Thermochemistry and Types of Reactions Test - 4/24
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
5 types of chemical reactions
Synthesis
Decomposition
Single replacement
Double replacement
Combustion
synthesis reaction
composition or combination reaction
Substances react to form a compound - “to build”
Substance + substance yields compound
A + B → AB
Synthesis rules: metal oxides + water → ?
Metal hydroxide
Synthesis rules: nonmetal oxides + water → ?
oxyacids
Synthesis rules: Metal oxides + nonmetal oxides → ?
salts
Decomposition reaction
compound produces 2 simpler substances
Opposite of synthesis reactions - “break apart”
Often requires energy (heat, light, or electricity) to occur
Compound yields substance + substance
AB → A + B
Decomposition rules: metal carbonates → ? + ?
metal oxide + carbon dioxide
Decomposition rules: Metal chlorates → ? + ?
Metal chloride + oxygen gas
Decomposition rules: Metal hydroxides → ? + ?
metal oxides + water
Decomposition rules: oxyacids → ? + ?
nonmetal oxides + water
single replacement reaction
one element replaces a similar element in a compound - ions switch places
Element + compound yields element + compound
A + BC → AC + B
Cationic single replacement reaction
metals (+) switch places
Anionic single replacement reaction
nonmetals (-) switch places
double replacement reaction
ions of 2 compounds in aqueous solutions switch places to form 2 new compounds - cations (+) switch
Compound + compound yields compound + compound
AB + CD → AD + CB
Result of most double replacement reactions are either (3): formation of a…
precipitate
Water (neutralization reaction)
Gas
Double replacement reactions: formation of water (neutralization reaction)
reaction between an acid and a base
Produces a salt (ionic compound) and water → always the products
Double replacement reaction: formation of a precipitate
produces a precipitate (solid compound) and an aqueous compound
Insoluble product = precipitate
combustion reaction
substances react with oxygen releasing a large amount of energy
Hydrocarbon + O2→ CO2 + H2O
Most common combustion reaction is between a hydrocarbon and oxygen
Products will always be carbon dioxide and water
Almost all chemical reactions are accompanied by a…
change in energy
energy is either absorbed or released as heat, also known as…
thermal energy
Thermochemistry is the study of the … as heat during chemical reactions and physical changes
transfer of energy
First Law of Thermodynamics: the total energy of the universe is … and can neither be created nor destroyed; it can only be …
constant
Transformed
energy is the … and can take many forms.
capacity to do work
The forms of energy we deal with in chemical reactions are (3):
Potential energy is stored energy or the energy of position - energy stored within the bonds between atoms → takes energy to break the bonds of the reactants in a chemical reaction, so the energy is absorbed
Kinetic energy is the energy of motion - when the bonds of the reactants are broken, potential energy transforms into kinetic energy
Thermal energy (heat)
What happens when a chemical reaction takes place (4)?
Bonds of the reactants are broken → takes energy
If the energy is not enough to break the bonds of the reactants, the reaction will not occur
Then, atoms are rearranged
Finally, new bonds are formed (products) → releases energy
Breaking bonds … energy
Forming bonds … energy
requires
Releases
Reactants have … stored in the bonds
potential energy
When the reactants undergo a chemical reaction, the atoms are …
rearranged - kinetic energy
products have … stored in the bonds
potential energy
Temperature is a measure of the … of the particles of matter
average kinetic energy
The greater the kinetic energy of particles of matter …
the hotter it feels
K = ?
C + 273
The ability to measure temperature is based on …
energy transfer
Heat is a form of energy that is transferred between matter due to a …
difference in temperature
Heat energy always moves spontaneously from … to …
higher temperature to lower temperature
Heat is usually measured in the SI unit … and is a very small unit of heat → … are commonly used
1 kJ = ? J
Joules (J)
Kilojoules (kJ)
1 kJ = 1,000 J
calorie (cal) = the quantity of heat needed to …
1 calorie = ? J
raise the temperature of 1g of pure water 1 degree C
1 calorie = 4.184 J
system
Area where the reaction takes place (inside a flask, dish, or other reaction vesicle)
Surroundings
everything outside the system
exothermic chemical reaction
Reactants → products + energy
Release energy
potential energy stored in the bonds of the reactants is greater than the potential energy stored in the bonds of the products → energy is lost
Extra energy (thermal energy) is released from the system and into the surroundings → surroundings become warmer
Feels hot
endothermic chemical reaction
Reactants + energy → products
Absorb energy
more potential energy in the bonds of the products than in the bonds of the reactants → energy is gained
Extra energy is absorbed from the surroundings → surroundings become cooler
Thermal energy is supplied to the system from the surroundings → feels cold
Negative enthalpy = … of energy
loss
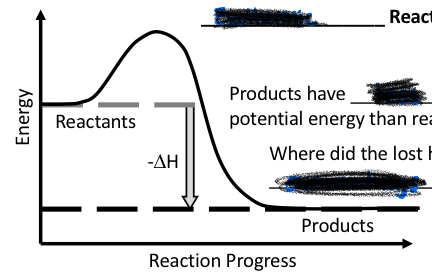
Endothermic or exothermic reaction?
