Metals - A0S 1 - Chapter 4
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Easy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Properties Of Iron
Soft, malleable, conductive, thermal conductor, forms alloys
Uses of Iron
Buildings, machines, vehicles, infrastructure (coated with non-corrosive material as it can corrode)
Properties Of Aluminium
low density, soft, malleable, ductile, can form alloys, excellent conductor.
Properties Of Titanium
High density, low boiling point, readily forms alloys
Properties Of Gold
Shiny, good electrical and thermal conductor, unreactive, can form alloys.
General Properties Of Metals
High density
High melting points
Good thermal and electrical conductors
Malleable
Ductile
High Tensile Strength
Lustrous
Low ionization energies
Transition Metals vs. Main group metals
Transition Metals are harder, higher densities and melting points, stronger magnetic properties
Cations
Metals loose electrons to become positively charged
Model Of Metallic Bonding
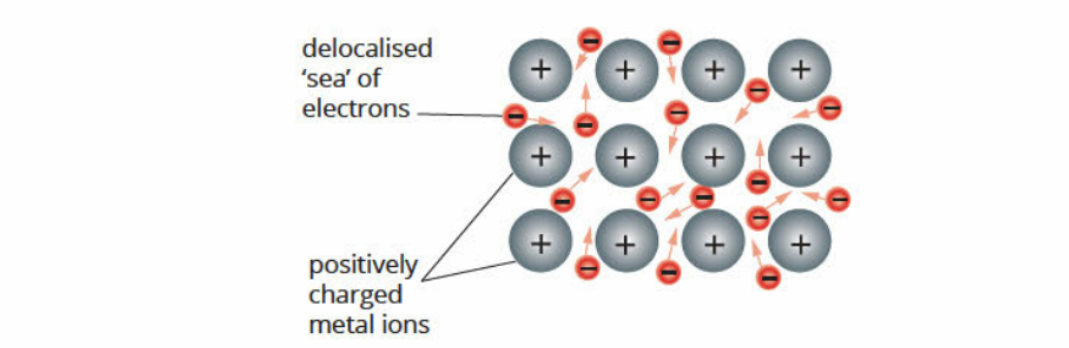
Limitations Of Bonding Model
Range of melting points, hardness of different metals
Differences in electrical conductivity amongst metals
Magnetic nature
Metal + Oxide
Metal Oxide (usually in the prescence of heat)
Mineral
Natural occurring Substance from where the element is extracted (as an ore)
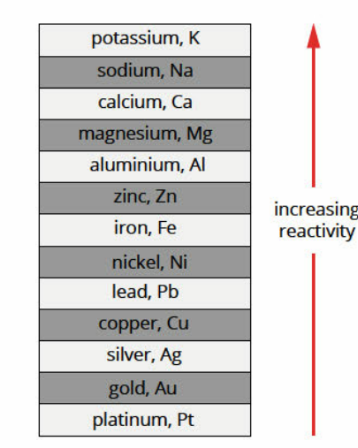
Table Of Reactive Metals
“Please Stop Calling Me A Zebra, I like Cute Silly Goofy Penguins.”
In-situ leaching
Pumping injections and retrieving the metals in a liquid form, by bringing them up to the surface.
Electrolysis
Passing an electrical current through the metal to retrieve it - requires a lot of lot electricity to do so.
Smelting
Melting the ore components of the mineral to retrieve the original mineral.
Things Affected By Mining
Land, Water, Air, Biodiversity
Linear Economy
Retrieval of minerals - manufacture - use - dispose
Circular economy
Reusing and recycling materials for further use
Reasons for circular economy
Resources becoming scarcer
Prices of resources are becoming larger
In order to reduce carbon footprint
Increasing demand for new products with not enough reasources
Blast Furnace
Used To Extract Iron from Iron Ore
Parts Of Recycling
Collection
Preparation for recovery (sorting)
Smelting
Purification
Ferrous Vs. Non-ferrous
Ferrous: Contains iron, steel
Non-ferrous: Other metals
Primary Smelter Vs. Secondary Smelter
Primary Smelter: Used to extract metal from their natural/ore state
Secondary Smelter: Designed specifically to smelt scrap metal
Energy saved by recycling aluminum
95%
Group 1 metal properties
very reactive
try to loose the one electron
react vigorously with water
very soft, low density
low melting point and lustrous
Group 2 metal properties (earth metals)
reactivity with water increases down a group
higher melting point than group 1 metals
more stronger than group 1 metals
Transition Metals Properties
not very reactive
High melting and boiling points (generally, much higher than Group 1 and 2).
High densities.
Hard and strong.
Excellent conductors of heat and electricity.
Lustrous (e.g., copper's reddish luster, gold's yellow luster).
Post Transition Metals
Physical Properties:
Softer than transition metals.
Lower melting points than transition metals.
Lower densities than most transition metals.
Can be brittle (e.g., bismuth) or relatively soft (e.g., lead).
Often exhibit some covalent character in their bonds.
Some can be amphoteric (react with both acids and strong bases, like Aluminum).
Why Can’t Covalent Compounds Conduct Electricity
Don’t have free moving particles
Fixed particles
Why are metals malleable, ductile
have more attractive forces in between particles than repulsive forces
Why Are metals shiny
have delocalised electrons
why do metals have hard/high boiuling points
Force between particles are strong
How are metals insoluble
energy required to break bonds> energy released when ions are hydrated
Thermal Conductivity
the ability to transfer heat
Thermal Conductivity among the materials
Type | Thermal Conductivity | Electrical Conductivity |
|---|
Ionic Lattice | Moderate (when solid), good (molten) | ❌ Solid: No |
Covalent Compound | Poor | ❌ No |
Covalent Lattice | ❌ Most: Poor | ❌ Most: No |
Metallic Lattice | ✅ Excellent | ✅ Excellent |
Why Is Covalent lattices bad at thermal conductivity
No delocalised electrons
Atoms are too far apart to vibrate and hit one another, thus transferring energy
“ate” vs ‘“ite” vs “ide"
🔁 Summary Table
Suffix | When used | Example |
|---|---|---|
-ide | Binary compound (2 elements only) | Sodium chloride |
-ate | Polyatomic ion with more oxygen | Nitrate (NO₃⁻) |
-ite | Polyatomic ion with less oxygen | Nitrite (NO₂⁻) |
per- -ate | Most oxygen in a series | Perchlorate (ClO₄⁻) |
hypo- -ite | Least oxygen in a series | Hypochlorite (ClO⁻) |
What Moves In Metals
On the valence electrons - the positive ions are fixed