Immunology Lecture 19: Activation of T lymphocytes
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
Central Tolerance (Negative Selection) develops in the _____________________________ and is the process that ___________ or _________ developing lymphocytes whose antigen receptors bind strongly to __________
- primary (central) lymphoid organs
- eliminates or alters
- self antigens
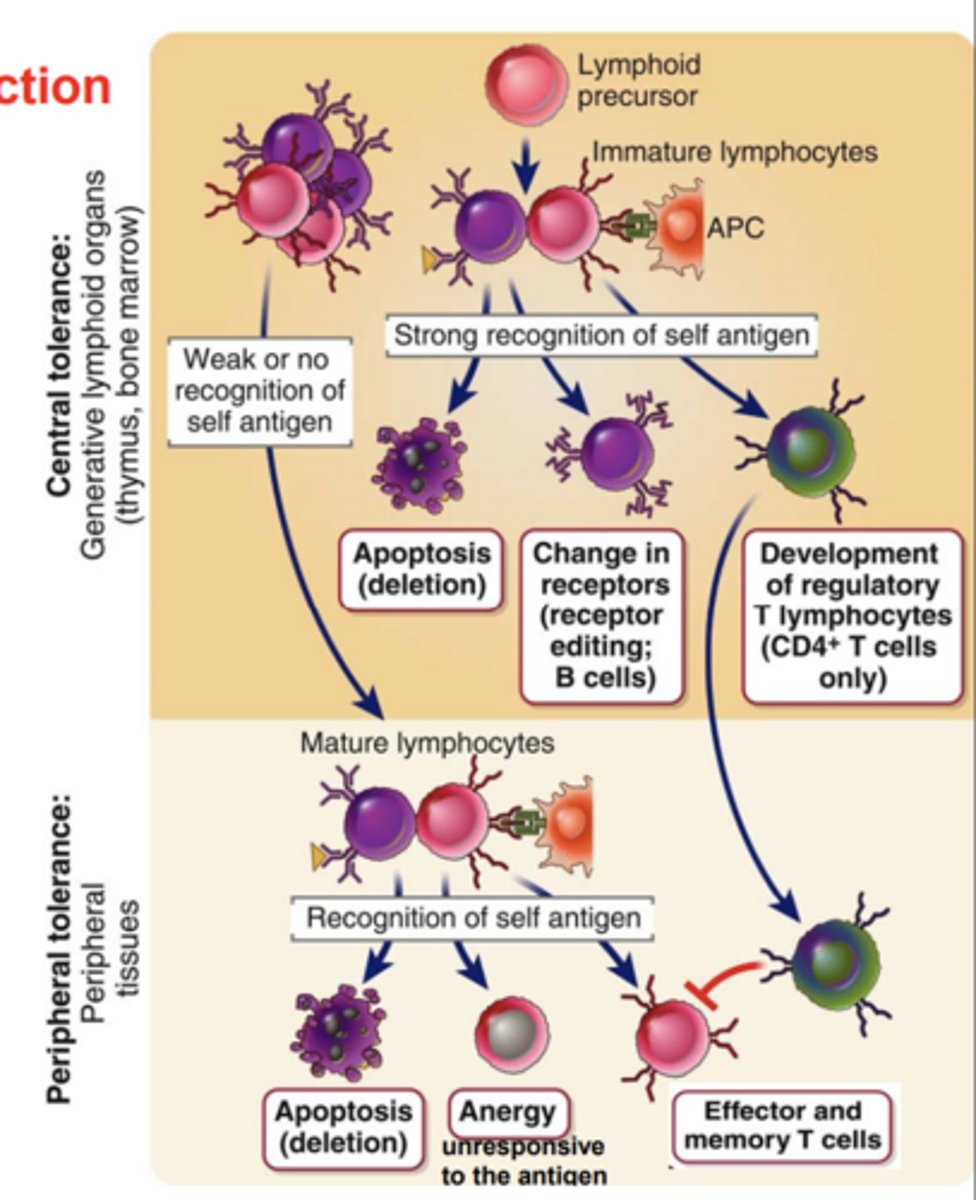
Developing T cells with a high affinity for self antigens are eliminated by....
apoptosis (colonel deletion) or form regulatory T cells (Tregs)
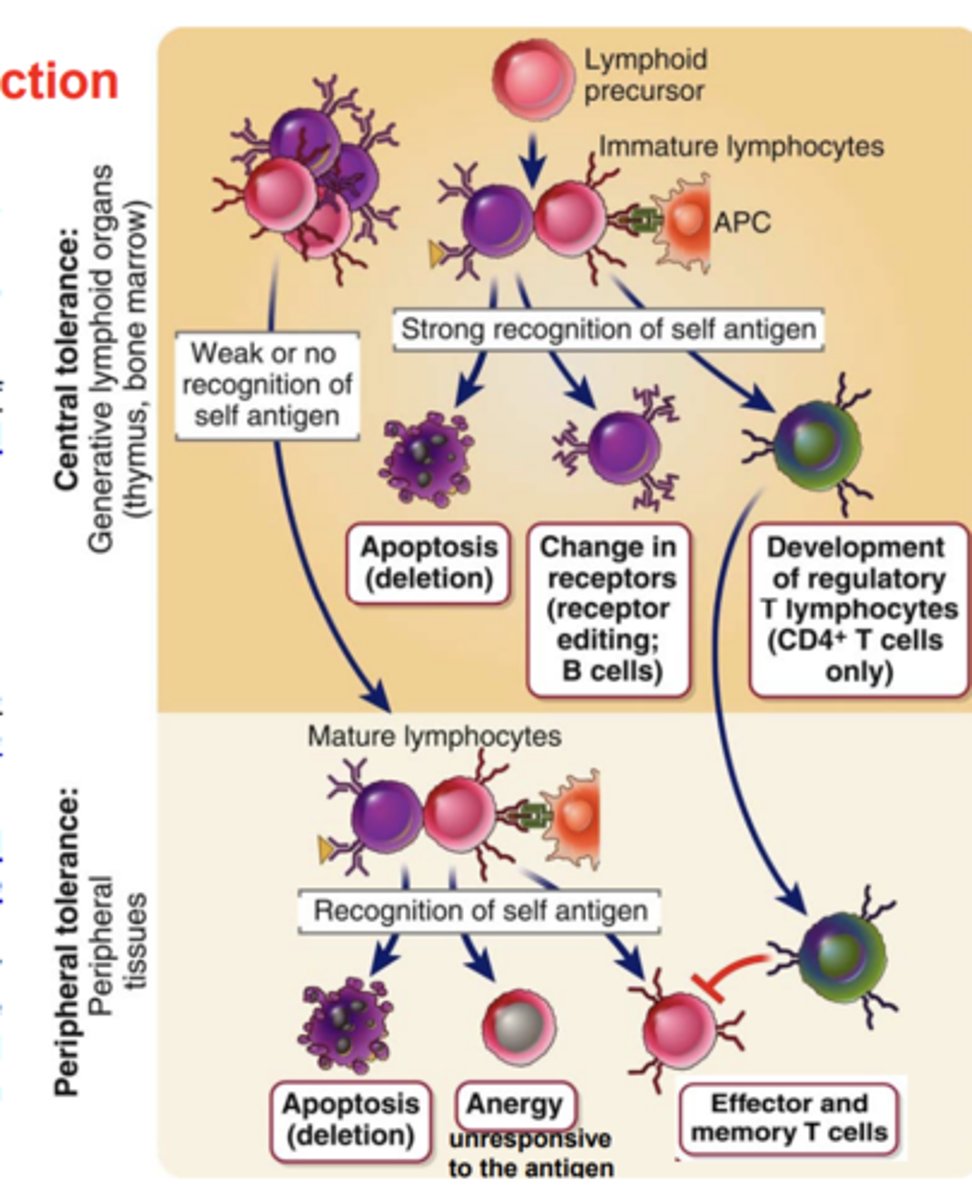
Peripheral tolerance (Positive selection) takes place in....
peripheral tissues.
In the T cell lineage, what does positive selection ensure?
ensures the maturation of T cells whose receptors recognize self MHC molecules
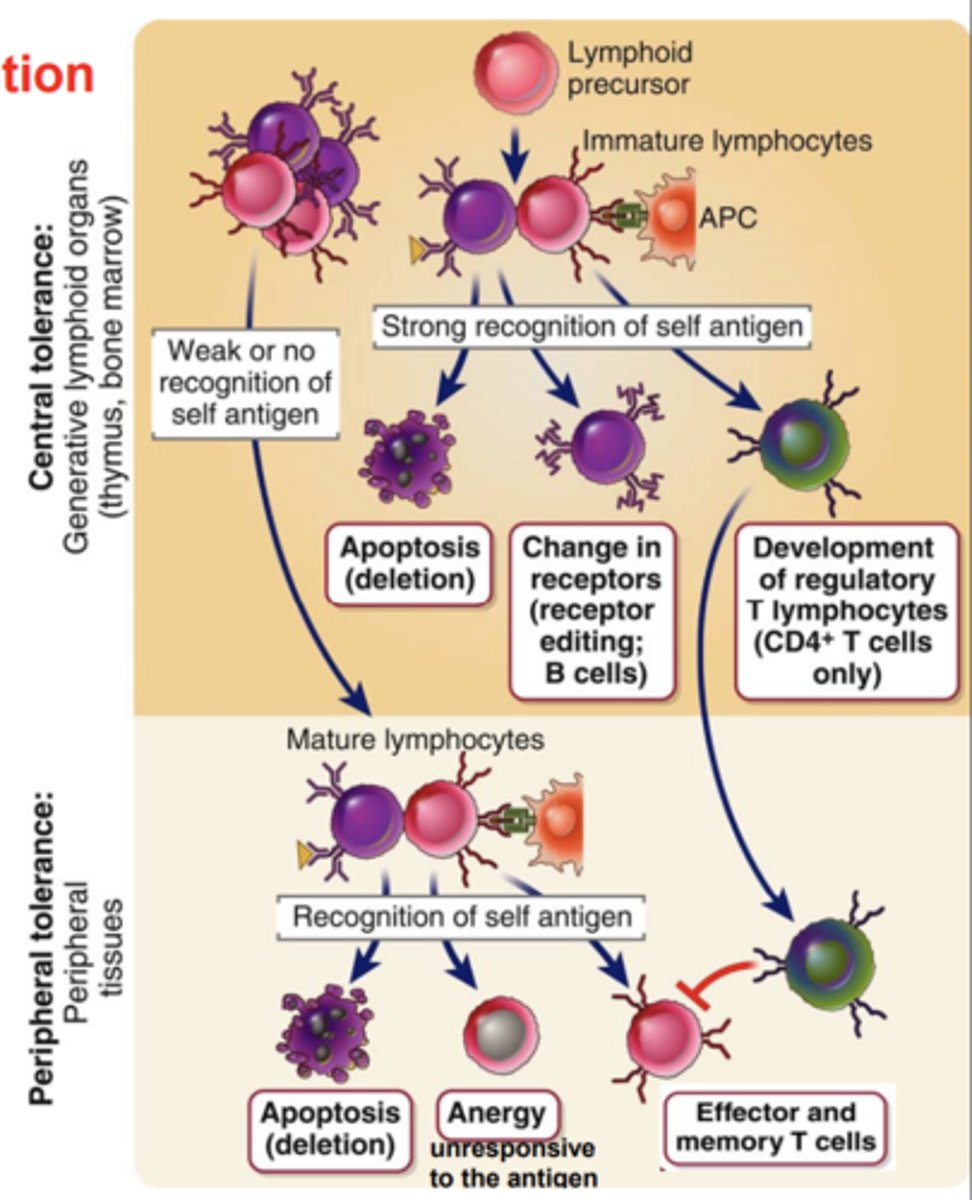
The expression of the coreceptor on a T cell (CD8 or CD4) is matched to the recognition of...
the appropriate type of MHC molecule (class I or II)
Mature T cells whose precursors were positively selected by self MHC molecules in the ________ are able to recognize____________________________ displayed by the same self MHC molecules on APCs in ____________________
- thymus
- foreign peptide antigens
- peripheral tissues
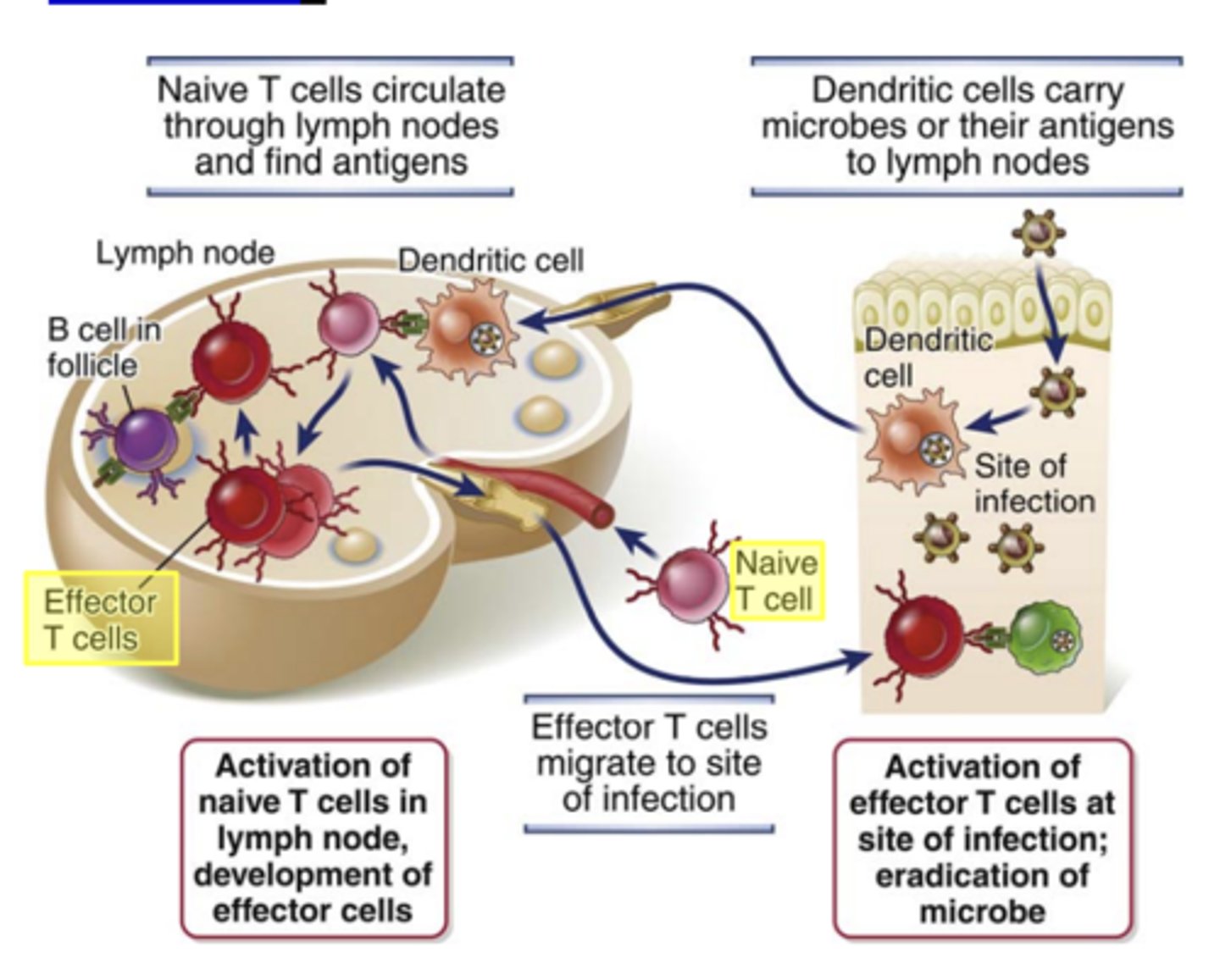
The initial activation of naive T lymphocytes occurs mainly in ___________________________, through which these cells normally circulate and where _________________ are concentrated and presented by ________________
- secondary lymphoid organs (nodes, spleen, and mucosal lymphoid tissues)
- foreign antigens
- mature DCs
T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Stem cell stage****
- C-KIT+
- CD44+
- CD25-

T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Pro-T stage****
- C-KIT+
- CD44+
- CD25+

T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Pre-T stage
- C-KIT+
- CD44-
- CD25+

T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of Double Positive stage***
- CD4+, CD8+
- TCR/CD3lo
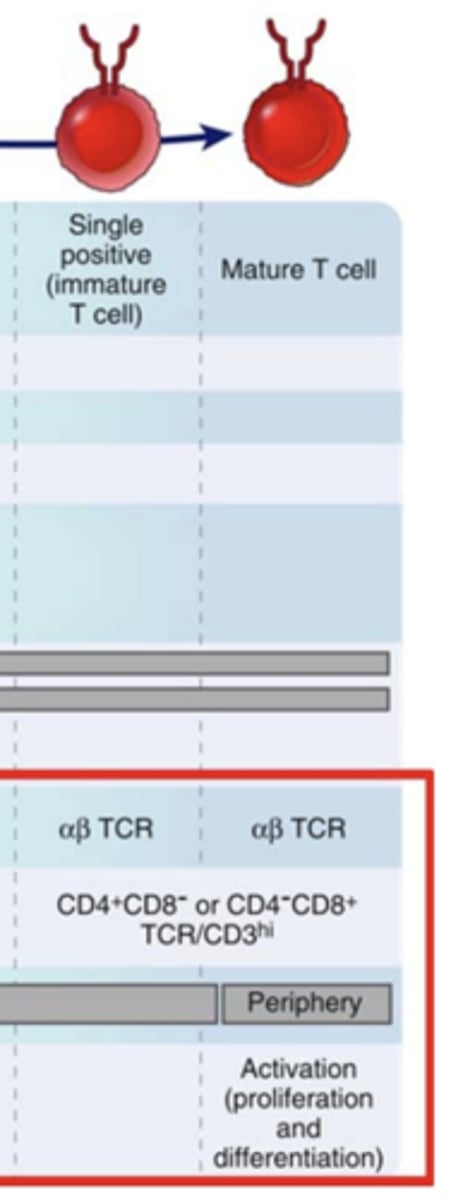
T lymphocyte development: Surface markers of stages Single positive (immature T cell) and Mature T cell
- CD4+, CD8- OR CD4-, CD8+
- TCR/CD3hi

CD3 = ?***
(how do you calculate?)
