Food Tech: Micronutrients & nutrients in food
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Details of Iron: Function, source, deficiency
Mineral
Iron prevents anaemia
Iron forms haemoglobin for RBC which carries oxygen
Red meat, green leafy veg
Details of Calcium: Function, source, deficiency
Mineral
Strong bones, teeth
Dairy, green leafy veg
Deficiency cause osteoporosis
Details of Fluoride: Function, source, deficiency
Mineral
Strengthens email on teeth
Fortified water
Dental cavities
Details of Magnesium: Function, source, deficiency
Mineral
For healthy immune system, bones and teeth
Spinach and brown rice
Cramps and muscles spasm
Details of Sodium: Function, source, excess
Mineral
Regulates water content in body
Salt
Excess causes High blood pressure, heart disease and stroke
Details of Iodine: Function, source, deficiency
Mineral
Regulates hormones in the thyroid
Seafood
Lethargic, tired
Details of Vit A: Function, source, deficiency
Fat soluble
Iron, metabolism, skin and vision
Whole milk, green leafy veg, carrots (Beta CAROTENE)
Excess: liver and bone damage
Deficiency: Night blindness
Good eyesight, growth, immune system, skin
antioxidant
Details of Vit D: Function, source, deficiency
Fat soluble
Absorb calcium, bones, teeth
Oily fish, eggs, fortified cereal
Weak bones, teeth, osteomalacia (adults)
Details of Vit E: Function, source, deficiencies & excess
Fat Soluble
Skin, eyes, antioxidant (protect cells from free radicals)
Sunflower seed oil, nuts
Too much: interfere w blood clotting, nausea, blurred vision
Too little: Rare but weak muscles, sight problems
Details of Vit K: Function, source, deficiency
Fat soluble
Helps clot blood & heal wounds, immune system & bones
Leafy greens, cereals and veg oils
Can’t have too much
Rare to have too little but can cause uncontrolled bleeding in newborns
Details of Vit B’s: Function, source, deficiency
Vitamin | Function | Source | Deficiency |
B1 (Thiamin) | Releasing energy + Nervous system | Whole grains & dairy | Beriberi (Nervous system) |
B2 (Riboflavin) | - | - | Cracking skin at mouth, swollen tongue |
B3 (Niacin) | - | - | Pellagra (diarrhoea, dementia, dermatitis) |
B9 (Folate) | Neural tube development | Whole grains, green leafy veg | Spina bifida (unborn babies) |
B12 (Cobalamin) | Energy production, protect nerve cells | eggs, milk | Pernicious anaemia |
B1, B2, B3, B12 - Releasing energy & Dairy
B9 - Neural tube development & Whole grains
Details of Vit C: Function, source, deficiency
Ascorbic Acid
Water soluble
Iron absorption, antioxidant, collagen production
Citrus fruits, green veg
Bleeding gums & anaemia
What vitamins a fat-soluble? What does this mean?
A D E K
Found in fatty foods like meat and fish
What are the water-soluble vitamins? What does this mean?
B’s C
Dissolvable in water so cannot be stored in the body and must be consumed daily
What does B1 do, where is it found and what problems does too little cause?
Thiamin | Helps nervous system & energy release from foods | Bread, pasta, rice, peas, eggs, liver | Tiredness, weak muscles & beriberi (severe disease) |
What does B2 do, where is it found and what problems does too little cause?
Riboflavin | Energy release from foods & tissue repair | Milk, eggs, cheese, leafy greens | Dry skin, sore throat, mouth sores |
What does B3 do, where is it found and what problems does too little cause?
Niacin | Energy release, nervous system, skin | Wheat, nuts, meat, fish | Pellagra (disease: fatigue, depression, memory loss) |
What does B9 do, where is it found and what problems does too little cause?
Folic Acid / folate | growth, healthy babies, B12 - red blood cell making | Liver, peas, leafy greens | Anaemia, tiredness, weak muscles, mouth sores |
What does B12 do, where is it found and what problems does too little cause?
Cobalamin | Nervous system & B9 - red blood cell making | Milk, eggs, meat, fish | Tiredness, nerve damage (vegan most risk) |
What does Vitamin C do, where is it found and what problems does too little cause?
Ascorbic acid | Protect body from infection, healthy blood vessels, heal wounds | Citrus fruits, tomatoes, green veg, strawberries, potatoes | Anaemia, scurvy (tiredness & bleeding gums) Cancer risk (C is antioxidant) |
How can you prevent the loss of vitamins before consuming fruit & veg
Prepare just before needed
Don’t let sit in water
Chop larger chunks (smaller SA)
Don’t peel or peel thinly
What are antioxidants?
