Excretion, osmoregulation, and temperature regulation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
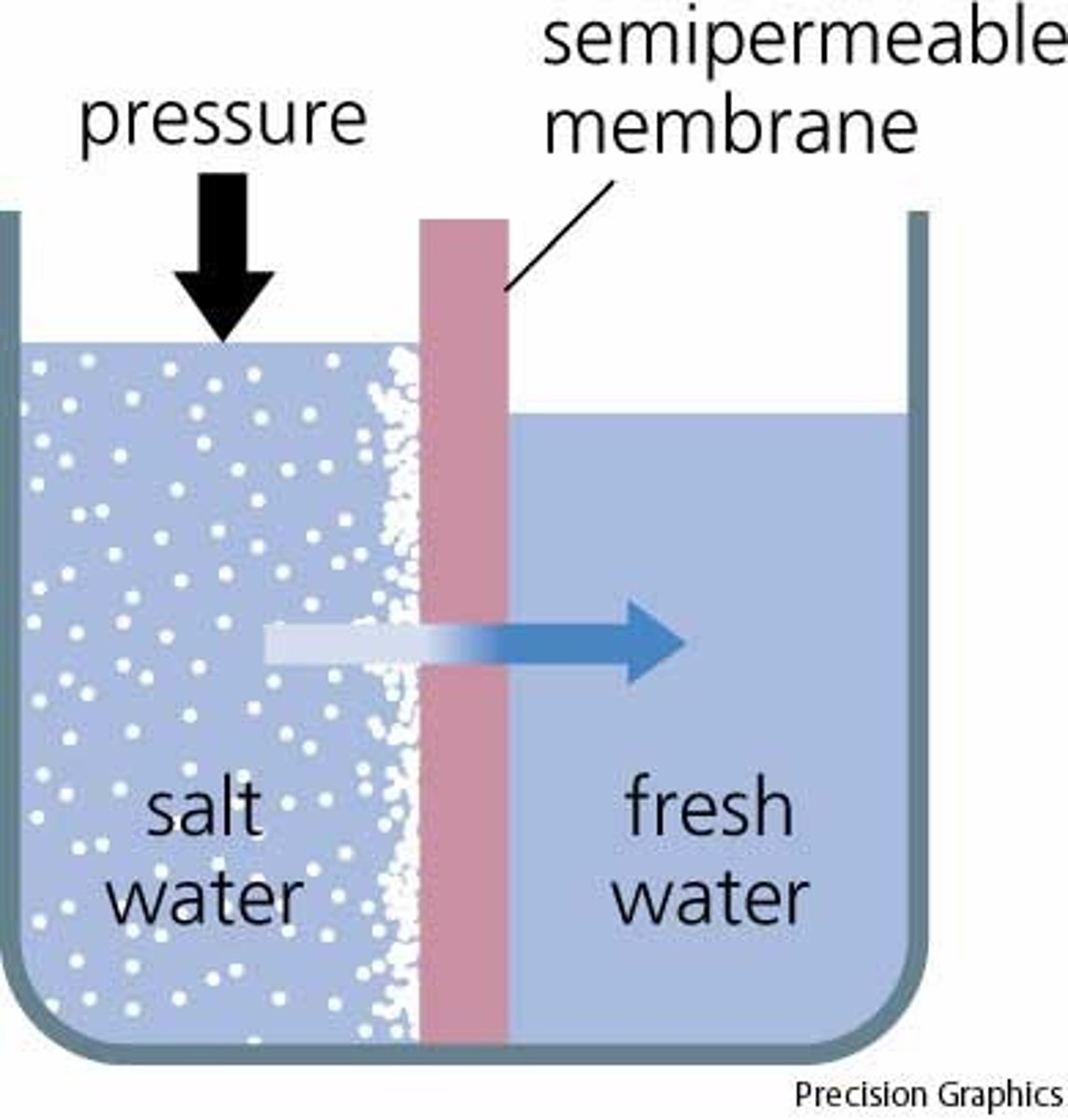
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
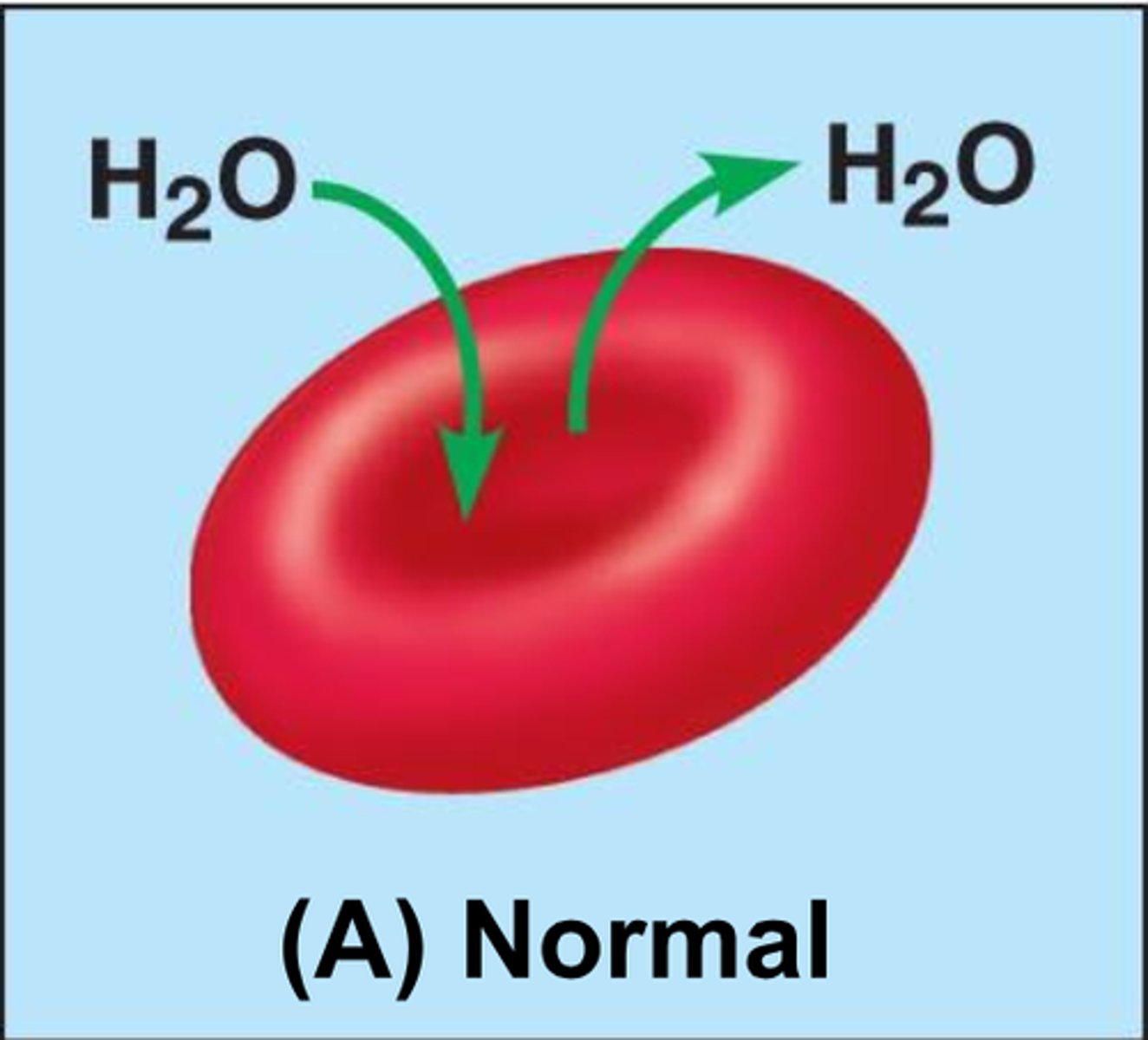
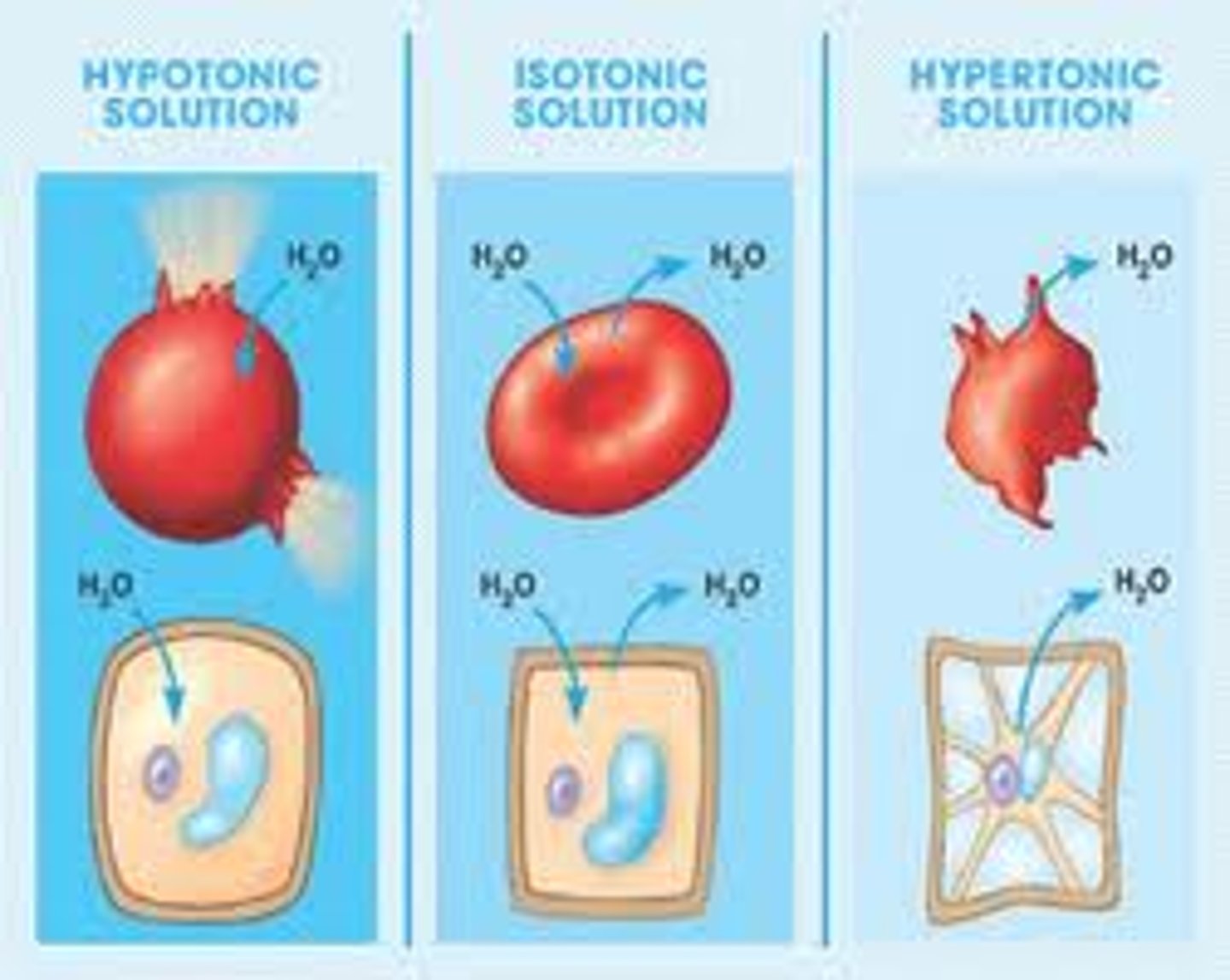
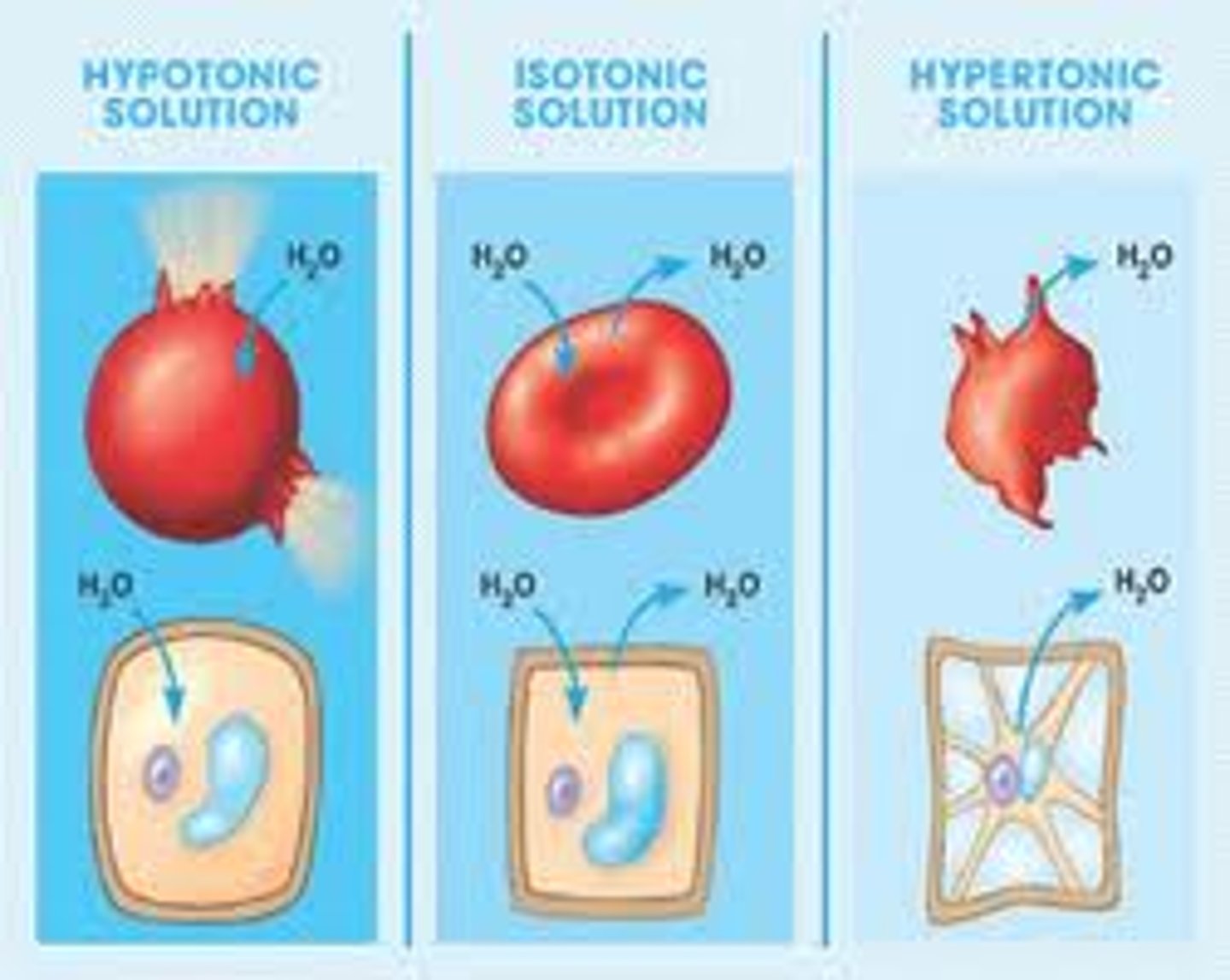
Isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
-eg cytoplasm
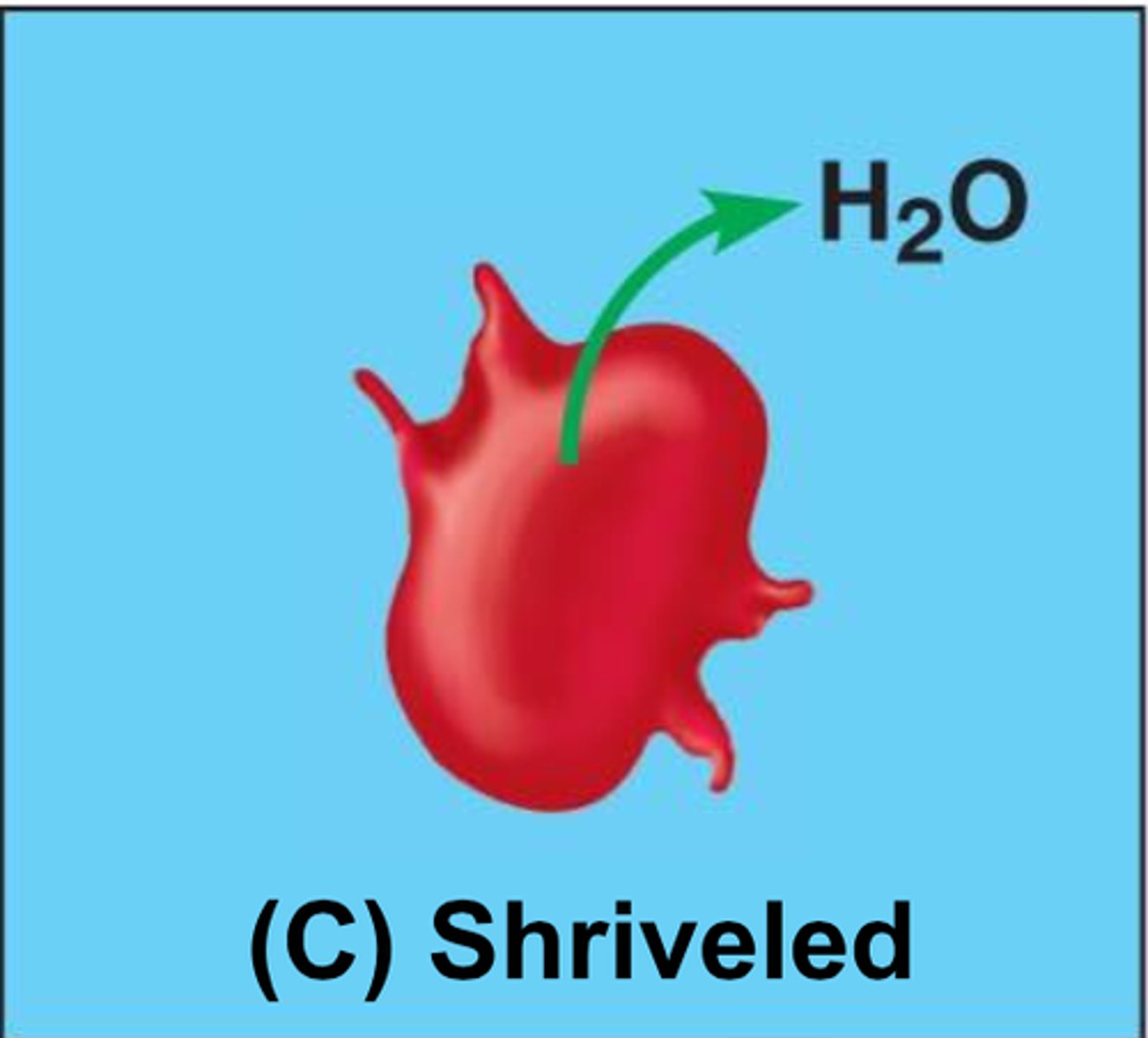
Hypertonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is GREATER than that of the cell that resides in the solution
