IB ESS Topic 4 - Water and Aquatic Food Production Systems
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
middle ground (neither renewable or non-renewable) water storages
groundwater aquifers - take a long time to replenish (currently used unsustainably)
evapotranspiration (EVT)
the water lost by plants (especially trees in rainforests) through their leaves
surface run-off
water which does not infiltrate the soil, bu flows along the surface
withdrawals (a human effect on water systems)
water is used for domestic use, irrigation in agriculture and in industry
discharges (a human effect on water systems)
the addition of pollutants to water
e.g. chemicals from agriculture, fertilisers, sewage.
changing the flow (a human effect on water systems)
building roads and channeling water rivers underground or in concreted areas
canalising - straightening large sections of rivers
use of dams, barrages and dykes; making reservoirs
diverting flow (a human effect on water systems)
many rivers are led way from important/urbanised areas
some are led to dams to increase storage
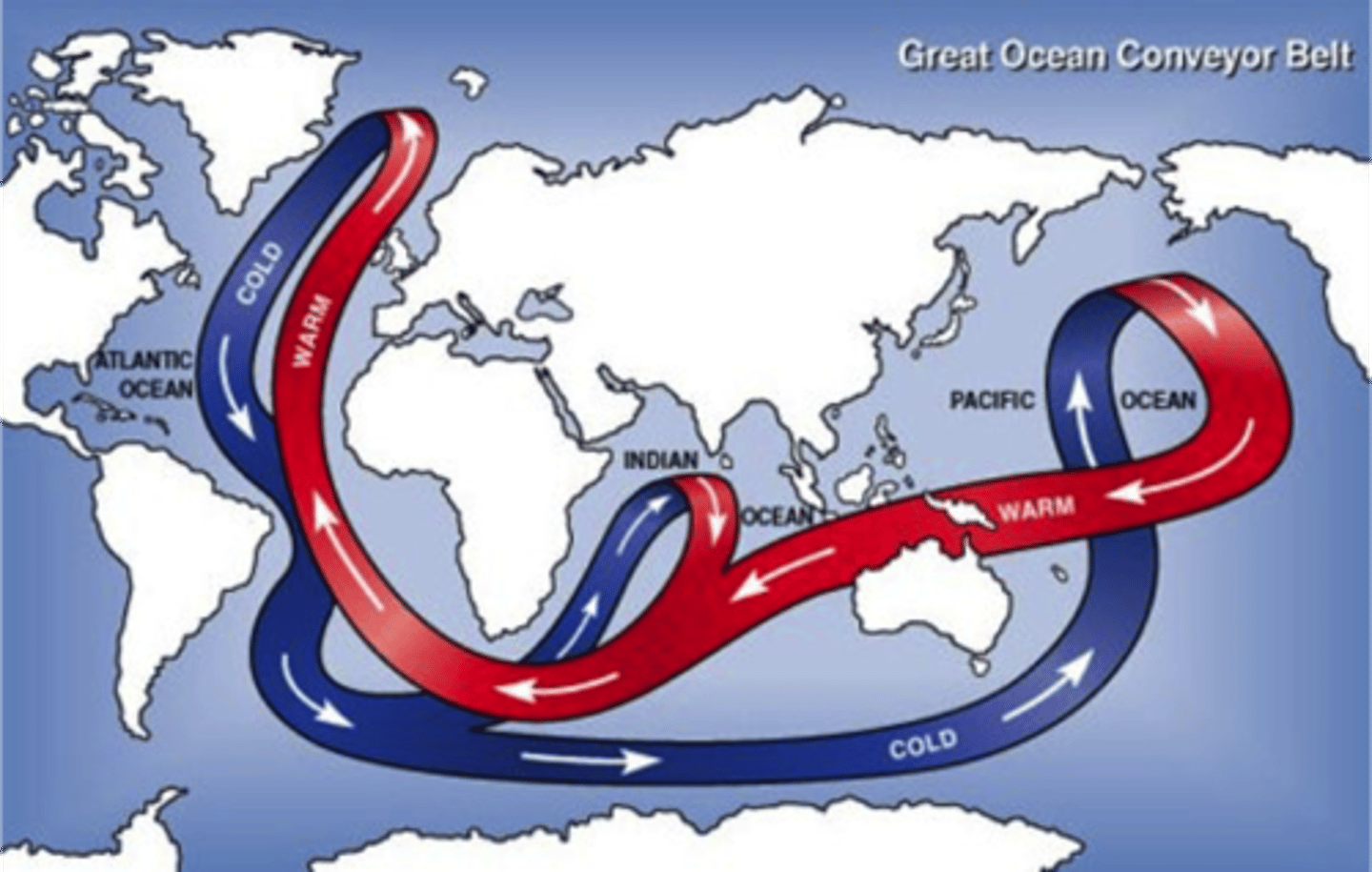
great ocean conveyor belt (diagram)
the huge oceanic currents which circulate the globe
Neutral phase (ENSO) conditions
trade winds blow warm air and water from the east to the west Pacific
cold water is drawn up from the deep on the western coasts of the americas (carrying nutrient rich waters = fertile waters - many fish)
air rises in the western Pacific and circulate back to the eastern Pacific
fishery
when fish are harvested in some way - includes capture of wild fish and aquaculture (fish farming)
90% is marine - 10% is freshwater
the tragedy of the commons
is an economic theory of a situation within a shared-resource system where individual users acting independently according to their own self-interest behave contrary to the common good of all users by depleting that resource through their collective action
e.g. individual countries using the ocean as a resource, and so over-exploitation is occuring
maximum sustainable yield (MSY)
the increase in natural capital that can be exploited each year without depleting the original stock or its potential to replenish itself - use of this leads to sustainability
may lead to depletion of a population in bad breeding (recruitment) years
interception loss
water which is retained by plant surfaces and which is later evaporated away or absorbed by the plant
throughfall
water which either falls through gaps in the vegetation or which drops from leaves, twigs, or stems
impacts of urbanization on water systems
decreased EVT & interception; decreased infiltration; lowered groundwater table; increased surface runoff; increased flood potential; increased stream sedimentation
MEDC
More economically developed country: a highly industrialized country with high average GNP per capita.
LEDC
Less economically developed country: a country with low to moderate industrialization and low to moderate average GNP per capita.
per capita
per person
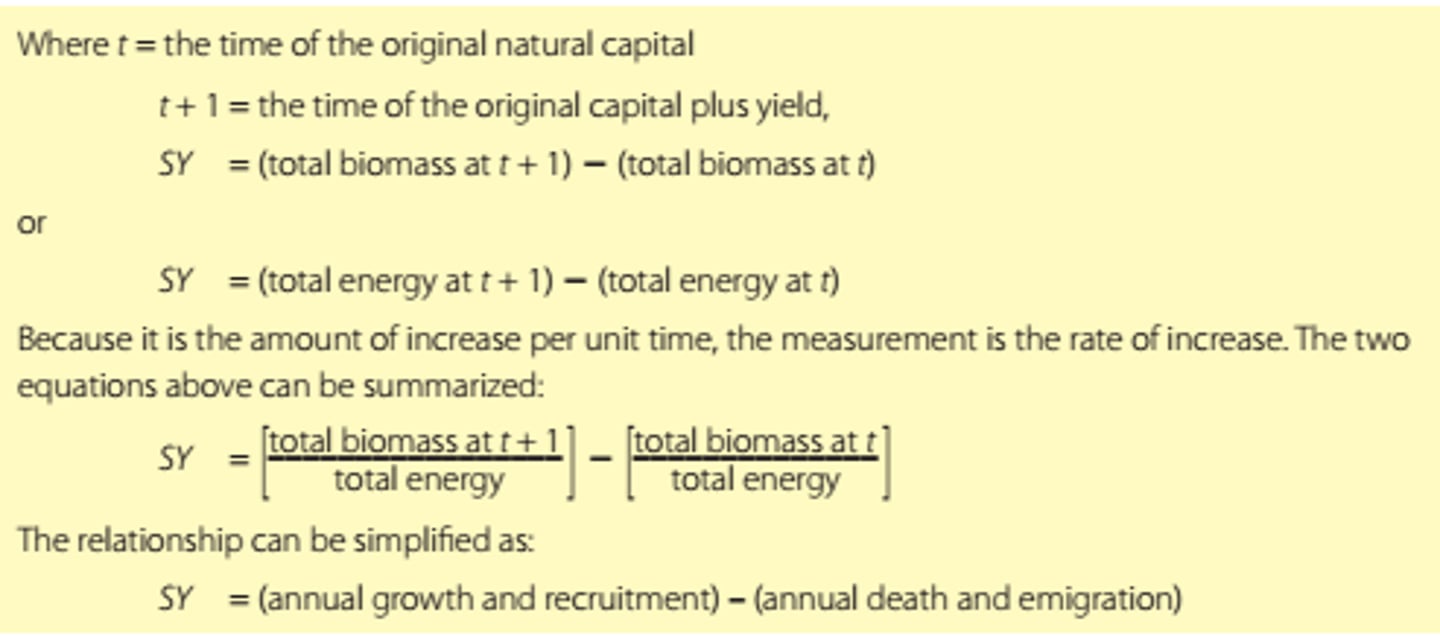
Sustainable Yield (SY)
calculated as the rate of increase in natural capital that can be removed without depleting the original stock or its potential for replenishment
Equation = (annual growth and recruitment) - (annual death and emigration)
eutrophication
