Physics 2 Lab
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Inside a Faraday cage the electric field
is zero
The charges generated by the VDG are because of
Frictional forces
Which of the following materials can be used to construct a Faraday cage?
None of these (semiconductor, non-conductor, insulator)
Which of the following statements is correct?
A photon has no charge
An inductive charging (i.e. the reason why we used the smaller dome in the lab) acquires the opposite charge than the main Van de Graaf (VDG) dome is because
The repelling forces between electrons
The typical radius of an atom is closer to
10^-15m
An electrostatic luminous spark is a result of which of the following?
Collisions between ions or electrons and air molecules
One argues that because the proton is much larger in mass than the electron, it creates a much stronger electric field at the same distance than the electron does. This statement is
False
The size of the VDG dome determines
All of these on the list (the electric potential magnitude on the surface of the sphere, how long the sparks can reach, how much charge is stored)
Which of the following choices best represents the likely “byproducts” when accelerated electrons collide with air molecules?
A photon
At its natural state, air is
an electrical insulator
At any given time, there are electrons in the air that we breathe. This statement is:
True
The charges on the VDG reside
on the surface
Which of the following quantities does the breakdown voltage of a gas depend on?
All of these (partial pressure, density, temperature)
The electric field at the center of the VDG dome is
Zero
The sound from the electrostatic luminous spark we observed in the lab is a result of
None of these on the list (the electron reduction from excited atoms, the photons produced from excited atoms, the electron production from exicted atoms)
A student argues that the light that is produced during the VDG spark is due to the thermal expansion of the surrounding air. This statement is
False
The neutron is much less massive than the proton. This statement is
False
Inductive charging is due to which of the following?
The Coulomb force
Where do charges reside on a randomly shaped conductor?
They always reside at the surface
The electron is less massive than the proton. This statement is:
True
The resistance of the semiconductor we studied in the lab:
exhibited non-Ohmic behavior
Ohm’s law is always obeyed across all electronic devices (e.g. bulbs, resistors, semiconductors, etc.). This statements is:
False
Momentum exchange between electron collisions is one of the parameters that determines the resistivity of a wire. This statement is:
True
Ohm’s law in AC and DC domain treats an equivalent resistor (i.e. combining more than one resistors into one) the exact same way. This statement is:
True
Ohm’s law in AC and DC domain treats an equivalent resistance (i.e. combining more than one resistors into one) the exact same way. This statement is:
True
The basic function of an oscilloscope is to return the electric potential difference across ANY element in a circuit with respect to which of the following?
Ground
Two different resistors in series connected to an AC supply will ALWAYS exhibit:
no voltage phase difference
The basic function of an oscilloscope is to return the electric potential difference across ANY element in a circuit with respect to which of the following?
Ground
Two resistors R1 and R2 are connected in a parallel AC circuit but R1 gets hotter faster than R2. Which of the following conclusions can be safely assumed?
R2 > R1
Is the statement “Ohm’s law is ALWAYS obeyed across all electronic devices” true or false?
False
Three 10-Ohm resistors that are made from the same material are connected in series. Which of the following quantities will ALWAYS be the same for the three resistors?
Current, voltage, and resistivity
Momentum exchange between electrons is one of the parameters that determines the resistivity of a wire. This statement is:
True
Both Kirchhoff rules are NOT valid for AC current. This statement is:
False
The relative mean square (rms) quantity for electric potential in AC is ALWAYS:
greater than the numerical average of AC electric potential
In the lab we experimented on resistors in series in the AC domain. When we increased the frequency without changing anything else, we observed that the current of the circuit:
remained the same
Two resistors in parallel are made of the same material and have the same length and cross-section. Which of the following quantities will always be the same for these two resistors?
All of these on the list (current, resistance, voltage, resistivity)
Three 10-Ohm resistors that are made from the same material are connected in series. Which of the following quantities are the same for these three resistors?
All of these on the list (voltage, resistivity, current)
The phase difference between the AC voltages of two resistors in series dependent on which of the following?
This is no phase difference
Is the relative mean square(rms) quantity for electric potential in AC ALWAYS greater than or less that the numerical value of the AC electric potential?
Greater than
In an AC (sine-wave) domain, the time-series of the voltages between the capacitor and the entire circuit will ALWAYS be:
None of these (exactly 90, exactly 180 out of phase, exactly in phase)
In an AC (sine-wave) domain, the time series of the voltages between the capacitor and the resistor will ALWAYS be:
exactly 90
One of the major difference between DC and AC (sine-wave) that when the circuit includes a capacitor is that:
the capacitor has resistance, but dependent on frequency
In your lab experiment, you deduced that the speed of a capacitor discharging in a DC circuit is dependent on which of the following quantities?
Both on capacitance and resistance
Which of the following will cause the capacitance to increase?
None of these (increase the plate separation, increase the voltage across the capacitor, decrease the charge on the plates)
In your lab experiment, you deduced that as the AC source frequency increases in an RC in parallel, then the rms voltage across the entire circuit:
remains the same
In your lab experiment, you considered a capacitor and resistor in series in AC (sine-wave) domain. Did the time-series of the voltage across the capacitor ever become zero?
Yes
The plates of an isolated parallel plate capacitor with a capacitance C carry a charge Q. What is the capacitance of the capacitor if the charge is increased to 2Q?
C
In your DC experiment, when the capacitor was just beginning to charge the current in the circuit was:
maximum
In your lab experiment, you observed that the discharging capacitor would exhibit:
the opposite polarity than it was charged at
Which of the following quantities is the capacitance dependent on?
Geometry and dielectric only
One of the major differences between DC and AC is that when the circuit includes a capacitor and a resistor in series, then:
the capacitance reactance depends on frequency
In you lab experiment, you deduced that as the AC source frequency increases in an RC in series, and the rms voltage across the resistor approached which of the following values?