Exothermic reaction
Products have less potential energy than reactants
Lost heat energy goes to the surroundings
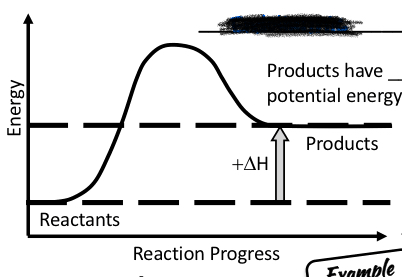
Endothermic or exothermic reaction?
Endothermic reaction
Products have more potential energy than reactants
Gained heat energy comes from the surroundings
Positive enthalpy = … of energy
gaining
activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to overcome the bond energies of the reactants (break the bonds and get the reaction started)
Calorimetry
measurement of heat flow into or out of a system during a reaction or a physical change
heat released by the system is equal to … by the surroundings
Or, heat absorbed by the system is equal to … by the surroundings
heat absorbed
Heat released
In calorimetry, an instrument called a … is used to measure … by the system and its surroundings
calorimeter
Heat energy lost or gained
Calorimeter
insulated device used to capture all of the heat either absorbed or released by a reaction
Used to measure the exact amount of energy that enters or leaves during a chemical reaction
Water is used to surround the reactions b/c it is stable nad has a high specific heat
The amount of heat absorbed or released during a physical or chemical change can be measured by the change in temperature of a … of water
The thermometer records water temperature. The water either absorbs energy from the sample, or transfers energy to the sample
known quantity
Change in temperature depends on (3):
Amount of heat energy added
Mass of the substance (how much substance) - a small amount of substance can be heated faster than a larger amount
Composition of the substance (what the substance is made of) - ex: metals heat faster than water
Specific heat
amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 Celsius
depends on the physical properties of the substance - how good it is at absorbing energy
Heat quickly = low specific heat
Heat slowly = high specific heat
Varies depending on the state of the material
water specific heat = ?
4.184 J/g°C
specific heat formula
q = mcΔT
enthalpy
heat of a substance at constant pressure
no way to directly measure the enthalpy of a system, so we measure the change in enthalpy
Enthalpy change
amount of heat that is absorbed or released by the system under conditions of constant pressure
Equal to the difference between the enthalpies of the products and the reactants
(ΔH) = Hproducts - Hreactants
Heat of reaction
the amount of heat that is absorbed or released during a chemical reaction when the coefficients equals the number of moles
Thermochemistry equation
shows the amount of energy lost or gained during a reaction as part of the chemical equation
Most ionic compounds ionize in water (soluble in water). The water molecules pull the ionic compound into its …
component ions
The formation of an insoluble solid product (…) is the driving force of an aqueous reaction to occur
precipitate
The attraction between the ions of insoluble compounds is … than the attraction of the ions to water
stronger
spectator ions
Ions in an aqueous solution that sit around and watch the reaction
net ionic equations
shows only those particles involved in the reaction and is balanced in number of atoms and charge
When heat is absorbed by a substance, what happens to the kinetic energy of the particles in the substance?
The kinetic energy increases
When two chlorine atoms combine to form a molecule of chlorine, do the reactants or products have a higher potential energy content?
reactants have more potential energy → forming bonds releases energy
Exothermic - reactants → products + energy
A sample of metal, at 120 degrees C, is placed into a calorimeter whose water is at a temperature of 10 degrees C. What will happen?
The water and metal will adjust to the same temperature between 10 degrees C and 120 degrees C.