the nutrient enrichment of streams, ponds, and groundwater through addition of nitrogen and phosphorous that causes algal blooms, oxygen starvation and biodiversity decline
dead zone
In a body of water, an area with extremely low oxygen concentration and very little life
water budget
a quantative estimate of the amount of water in different storages - the distribution of water on Earth - 97% salt, 3% fresh - mostly in ice caps and glaciers (68.7%)
turnover time
the average time it takes a water molecule to enter and leave a part of the hydrological system so that the water is completely replaced
renewable water storages
atmospheric water and rivers - quickly replenished
non-renewable water storages
oceans and icecaps - they would take 100s of years to replenish if used
what powers the hydrological cycle
energy from solar radiation and the force of gravity drive the water cycle - which drives the world's weather systems
precipitation
the movement of water from the atmosphere to the land in the form of rain, hail, sleet, or snow
evaporation
liquid water changing state to gaseous water (water vapour)
infiltration
water sinking below the surface into the soil
condensation
gaseous water (water vapour) which turns to liquid - especially in clouds causing rain
advection
wind-blown movement
flash flood
a sudden rush of water caused when rainwater or snowmelt cannot infiltrate the soil and runsoff on the surface
ocean currents
movements in the sea both vertically and horizontally - move in specific directions, and some have names
surface currents
the movement of the ocean in the upper 400m - movement is due to wind
deep water currents
aka thermohaline currents - caused by difference in temperature and salt concentration
hot water rises (less dense) - cold water sinks
water with a high salt concentration sinks (is more dense) - lower concentrations rise
climate
the weather patterns experienced by different locations
El Nino Southern Oscillations (ENSO) conditions
trade winds weaken allowing warm waters to spread to the east
this causes warm are to rise in the middle of the Pacific
cold mineral rich water is pushed up in the middle of the Pacific causing fish to be found too far off shore for fishermen in small boats
La Nina (ENSO) conditions
an overdrive of the neutral phase - the trade winds blow harder - the temperature difference between east and west increases
more evaporation and therefore rain in the west
desalination plants
removing salt from saline water to create potable (drinking) water
requires a lot of energy - extra salty water is often released back into the ocean damaging sea-bottom ecosystems (the salt water sinks)
domestic water use
water used for drinking, washing and cleaning at home
agricultural water use
water used for irrigation (water for crops) and for animals to drink
water crisis
the UN's term to describe the situation we are in today where up to 40% of humans alive do not have access to sufficient clean water
industrial water use
water used for processes such as machine cooling, manufacturing and mining
20 litres of 40 litres?
the WHO (World Health Organisation) and Agenda 21 state that every human should have/needs access to this much water per day (on average)
much of the world has far less - other considerably more
water scarcity
how much water we have and how we use it
there may be enough water in an area, but then it is diverted for non-domestic use
sources of freshwater
surface freshwater - rivers, streams, reservoirs and lakes
