chapter 10 - atomic emission spectroscopy
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
emission spectroscopy
requires the use of very high temperatures of atomization sources to excite atoms
**there is no need for a source lamp
advantages of AES
show lower susceptibility to chemical interferences
good emission spectra result for must elements under a single set of excitation conditions
spectra for many elements can be recorded simultaneously
atomization is high
chemical interference is low
oxidation is low
advantages of plasma sources
they permit determination of low concentrations of elements that tend to form refractory compounds
permit the determination of nonmetals
plasma emission methods have concentration ranges of several orders of magnitude
few chemical interference
atomization occurs in a chemically inert environment, enhancing the lifetime of the analyte by preventing oxide formation
the temperature cross section of the plasma is relatively uniform (self-absorption and self-reversal are not observed as often)
plasma produces significant ionization, making it an excellent source for ICPMS
sources for emission spectra
plasmas
arcs
sparks
**are complex and comprise hundreds/thousands of lines
plasma
→ a homogeneous mixture of gaseous atoms, ions, and electrons at a very high temperature
***popular source for plasma is argon
types of plasma
inductively couples plasma (ICP)
microwave induced plasma (MIP)
direct coupling plasma (DCP)
what is the ICP source?
torch; consists of 3 concentric quartz tubes through which streams of argon gas flow, as spark is created in the argon, creating Ar+ and e-. the induction coil has a high AC current through wires at 27 or 41 MHz radio frequency. the current ins the wires sets up a magnetic field around the wire
what do ions do in the alternating B field of ICP?
ions oscillate around the annular region: positive ions are going one way while negative electrons are going the other way. as the AC changes positive to negative, they spin the other way. this heats up the region up to 10,000 K
what is the optimal observation region in ICP? what is the desolvation/atomization region?
8000-6000 K
more than 10,000 K
what are disadvantages of ICP?
it is an “argon hog” with argon having a flow rate of 10-15 L/min
there is an increased probability of spectral interference so they require higher resolution
expensive optical equipment is required
the procedure require less operator skill to yield satisfactory results
the excited state populations are small relative to ground states
ICP depends strongly on temperature
what is a refractory compound?
a compound that is highly resistant to thermal decomposition
how are wavelengths selected on the post-excitation end of the AE instrument?
a monochromator is used to see the emission as atoms return back to their ground states as they rise in the plasma and cool. there are very few interferences, and this allows for simultaneous analysis of multiple atoms
is MIP or ICP more inexpensive?
MIP is cheaper because the plasma can’t be sustained with nitrogen or air where ICP needs argon
when should one use internal standards in ICP?
when they need highly accurate/precise results, they can also be used when drift needs to be accounted for
why are ionization interferences less severe in ICP than they are in flame emission?
the large electron concentration from ionization of the argon maintains a fairly constant electron concentration in the plasma
how do you find the concentration of an unknown using an emission calibration curve?
use the equation concx = (b*concspike)/(m*volspike)
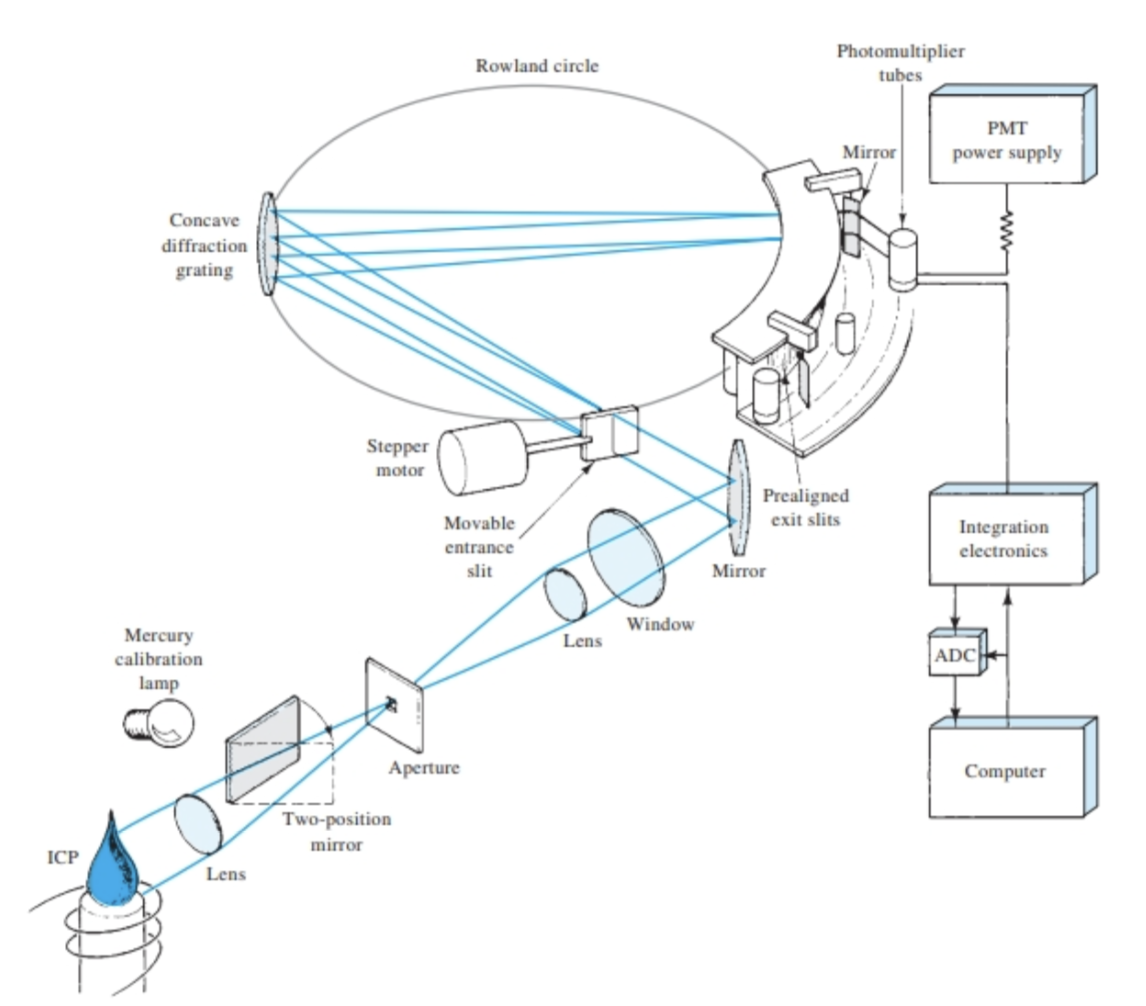
be able to draw a block diagram of the components within a successful ICP instrument capable of doing elemental analysis