AP Macro Unit 1 Review Topics
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Economics
The social science concerned with the efficient use of limited or scarce resources to achieve maximum satisfaction of human material wants
Economizing problem
Humans wants are unlimited, resources are limited
Scarcity and Choice
Resources can only be used for one purpose at a time, scarcity requires that choices be made
Opportunity Cost
the value that must be given up (sacrificed) to obtain it
Factors of Production
Land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship
Marginal Benefit
The additional benefit or value gained from consuming or producing one more unit of a good or service
Marginal Cost
The economic cost to produce one additional unit of a good or service
Abstractions
Economic principles, theories, or models are abstractions, simplifications which attempt to find the important connections and relationships of economic behavior
8 Economic Goals
Economic Growth
Full Employment
Economic Efficiency
Price level stability
Economic Freedom
Equitable distribution of income
Eoconmic Security
Balance of trade
Trade deficit
Your country buys more products from foreign countries than foreigners purchase from you (america)
Trade surplus
Your country sells more goods to foreign countries than you buy from them
Fiscal budget
What a government earns in taxes and spends
Fiscal deficit
The government spends more than it takes in in taxes
Fiscal surplus
The government earns more in taxes than it spends
Adam Smith
The Wealth of Nations (1776)-invisible hand of economics/capitalism (laissez faire economics)
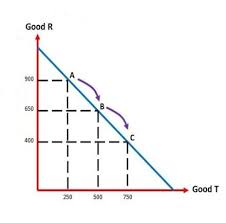
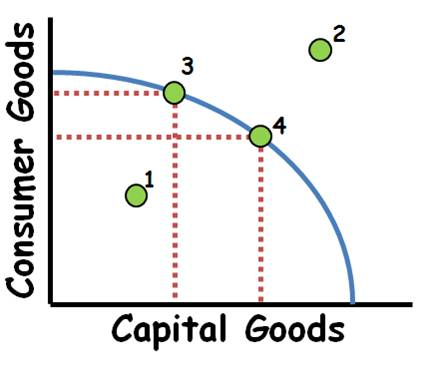
PPC
Points 3 & 4 are efficient, point 1 is inefficient, point 2 is impossible
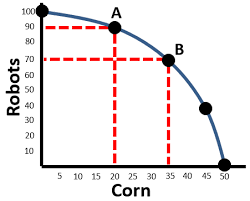
Increasing OC-PPC
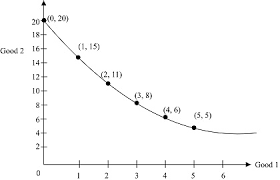
Decreasing OC-PPC
Constant OC-PPC