underground aquifers
aquifer
a layer of porous rock sandwiched between two layers of impermeable rock
refills where the porous rock meets the surface as water infiltrates
(flow can be as little as 1-10m per centrury - therefore refilling is extremely slow)
aquitard
the impermeable rock above (upper) and below (lower) the permeable rock forming an aquifer
grey water
water used in the home for cleaning, brushing teeth, showering etc
often is not really dirty, but drains the same way as sewage
black water
sewage - the water containing human waste - may carry disease-causing bacteria or parasites
water wars
the conflict caused by dispute over water sources - often when sources are shared e.g. Israel, Gaza and Egypt
marine ecosystems
oceans, mangroves, estuaries, lagoons, coral reefs, deep ocean floor
very diverse and have high stability and resiliene
continental shelf
the extension of the continents under the seas and oceans - creates shallow water
important because:
- 50% of productivity in only 15% of its area
- upwellings bring nutirent-rich water to continental shelf
- higher light penetration/insolation
- countries can claim it as theirs to exploit and harvest
phytoplankton
single-celled organisms that can photosynthesis and are the most important producer in in the oceans, producing 99% of primary productivty - crucial in supporting oceanic food webs
zooplankton
single-celled animals which feed off of phytplankton and their waste - crucial in supporting oceanic food webs
Solar Radiation
transfer of radiant energy from the sun; drives the hydrological cycle
Average turnover times in the hydrological cycle
37,000 years in the ocean; 16,000 years in ice caps; 300 years in groundwater; 12-20 days in rivers; 9 days in the atmosphere
stemflow
water which trickles along twigs and branches and finally down the main trunk
transpiration
process by which water vapor escapes from living plants and enters the atmosphere
infiltration capacity
The maximum rate at which rain can be absorbed by a soil in a given condition
Overland flow
water that flows over the land's surface (aka surface runoff)
sublimation
conversion of a solid into a vapor with no intermediate liquid state
freezing
change of liquid water into solid ice below 0°C
melting
change from solid ice to liquid water when temperatures rise above 0°C
stream-flow aka currents
movement of water in channels (i.e. streams and rivers)
flooding
the covering (inundation) of normally dry land by water
irrigation
addition of water to areas where there is insufficient water for crop growth
impacts of deforestation on water systems
increase of light intensity, temperature, wind speed and ground level moisture; organic matter decomposes more quickly; raindrop impact increases; evapotranspiration rates decrease; overland runoff increases
salinity
concentration of dissolved ions in seawater; mean = 35 parts per thousand (ppt)
density
Mass per unit volume; changes in ocean based on temperature, salinity and pressure
Great Ocean Conveyor Belt
a global thermohaline circulation, driven by the formation and sinking of deep water and responsible for the large flow of upper ocean water
specific heat capacity
the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of water by one degree Celsius (water has to absorb 4.184 joules of heat for the temperature of one gram of water to increase by 1°C).
