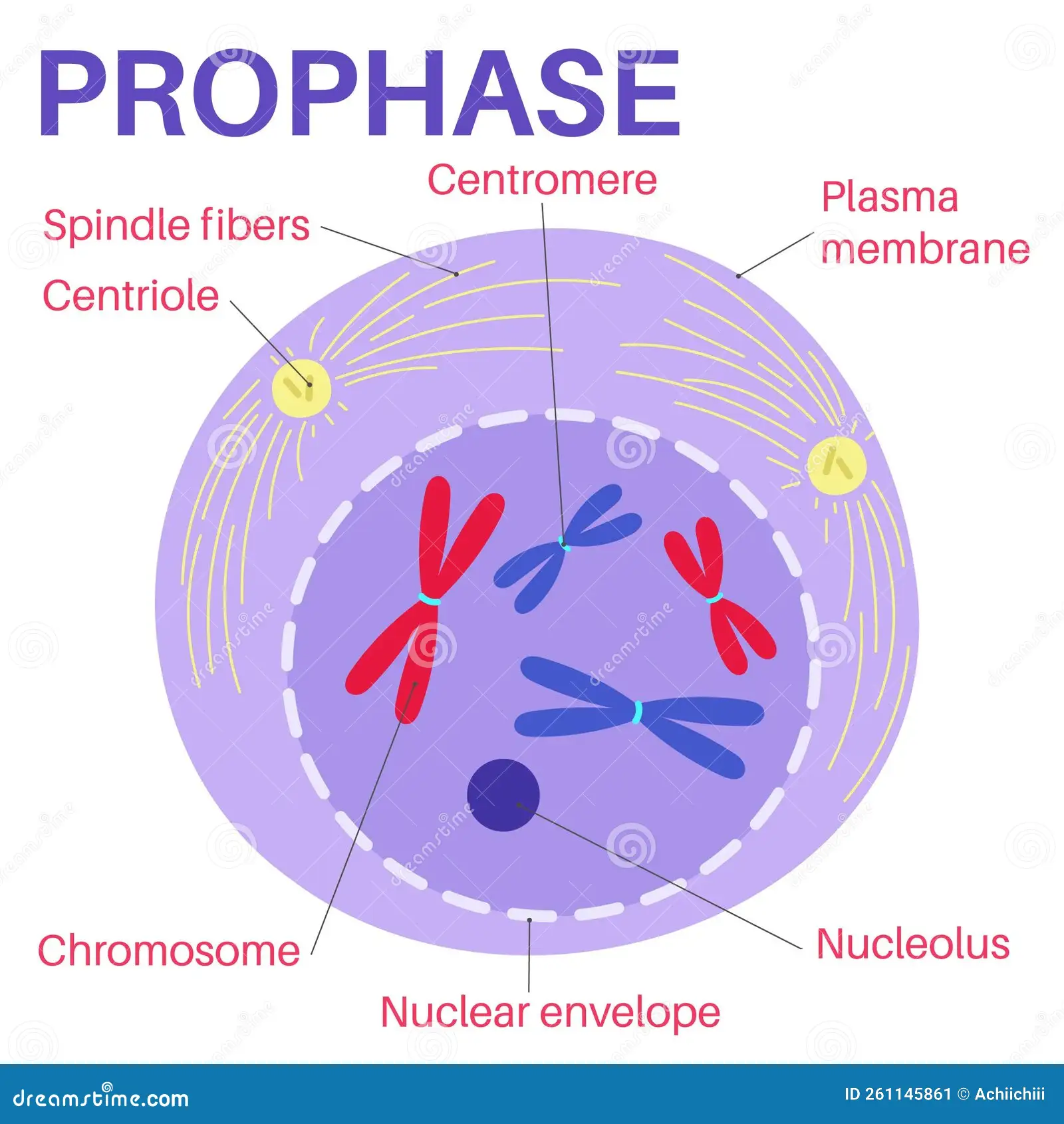
What happens in prophase?
DNA condense into chromosomes, moves toward spindle of the cell, nuclear membrane dissolves, chromosomes align at equator.