Protect our bodies from free-radicals which can damage our cells leading to cancer and heart disease
What are six minerals, their function, source and problems of (1) too much or (2) too little
Calcium | Bones, teeth, nerves, muscles | kidney stones / osteoporosis |
Iron | Forms haemoglobin for blood cells | nausea / anemia |
Sodium | (salt) Controls water content | High BP / nausea |
Phosphorus | Healthy bones & teeth | Hard to absorb calcium / Weak muscles |
Potassium | Cardiovascular health & balance fluids | Nausea / Irregular heartbeat |
Magnesium | Release energy & bones | nausea / Lack of appetite |
All found in leafy green veg ex. phosphorus (dairy, meat, fish)
What are the trace elements, their source, function and problems with (1)too much or (2)too little
Fluorine | Strengthens teeth, enamel | Brown teeth & bone issues / weak teeth |
Iodine | Makes some hormones | Rare - affect thyroid gland function / Goitre (neck swelling) |
Why is water needed in our diet?
Regulate body temperature
Helps kidneys flush out toxins and waste through urine
Transports nutrients, O2 and CO2 around the body
What does a lack and excess of water cause?
Headaches
Weakness, sickness
Quick heartbeat
Being confused
Dark-coloured urine
Too much → Water intoxication. Kidneys can remove water quick enough → headaches, nausea, vomiting
Recommend 6-8 glasses per day
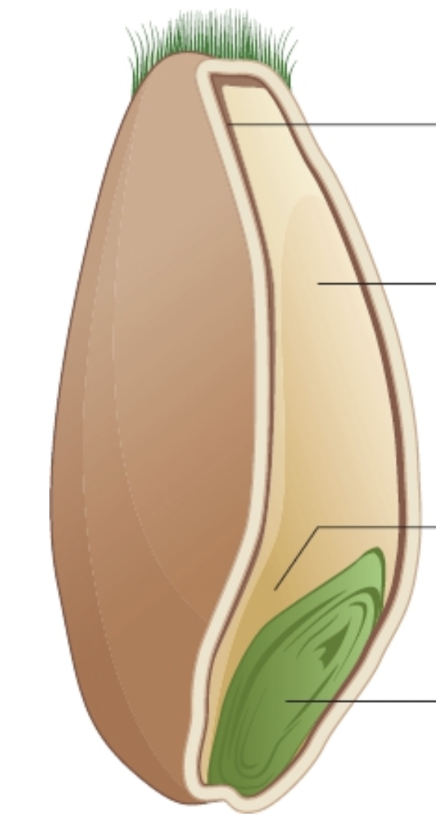
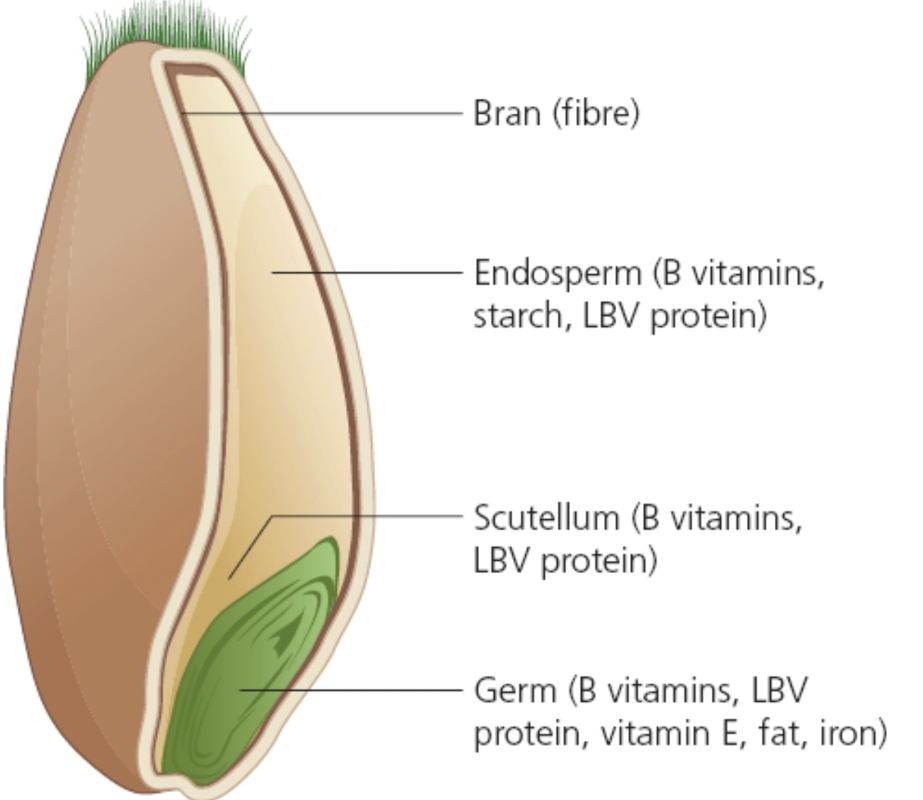
Label the nutrients in wheat

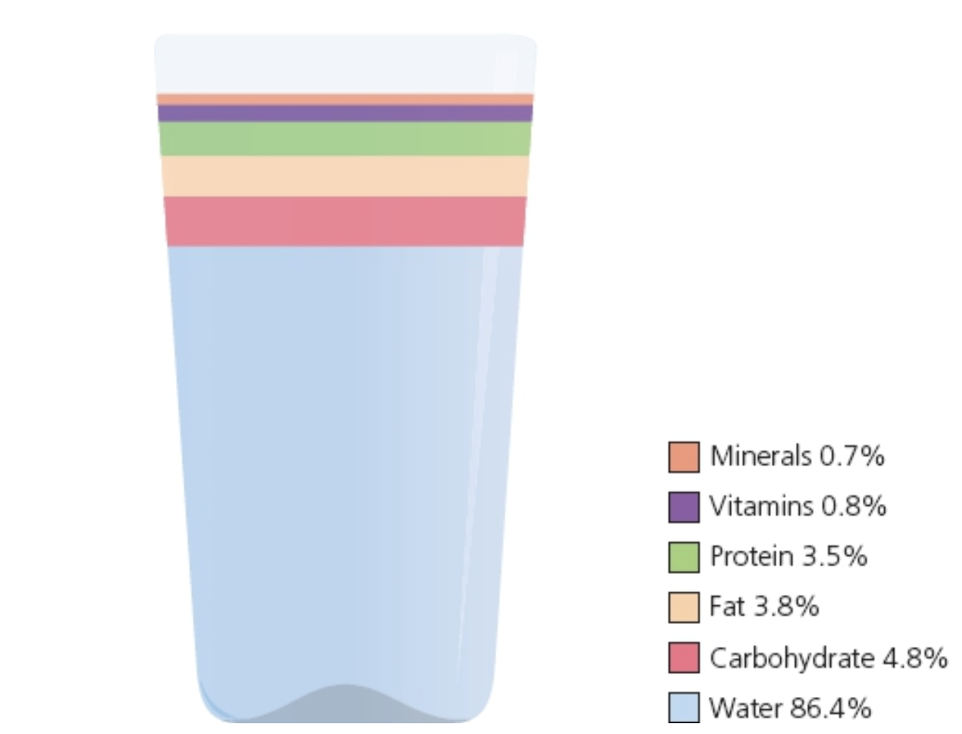
Label the nutrients in milk
