Shoulder Disorders
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
downward, tip, sprain, pain, tender, AC, crossbody
Acromioclavicular (AC) Joint Injuries: Mechanism and S/S
Mechanism of Injury
-Direct __________ blow to the ___ of the shoulder (hit, fall)
-______, subluxation/dislocation/separation
S/S
-____ to top of shoulder
-_______, swollen __ joint, possible step off
-Decreased ROM
-Positive ___________ test

Grade I
What grade is this AC joint injury?
-Partial tear of the AC ligament
-Contusion/sprain
Grade II
What grade is this AC joint injury?
-Torn AC ligament
-Subluxation or partial displacement, will see widening of the joint space
Grade III
What grade is this AC joint injury?
-Torn AC/coracoclavicular ligament and capsule
-Complete dislocation
Grade IV
What grade is this AC joint injury?
-Clavicle displaced posterior and buttonholed through trapezius fascia
Grade V
What grade is this AC joint injury?
-Severe displacement of the clavicle with clavicle superior to acromion
Grade VI
What grade is this AC joint injury?
-Distal end of clavicle is locked inferior to the coracoid
x-ray, I-III, sling, ROM, IV-VI, reconstruction
AC Joint Injuries: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis
Clinical
_-___ → normal AC joint width is 1-3 mm
-Treatment: Non-Surgical (Grade _-___)
_____ (2-4 weeks)
Ice
NSAIDs
Early ___ exercises as tolerated
-Treatment: Surgical (Grade __-__ and sometimes III)
Refer to ortho
ORIF with ______________ of coracoclavicular ligament
pain, arthritis, NSAIDs, resection
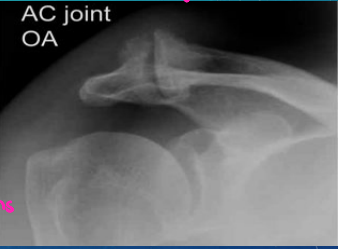
AC Joint Arthritis
-Chronic _____ at the AC joint. One of the first joints to be affected by arthritis
-The pt may report pain with movement across the body or up by the head
-Diagnosis
X-ray evidence of __________ → joint space narrowing and osteophytes
-Treatment
________, injections, and surgical ________ if conservative treatment failed
abduction, external rotation, abduction, internal rotation
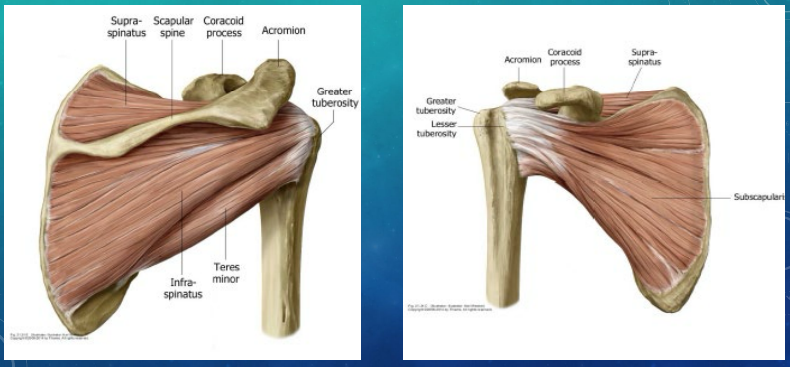
Rotator Cuff Muscles
-Muscles that insert on the greater tuberosity:
Supraspinatus (MC injured) → __________ and external rotation