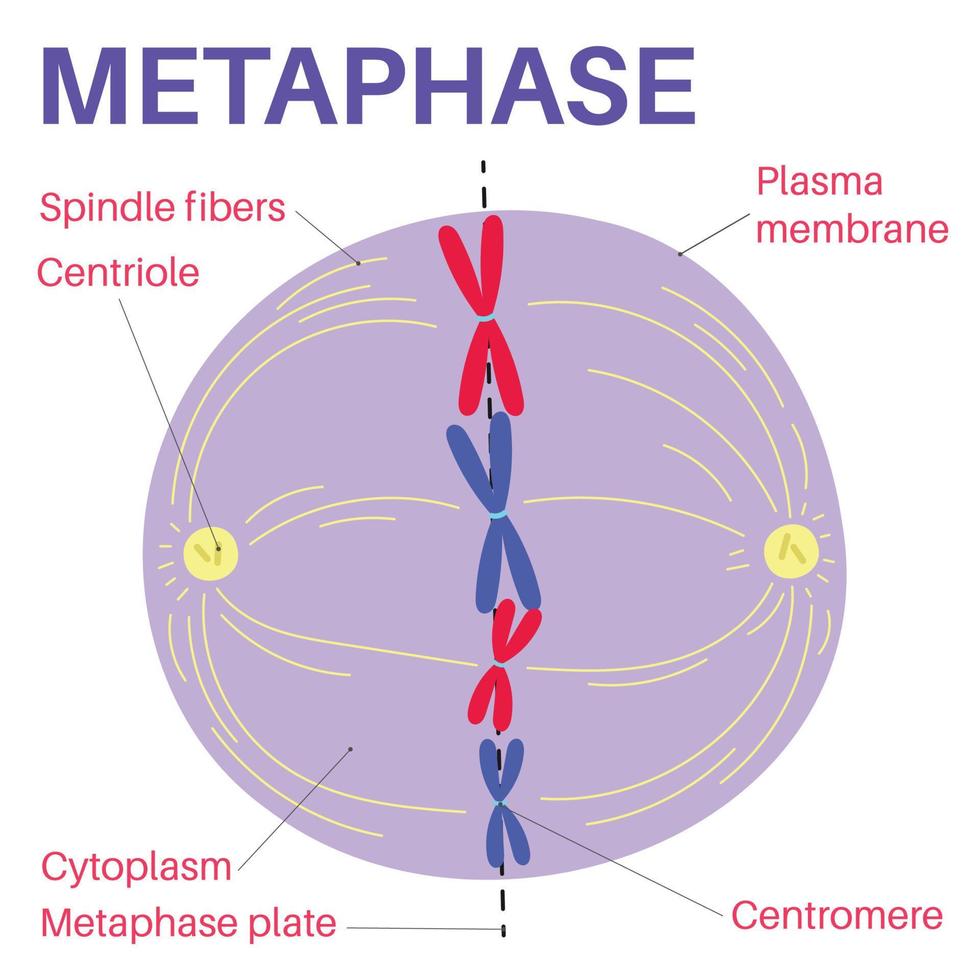
what happens in metaphase?
chromosomes align in the middle, spindle fibers attach to kinetichore (where cheomatid connects) on each chromatid
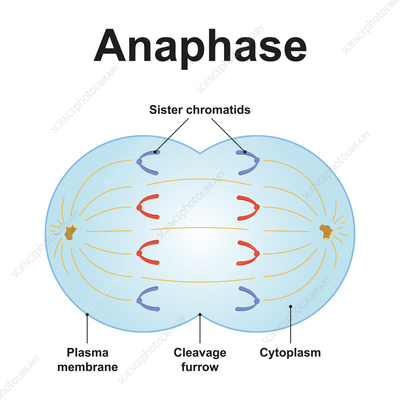
what happens in anaphase?
chromatids separate at centromere and cell widens
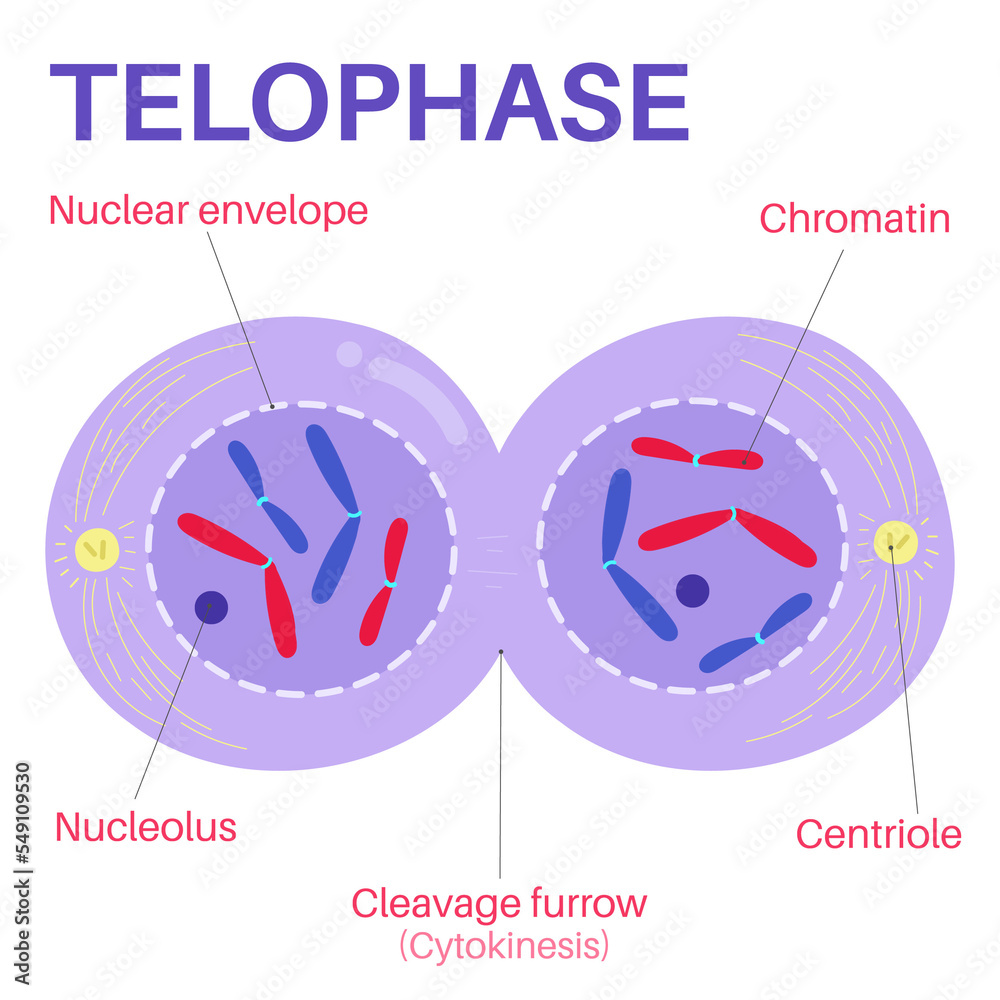
what happens in telophase?
the nucleus reforms, cleavage furrow forms, cell becomes very close to separating, and chromosomes unravel
What is cytokinesis?
The process in cell division where the cytoplasm of a parental cell is divided into two daughter cells, following the completion of mitosis.
What phase is the cell in for most of its life?
Interphase
What happens in the S phase?
The S phase (synthesis phase) is the part of the cell cycle where DNA is replicated, resulting in the duplication of the chromosomes in preparation for cell division.
What happens in the G2 phase?
The G2 phase is the stage of the cell cycle where the cell undergoes final preparations for mitosis, including the synthesis of proteins necessary for cell division and the final checks for DNA replication accuracy.
What is an oncogene? What are it’s functions?
An oncogene is a mutated version of a proto-oncogene, and they call cause the cell to multiply uncontrollably or divide unchecked — which can cause cancer.
Protoncogene
Non-mutated oncogene that codes for healthy cell growth and division.
What is a tumor surpressor gene? What does it do?
A tumor suppressor gene codes for proteins which function to control cell division, and ensure it only occurs when necessary.
What are the purpose of cell checkpoints in the cell cycle?
They make sure that the cell is taking the proper precautions before entering “M” phase and that things like DNA replication are moving smoothly, so that the cell can successfully divide in mitosis.
Cyclins
Cyclins inhibit proteins that block DNA synthesis/replication from occurring, so they can promote the production of proteins needed for mitosis.