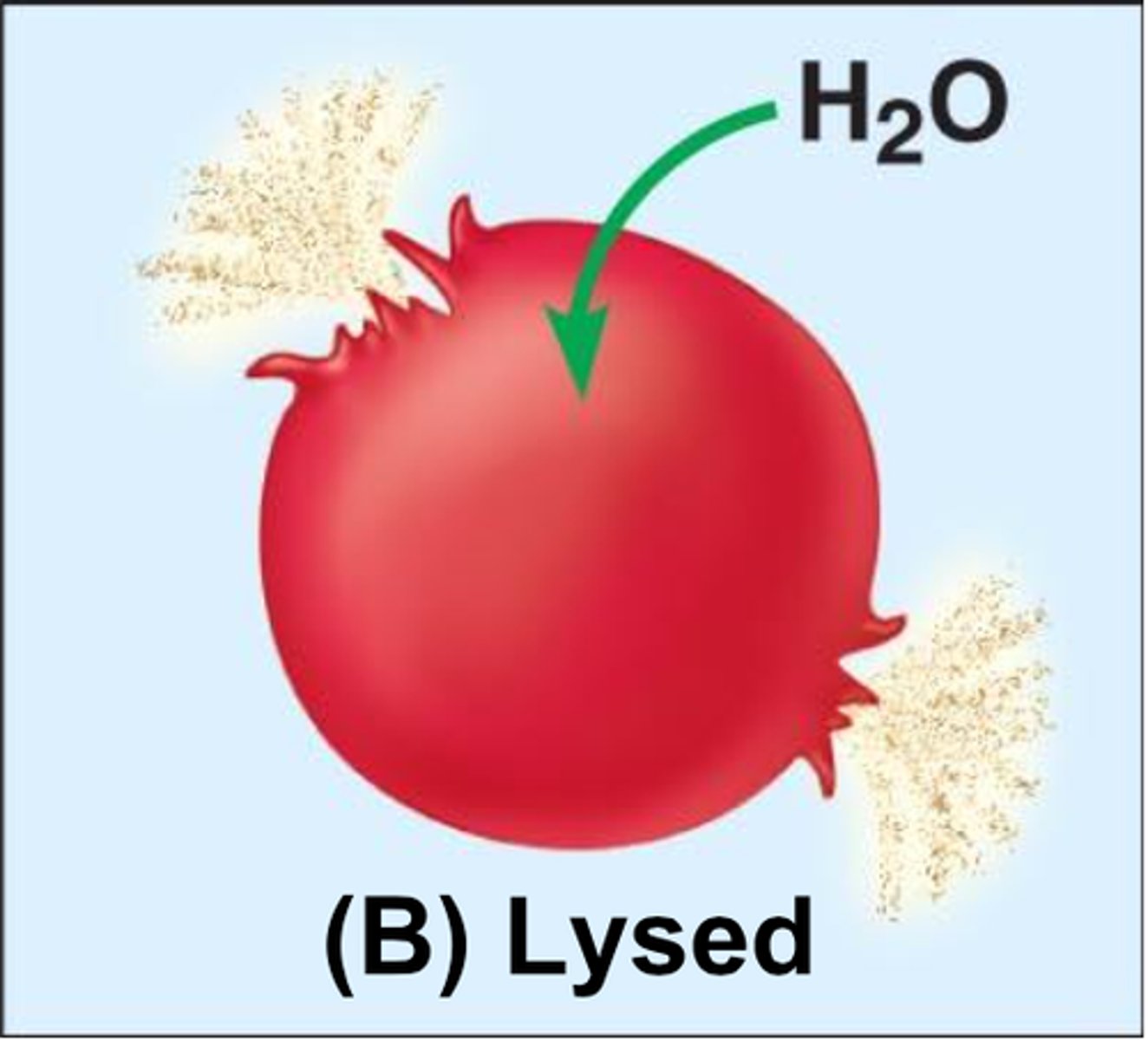
Hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is LESS than that of the cell that resides in the solution
Osmoregulation
balance of salt and water in the body
Isosmotic
animals at same total solute concentration as surroundings
hypoosmotic
animal at lower concentration than surroundings
hyperosmostic
animal at higher concentration than surroundings
Osmoconformers