CD3= CD4 + CD8 ****

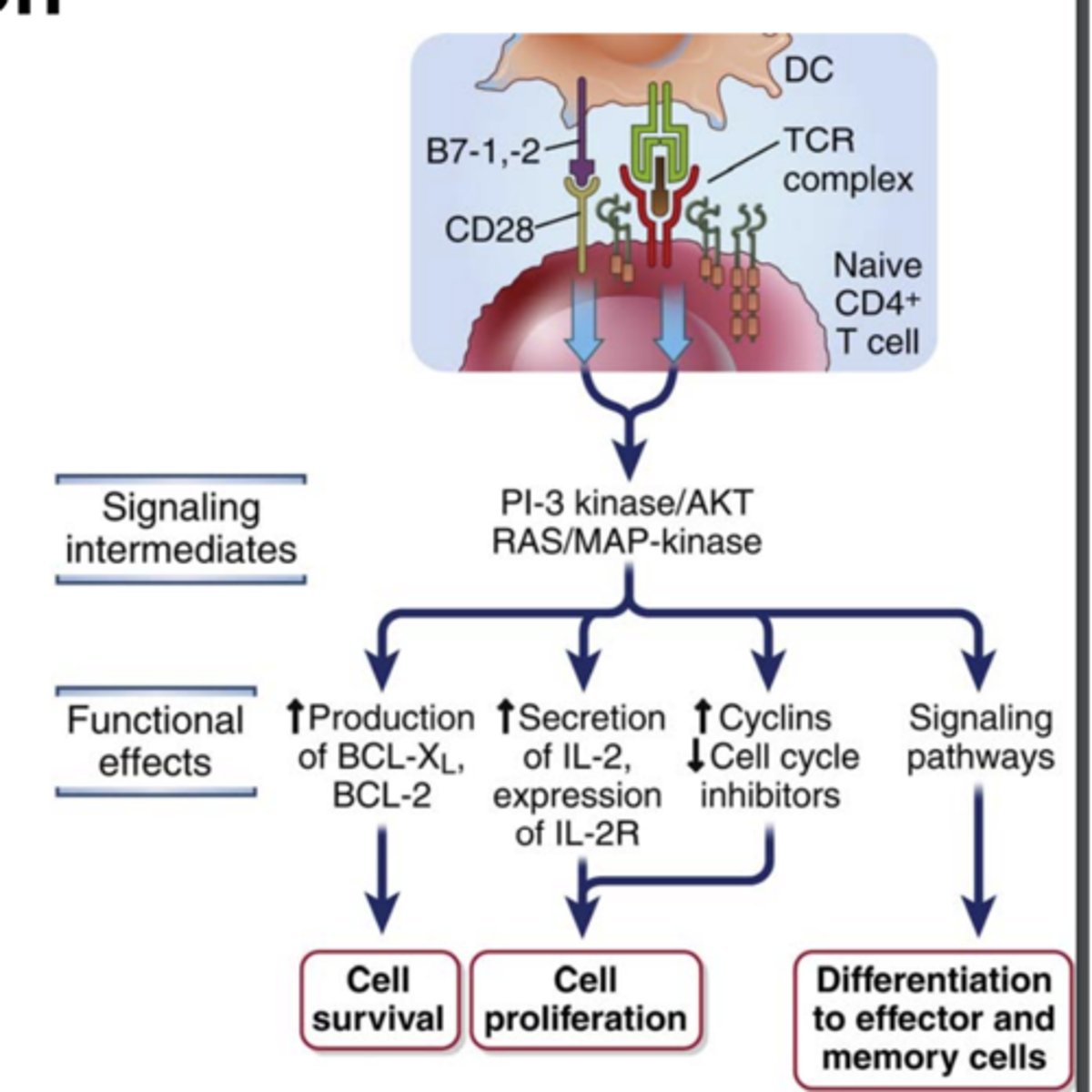
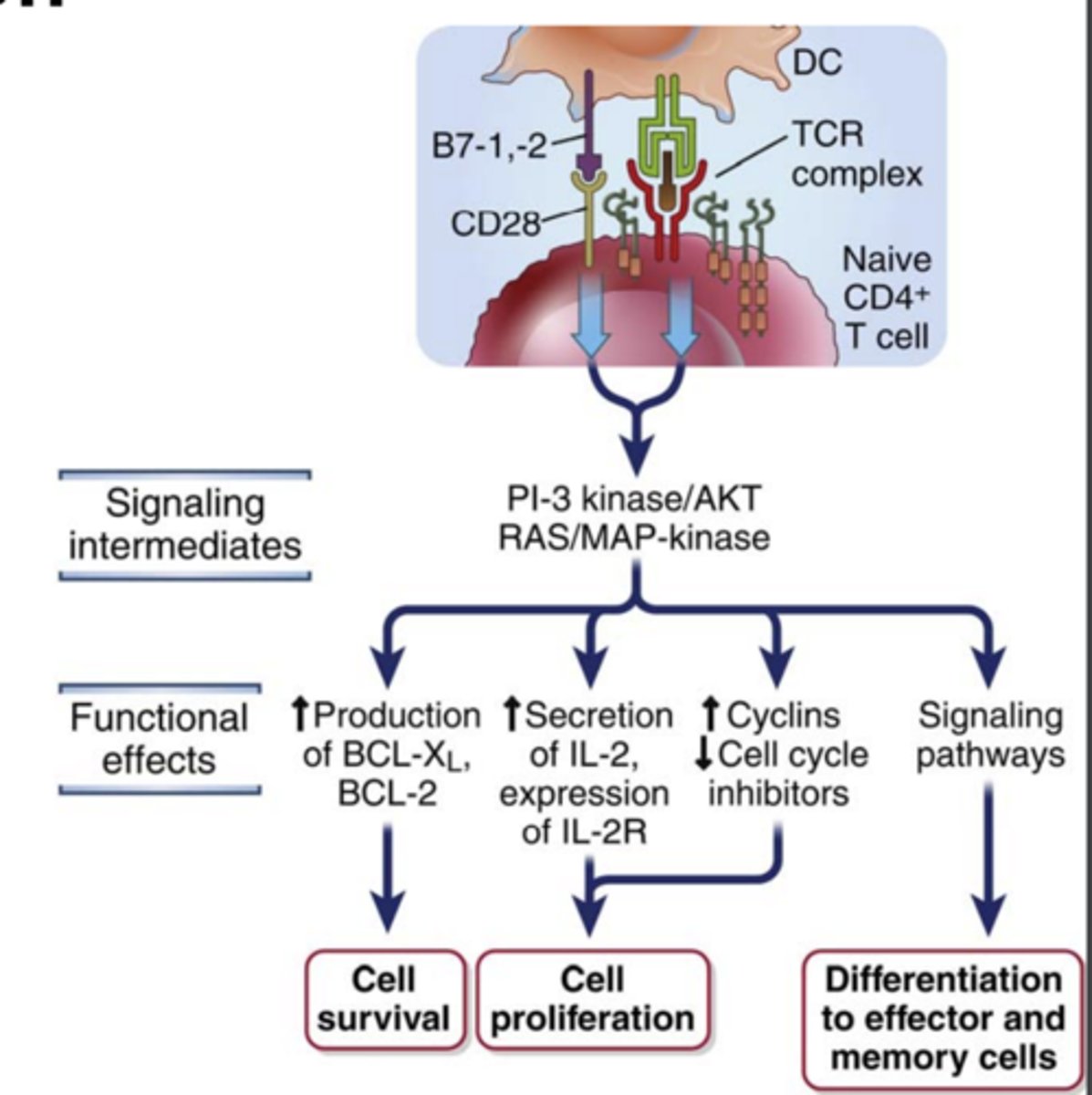
Antigen recognition together with other activating stimuli induce several biologic responses in T cells including: (3)
1) Cytokine secretion and increased cytokine receptor expression;
2) Proliferation, leading to an increase in the numbers of cells in the antigen-specific clones (called clonal expansion)
3) Differentiation of the naive cells into effector and memory lymphocytes
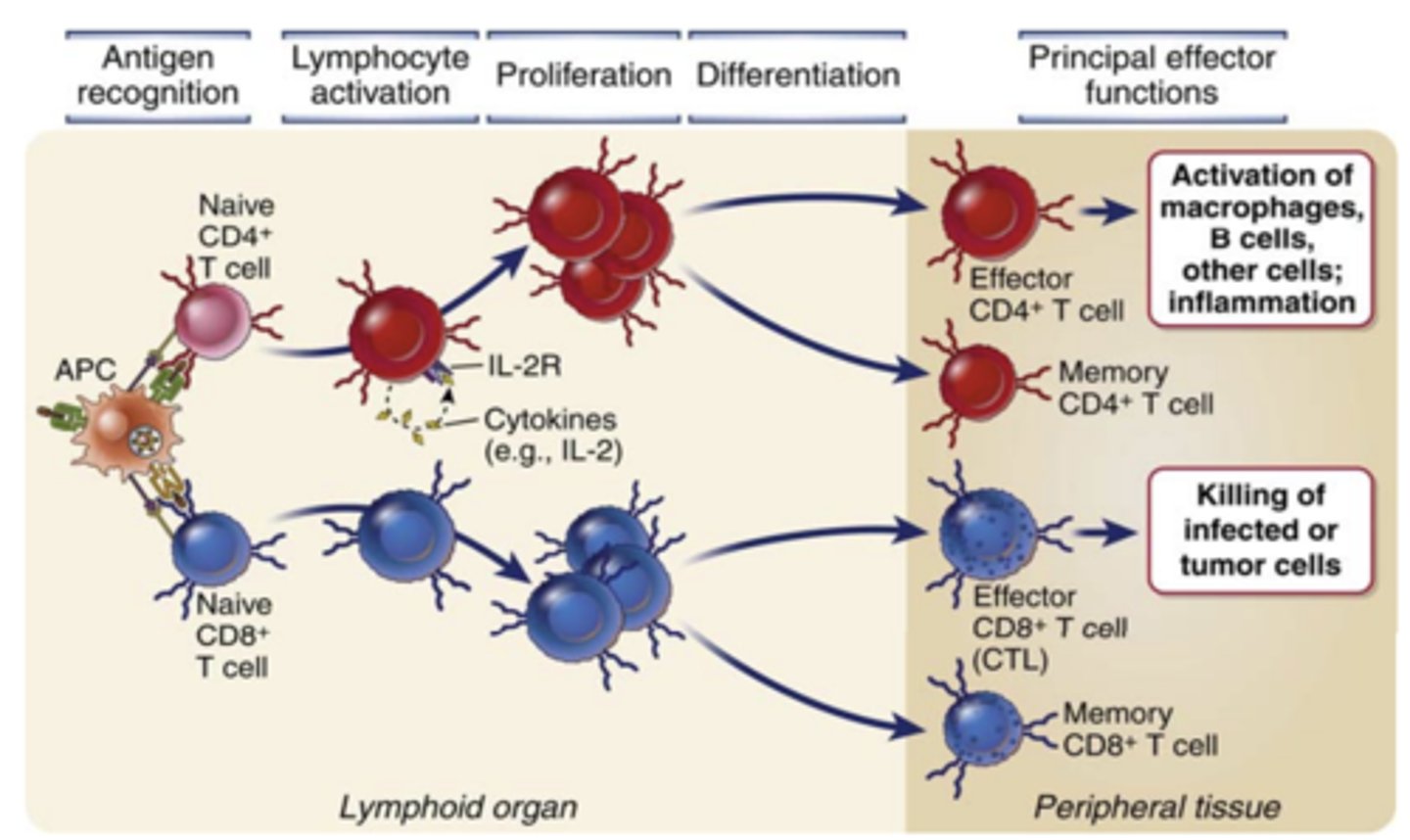
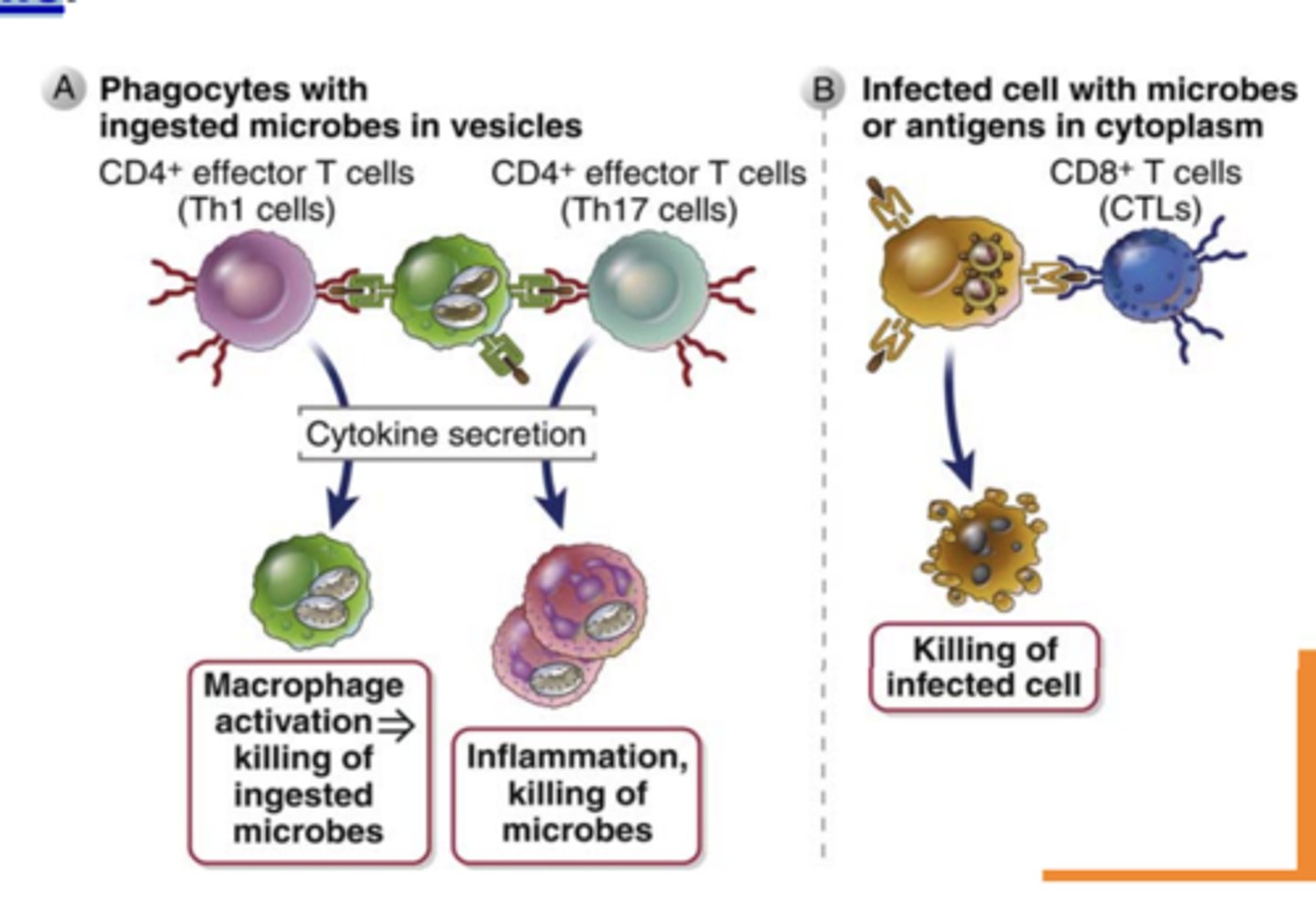
What do effector CD4+ T cells (helper T cells) → recognize and activate?
