Practical Lab 1: The Microscope and the Cell
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This set of flashcards covers key vocabulary regarding the use of microscopes, cellular biology, and essential lab procedures.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Compound Microscope
An optical microscope that uses multiple lenses to magnify small objects, allowing observation of microscopic structures.
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells that lack a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, typically found in bacteria and blue-green algae.
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells that have a clearly defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, including plant and animal cells.
Resolution
The ability to distinguish fine details in an image; higher resolution means that two close points can be seen separately.
Temporary wet Mount
A temporary slide preparation in which a specimen is suspended in a liquid and covered with a coverslip for microscopic examination.
Permanent wet mount
A slide preparation where specimens are preserved in a medium that hardens and does not evaporate, allowing for long-term storage.
Magnification
The process of enlarging the appearance of an object through the use of lenses.
Iris Diaphragm
A component of the microscope that regulates the amount of light passing through the condenser and onto the slide.
Cell Wall
A rigid outer structure surrounding plant cells that provides support and protection.
Vacuole
A membrane-bound organelle in cells that stores substances; large in plant cells for maintaining turgor pressure.
Nucleus
The membrane-bound organelle that contains genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell's activities.
Cytoplasm
The fluid substance within a cell that contains organelles and is the site of many metabolic processes.
Chloroplast
A membrane-bound organelle found in plant cells that is responsible for photosynthesis.
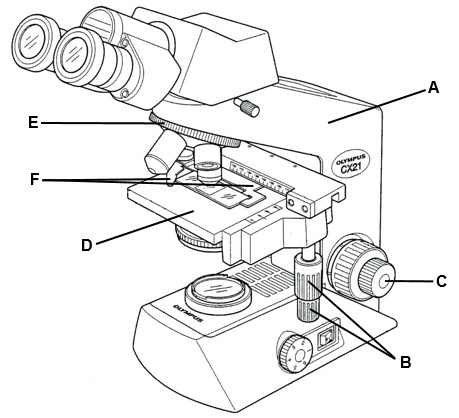
Label each part
a) arm
b) specimen holder knob
c) fine adjustment knob
d) stage
e) revolving nose piece
f) specimen holder
Total Magnification
The combined magnification power of the ocular and objective lenses in a microscope.
Diopter Adjustment
A knob on the microscope that compensates for differences in vision between the two eyes.
Fine Adjustment Knob
A part of the microscope used for making small adjustments to focus the image.
Coarse Adjustment Knob
A larger knob on the microscope used for making rapid adjustments to focus the image.
How to find scale of a drawing
Scale of drawing= (drawing diameter) divided by (the actual diameter of the specimen)
How to find true diamter?
True diameter = (field diameter) x (linear fraction)
What do plant cells have that animal cells don’t
A large central vacuole, cell wall (only cell membrane), and chloroplasts.
Explain image reversal
A phenomenon where the image seen through the microscope appears upside down and reversed from left to right.