Infraspinatus → __________ __________ and abduction
Teres Minor → external rotation and __________
-Muscles that insert on the lesser tuberosity:
Subscapularis → _______ __________ and assisting in abduction and adduction
overhead, impingement, pain, overhead, Neer’s, night, pain, no, weakness
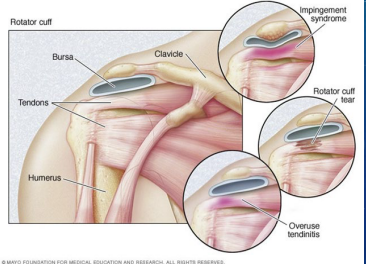
Rotator Cuff Tendinosis and Subacromial Bursitis
-Mechanism of injury:
Repetitive ___________ activity, acute trauma/injury, ____________ syndrome
-S/S:
Shoulder _____ especially with ___________ activity
Possible + Painful arc sign, _______’_, and Hawkins
Occasional _______ time pain
Limited AROM d/t _____ (PROM > AROM) → __ muscle atrophy, no or very limited __________
-Treatment:
Rest, ice, NSAIDs
PT, steroid injections
entrapment, acromion, subacromial, repetitive, lateral, abduction, Neer’s, Hawkins
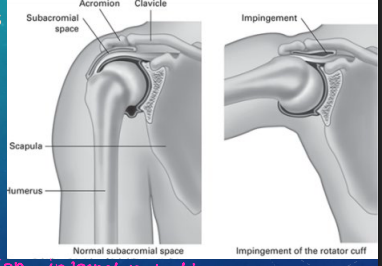
Impingement Syndrome: Background and S/S
-______________ of the RTC muscles/bursa by the ___________
-_____________ impingement is the most common
-Mechanism of Injury:
___________ use (overhead work), trauma, arthritis, and curved acromion
-S/S:
________ shoulder pain that is worse with _________ and internal rotation
Positive _____’_ and ___________ signs
MRI, NSAIDs, 6-12
Impingement Syndrome: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis:
Clinical
___ to r/o RTC tear if highly suspicious or not improving with treatment
-Treatment:
Rest, ice, ________
PT, steroid injection
Surgery should be considered if the patient has not improved after _-__ weeks
fall, repetitive, impingement, partial, weakness, full
RTC Tears: Background
-Mechanism of Injury
Acute injury → _____ or forceful pull on the arm
Chronic injury → _________ use and irritation or chronic __________
-Types
______ thickness tear → can progress to full thickness tear. The pt will have pain with little to no __________
____ thickness tear → increased pain and weakness
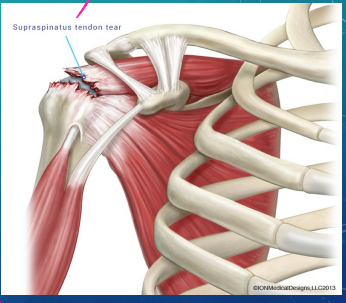
overhead, night, weakness, abduct, externally, atrophy
RTC Tears: S/S
-Moderate to severe pain especially when attempting _________ activity
-_____ pain