antigens of microbes ingested by macrophages or B cells and activate
Effector CD4+ T cells (helper T cells) activate.....
macrophages to kill phagocytosed microbes
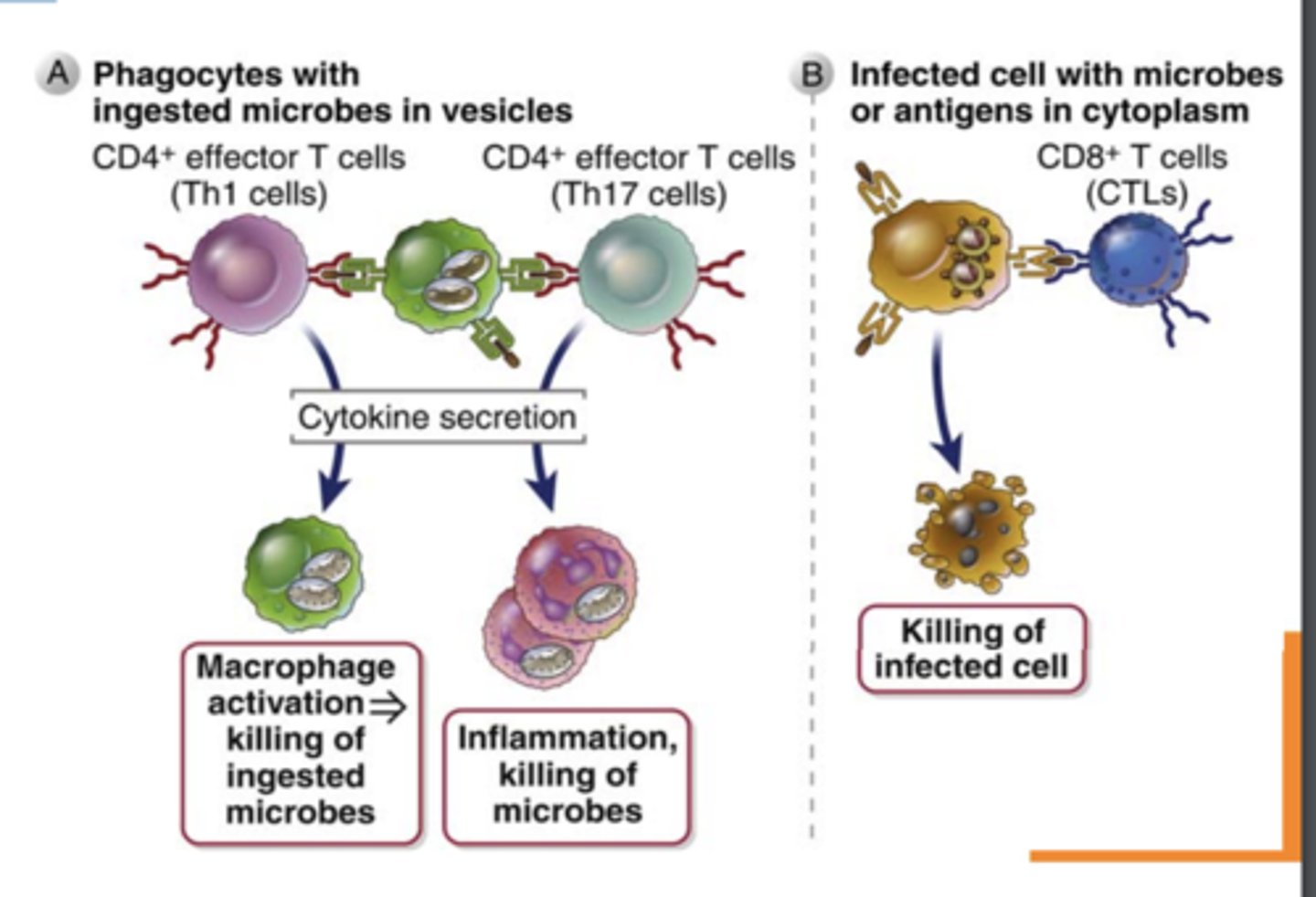
Effector CD4+ T cells (helper T cells) secrete cytokines that recruit different types of leukocytes, such as ______________ and ___________ that destroy different kinds of pathogens
- eosinophils and neutrophils
What do naïve CD4+ T cells produce on activation? ******
produce mostly IL-2 ******
Effector CD4+ T cells (helper T cells) remain in lymphoid organs and help B cells......
differentiate into antibodysecreting plasma cells and memory cells
Effector CD8+ T Cells (cytotoxic T lymphocytes, CTLs) directly recognize....
antigens on infected or tumor cells
Effector CD8+ T Cells (cytotoxic T lymphocytes, CTLs)
1. Kill......
2. Secrete cytokines that...
1. infected or tumor cells
2. activate macrophages and induce inflammation
What does the proliferation of T lymphocytes and their differentiation into effector and memory cells require? (3) ****
1. Antigen recognition
2. Costimulation ***
3. Cytokines
needed to fully activate T lymphocyte
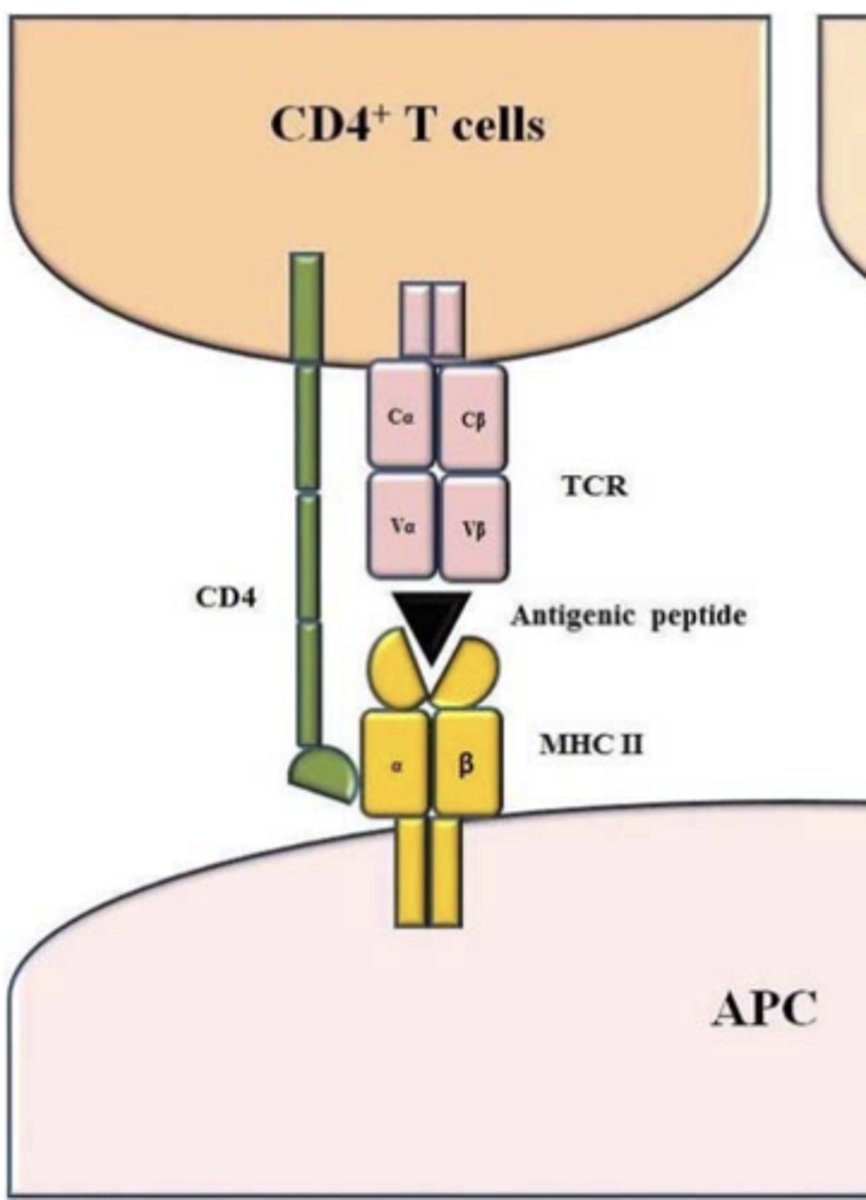
CD4+ T lymphocytes recognize _____________________ displayed by APCs (DCs, B cells and macrophages)
peptide-class II MHC complexes
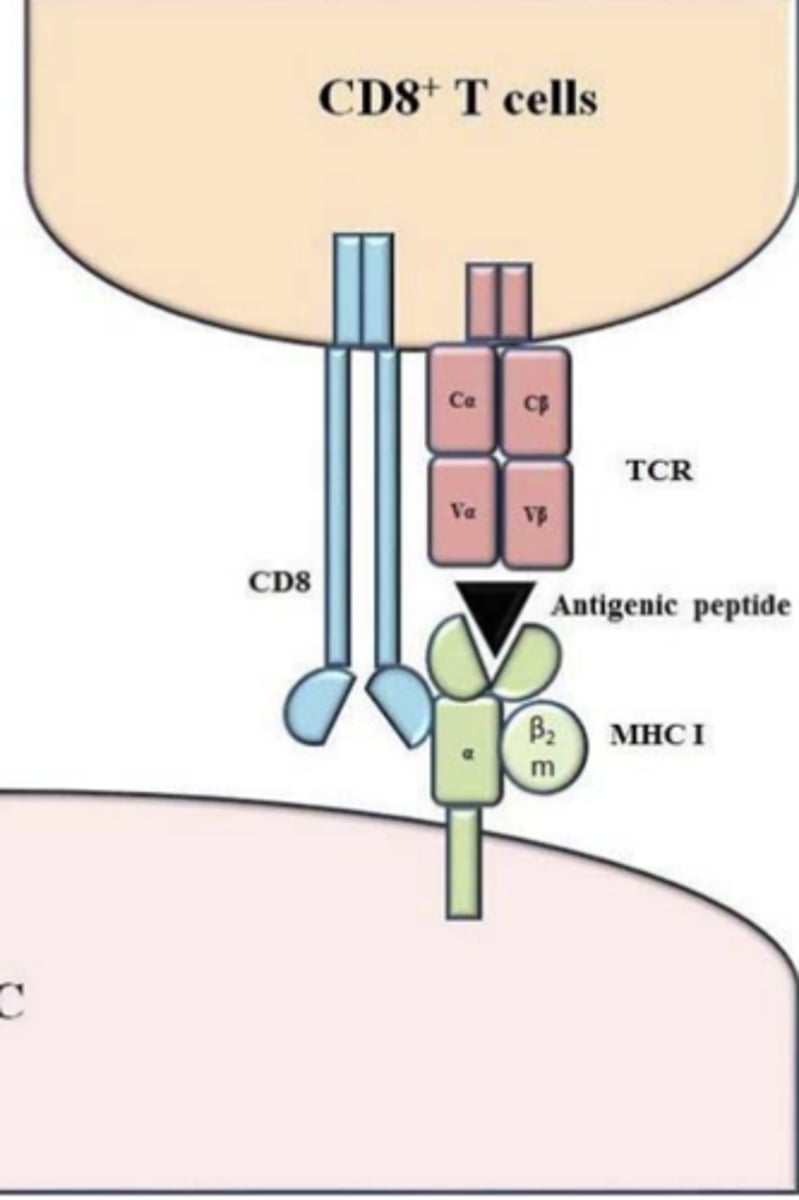
CD8+ T lymphocytes recognize __________________ displayed by APCs (any nucleated cell can present antigens)
peptide-class I MHC complexes
The proliferation and differentiation of naïve T cells require __________________ provided by molecules on APCs, called ________________, in addition to ________________ signals
- additional signals
- costimulators
- antigen-induced signals
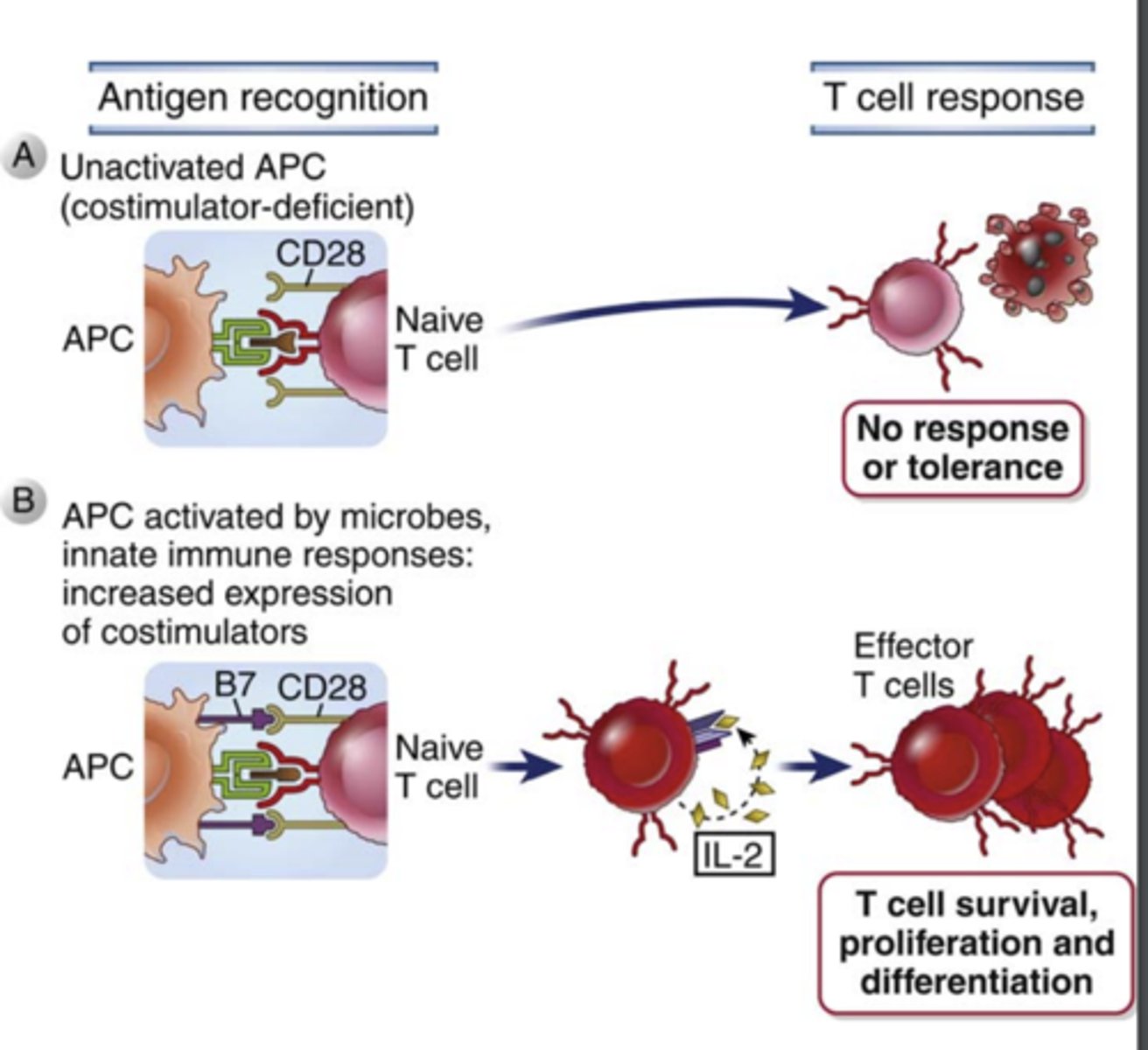
In the absence of costimulation, T cells that encounter antigens fail to ______________, enter a state of prolonged _____________________, or die
- respond
- unresponsiveness
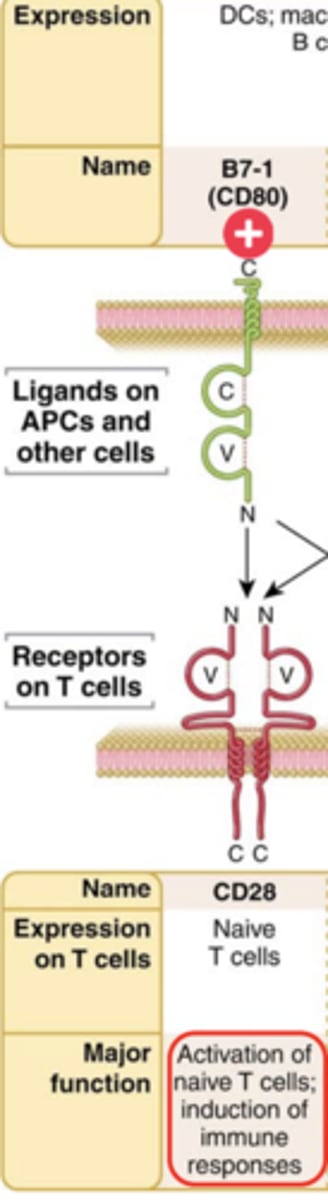
The best costimulatory pathway in T cell activation involves the T cell surface receptor _________, which binds the costimulatory molecules ___________ and ______________ expressed on the surface of activated APCs (DCs, macrophages, and B lymphocytes)
- CD28
- B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86)
What is the expression of B7 costimulators increased by?