hydrological cycle
the movement of water between atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, biosphere, and pedosphere; closed system at global scale
siltation
The accumulation of sediments, primarily silt, on the bottom of a reservoir.
Blue Planet
Earth's name due to the fact that 70% of Earth is covered with water
the Walker Circulation
the winds which travel west across the Pacific, rise in the west (eastern coast of Australia), travel east again, and sink in the east (Western coast of the Americas)
saline
salt water - this is the majority of Earth's water
UNCLOS
The UN Convention on the Laws of the Sea - in 1982 they designated the continental shelf as belonging to the country from which they extend
DOM
dead organic matter
waste created by living organisms as they grow and die
benthic
organisms living on or in the sea bed
pelagic
organisms living surrounded by water from above the sea bed to the surface
FAO
Food and Agriculture Organisation:
- more than 70% of world fisheries are fully exploited, in decline, seriously depleted or too low to allow recovery
aquaculture
the farming of aquatic organisms in both coastal and inland areas involving human intervention in the rearing process to enhance production (FAO)
benefits of fish
high in protein, contains important lipds (fats and oils), low in bad fats, provides
on average, people eat 20 kg of fish and only 8 kg of meat
vegetarian farmed fish
solution to sustainable aquaculture - the United States Department of Agriculture has proven that there are eight species of carnivorous fish which can gain enough nutrients on a diet excluding other fish
China's production of farmed fish
62% of all farmed fish - mostly carp or catfish - often grown in rice paddies (DOM and waste provides nutrients for the rcie)
rice - fish farming
a system whereby fish are reared in rice paddies - the fish eat insect larva and algae and produce waste which the rice uses as fertiliser
over-exploitation of fisheries
fishing at an unsustainable level - over-fishing (we are too good at catching fish)
- commercial fishing has high technology to aid in catching efficiency
- fishing fleeting are larger with modern refrigeration (to stay out longer)
- within a fishing fleet there are now also processing ships
- indiscriminate fishing gear catches all organisms whether they are the target species or not (by-catch)
- trawlers drag huge nets along the seabed destroying the benthic ecosystems
fish stock
the population of fish in a given area that are harvested
Sustainable yield equation
overfishing
harvesting fish to the point that species are depleted and the value of the fishery reduced
water pollution
The contamination of streams, rivers, lakes, oceans, or groundwater with substances produced through human activities; includes sewage, industrial discharge, solid domestic waste, pipelines, energy waste, atmosphere dissolution, oil spills, aquaculture farms, storm water runoff
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
a measure of the amount of dissolved oxygen required to break down the organic material in a given volume of water through aerobic biological activity
water quality tests include
biological oxygen demand, chemical oxygen demand, turbidity, ammonia, dissolved oxygen
biological indicators of water quailty
dissolved oxygen, pH, phosphate, nitrate, salt (chloride), ammonia
indicator species
Species that serve as early warnings that a community or ecosystem is being degraded; often faster and cheaper to measure population than concentration of specific pollutant
trent biotic index
A measurement of levels of pollution in aquatic ecosystems, based on indicator species which tend to disappear from a river as the level of organic pollution increases; has a maximum value of 10
biotic index
indirectly measures pollution by assaying the impact on species within the community according to their tolerance, diversity and relative abundance
natural eutrophication
a natural process that occurs in an aging lake or pond as that body of water gradually builds up its concentration of plant nutrients.
anthropogenic eutrophication
Occurs through the increase of phosphates and nitrates through human intervention