An organism that allows its internal salt concentration to change with the salinity of the surrounding water
stenohaline
animals that cannot tolerate substantial changes in external osmolarity
Euryhaline
animals that can survive large fluctuations in external osmolarity
Hyperosmotic regulator
an aquatic animal that maintains a blood osmotic pressure higher than the osmotic pressure of the water in which it lives
Osteichthyans
bony fish
Chondrichthyans
sharks and rays
-retain urea in blood to raise osmolarity
-isosmotic
Urea
major nitrogenous waste excreted in urine
How is water gained?
it is gained by drinking and eating
How is water lost?
is it lost by evaporation, excretion of wastes
How is water conserved?
is it conserved by concentrated urine and behavioural strategies
ammonia
nitrogenous waste is excreted in the form of ammonia and takes a large amount of water
Uric acid
nitrogenous waste produced by insects, birds, and reptiles
-non-soluable and non toxic
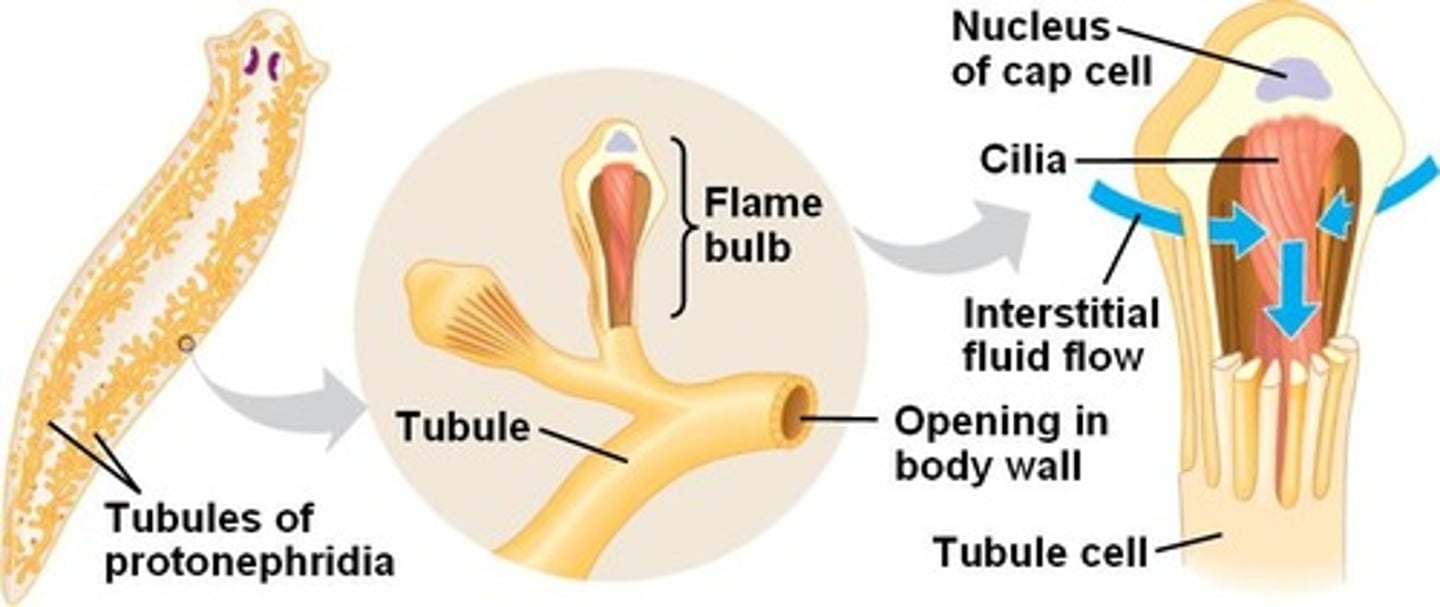
What is the simplest excretory system?