What does this ensure?
- microbial products and innate immune responses to infections
- ensures that T lymphocytes are activated only when needed
CD28 and ICOS (inducible costimulator, CD278) have ______________ function
costimulation function
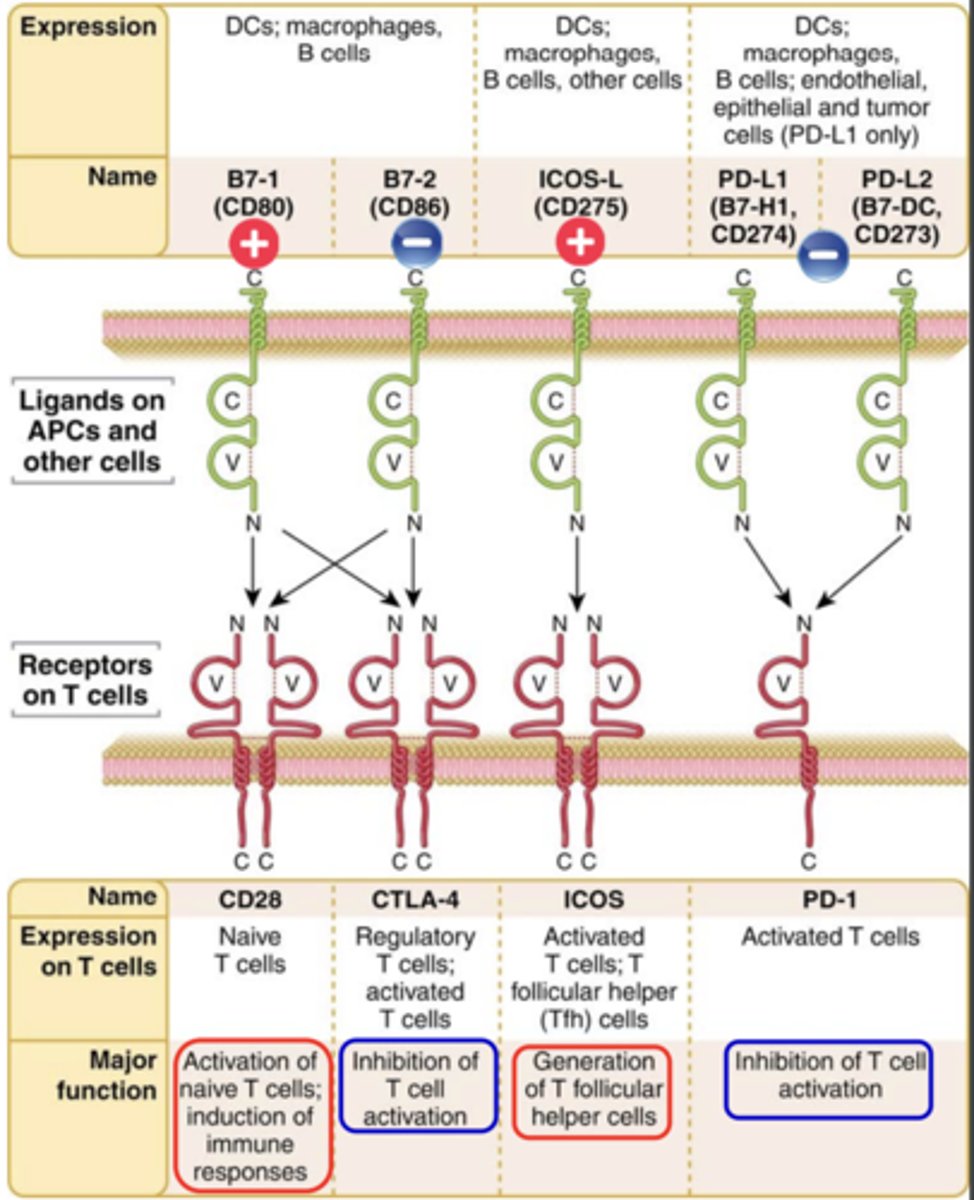
CTLA‐4 (cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4, CD152) and PD‐1 (programmed cell death protein 1, CD279) are....
What are these pathways crucial for?
inhibitory receptors (co‐inhibiton) -> (immune checkpoints)
- Regulators of the immune system
- These pathways are crucial for self‐ tolerance
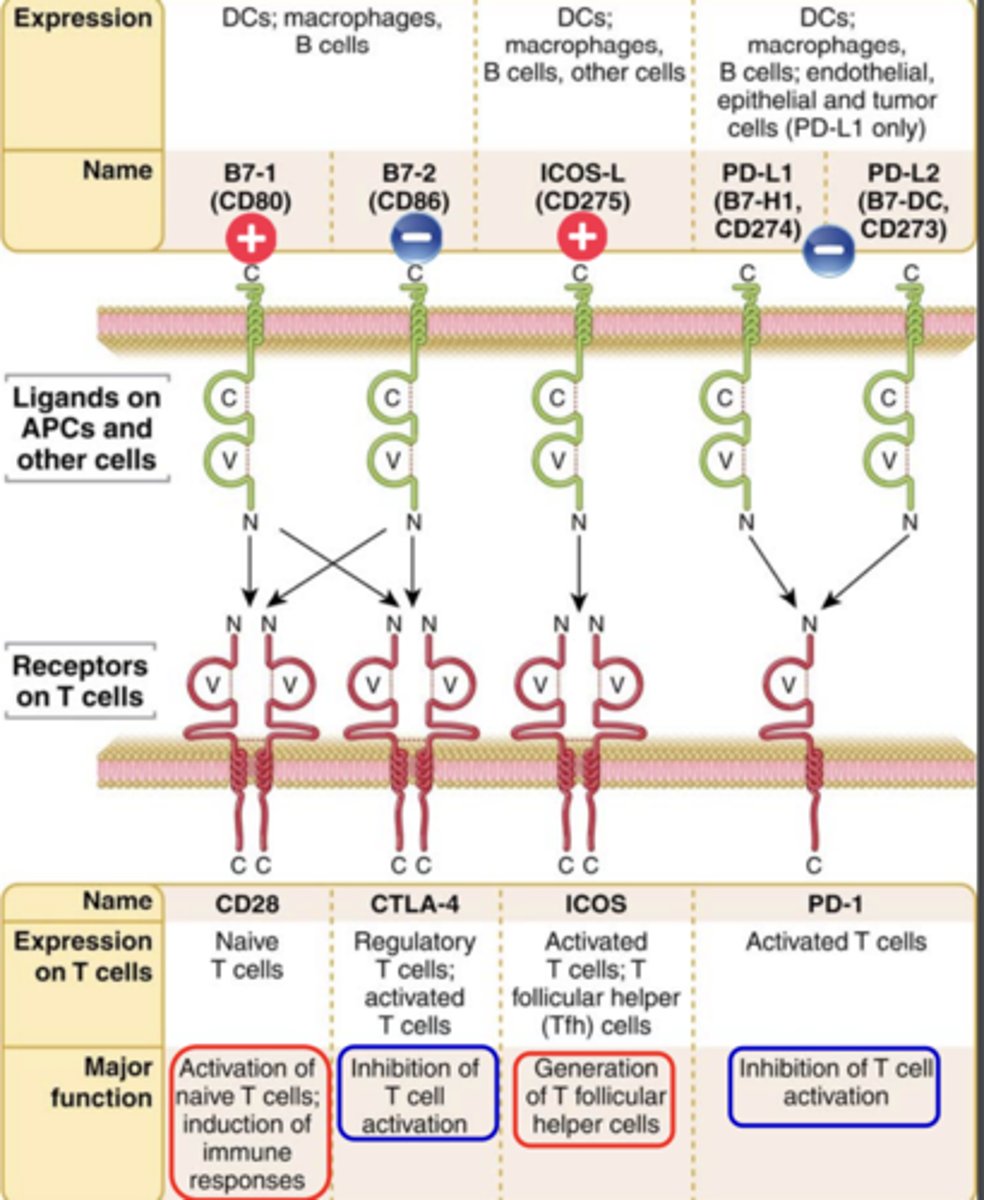
CD28:
Ligand that binds to it:
Expression on T cells:
Major function:
Ligand that binds to it: B7-1 (CD80)
Expression on T cells: Naive T cells
Major function: Activation of naive T cells; induction of immune responses**
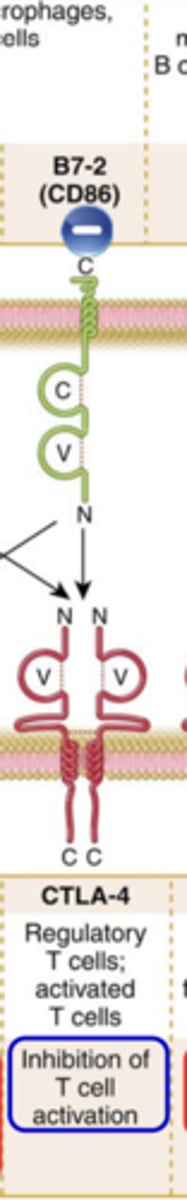
CTLA-4:
Ligand that binds to it:
Expression on T cells:
Major function:
Ligand that binds to it: B7-2 (CD86)
Expression on T cells: Regulatory T cells; activated T cells
Major function: Inhibition of T cell activation ***
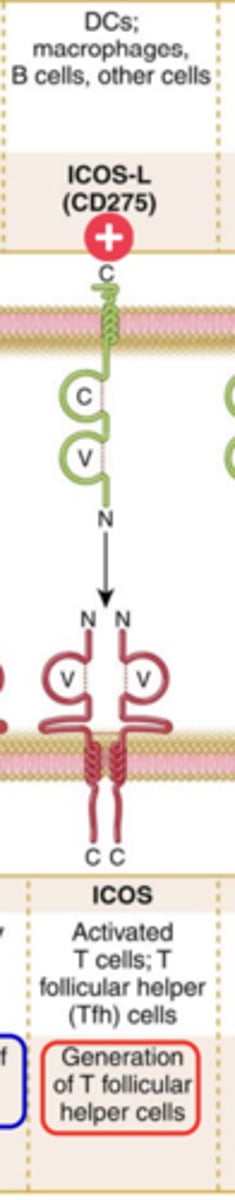
ICOS:
Ligand that binds to it:
Expression on T cells:
Major function:
Ligand that binds to it: ICOS-L (CD275)
Expression on T cells: Activated T cells, T follicular helper (Tfh) cells
Major function: Generation of T follicular helper cells***
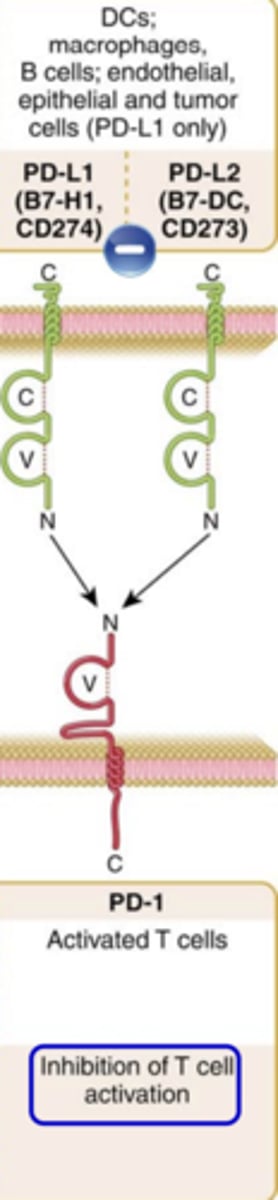
PD-1:
Ligand that binds to it:
Expression on T cells:
Major function:
Ligand that binds to it: PD-L1 (B7-H1, CD274) and PD-L2 (B7-DC, CD273)
Expression on T cells: Activated T cells
Major function: Inhibition of T cell activation***
Which TNF superfamily membrane protein is expressed primarily on activated T cells?****
CD40 ligand (CD40L)****
(affect CD4+ T cell most, CD8+ not so much)
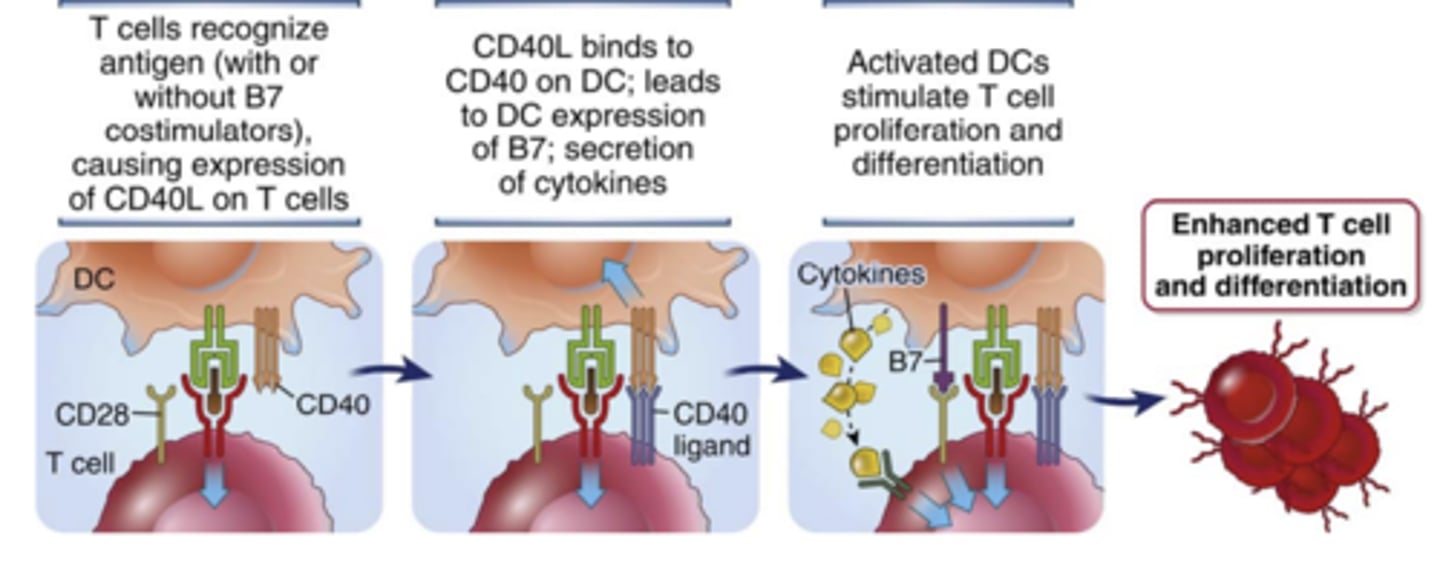
CD40 is a member of the _________________.