-Moderate shoulder muscle ____________ → inability to _____ arm, unable to __________ rotate arm against resistance, and drop arm test positive
-Muscle ________ of shoulder
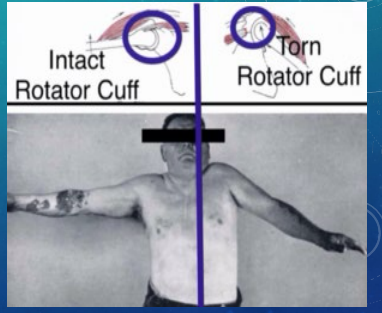
ice, steroid, humeroacromial, elevation, glenoid, surgery
RTC Tears: Treatment
-1st line → rest, ___, NSAIDs, PT
-2nd line → ______ injections
-X-ray → show reduced _____________ space; superior humeral ________ in comparison to the ______ possible
-Ortho referral → may need _______ if the pt fails conservative treatment within 6 months or they have a complete tear
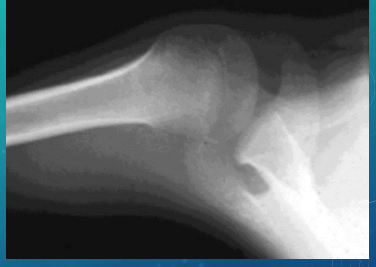
active, passive, >, DM, injury
Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder): Background
-Global limitation of _____ and _________ shoulder ROM
-Epidemiology:
5th-6th decades
F _ M
__ and other systemic illness are at an increased risk
-Etiology:
Idiopathic
Secondary to shoulder ________
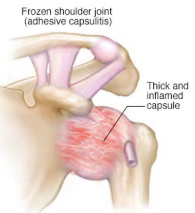
2-9, pain, stiffness, adhesive, 4-12, loss, improving, return
Adhesive Capsulitis: Staging
-1st Stage/Painful Phase (_-_ months)
Diffuse, severe, and disabling shoulder ____ and increasing ___________
-2nd Stage/Intermediate (_________) Phase (_-__ months)
Stiffness and severe ____ of shoulder ROM
Pain gradually ___________
-3rd Stage/Recovery Phase (lasts up to 2 years)
Gradual _______ of ROM (often incomplete recovery)
Pain resolves
NSAIDs, PT, surgery
Adhesive Capsulitis: Treatment
-Acetaminophen/________
-Home exercises and __
-Steroid injections
-________ → if conservative measures fail (after 12 months)
overuse, anterior, biceps, proximal, distal
Biceps Tendinitis: MOI and S/S
-Mechanism of Injury:
Frequent pulling, lifting, reaching, throwing
__________ injury
-S/S:
__________ shoulder pain that is aggravated by lifting, pulling, and overhead activity
Radiation over ______
TTP over ________ (bicipital groove) or _______ tendon
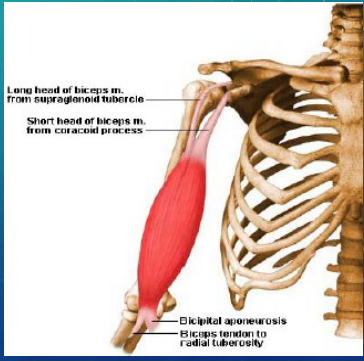
Speed’s, MRI, rupture, thickening, rest, steroid
Biceps Tendinitis: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Special tests (proximal tendon):
______’_ and Yergason’s tests
-Diagnosis:
Clinical
US or ___ if concerned about ______ or RTC injury. Will show _________ and tenosynovitis of the tendon