Cyclin Dependent Kinase
What is a second messenger?
different from ligand, carries message into cell and amplifies it
What does endocrine mean in cell signaling?
Endocrine signaling refers to the process by which hormones are secreted into the bloodstream by glands, traveling to distant target cells to elicit a physiological response.
What is direct contact in cell signaling?
Direct contact in cell signaling occurs when cells communicate through physical connections, such as gap junctions or surface molecules, allowing for the transfer of signals and materials.
What is a signal transduction pathway?
A signal transduction pathway is a series of molecular events and interactions that lead to a specific cellular response when a signaling molecule activates a receptor on the cell surface.
What are the steps of signal transduction?
Reception: A signaling molecule binds to a specific receptor on the cell surface. 2. Transduction: The receptor undergoes a conformational change, activating a series of signaling proteins inside the cell. 3. Response: The signal is amplified and results in a specific cellular response, such as changes in gene expression or cell behavior.
Simplified steps of signal transduction?
Receptors → transduction → secondary messengers → target cell
What does it mean to metastisize?
To spread damaged cells (cancerous) to new tissue.
What is a phosphorylation cascade?
It is when relay molecules (such as protein kinases) exchange phosphate groups in chain reactions, resulting in a cellular response
How is cAMP made?
ATP is converted to cAMP
What do second messengers target?
Protein kinases
What are transcription factors?
Proteins that help turn specific genes “on” or “off” by binding to DNA
What is a G-protein?
G-proteins are molecular switches that relay signals from receptors on the cell surface to target molecules inside the cell, playing a key role in signal transduction pathways.