What kind of cells is it expressed on?
- TNFR superfamily
- B cells, macrophages, and DCs
(not the ligand)
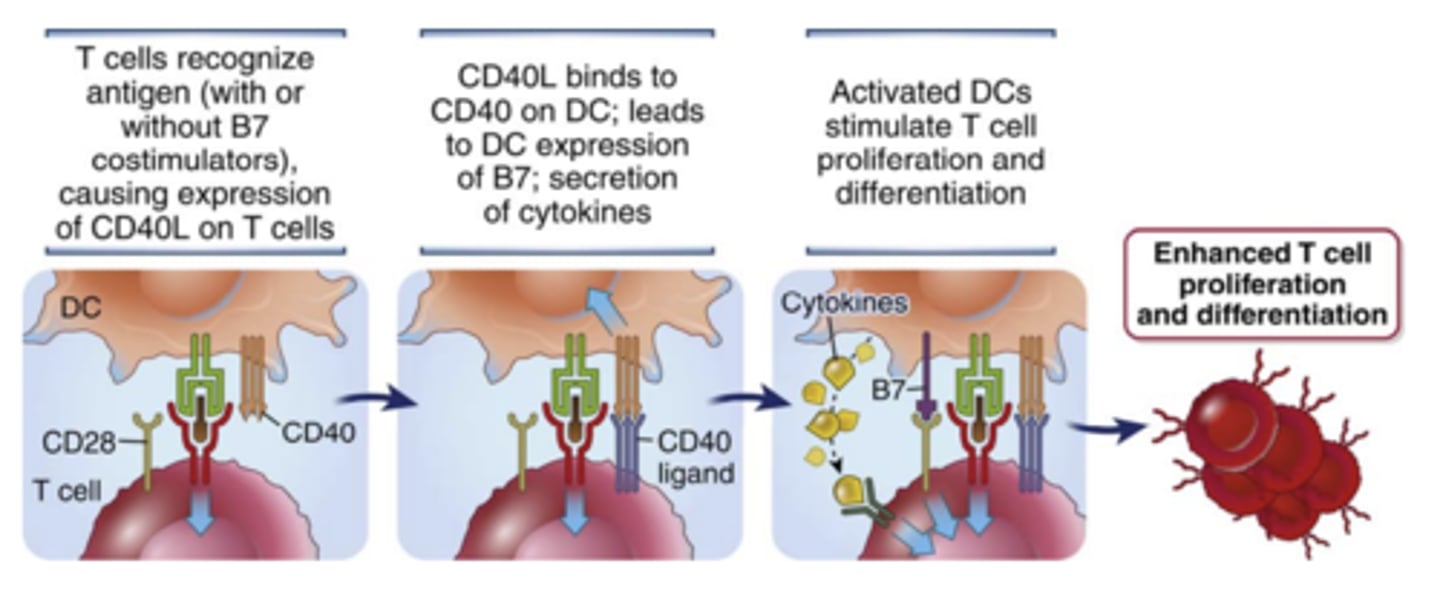
What does the interaction of CD40L on T cells with CD40 on APCs enhance? How does it enhance it?
enhances T cell responses by activating the APCs
Therapeutic agents have been developed for controlling injurious immune responses by inhibiting costimulation, called....
costimulatory blockade (Inhibition of T cell activation)
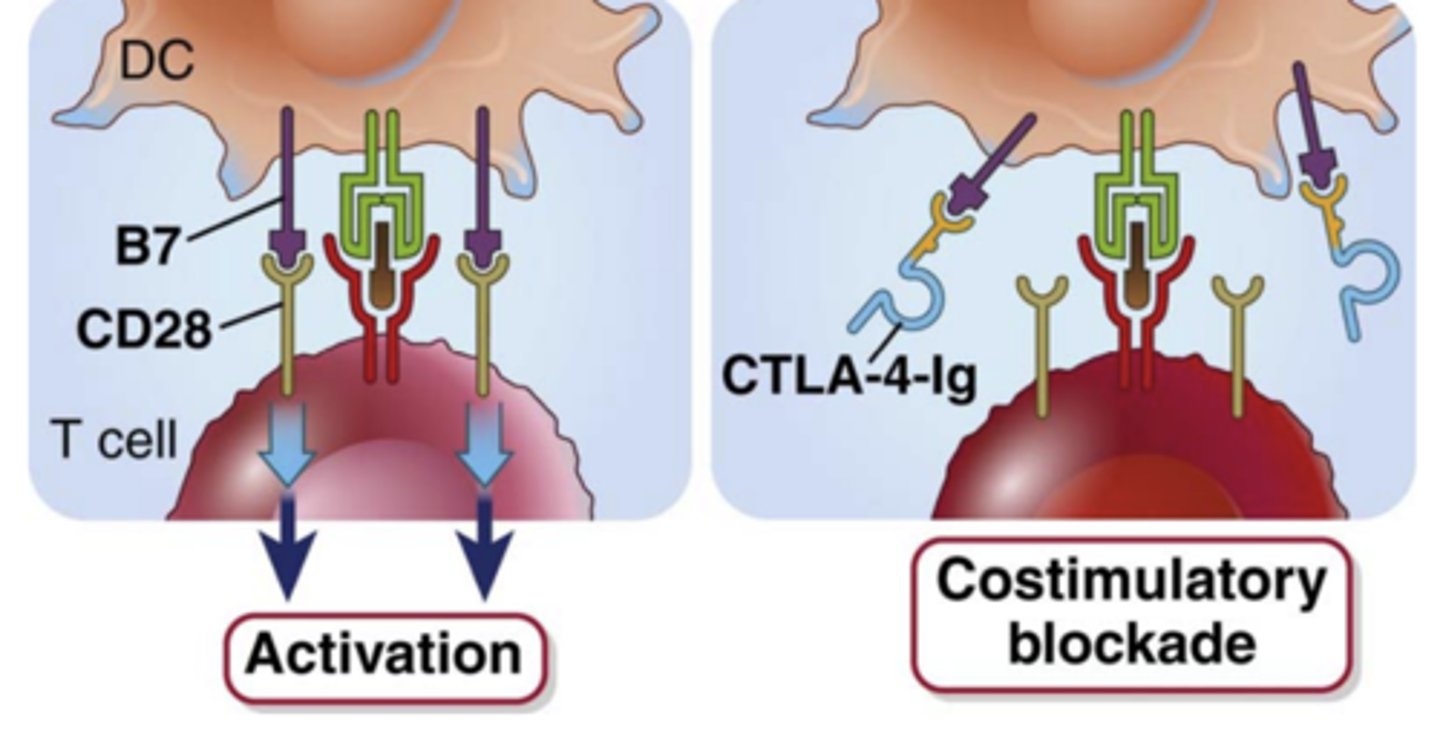
What does the fusion protein, CTLA-4-Ig consist of?
- the extracellular domain of CTLA-4
- the Fc portion of human IgG
CTLA-4-Ig binds to ____________ and ____________ and blocks the _____________ interaction
- B7-1 and B7-2
- B7:CD28
What is CTLA-4-Ig is an approved therapy for?
rheumatoid arthritis and transplant rejection
Inhibitors of the CD40L:CD40 pathway are in clinical trials for.....
transplant rejection and autoimmune diseases
T/F: CTLA-4 has a lower affinity for B7 than CD28 does ++++
FALSE
CTLA-4 has a higher affinity for B7 than CD28 does *****

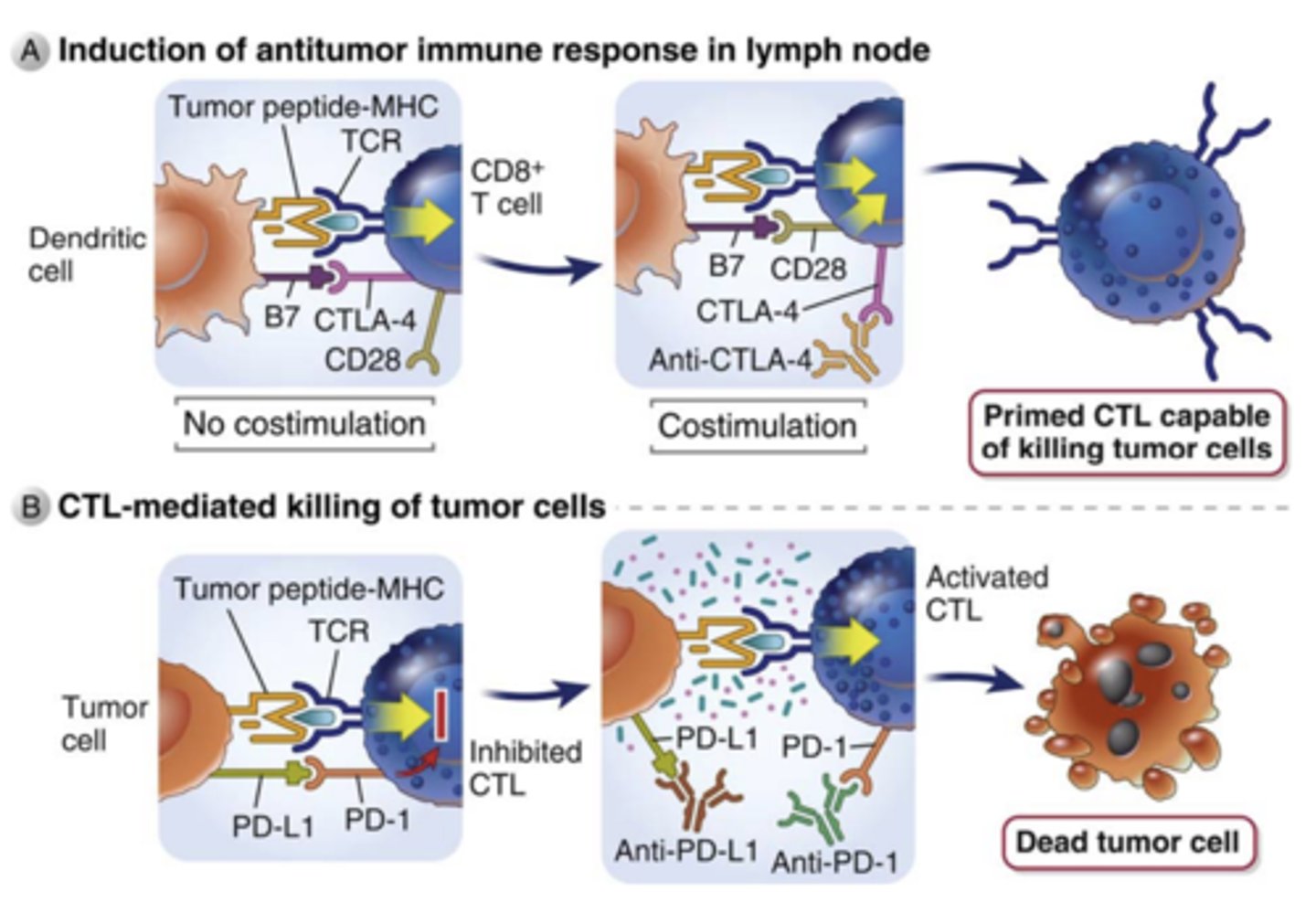
1. What are antibodies that block the CTLA-4 and PD-1 inhibitory receptors approved for?
2. How do they work?
1. approved for the immunotherapy of tumors
2. work by preventing CTLA-4 or PD-1 from binding their ligands, thereby reducing inhibition and thus enhancing T cell activation
After activation by antigen recognition and costimulation, there are characteristic changes in.....
