BioE demography and sampling
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Demographics
the study of statistics such as births, deaths, income, or the incidence of disease, which illustrate the changing structure of human populations.
6000 years ago
Date of the earliest demographic activity
John Graunt (1662)
“Father of demography” “Natural and Political Observations Made Upon the Bills of Mortality”
19th Century Population Centered Demography
The 19th century brought about different populations’ needs and thus demography was adjusted to fit the need of certain populations
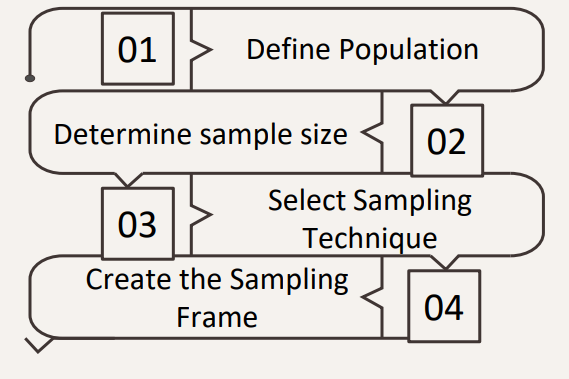
Steps in Executing Sampling
Cochran’s Sampling Formula
e = precision
p = estimated proportion of the population with the desired attribute and contains trait of interest
q = 1-p
Z = a constant from the Z-table (depending on alpha), based on alpha
² = alpha
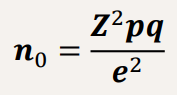
Yamane’s Sampling Formula
N = population size
e = precision (significance – Inverse of confidence interval)
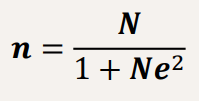
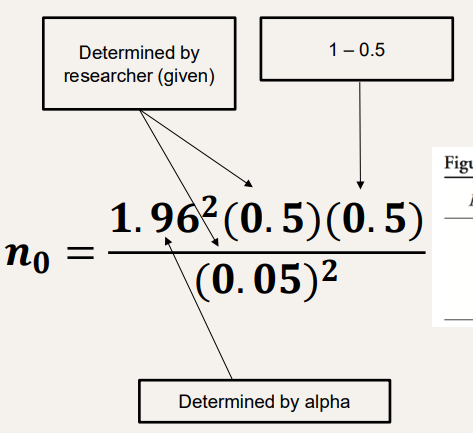
n0 = 1.96²(0.5)(0.5)/(0.05)²
What is the right order of formula and how do you solve this?
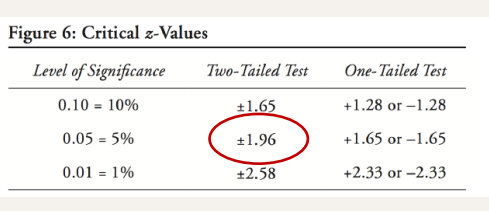
384.16
What is the answer to this solution?
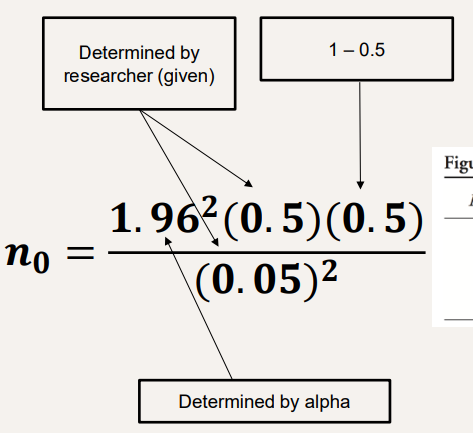
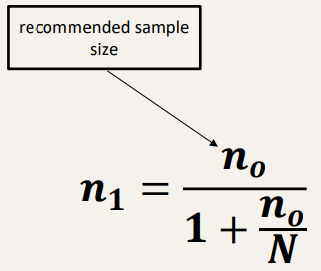
What formula do you use for Cochran’s Correction
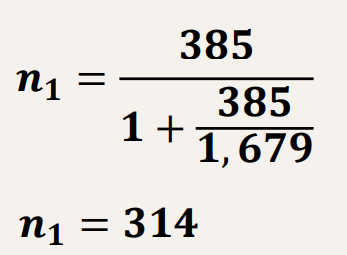
How do you solve for Cochran’s Formula-correcting for smaller populations where N=1679
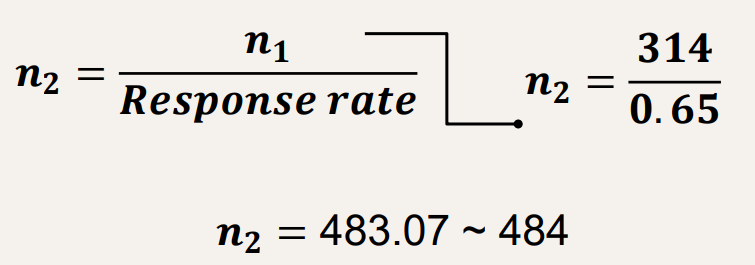
In Response Rate correction, adjusting for unresponsiveness and assuming only 65% only respond, what formula will be used? and what is the answer?
n
What is the symbol of sample in demographics
Probability and Non-Probability
Two general techniques in Sampling
Probability
All members of the population has an equal chance to be selected
Non-probability
Sampling is intentional and purposeful
Simple Random
type of probability sampling where the best sampling technique is to obtain a representative sample
Stratified
type of probability sampling where the population is divided into smaller groups/strata
Systematic
type of probability sampling where every nth element chosen at random and in predetermined succession
Cluster
type of probability sampling where population is divided into clusters. Clusters are selected as samples
Stratified Sampling Formula
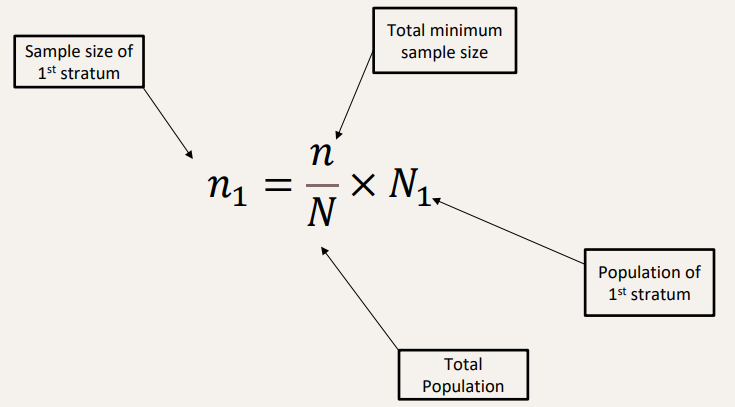
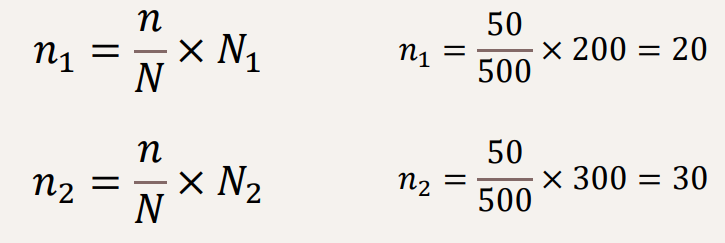
Solve this problem

Purposive
type of non-probability sampling where samples are selected based on what is required
Quota
type of non-probability sampling where samples are taken based on a set of predetermined criteria
Convenience
type of non-probability sampling where the nearest and most accessible samples are taken
Snowball
type of non-probability sampling where samples are referred to by already participating samples