Parasitt credit 1: Metamonoda: Giardia (diplodida) and Trichomonas (trichomonadida)
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
1. What genus belongs to heteroxenous coccidea?
- Cystoispora
- Sarcocystis
- Toxoplasma
- Neospora
The infectious stage of cystoisporosis?
- Sporulated oocyst
- 2 sporocysts
- 8 sporozoits
Cystoisporosis of pigs caused by which genera?
- C. suis
- C. almaataenis
- C.neyrai,
all in small intestine
Cystoisporosis of cats caused by?
- C. felis
- C.rivolta (cati),
in small intestine
Cystoisporosis of dogs caused by?
- C. canis
- C.ohioenis
-C. burrowsi
Endogenous development of cystoispora felis in a parathenic host takes place?
In rodent mesenteric lymph nodes
Cause of neonatal diarrhea in piglets?
Cystoispora suis
Sporulation of genus Sarcocystis occurs where?
Sporogony: endogenous inside the definitive host/final host (in small intestine).
Final hosts: carnivores and man.
Sarcocystis is transmitted by?
Predator-Prey life cycle:
The infective cysts containing bradyzoits is present in the muscle tissue of intermediate host.
The definitive host (carnivore or man) eats the meat and the sarcocyst with bradyzoits are transmitted.
Final host of sarcocystis is?
carnivores and man
Sporogony of sarcocysts is in?
lamina propria of final host (endogenous in small intestine of final host. Same as gamogony)
Merogony/Schizogony in sarcocystis occurs in?
intermediate host (herbivores, omnivores, birds)
Laboratory procedure for detection of sarcocysts in intermediate host?
ELISA of biopsy test, or post mortem digestive method to detect microcysts, histology or meat inspection to detect the macrocyst. (for detection in DH, sporulated cyst in feces is detected by flotation method (2 sporocysts, 8 sporozoites)
What is intravital diagnosis of sarcocystis?
- Biopsy of specimen
- Serological test
Cryptosporidium vs Sarcocystis?
Both: endogenous sporogony.
- Cryptosporidium: one host
- Sarcocystis: 2 hosts
Intermediate and definitive host in Sarcocystis cruzi/bovicanis?
- IH: bovine
- DH: dog
Intermediate H and Final H of Neospora?
- Inter H: eq, cow -> abortion. - Final H: dog
The development stages of Toxoplasma gondii are localized in all kind of cells of the IH except?
Erythrocytes
Final host of Toxoplasma gondii is?
- FH: Cat
- IH: mammals, birds
Gamogony of toxoplasma gondii occurs in the small intestine of?
Cat (final host)
Merogony of toxoplasma gondii occurs in?
- Final host (cats intestine).
- Sporogony: external.
Pathology of Toxoplasma?
- Enteritis,
- lymphadenopathy,
- pneumonia,
- encephalitis,
- nephritis,
- anorexia,
- weight loss,
- lethargy,
- dyspnoea,
- ocular signs.
- Trophozoits diretly destroy host cells.
- Lymph node infection, - local hypersensitivity,
- blood vessel blockage,
- abortions,
- stillbirth,
- choriotinitis,
- hydrocephalicus
SKJER IKKE AT EG HUSK ALT D HÆR!!!!
Size of oocyst of Toxoplasma?
10-12 micrometers
- 2 sporocysts
- 8 sporozoits
How are humans infected by toxoplasma gondii?
- Ingestion of sporulated oocysts,
- pseudocysts/tachyzoits or tissue cyst/bradyzoites (undercooked or raw meat),
- contaminated water,
- contact with cat feces,
- raw vegetables,
- transplacental infection,
- congenital infection,
- organ transplant
- blood transfusion
What are the differences of tachyzoites and bradyzoites of toxoplasma gondii?
Motile coccidians
Tachyzoites:
- active replicating stage,
- divide fast
- found in pseuocysts in various tissues
Bradyzoites:
- dormant stage,
- divide slower
- found in tissue cysts in myocard, CNS and skeletal muscle
Phylum of trichomonas?
parabasala
Which genera belong to the order trichomonadida?
Trichomonas and Histomonas
According to number of anterior flagella, trichomonas are divided into:
- Ditrichomonas
- Tritrichomonas
- Tetratrichomonas
- Pentatrichomonas
Who has hydrogenosomes?
trichomonas spp.
The solid axis of the trichomonad cell forms?
Axostyle
Trichomonas reproduce by?
binary fission
How many flagella has trichomonas foetus?
3 anterior, 1 (free) posterior
Tritrichomonas foetus is transmitted by?
intercourse and artificial insemination
(infected bulls = in reproductive tract)
Diagnosis of trichomoniosis?
T. Foetus in cows:
- vaginal and preputial samples
- Direct detection by microscopy
- culturing in diamonds medium (2-4 days)
- PCR.
Intravital diagnosis of bird trichomonosis is done by?
microscopy: swab of pharynx and crop mucosa
Way of transmission of tetratrichomonas gallinarum in birds?
feeding of young birds (contaminated water or food)
Location of Histomonas meleagridis?
Liver and cecum
Pathology of histomonas, What are its lesions?
- Mucopurulent typhilitis
- Purulent hepatitis
- Black head diseaseLesions:
- Perforation in cecum and liver
- Large inflamed cecum
- Yellow diarrhea
- Droopiness
What causes black head disease?
Histomonas meleagridis (in birds)
Where does histomonas reproduce?
cecal epithelium
Vector of histomonas meleagridis?
Heterakis gallinarum (roundworm - infect Birds)
Where is flagellated form of histomonas?
inside lumen and cecum
A protozoan cyst that contains four nuclei, median body and axonemes should be identified as?