the expression of various surface molecules in T cells
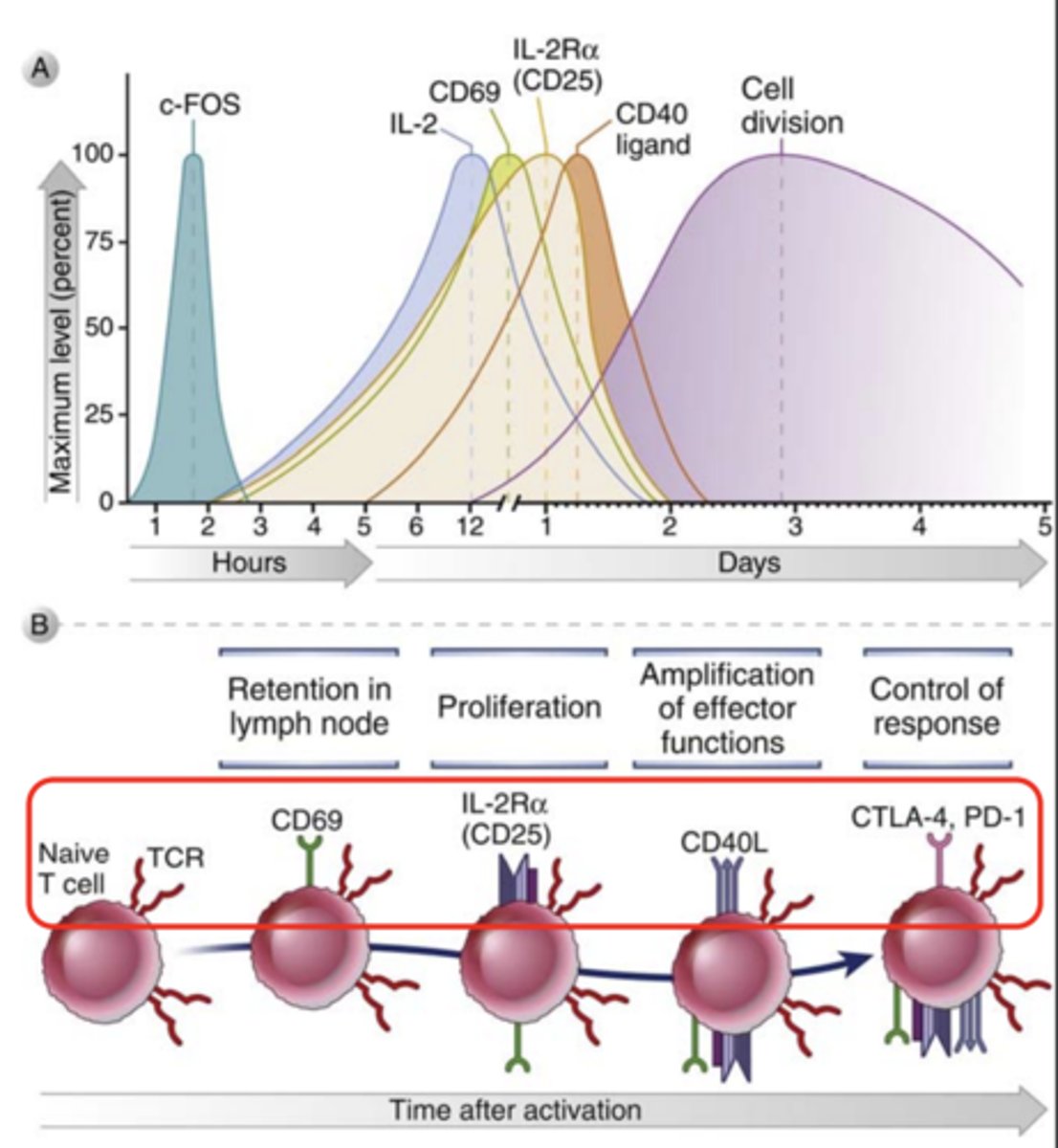
Various cytokines are involved in the ________________ and ______________ of antigen-stimulated T cells and in the effector functions of these cells
proliferation and differentiation
Most of these cytokines act on the cells that produce them (___________ action) or on nearby cells (____________ action)
- autocrine action
- paracrine action
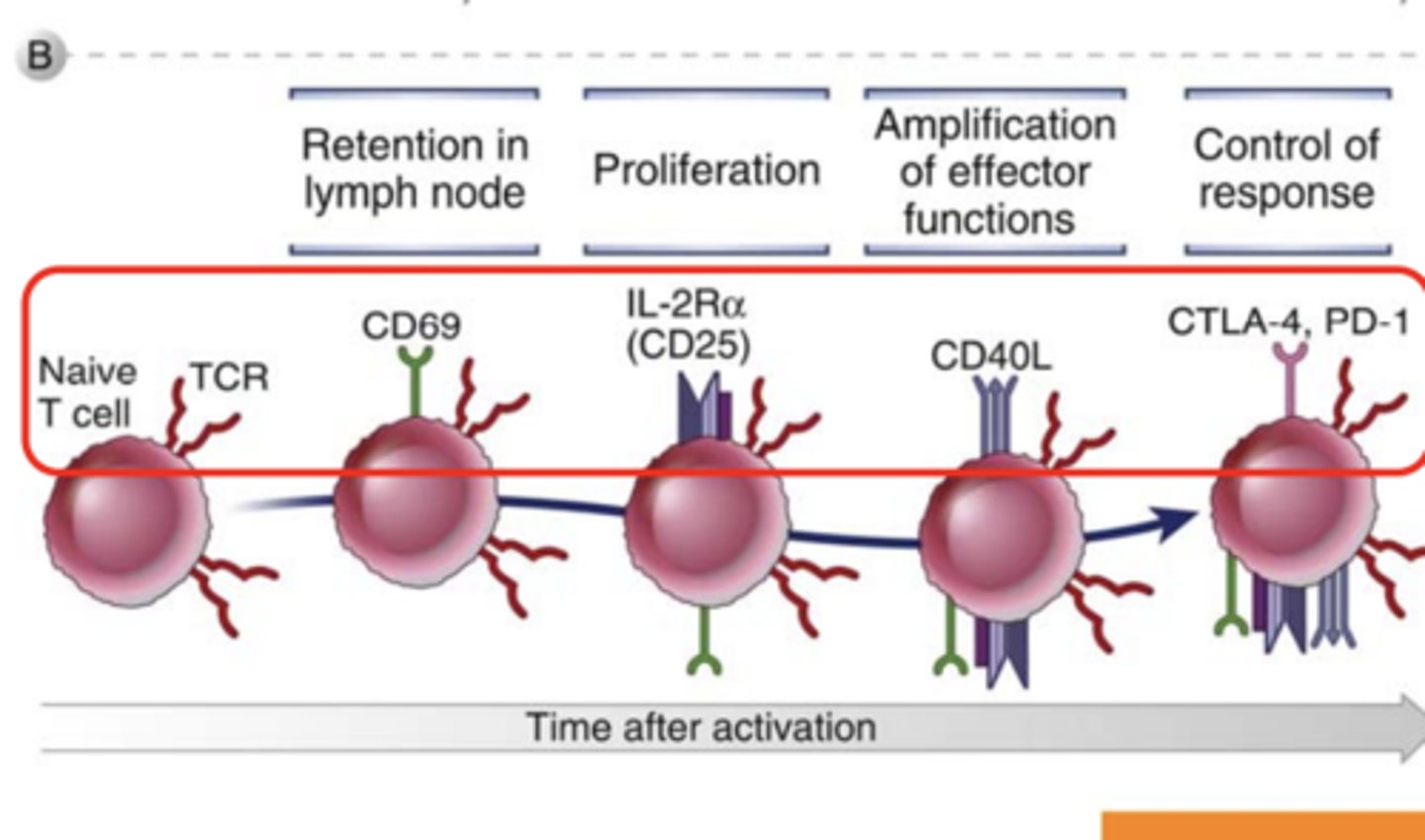
What is CD69? What cells is it expressed in?
an early activation marker expressed in hematopoietic stem cells, T cells, and many other cell types in the immune system
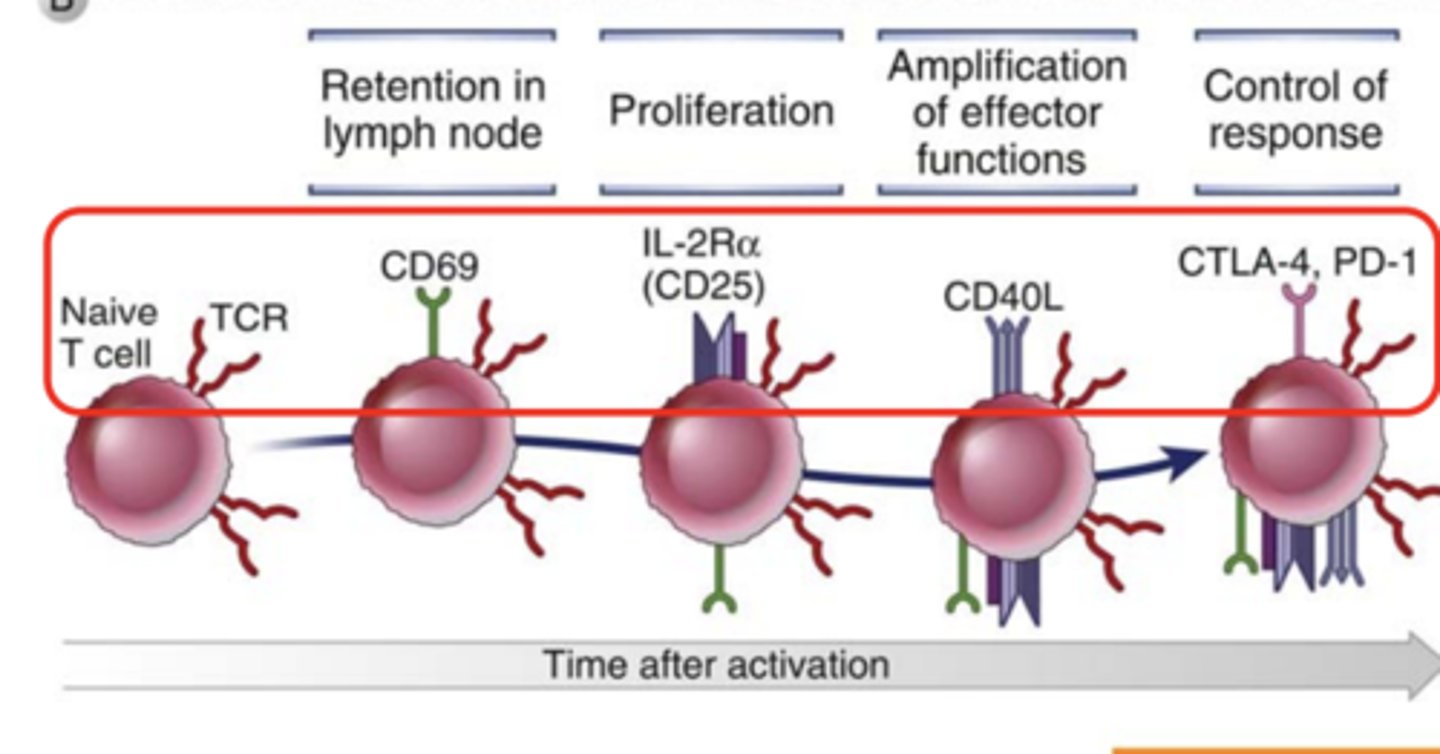
What markers are expressed in T cells in retention in lymph node? ***
CD69 *****
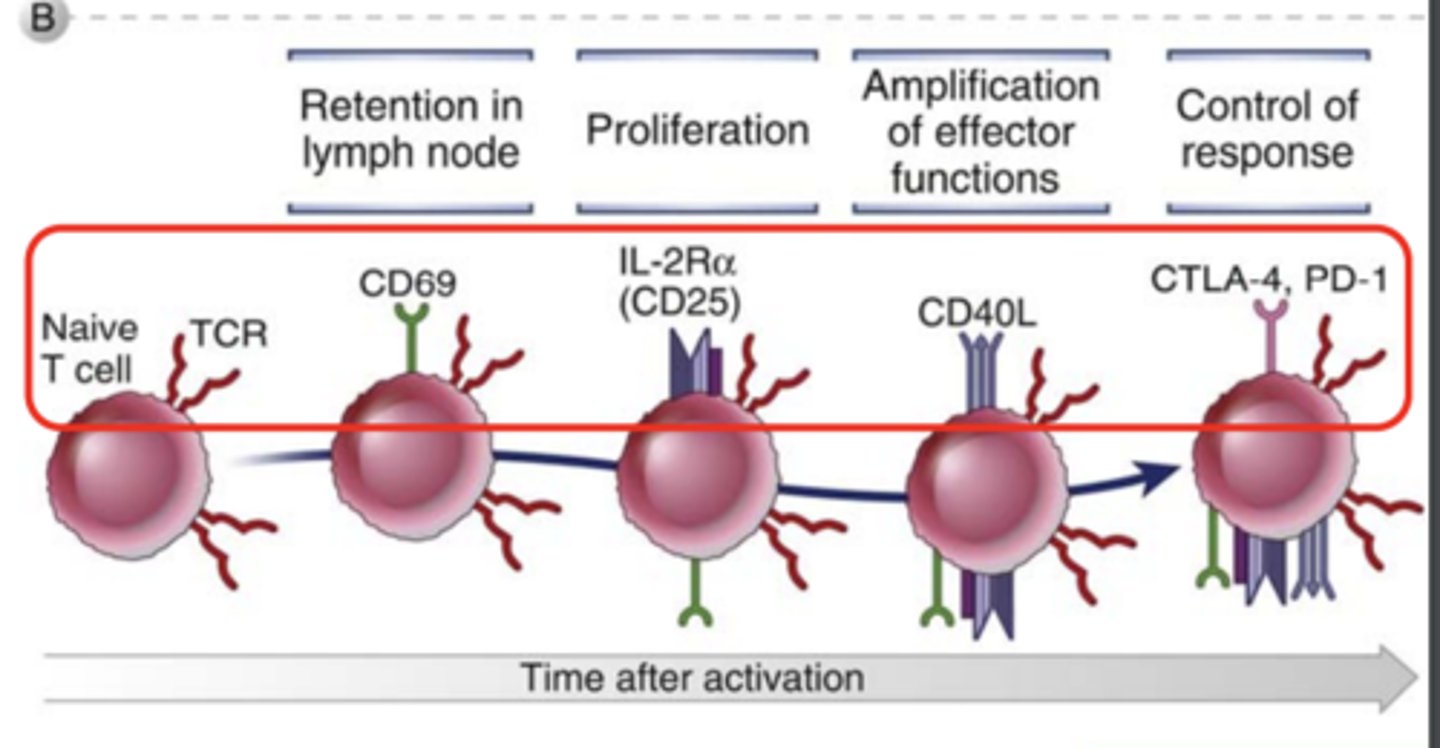
What markers are expressed in T cells in proliferation? *****
IL-2Ra (CD25)*****
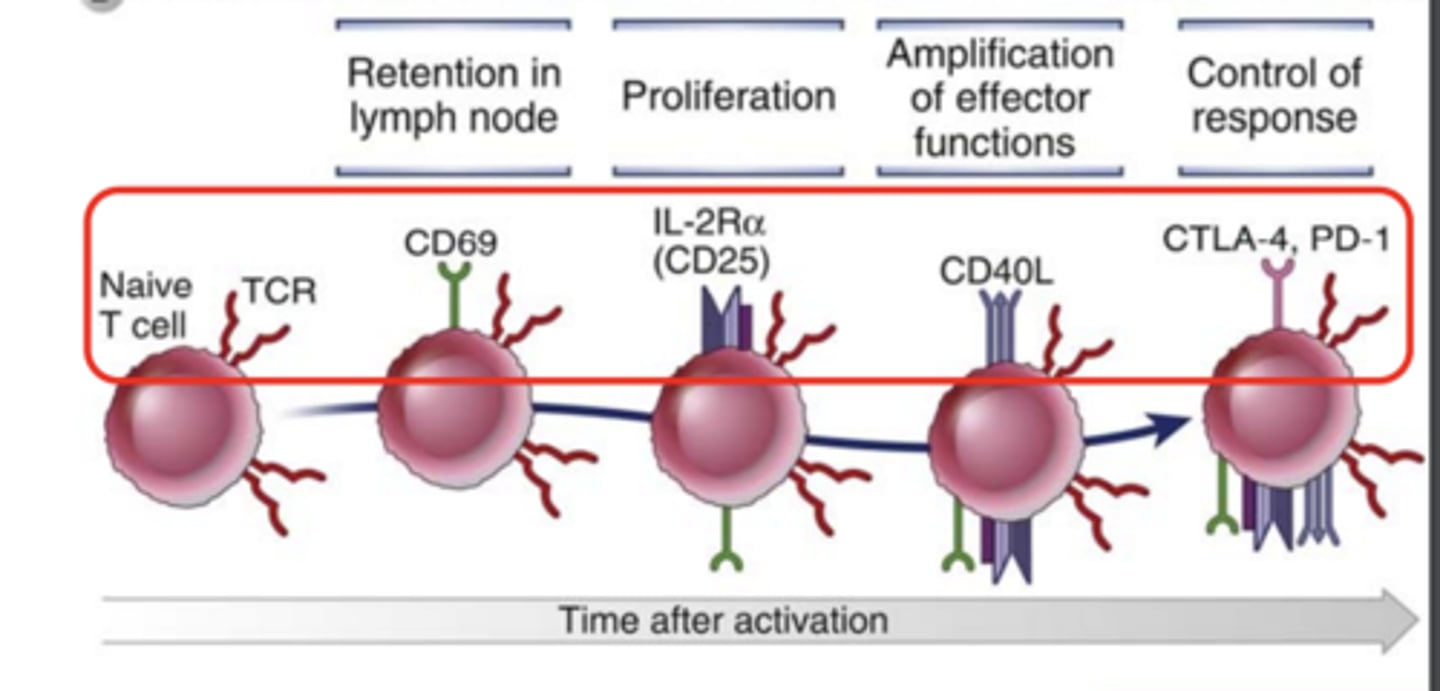
What markers are expressed in T cells in amplification of effector functions?*****
CD40L*****
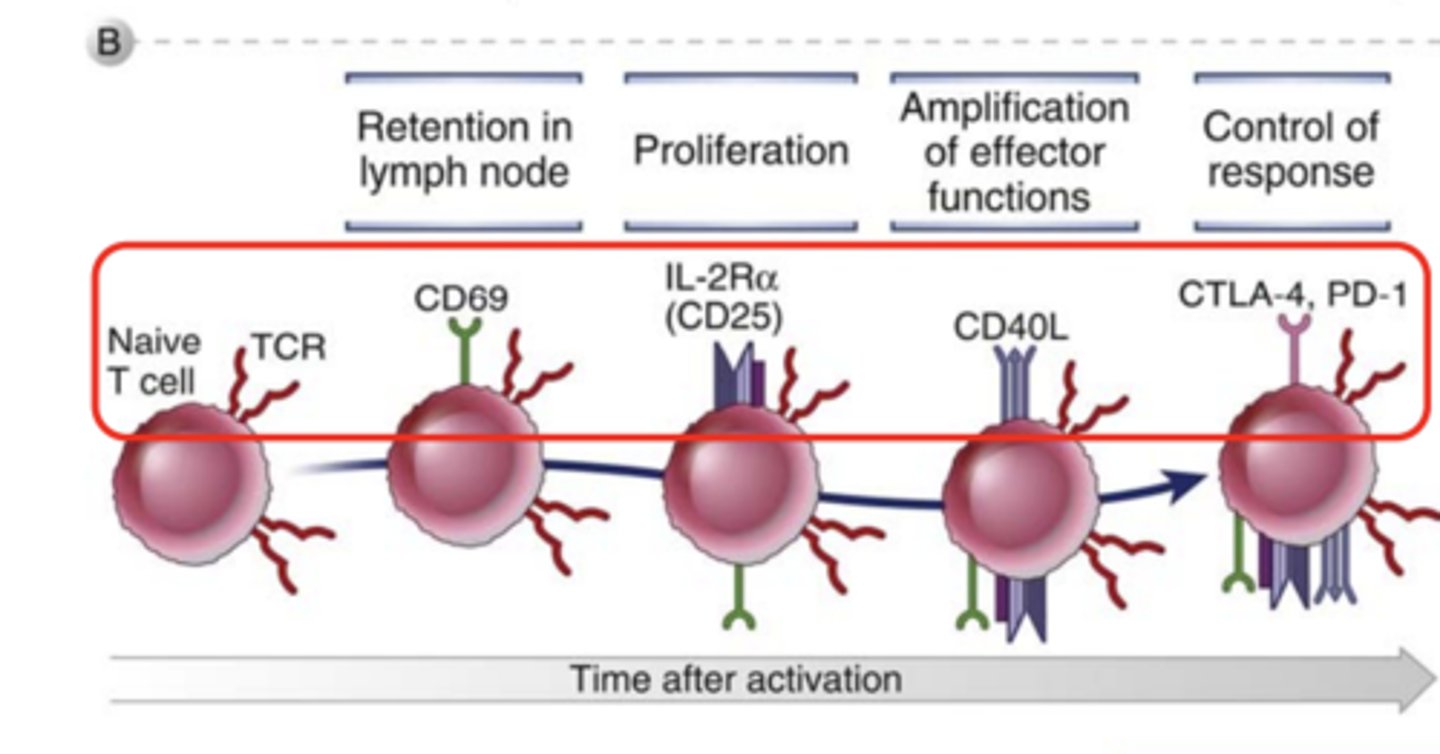
What markers are expressed in T cells in control of response? *****
