Electronegativity
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What does electronegativity mean?
The relative tendency of an atom in a covalent bond in a molecule to attract electrons in a covalent bond to itself.

Electronegativity and boiling point
Boiling point increases with increased electronegativity.
Does electronegativity increase or decrease across a period?
Increases
Why does electronegativity increase across a period?
Nuclear charge increases (because the number of protons increases) and the atomic radius decreases as the electrons in the same shell are being pulled in more
Therefore, the tendency to attract shared pairs of electrons increases, thereby increasing electronegativity.
Does electronegativity increase or decrease down a group
Decrease
Why does electronegativity decrease down a group?
- The distance between the nucleus and the outer electrons increases
- The shielding of inner shell electrons increases.
- Therefore, the tendency to attract shared pairs of electrons decreases, thereby decreasing electronegativity.
Why is C-Cl less reactive than C-Br?
Cl has a higher electronegativity than Br due to Cl's smaller size.
Electronegative atoms hold electrons more tightly, thus increasing the strength of the bond.
Therefore more energy is required to break the C-Cl bond
What is a polar covalent bond?
A covalent bond in which there is an unequal distribution of electrons
When do polar covalent bonds form?
When the elements in the bond have different electronegativities.
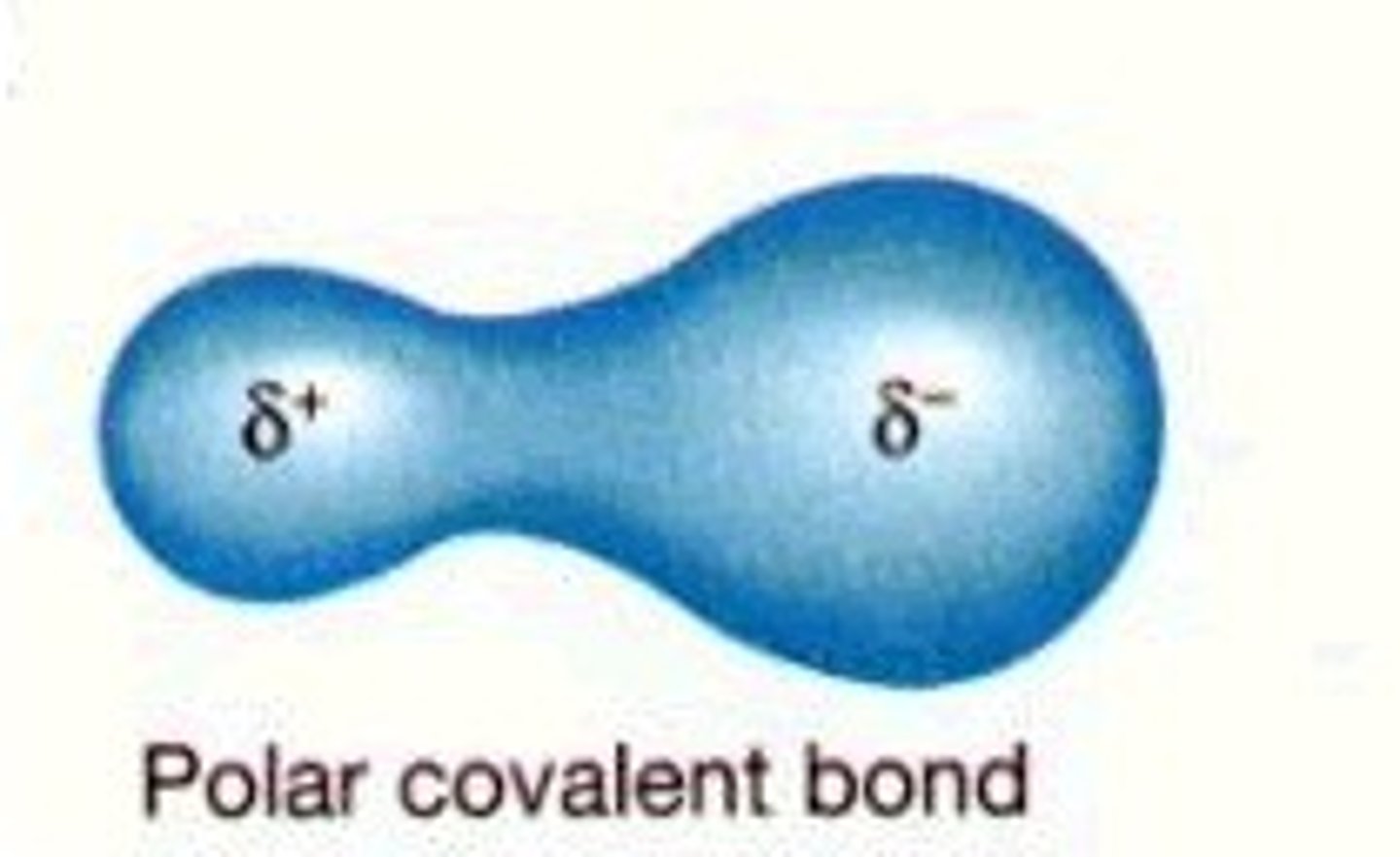
Formation of a permanent dipole?