Protonephridia (in flatworms) is the simplest system
Protonephridia
Excretory system consisting of flame cell bundles that remove waste and where diffusion occurs
-present in flatworms
metanephridia
Excretory system of body segments carrying nephridia that manage waste and materials
-present in earhtworms
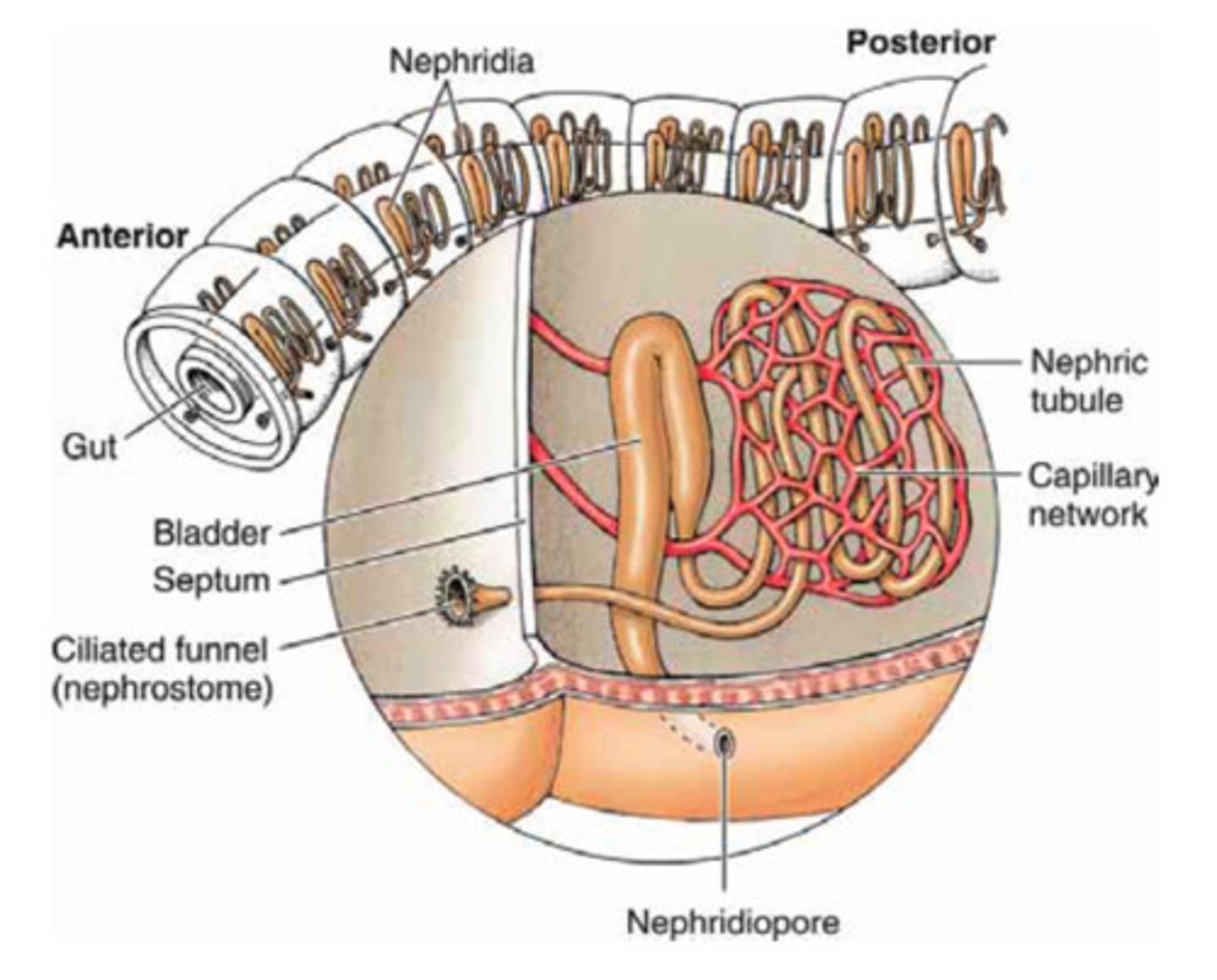
Nephridia
organs that remove metabolic waste inside metanephridia
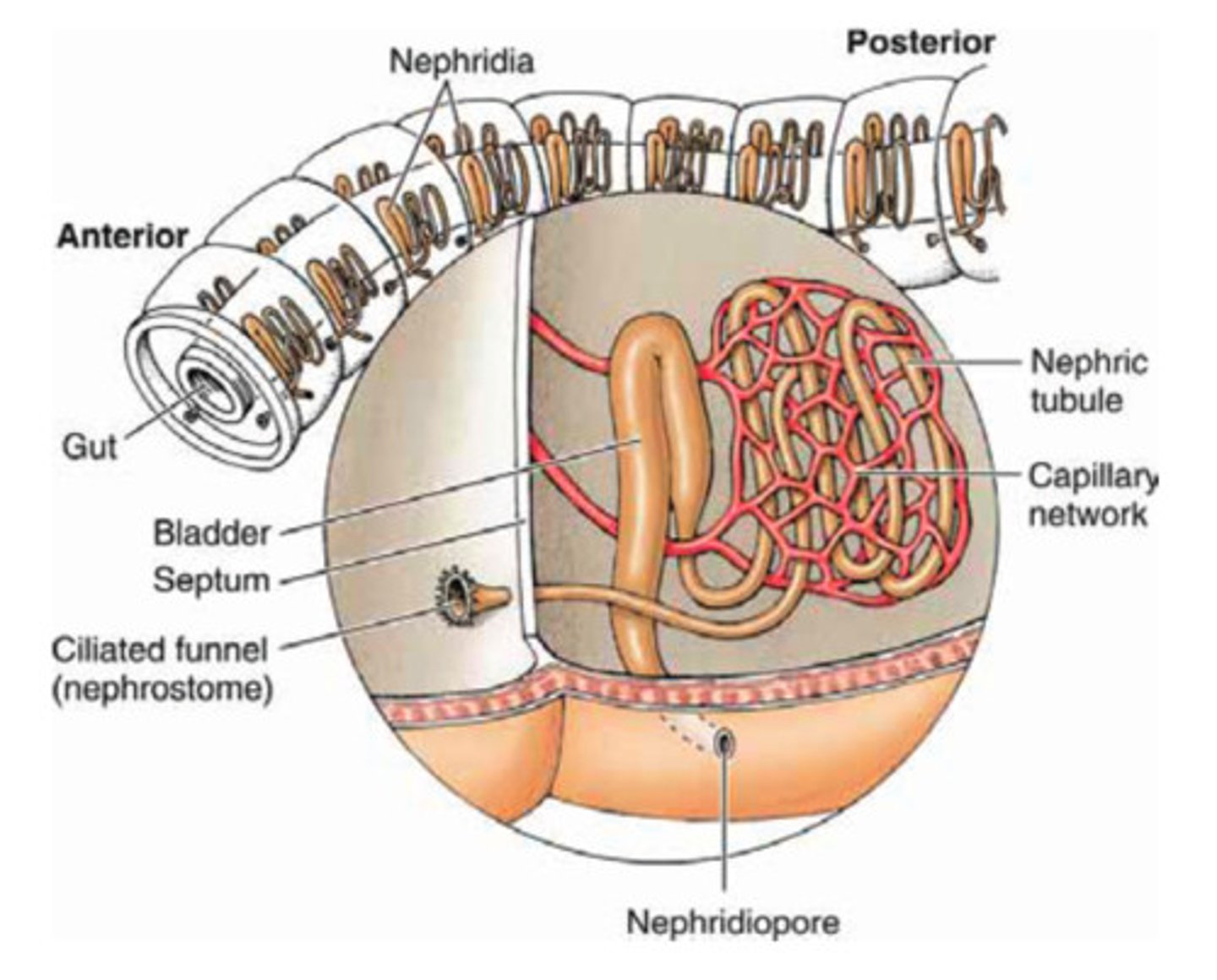
what are Antennal glands?