-Treatment:
1st line = ____, ice, NSAIDs, PT
______ injections are also an option, but they aren’t done very often
degeneration, contracted, pop, swelling, Popeye, squeeze
Bicep Tendon Rupture
-Mechanism of Injury
Chronic irritation/_____________
Sudden load to ___________ bicep → catching heavy object, shoveling
-S/S
“___”, pain, ecchymosis, __________
Proximal tendon = _________ deformity, which is only present in the rupture of the long heads
Distal tendon = rarely any deformity, bicep ________ and hook tests
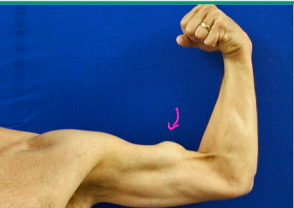
MRI, rest, ortho, asap
Bicep Tendon Rupture: Diagnosis and Treatment
-Diagnosis:
Clinical
US or ___, especially if the patient is considering surgery
-Treatment:
Ice, compression, ____
Proximal tendon = non-urgent _____ referral
Distal tendon = ortho referral ____
compression, upper, brachial plexus, injury
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
-_____________ of neurovascular structures supplying the _____ extremity
_______ ________ is the most common
Subclavian artery and vein are the least common
-Pathogenesis:
Developmental abnormalities → anomalous or cervical rib, muscular anomalies
_______ → hyperextension/flexion of the neck
Predisposing physical activities
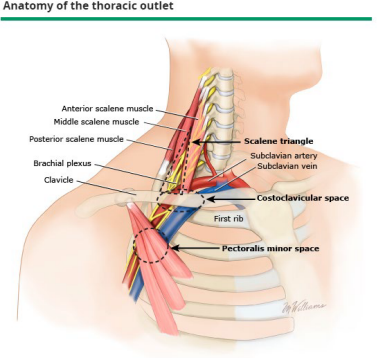
weakness, raising, neurogenic, ultrasound, PT, anticoagulation, surgery
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
-S/S
Pain, numbness, ___________
Swelling
Provoked by _________ arm above head for 60 seconds
-Diagnosis
Perform thorough neuro/vasc exam
Electrodiagnostic eval → __________ (brachial plexus)
Vascular studies → duplex ______________
CXR → bony abnormalities
-Treatment
Neurogenic → __ and NSAIDs, surgery if fail non-operative treatment
Venous → _____________/thrombolysis; occasionally surgery
Arterial → _______ is the most common treatment
abducted, posterior, abducted, resists, axillary
Anterior Shoulder Dislocation
-Most common dislocation
-Mechanism of Injury:
Blow to _________, externally rotated, and extended arm
Blow to __________ humerus or fall on outstretched arm (less common)
-S/S:
__________ and externally rotated arm (elbow pointing out)
_______ all movement
Prominent acromion → “squared off” shoulder (positive Sulcus sign)
Evaluate _______ nerve and vasculature
X-ray, subcoracoid, subglenoid, Hill-Sach’s, Bankart
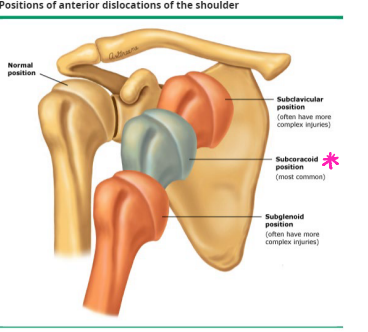
Anterior Shoulder Dislocation: Diagnosis
-_-___ (axillary and scapular Y view)
Humeral head in ___________ (most common)
Subclavicular or ___________ position
-Associated fractures
____-_____'_ Deformity → cortical depression in the humeral head (groove fracture)
Bony _______ Lesion → bony vs soft tissue, disrupted glenoid labrum with or without bony avulsion
Greater tuberosity fracture
-MRI if concerned about soft tissue injury
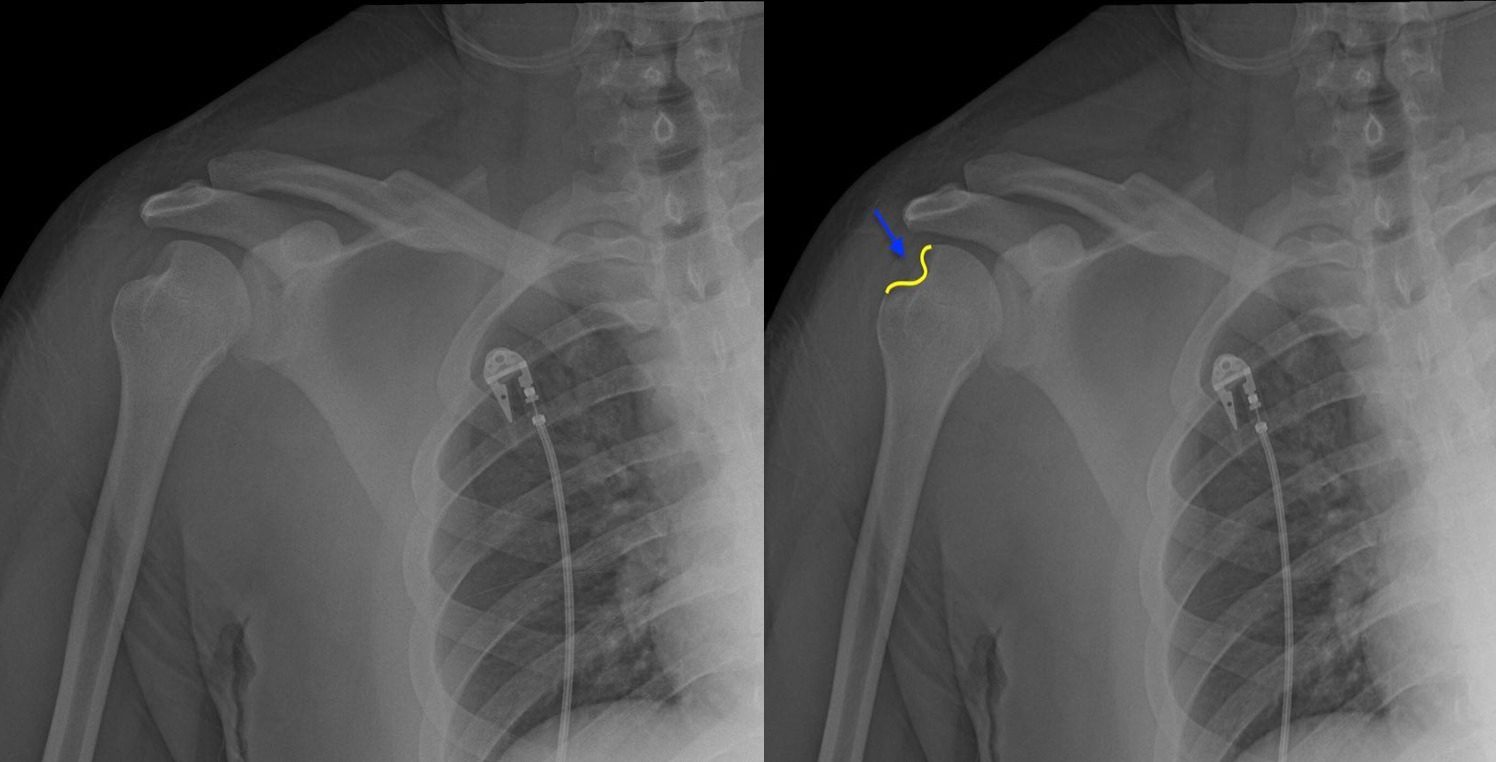
Hill Sach’s Deformity
What deformity is shown in this xray?
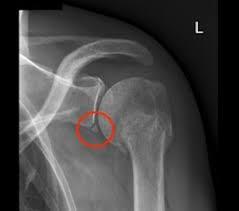
Bony Bankart Lesion
What lesion is shown in this xray?
reduction, post, Milch, traction, sling, swathe, ROM, Bankart
Anterior Shoulder Dislocation: Treatment
-Immediate ___________ with ____ reduction x-ray
-Reduction techniques:
Scapular manipulation, external rotation, _____ technique, Stimson Technique (least traumatic), and _______ countertraction
-Immobilized with a _____ and _______ 2-4 weeks
-Start ___ exercises at 2 weeks
-________ lesions typically require surgery
anterior, adducted, seizure, electric, posterior, flattening, unable, x-ray
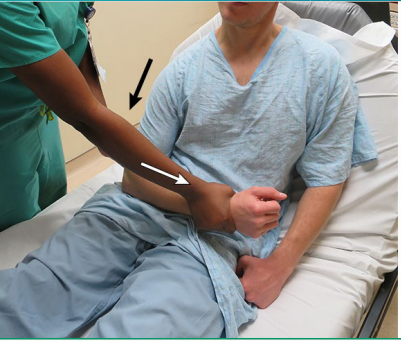
Posterior Shoulder Dislocation (Rare)
-Mechanism of Injury
Blow to ________ shoulder
Axial load of an ___________ and internally rotated arm
Violent muscle contractions → ________ or _______ shock
-S/S
Prominence of ________ shoulder with anterior _________
Prominent coracoid
Adducted and internally rotated arm
________ to externally rotate
-Diagnosis → _-___
Light bulb sign
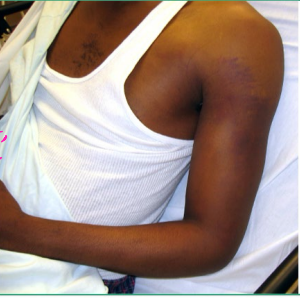
reduction, adducted, internally
Posterior Shoulder Dislocation: Treatment
-__________ and immobilization
Axial traction on ___________ arm with elbow flexed, apply traction and __________ rotate
-X-rays before and after reduction, recheck neurovascular status too
irreducible, greater, Bankart, instability
Shoulder Dislocations: Indications for Surgery