Approaches the rms of the source
Two capacitors are connected in series have the same charge density and same plate separation. Which of the following quantities will always be the same for these two capacitors?
Charge
In an AC (sine-wave) domain, the time-series of the voltages between the capacitor and the entire circuit will ALWAYS be:
None of these (exactly 90, exactly 180 out of phase, exactly in phase)
An electron, moving toward the west, enters a uniform magnetic field. Because of this field the electron curves upward. The direction of the magnetic field is:
towards the north
An electron moving in the +x-direction enters a magnetic field. If the electron experiences a magnetic deflection in the -y direction, the magnetic field in this region points in the
-z direction
Only an electromagnet can have a north magnetic pole without having a south magnetic pole. This statement is:
totally inaccurate
Ions having equal charges but masses of m and 2m are accelerated through the same potential difference and then enter a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to their path. If the heavier ions follow a circular arc of radius R, what is the radius of the arc followed by the lighter ion?
R/ square root 2
The EMF field, unlike the Coulomb electric field, is:
non-conservative
A change is accelerated from rest through a potential difference V and then enters a uniform magnetic field oriented perpendicular to its path. The field deflects the particle into a circular arc of radius R. If the accelerating potential is tripled to 3V, what will be the radius of the circular arc?
squ root 3 R
Two current-carrying wires can indeed exhibit attractive forces. This statement is:
correct
The transformer is a device that can increase the output of the input electric energy. This statement is:
absurd
Which domain does the creation of an electromagnet require?
Both AC and DC domains would work
A charged particle is moving with speed v perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field. A second identical charged particle is moving with speed 2v perpendicular to the same magnetic field. If the frequency of revolution of the first particle is f, the frequency of revolution of the second particle is:
f
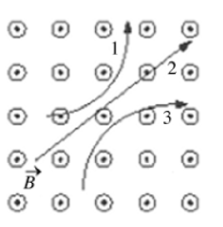
Three particles travel through a region of space where the magnetic field is out of the page, as shown in the figure. Which of the following choices best describes the charge of the three particles?
1 is negative, 2 is neutral, and 3 is positive
A vertical wire carries a current vertically upward in a region where the magnetic field vector points toward the north. What is the direction of the magnetic force on this current-carrying wire due to the magnetic field?
Toward the west
Guass’ law for magnetism essentially describes that:
there are no magnetic monopoles.
In this lab, you learned that if a coil is connected to a DC source, the moment we turn on the switch the current going through the coil:
will be zero
An RL circuit is connected to a constant DC voltage input of +5 V. When we turn on the power, then at that instant, the potential across the inductor:
will be -5 V
Which of the following transformers, if any, did you use in this lab?
Neither of these (step-up ideal transformer, step-down ideal transformer)
Like capacitance and resistance in an AC domain, inductance is a property of which of the following quantities?
Geometry
A coil (inductor) is in series with a resistor and an AC source. We turn on the power. What occurs the moment the current is trying to enter the coil?
The inductor will produce a magnetic field, which will further induce a current with direction opposite to the current in the circuit.
Faraday’s law only applies to materials that are paramagnetic (i.e. can be magnetized) such as iron. This statement is:
False
A transformer is a way to increase the electrical energy from one coil to the adjacent coil. This statement is:
False
When lowering the frequency in an AC LR circuit, then the inductance (L):
stays the same
Someone argues that a transformer, in fact, increases the electric potential energy of the outer coil. This person’s argument is blatantly:
false
When Ohm’s law is applied to two coils in series, the equivalent inductance is treated in the same way as which of the following circuit components?
Resistors
Joule’s law of heating suggests a linear relationship between temperature and time. What we actually observed was:
far from a straight line
The elapsed time we considered in order to find the liquid with the higher specific heat DID play a role. Based on your observations, is this argument true or false?
true
On which of the following parameters does the heat contained within an ideal gas depend?
None of these apply (volume, pressure, temperature)
From our experiment heating oil and water, we deduced that the speed at which each liquid heats up can also be dependent on which of the following?
The size of the molecules of the liquid
Which of the following statements can be described by the ideal gas law?
All of these statements (how fast gas molecules move and collide under different temperatures, the force exerted by collisions between molecules and the walls where the gas is contained, the momentum exchange from collisions between molecules as a function of temperature)
In the original Newton’s law of cooling, the type of liquid is utterly irrelevant. This argument is:
False
During your Boyle’s law experiment, why did you wait for a few seconds each time you pressed down the syringe?
To make sure that the process is isothermal
The PV = constant implies that
All of these (dT=0, dE=0, d(PV)= 0)
Someone argues that denser liquids must also have higher specific heat. Solely based on your experimental results, this argument is likely:
true
The area contained under a P-V graph is related to which of the following quantitates?
Energy
The term PV in the ideal gas law has units of:
Joule
On which of the following parameters does the heat contained within an ideal gas depend?
none of these on the list (temperature, volume, pressure)
Someone argues that we can freeze a liquid if we apply extreme pressure on it. This argument is:
True
Heat is a form of energy that relates to:
the energy flow from hot to cold
Which of the following methods did we use to ensure the simulation of an adiabatic decompression in our experiment?
The process was fast
Two beakers contain two liquids of the same mass. We heat them to the same final temperature, without any phase changes occurring. Which is true for the liquid that heats faster?
It has a smaller specific heat than the other.
We observed that the temperature probe near the bottom of the canister containing our liquid exhibited:
more time variations
The specific heat of two different liquids at the same temperature and pressure are:
likely different
An adiabatic process exchanges:
zero heat with the environment