paired excretory organ crucial for osmoregulation (maintaining fluid balance) and nitrogenous waste elimination located in the head of crustations
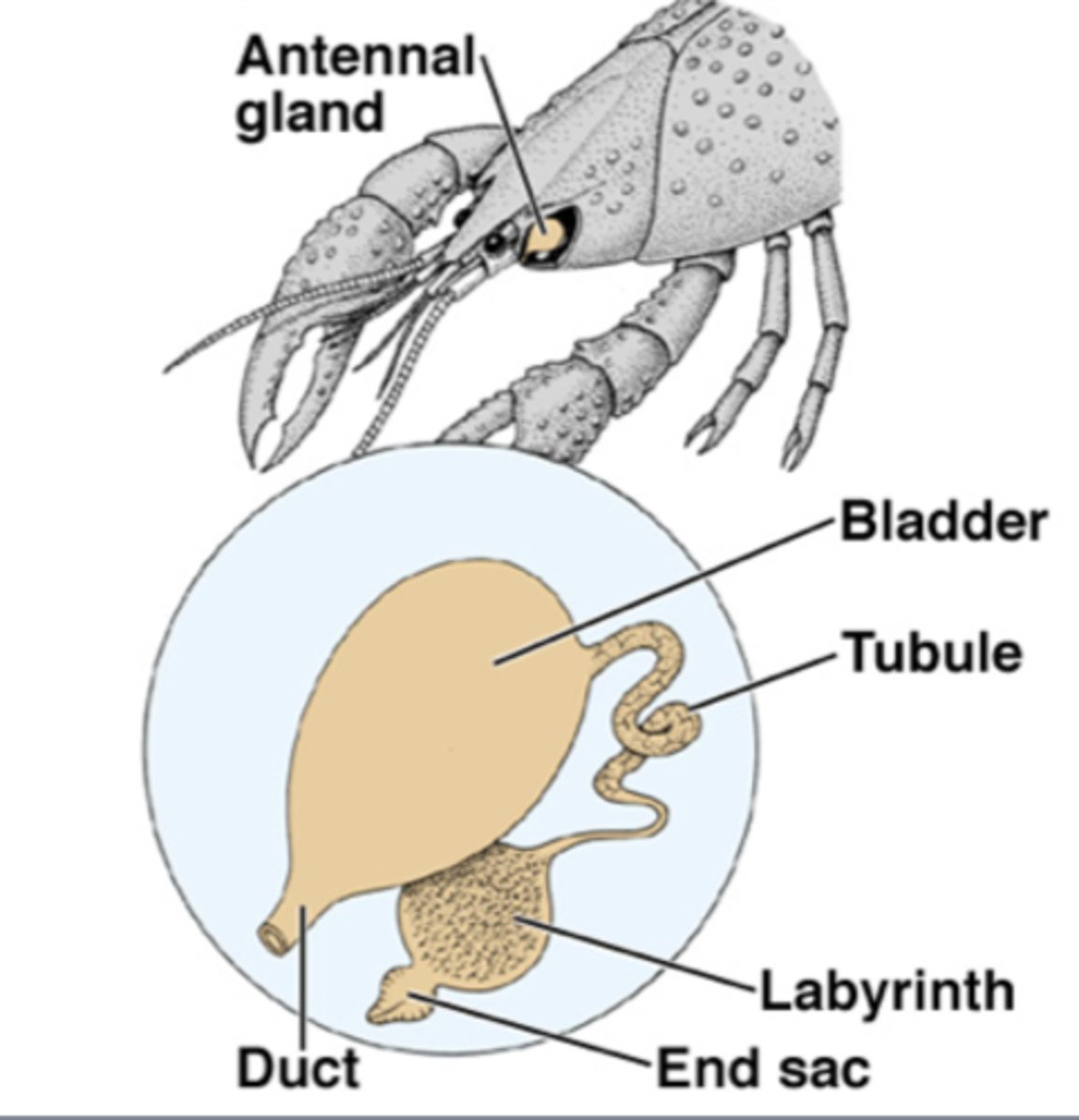
Malpighian tubules
Excretory system of insects that excrete metabolic wastes into the hindgut and are responsible for osmoregulation. Surround the gut
glomerular filtration (bowman's capsule)
1st step of urine formation, where blood plasma is filtered through the glomerulus, a network of capillaries within the kidney, to remove waste products, excess water, and other substances