-___________ dislocations
-Displaced ________ tuberosity fractures
-_________ fractures that create glenohumeral instability
-Recurrent __________ or activity limitations
anatomical, greater, older, >, falls, dislocations
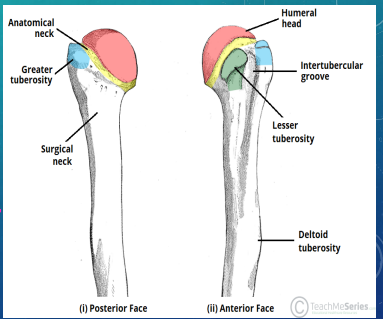
Proximal Humerus Fractures: Background
-Anatomy:
__________ neck, surgical neck, _________ tuberosity, and lesser tuberosity
-Epidemiology:
_______ adults ( > 60)
F _ M
-Mechanism of Injury:
____ (most common)
Direct blow
Violent muscle contractions
______________
pain, ecchymosis, adducted, axillary, Neer
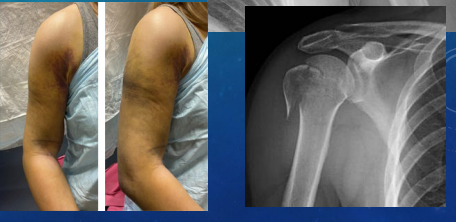
Proximal Humerus Fracture: S/S and Diagnosis
-S/S:
____, swelling, __________
Arm _________ against body
_______ artery and nerve may be injured, so be sure to check the pt’s neurovascular status distal to the injury
-Diagnosis:
Xray (AP, axillary, scapular Y views) → ______ classification
displaced, immobilization, repeat, 6-12, anatomic, displaced, nerve, open
Proximal Humerus Fractures: Treatment and Surgical Referral
-Treatment: Non-__________ or minimally displaced
____________ (sling), ice, pain meds, and PT
_____ x-rays to monitor for displacement
Healing time is _-__ weeks
-Surgical Referral:
Fractures of ________ neck (risk of avascular necrosis d/t circumflex artery)
__________ or comminuted fractures
_____/vascular injury
______ fracture
Fracture-dislocations

males, females, severe, radial, weakness
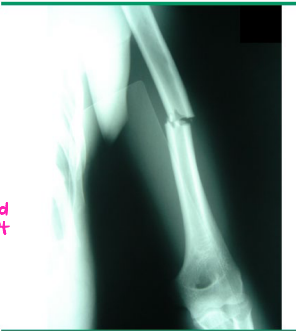
Midshaft Humerus Fractures: Background
-Epidemiology:
______ in 3rd decade → high velocity trauma
________ in 7th decade → low velocity falls
-S/S:
_______ arm pain, swelling, ecchymosis
_______ nerve most commonly injured → may see wrist, finger, and thumb extension ___________ and wrist drop
-Diagnosis:
X-ray
ortho, splint, functional, cast, ORIF, 10-14
Midshaft Humerus Fractures: Treatment
-Refer to ______
-Non-operative options:
Initial → sugar tong _____ or sling and swathe
Transverse → _________ brace
Nonsurgical displaced oblique or spiral → hanging ____ or functional brace
-Operative:
____ for open fracture, vascular, or brachial plexus injuries with pain and weakness
-Healing time = __-__ weeks