Milk being homogenised means that the fat globules have be broken up so they are evenly spread throughout the milk and larger fat doesn’t rise to the top.
Nutrients in Alternative milks (RIce, Oat and soya)

What are the nutrients in cheese?
SImilar to milk
Harder cheeses → more fat and protein (more liquid has been lost)
Source of calcium, Vit A, riboflavin (B)
Properties of meat
Muscle fibres surrounded by connective tissue
Made up of proteins: Collagen and elastin
Myoglobin protein & haemoglobin gives meat its colour
Fat inbetween tissues, keeps it moist
Fat soluble vitamins and B vits (if not lost in water), iron and water (74%)
Poultry has less fat than red meat
Nutrition in fish
Protein
Fat (less in shellfish, white fish)
Oily fish contain essential fatty acids (Omega 3) and Vit A & D
Minerals, calcium in bones of tinned fish
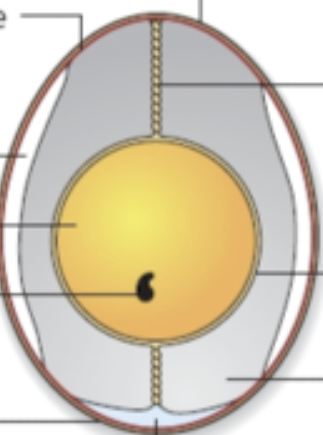
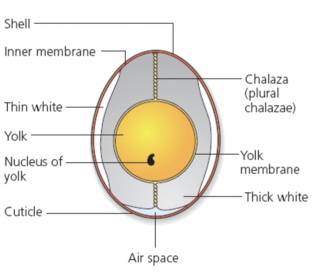
What is the structure and nutrition of eggs?
Egg white (60%) albumin which is the protein which expands and traps air when whisked
Egg yolk (30%) lecithin which is a natural emulsifier e.g. mayonnaise
Nutrition in differrent fats
Margarine → same fat as butter, less sat fat. Fortified with A & D
White fats → Oils, can replace lard, pastry
Oils - 100% fat unsat fat from veg oils
Animal fat
What are the nutrients in alternative protein foods?
Soya beans are HBV
Contain vits and minerals (often been enriched)
Fibre (often in Quorn and soya mince)
Low in fat
Mycoprotein (Quorn) is made from micro-organisms and normally has egg to bind it together.
Tofu made from soya beans