-Kidney uses osmolarity to make excretion more efficient
-Osmolarity of kidney affects rate of dissolved solutes (eg middle of kidney higher dissolved solutes)
-Osmotic pressure increases the closer to the center of kidney
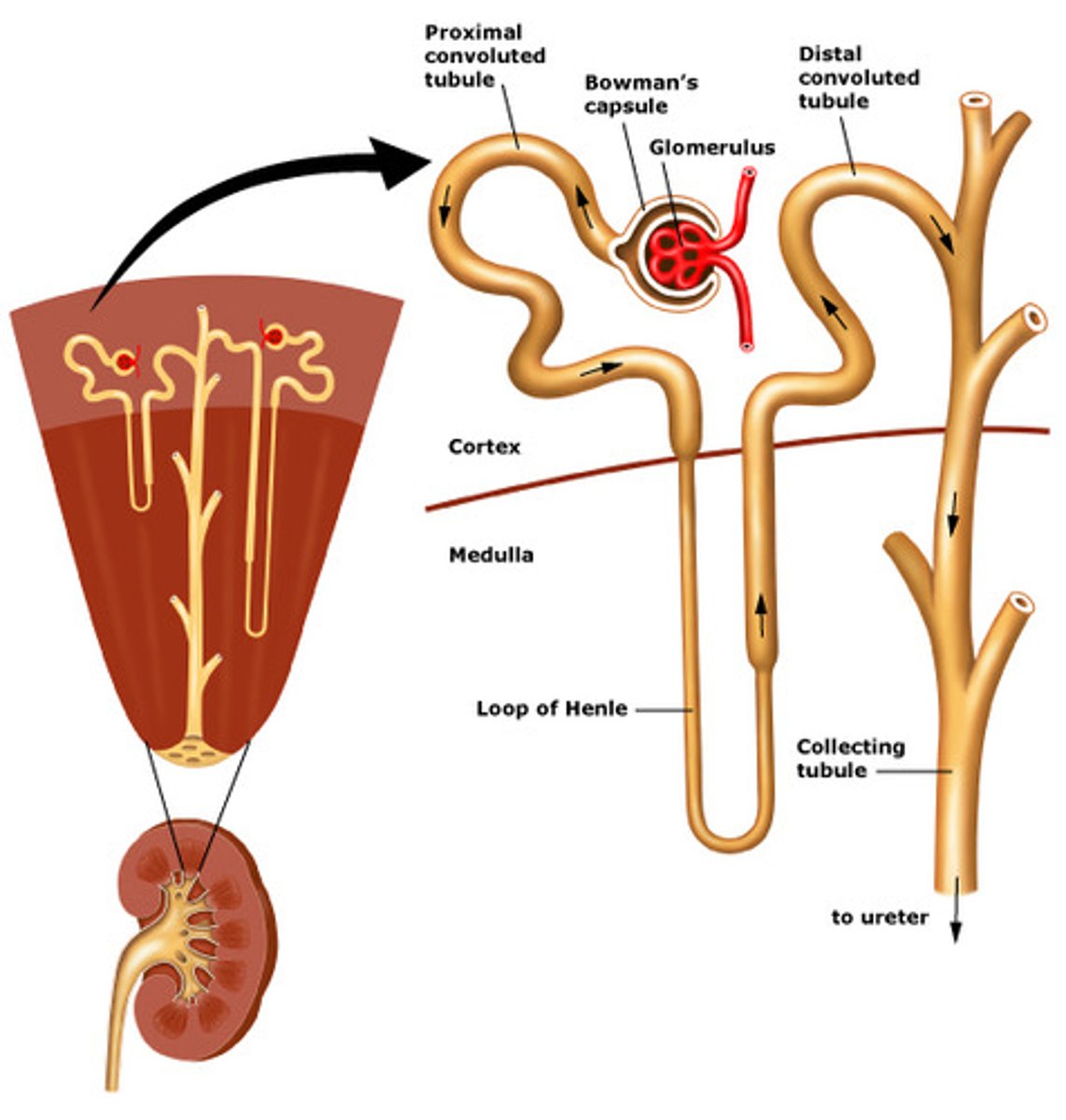
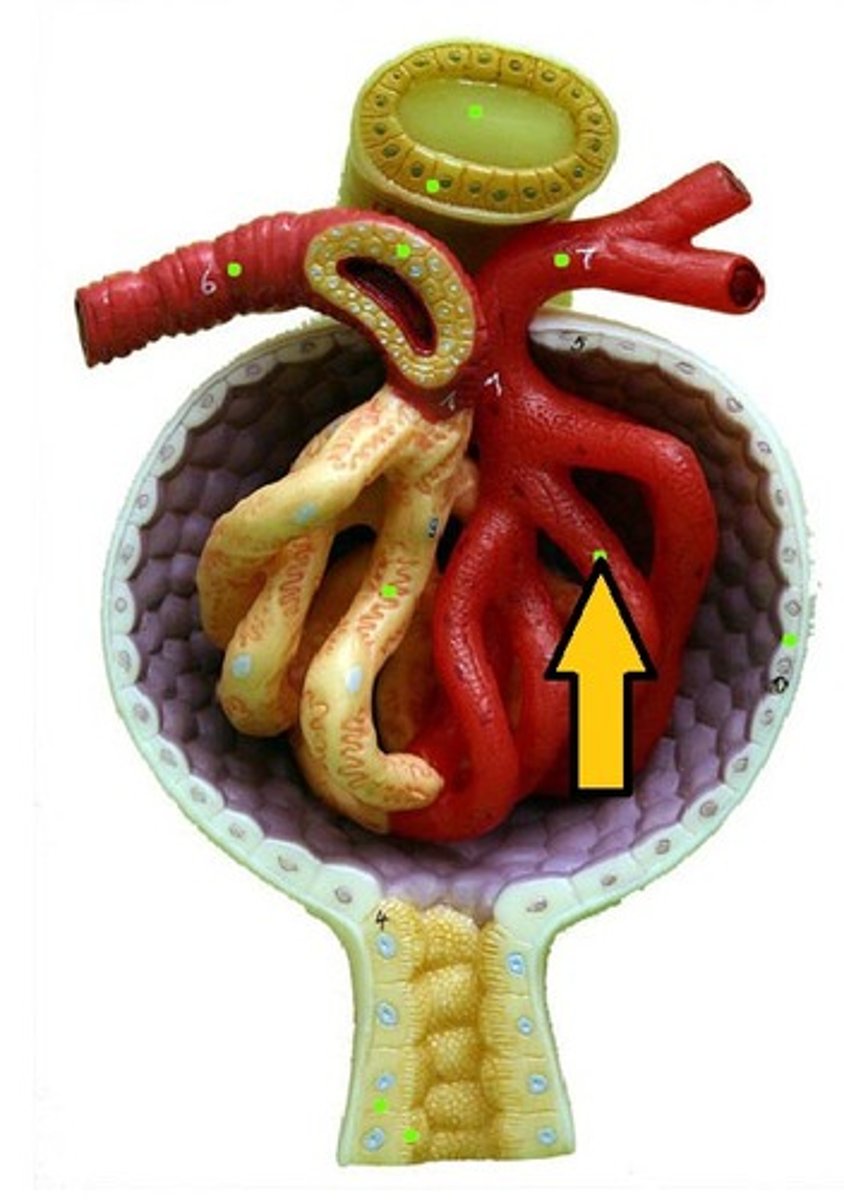
Glomerulus
A ball of capillaries surrounded by Bowman's capsule that are responsible for the selective ultrafiltration of plasma and the clearance of small solutes
tubular reabsorption
process of reclaiming water and solutes from the tubular fluid and returning them to the blood