CTLA-4***
PD-1****
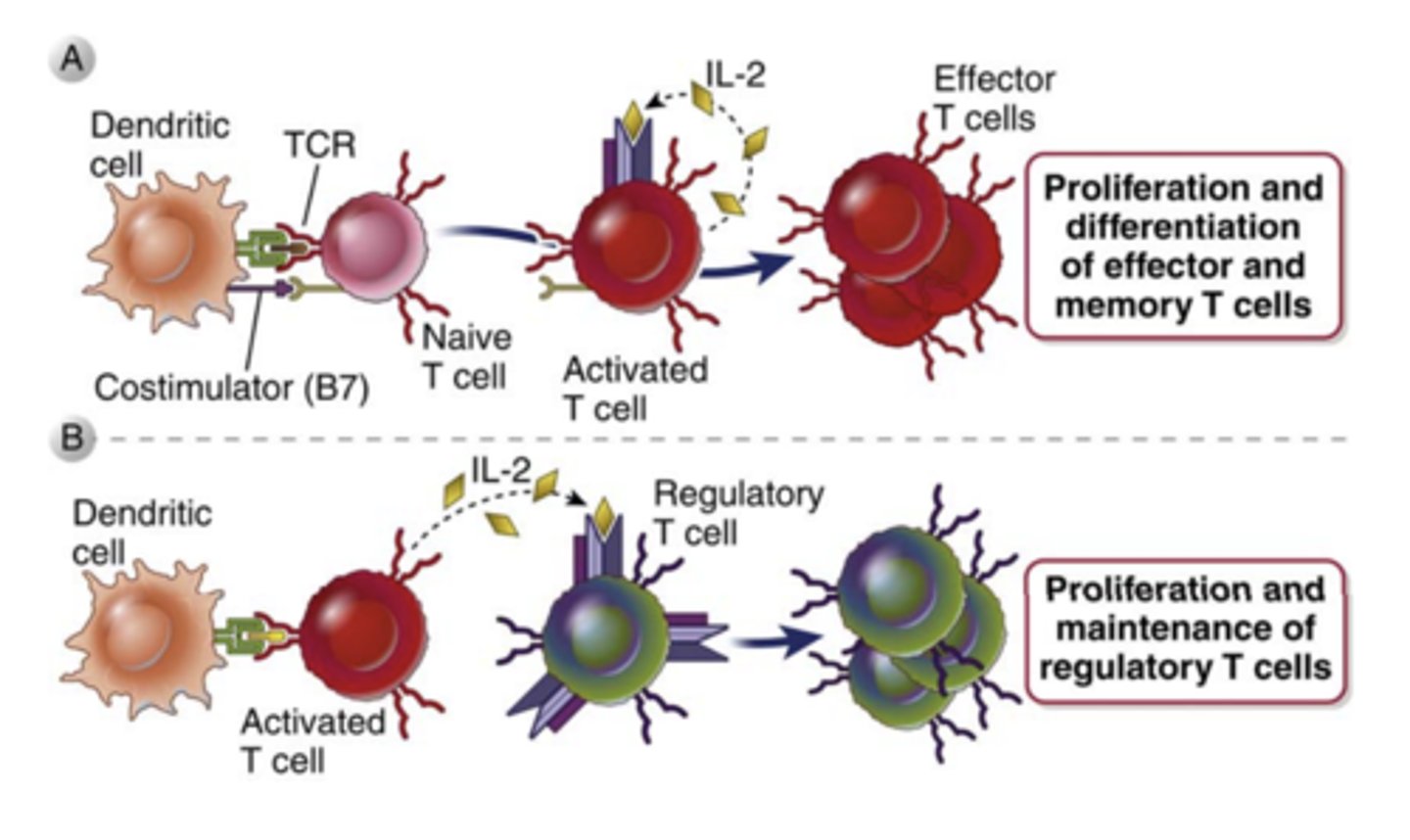
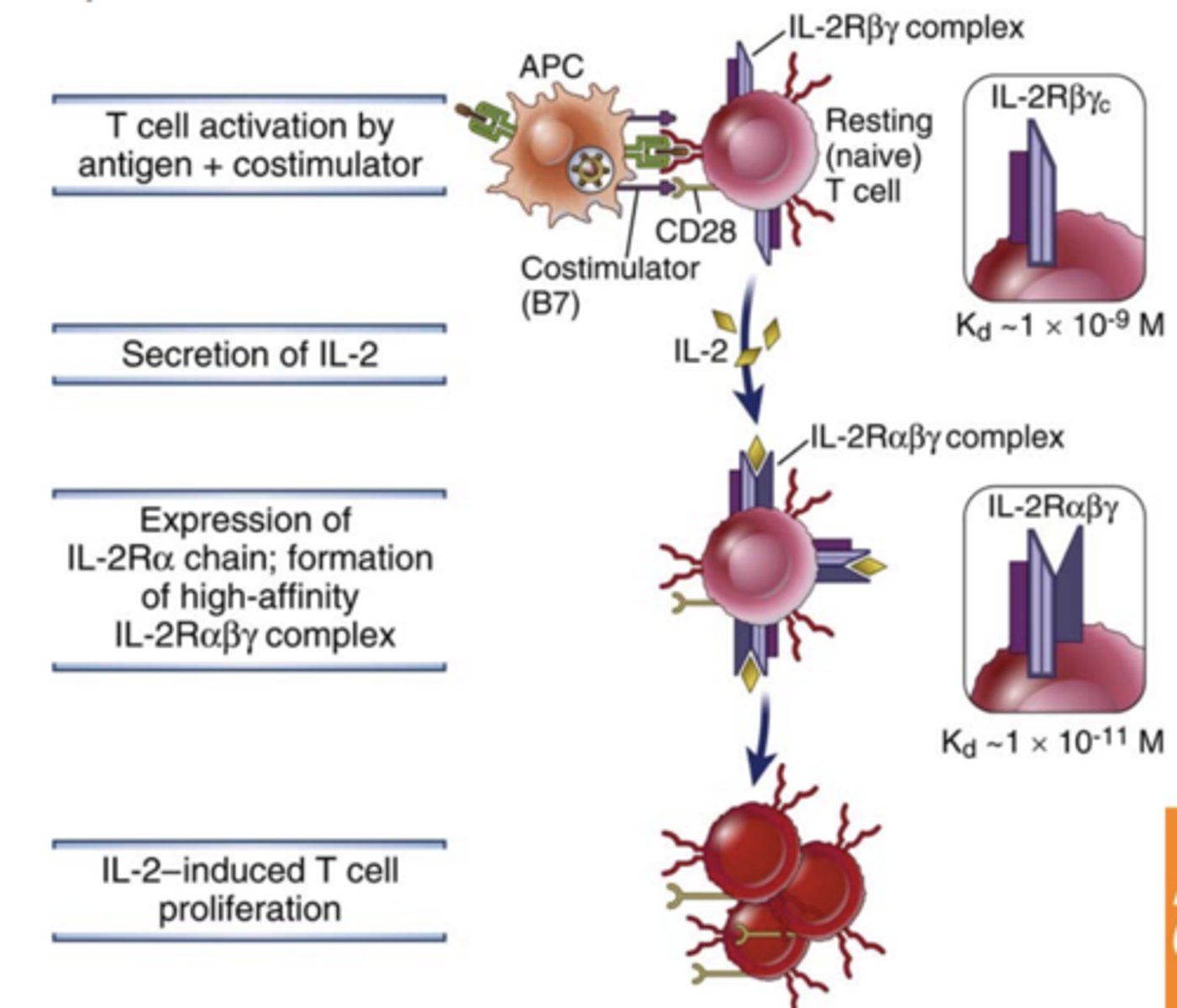
What is IL-2 and what does it play a major role in?
- it is a growth, survival, and differentiation factor for T cells
- plays a major role in the proliferation of antigen stimulated T cells and in the maintenance of functional regulatory T cells
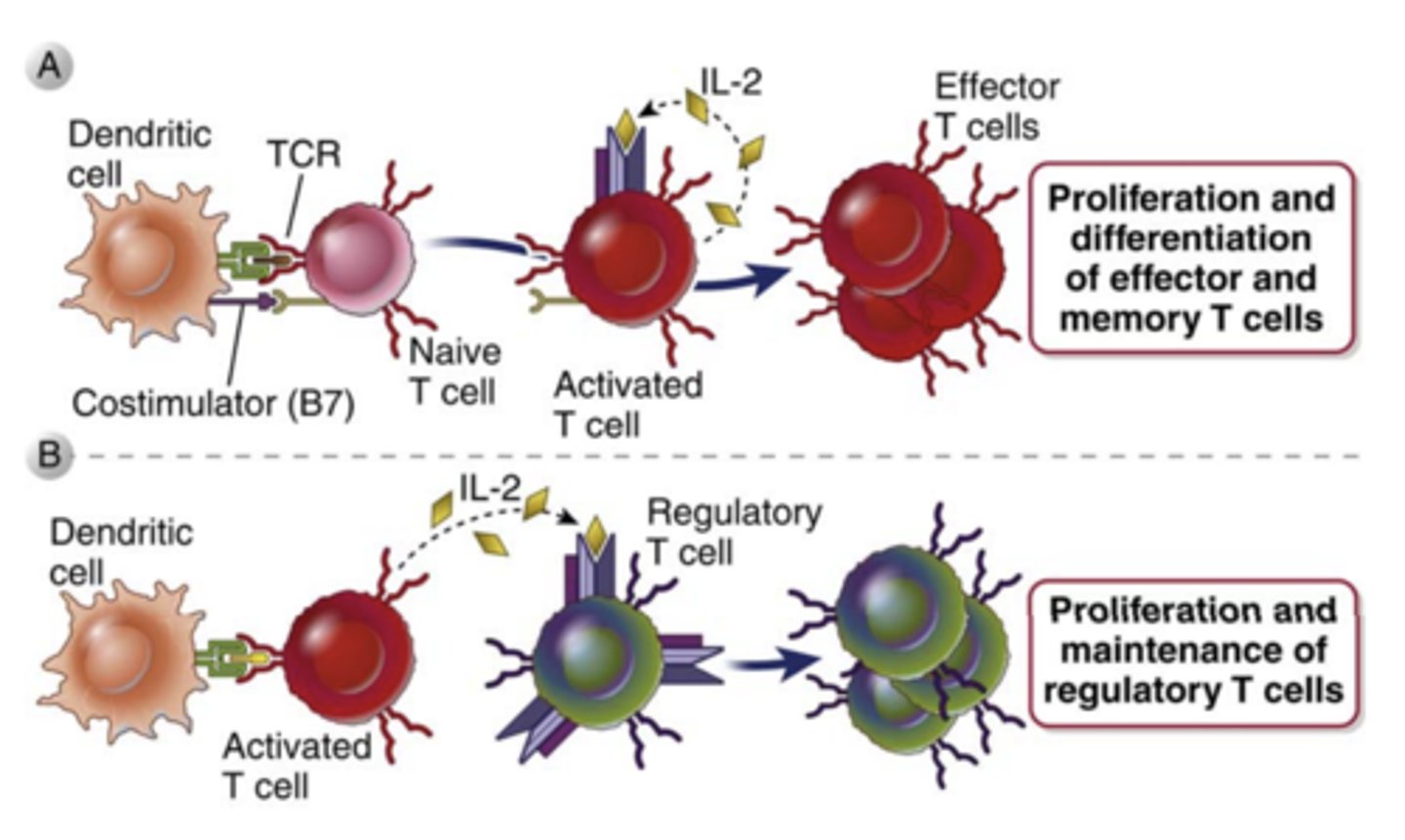
What IL-2 mainly produced by? ***
produced mainly by CD4+ T lymphocytes****** rapidly after recognition of antigen and costimulators
T/F: IL-2 production is slow and takes time
FALSE
IL-2 production is rapid and transient, starting within 1 to 2 hours after antigen recognition, peaking at about 8 to 12 hours, and declining by 24 hours
T cell proliferation in response to antigen recognition is mediated by a combination of signals from the ________________, ______________, and _____________________, primarily IL-2
- antigen receptor
- costimulators
- autocrine growth factors
- IL-2
What do T cell-mediated immune responses to an antigen usually result in the generation of?
