nomenclature + polyatomics + gas laws formulas
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
-ate
normal ending
-ite
one less oxygen
per-
one more oxygen
hypo-ite
two less oxygen
acetate ion
CH3COO-
chlorate ion
ClO3-
Iodate ion
IO3-
bromate ion
BrO3-
florate ion
FO3-
cyanide ion
CN-
hydroxide ion
OH-
nitrate ion
NO3-
permangatate ion
MnO4-
carbonate ion
CO32-
bicarbonate ion
HCO3-
peroxide ion
O₂²⁻
sulfate ion
SO42-
phosphate
PO43-
ammonium
NH4+
ammonia
NH3 (neutral)
arsine
AsH3 (neutral)
stibine
SbH3 (neutral)
water
H2O (neutral)
ozone
O3 (neutral)
phosphine
PH3 (neutral)
borane
BH3 (neutral)
two oxidation states: endings
-ic = higher oxidation state
-ous = lower oxidation states
two oxidation states: latin naming Fe2+ and Fe3+
Fe2+ = ferrous
Fe3+ = ferric
two oxidation states: latin naming Sn2+ and Sn4+
Sn2+ = stannous
Sn4+ = stannic
two oxidation states: latin naming Cu+ and Cu2+
Cu+ = cuprous
Cu2+ = cupric
two oxidation states: latin naming Au+ and Au3+
Au+ = auros
Au3+ auric
two oxidation states: latin naming Hg+ and Hg2+
Hg+ = mercurous
Hg2+ = mercuric
two oxidation states: latin naming Pb2+ and Pb4+
Pb2+ = plumbous
Pb4+ = plumbic
naming polyatomic oxyacids (contain oxygen, hydrogen, and smth else)
hypo-ite = hypo-ous acid
-ite = -ous acid
-ate = -ic acid
per-ate = per-ic acid
bi-
one hydrogen, reduces charge by +1
molar volume formula
mV = V/n
Density of an ideal gas
Dgas = mm/mV, this ONLY works for gasses

how to convert g/L to g/mL
divide by 1000 since the conversion is happening in the denominator
universal gas constant
R = 8.314 kPaL/Kmol (kilopascal litres/ Kelvin mol)
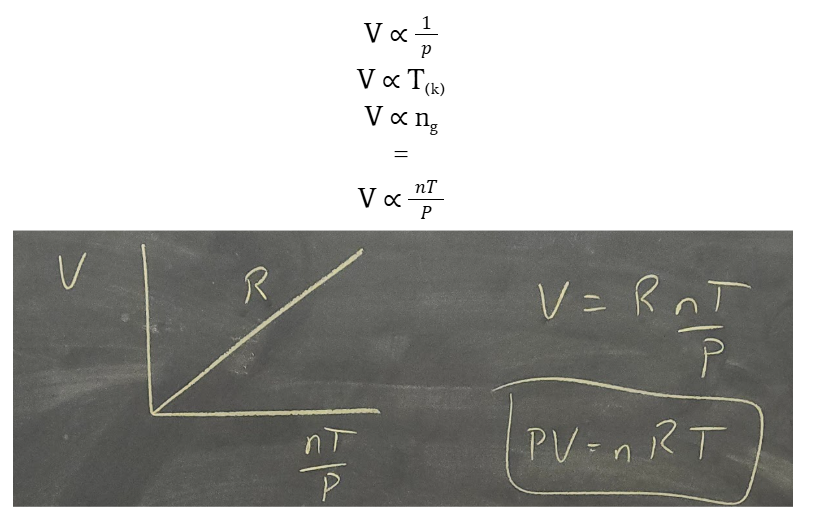
ideal gas law
R = PV / nT or PV = nRT
use ideal gas law to find molar volume
PV = nRT
V = nRT/P
V/n = RT/P
since V/n is molar volume, mV = RT / P
use ideal gas law to find density
D = m/V
V = m/D
substitute V = m/D into PV = nRT
Pm/d = nRT
Pm = nRTD
D = Pm/nRT
since m/n is mm, D = mmP/RT
since P/RT is mV, this is the same as D = mm/mV
use ideal gas law to find mm
substitute n = m/mm into PV = nRT
PV = mRT/mm
mmPV = mRT
mm = mRT/PV
boyle’s law
Volume is inversely proportional to pressure at constant T and n
P1V1 = P2V2
charles’ law
volume is directly proportional to temperature in Kelvin at constant P and n (moles per mass)
V1/V2 = T1/T2
Gay-Lussac’s law
pressure is directly proportional to temperature at constant n/m and Volume
P1/P2 = T1/T2
combined gas law
P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 at constant n/m and T in kelvin
Avagadro’s law/hypothesis
number of moles of gas is directly proportional to volume at constant T and P
n1/n2 = V1/V2
Density of a gas
Dgas = mm/mV at specific T and P
Density
D = m/v
use ideal gas law to find density
D = m/V
V = m/D
substitute V = m/D into PV = nRT
Pm/d = nRT
Pm = nRTD
D = Pm/nRT
since m/n is mm, D = mmP/RT
since P/RT is mV, this is the same as D = mm/mV
use ideal gas law to find molar volume
PV = nRT
V = nRT/P
V/n = RT/P
since V/n is molar volume, mV = RT / P
use ideal gas law to find mm
substitute n = m/mm into PV = nRT
PV = mRT/mm
mmPV = mRT
mm = mRT/PV
standard conditions
PSTP = 101.3 kPa
TSTP = 0.00000 degrees C or 273.15 K
mVSTP = 22.4 L/mol
Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure
PSATP = 100.0 kPa
TSATP = 25.00 degrees C = 298.15 kPa
mVSATP = 24.8 L/mol
universal gas constant
R = 8.314 kPaL/Kmol
Density of water at STP
1.00 g/mL
conversions of pressure
101.3 kPa = 1.00 atm = 760 mmHg or 760 torr