retains:
-amino acids
-glucose
-ions
-water
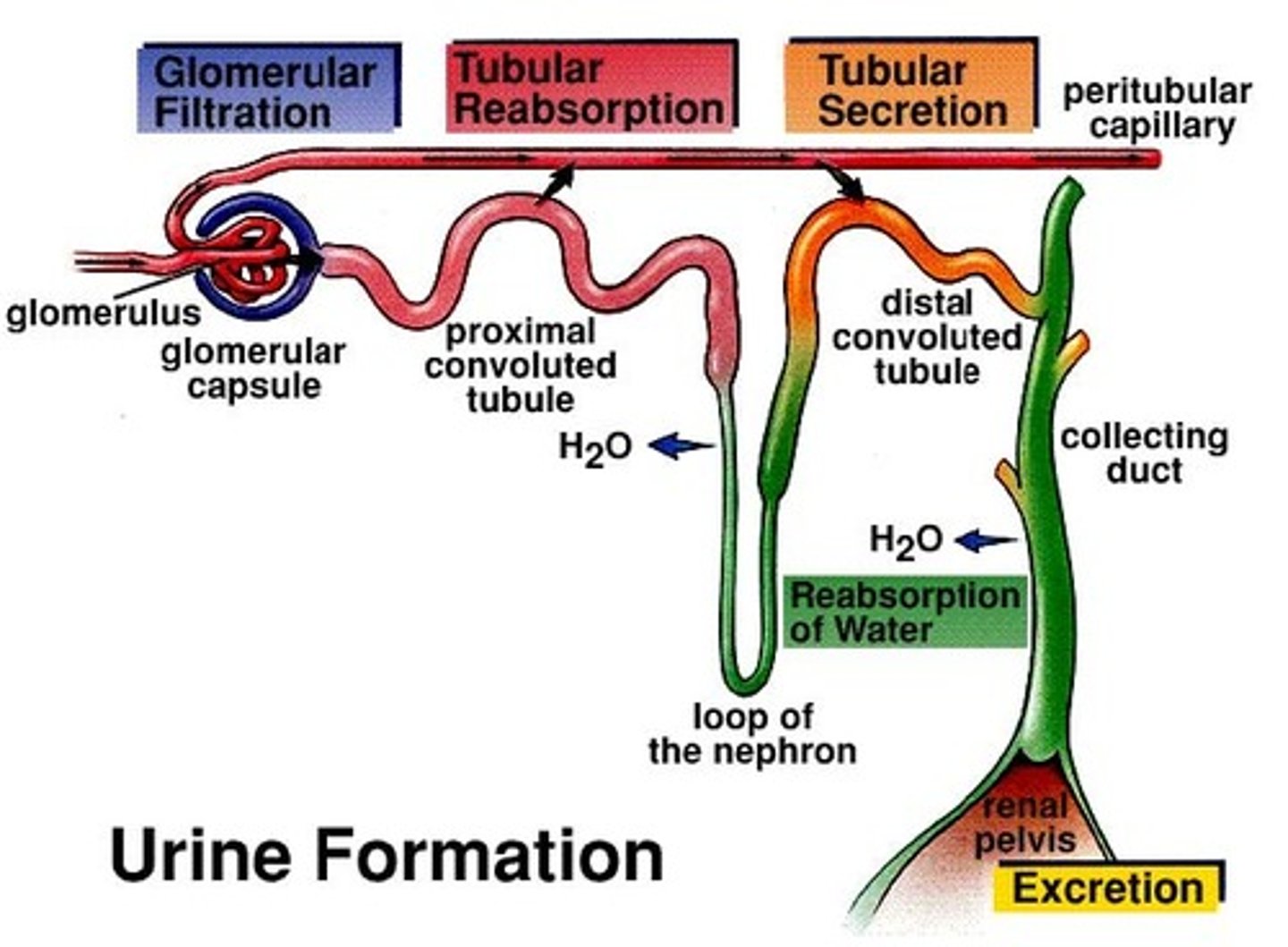
Tubular secretion
substances are moved from the peritubular capillaries into the renal tubular lumen
-ions are moved
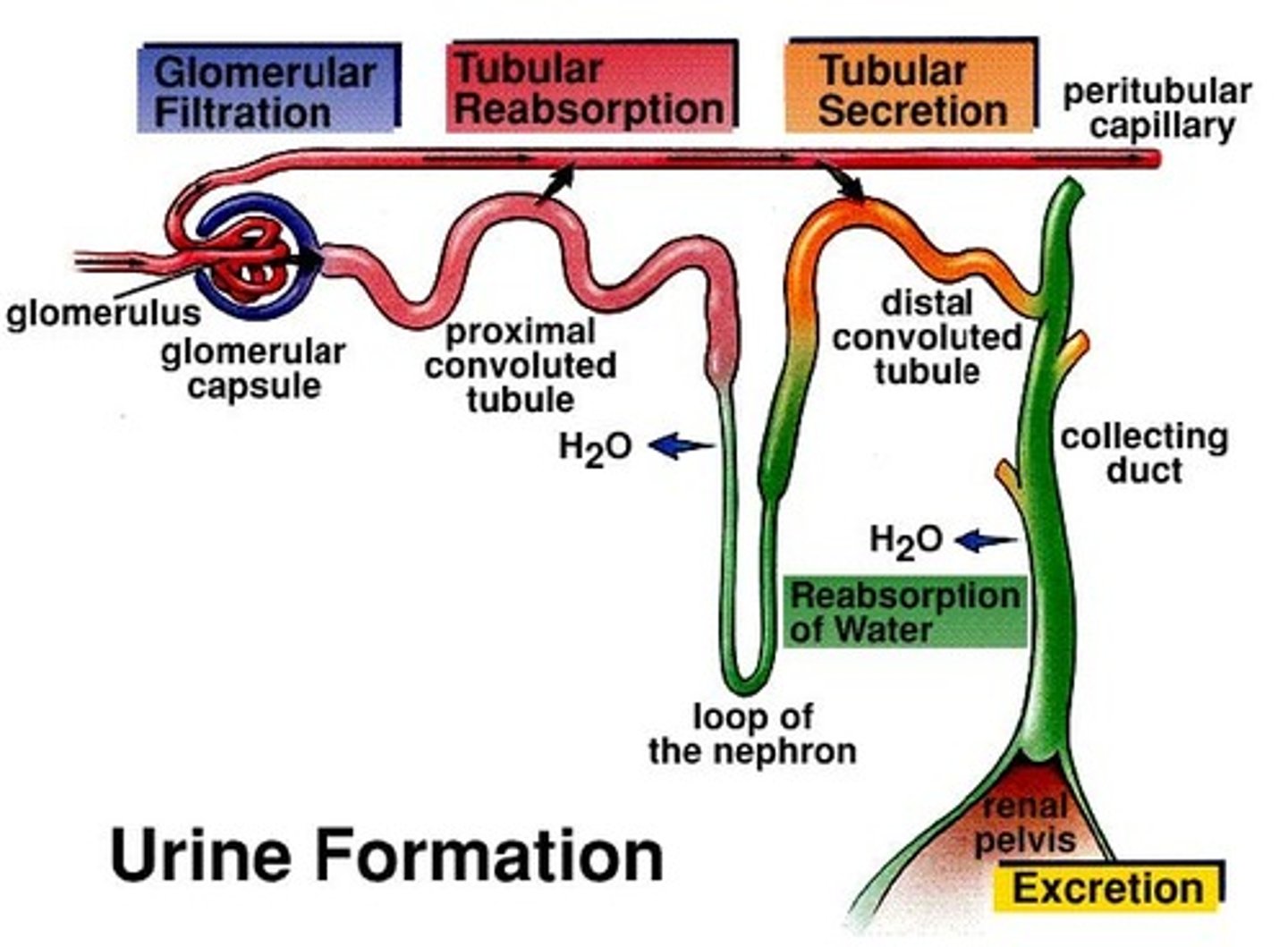
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
hormone that controls permeability of collecting duct to water
-inhibited by alcohol
Endotherm
metabolism generates heat to maintain a stable body temperature
Ectotherm
Organism's body temperature is dependent on environmental factors