memory T cells specific for that antigen, which may persist for years, even a lifetime
Memory cells express increased levels of ____________________, which may be responsible for their _______________ survival
- anti-apoptotic proteins
- prolonged
T/F: Memory cells respond more slowly to antigen stimulation than naive cells specific for the same antigen
FALSE
Memory cells respond more rapidly to antigen stimulation than naive cells specific for the same antigen
The maintenance of memory cells is dependent on _____________ but does not require __________________******
- cytokines
- antigen recognition*****
What is the most important cytokine for the maintenance of memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells?****
IL-7***
IL-7 also plays a key role in....
early lymphocyte development and in the survival of naive T cells
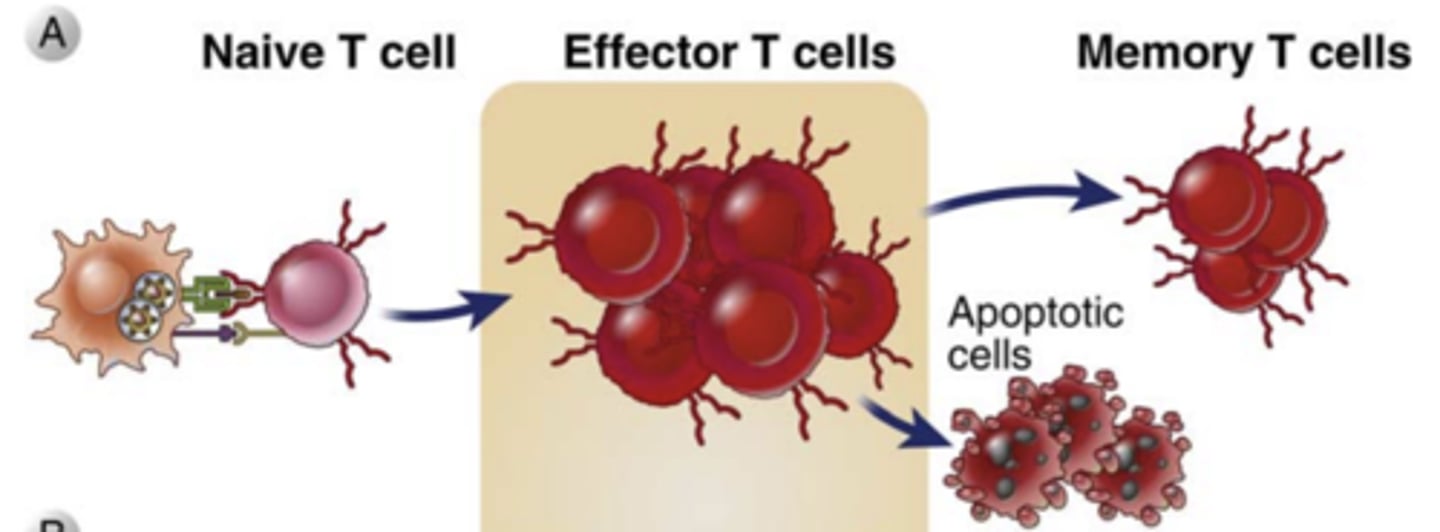
What does the elimination of antigen lead to? What is it responsible for maintaining?
leads to contraction of the T cell response, this decline is responsible for maintaining homeostasis in the immune system
Elimination of the antigen can also result in: (
- cell death (apoptosis)
- Inhibition of T cell activation

Inhibition of T cell activation results in: (2)
- Reduced activating signals
- Engagement of cell surface inhibitory molecules (PD-1 and CTLA-4)
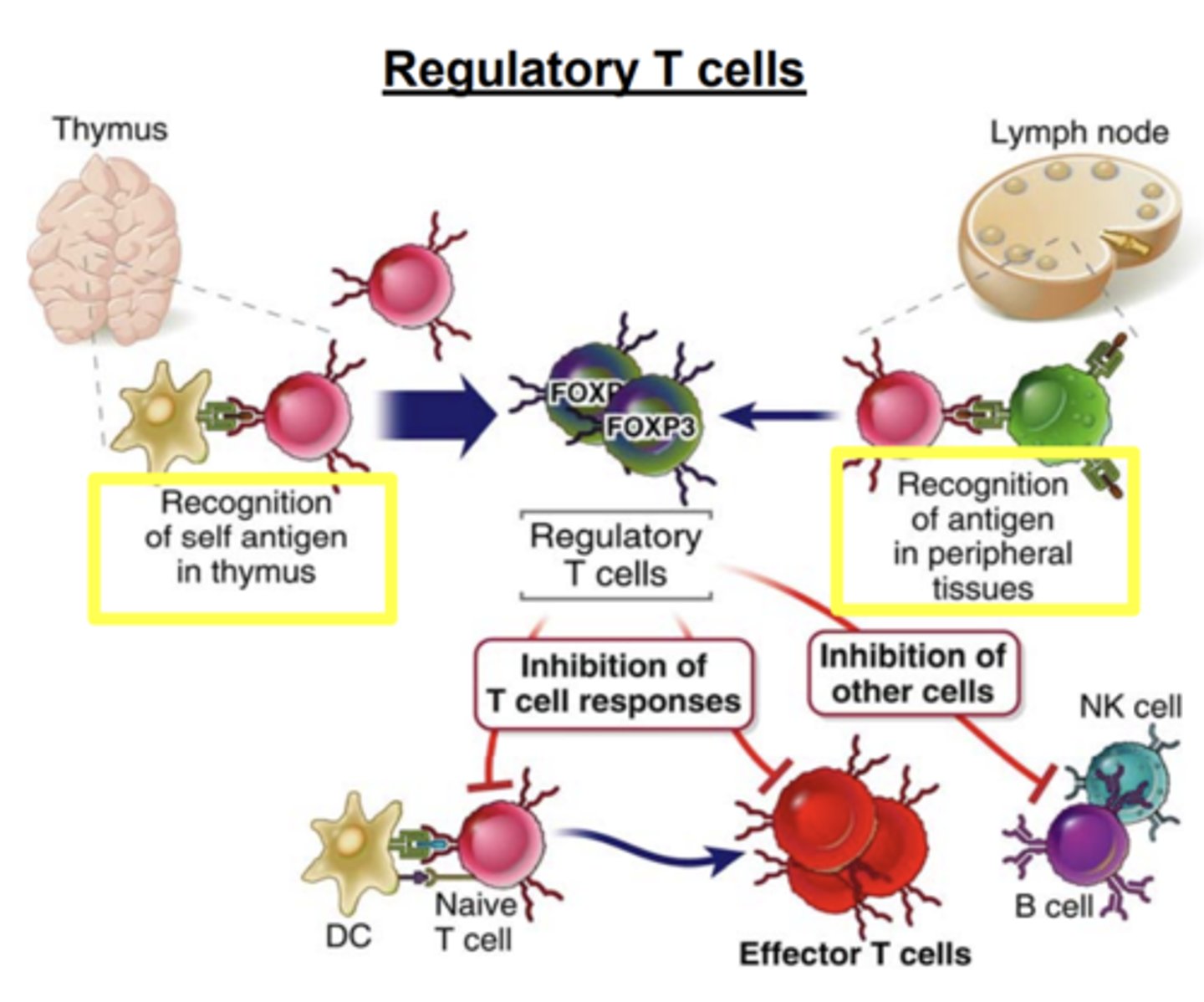
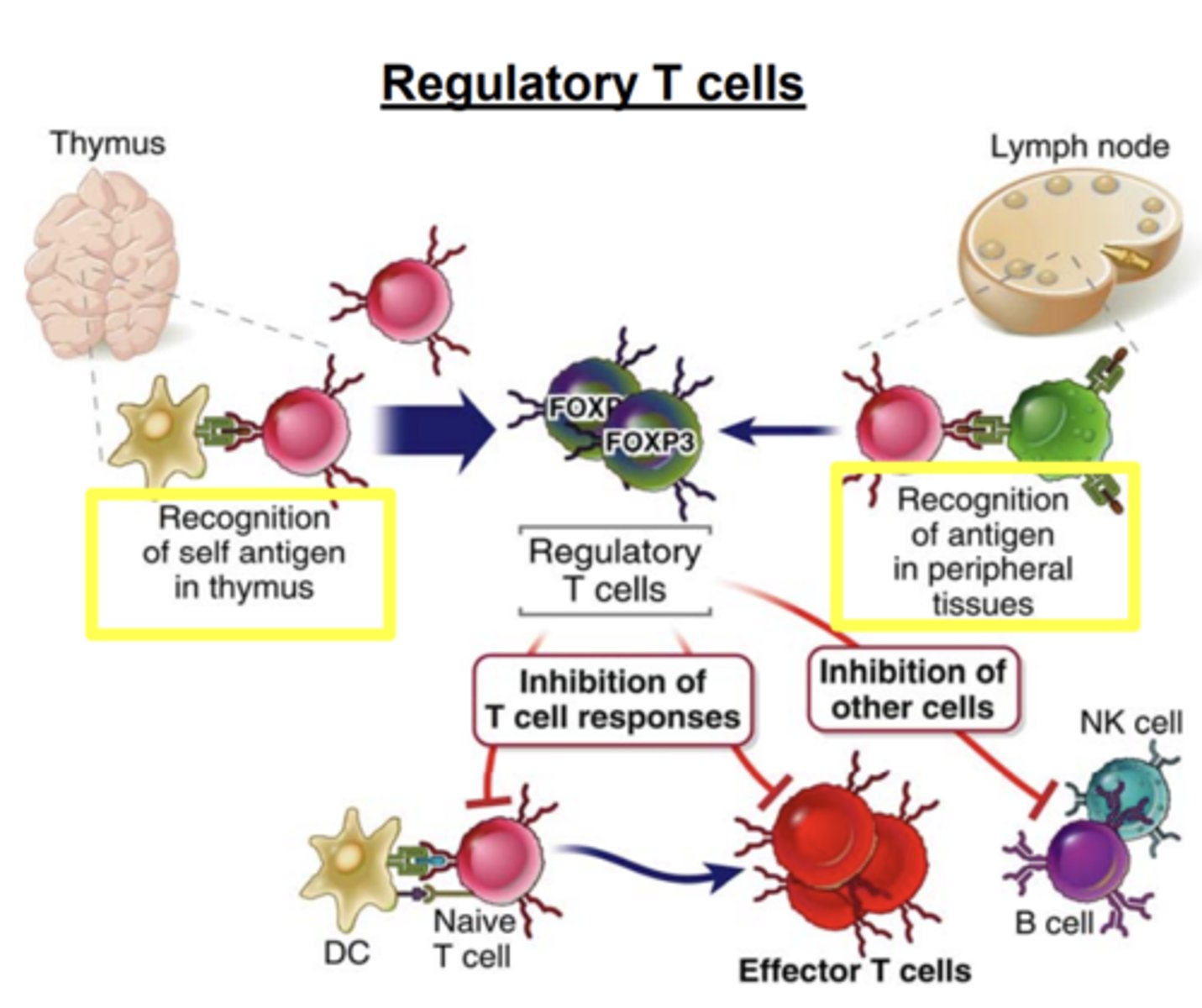
What do regulatory T cells inhibit? How do they inhibit it?
inhibit T cell responses, mainly by inhibiting the stimulatory ability of DCs, and also by suppressing T cell activation
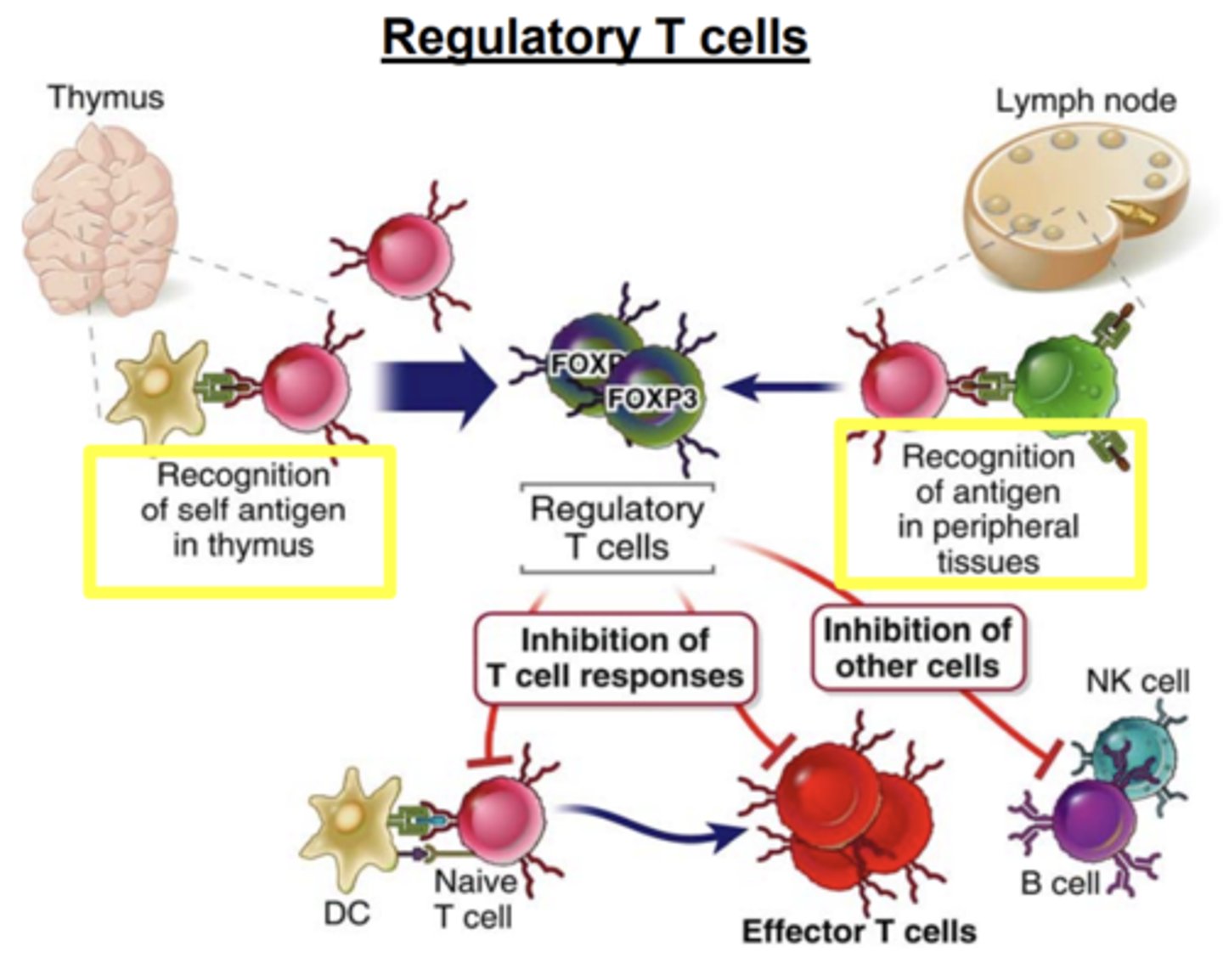
Tregs may also suppress ______________________ activation and inhibit the proliferation and differentiation of _____________
- B cell activation
- NK cells
What is T cell exhaustion
the response of T cells to chronic antigen stimulation
Chronic antigen stimulaton leads to
progressive loss of function:
- loss of their ability to produce IL-2 and TNFα
- loss of high proliferative capacity and cytotoxic potential, and eventually leads to their deletion