Cardiac Contractility
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
P2 - p.68-70; p.48-49
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
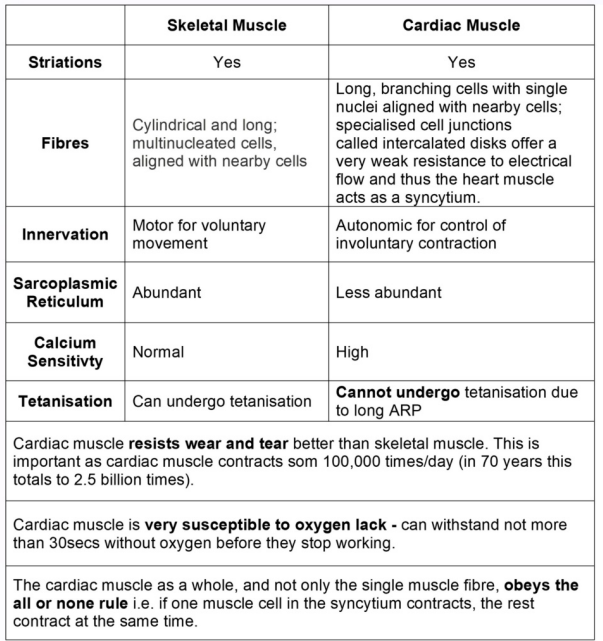
Skeletal vs Cardiac Muscle (photo)
no relaxation → no pumping
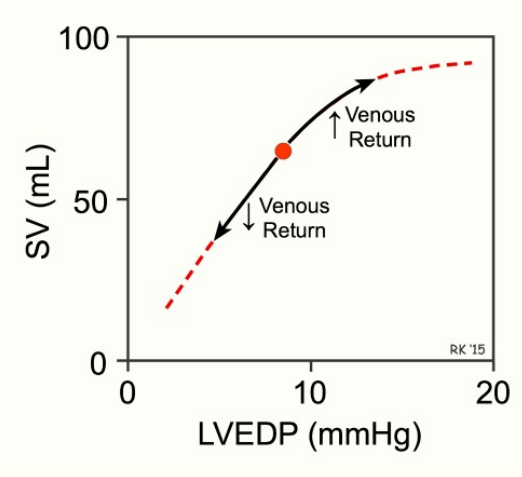
Frank-Starling law (4)
Strength of cardiac contraction is proportional to the initial length of cardiac muscle fibers
Increased blood volume at the end of diastole stretches the heart muscle → stronger systolic contraction
More blood entering the heart during diastole results in a stronger contraction during systole
photo: blood returning from veins - resp. system plays a roll in it
Cardiac T tubules (6)
5x larger diameter
25x larger volume
larger quantities of Ca2+
contain mucopolysaccharide
opens up to extracellular space
compared to skeletal muscle’s T tubules
Cardiac muscle contraction depends on what? (2)
Ca2+ stored in T tubules
Extracellular Ca2+
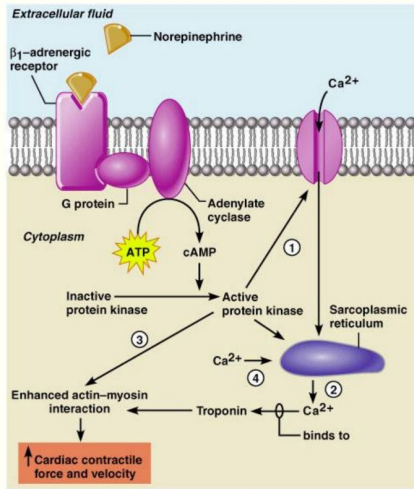
Sympathetic stimulation to the heart tissues (4)
Increases the strength of myocardial contraction
Phosphorylation of calcium channels lengthens their opening time
Increases calcium concentration in the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR)
Enhances actin-myosin interaction via kinase activation
Effect of Parasympathetic stimulation on Cardiac Contractility (2)
Affects mostly the atria, sparing the ventricles
Opposes the action of the sympathetic system
Inorganic ions in cardiac function (3)
Potassium (K)
Sodium (Na)
Calcium (Ca)
Potassium (K) - Inorganic ions (3)
Hypokalemia is most commonly a complication of diuretic therapy
Moderate hypokalemia increases contractility by higher depolarization and more Ca²⁺ influx
Severe hypokalemia causes heart rhythm problems and decreases effective contractility
Sodium (Na) - Inorganic ions (2)
Hyperkalemia causes smaller depolarization and less calcium influx, decreasing contractility
High sodium concentration depresses contractility by inhibiting calcium entry into mitochondria, lowering ATP availability
Calcium (Ca) - Inorganic ions (3)
Mild increase results in an increase in contractility
High increase can cause the heart to stop in systole
Very low calcium can cause the heart to stop in diastole
Hypoxia (2)
↓ oxygen supply, weakening contraction
↓ metabolism
pH in cardiac (4)
Acidosis inhibits myofibrillar responsiveness to Ca²⁺ by decreasing contractile protein sensitivity
by reducing Ca²⁺ binding to troponin C
Alkalosis can weaken contractility
by reducing available ionized calcium
Positive inotropic drugs (6)
Epinephrine (Adrenalin) and Norepinephrine (Noradrenalin) mimic the sympathetic system
Dopamine and Dobutamine stimulate beta receptors
Levosimendan sensitizes troponin C to calcium
Milrinone increases intracellular ionized calcium
Digoxin binds to and inhibits the sodium-potassium pump
increasing intracellular sodium and calcium content
Negative inotropic drugs (3)
Acetylcholine mimics the parasympathetic system
Beta blockers block the sympathetic system
Barbiturates decrease inward flow current during depolarization