Giardia duodenalis
For diagnosis of giardiosis we use what flotation solution?
Zinc sulphate (FAUST)
Giardia divides by?
binary fission
Giardia intestinalis (G. Duodenalis) is located where?
extracellularly
Giardia intestinalis/duodenalis belongs to which order?
Diplomonadida
Location of giardia in the host?
Attached to intestinal villi of small intestine
Pathology of Giardia?
Epithelial damage when trophozoite attaches to intestinal villi:
- Shortening of villi
- inflammation of crypts and lamina propria
- Lesions of mucosal cells
- Malabsorption
- enzyme deficiencies
2 forms of Giardia:
Trophozoites:
- vegetative stage
- pear shaped
- jejunum
- adhesive disc
Cyst:
- infective stage
- 4 nuclei
- 8-14 micrometer
- feces

Way of transmittion of giardia?
Contaminated water or food
Identification method of Giardia intestinalis?
- Flotation method with FAUST (cysts)
- Detection of coproantigen by rapid tests, ELISA, PCR
How many free flagellae has Tritrichomonas foetus?
3
Diagnosis of Sarcocytosis in Inter H
Digestive method
Final host of G. Ardeae
Bird
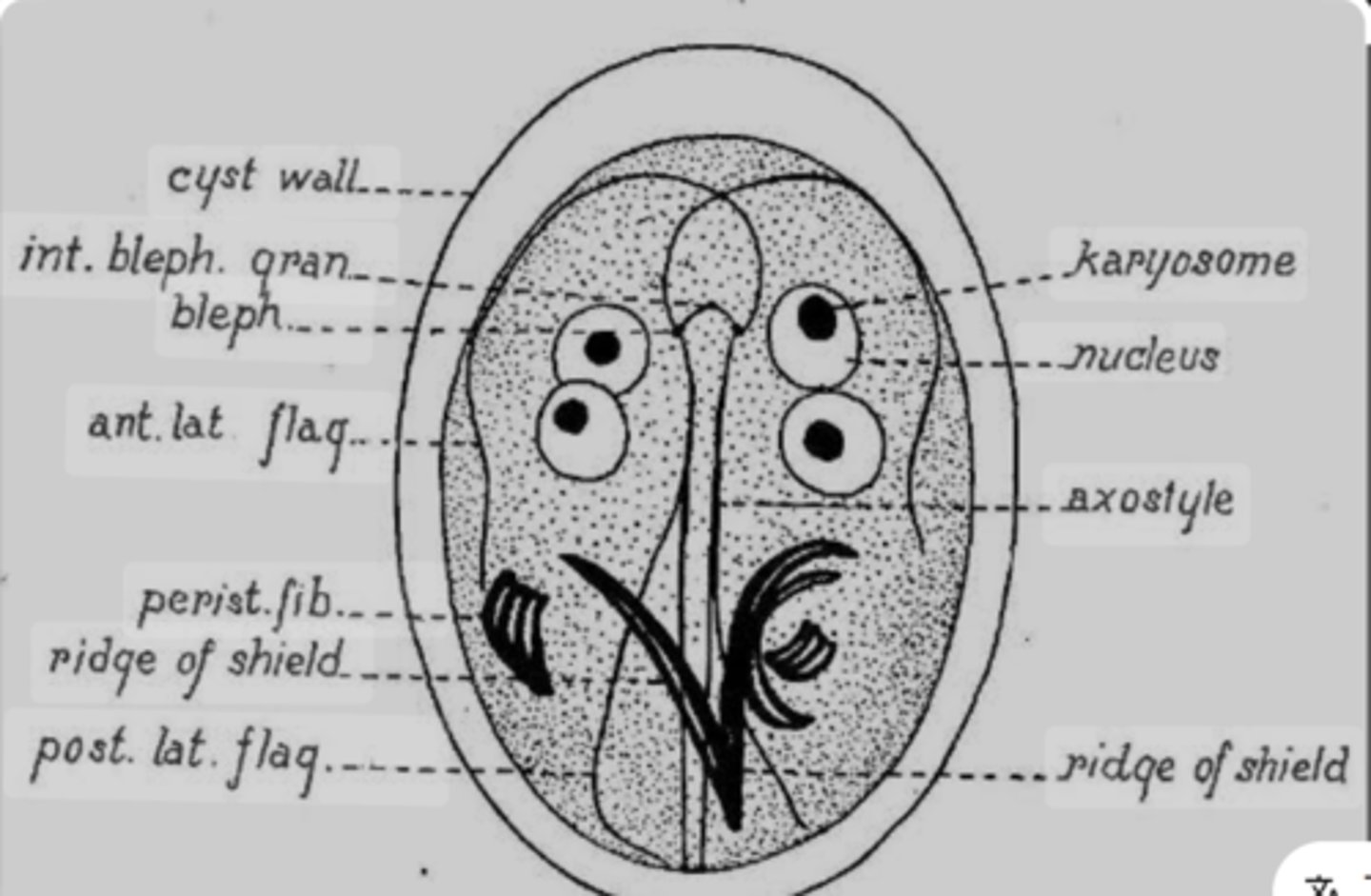
Picture, name and describe
Giardia cyst:
- Oval
- 4 nuclei
- 8-14 micrometer
- Feces
- thick, smooth wall
- Color: light brown/greenish (iodine or trichrome stains)
Picture, Name and describe
Sarcocystis - Musculocyst:
- in muscle of intermediate host
- 5-10 micrometers
- typical apicomplexa organelles are present
- Infective stage: definite host is infected by eating