A polar covalent bond has an unequal distribution of electrons in the bond
This produces a charge separation (a dipole), making δ+ and δ- ends.
What are symmetric molecules?
Molecules with all the bonds being identical (no lone pairs)
Are symmetric molecules 'polar'?
No
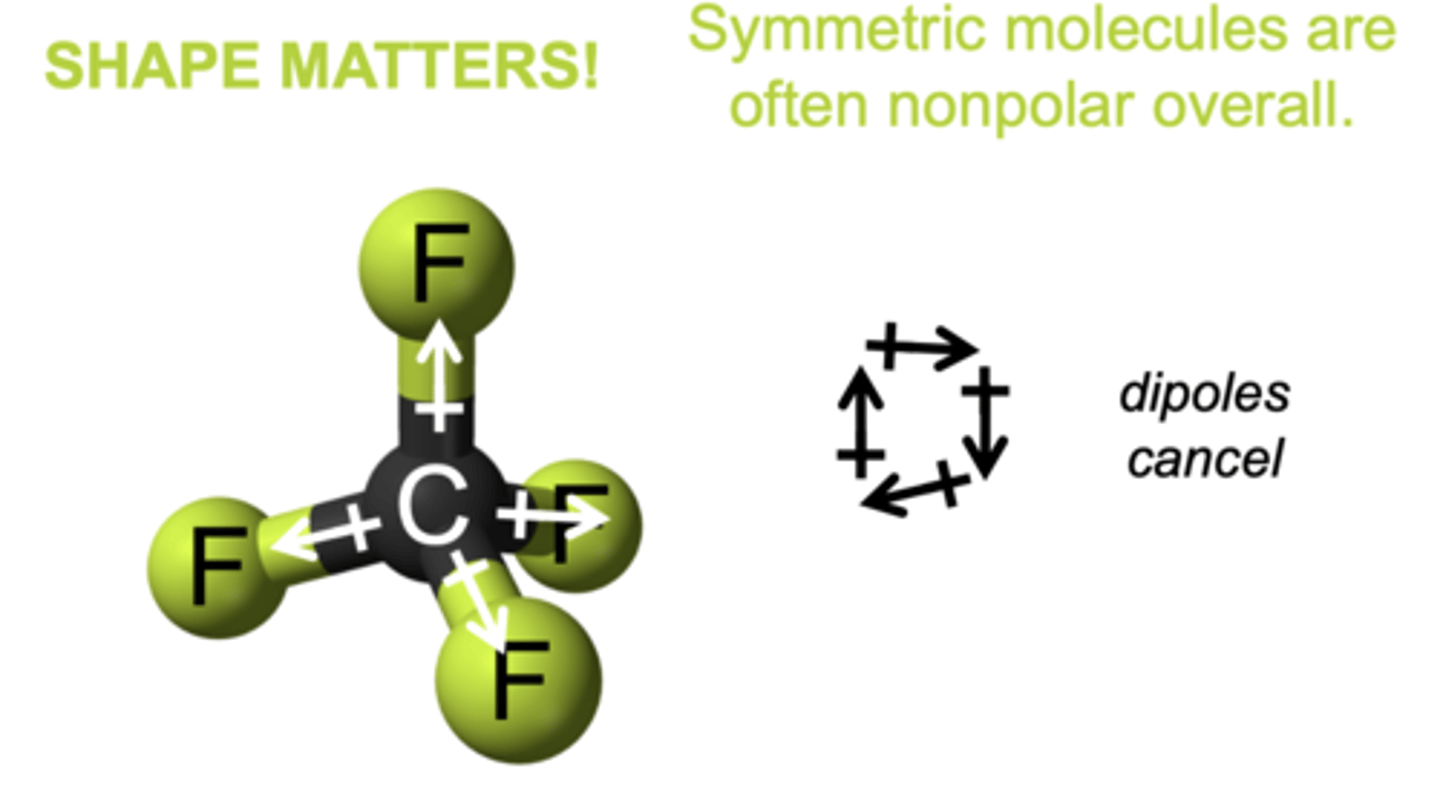
Why aren't symmetric molecules polar?
The symmetry of the molecules leads to the individual dipoles on the bonds 'cancelling out', so the molecule is non-polar overall.
Is CO₂ polar or non-polar?
It is a symmetrical molecule, so it is non-polar
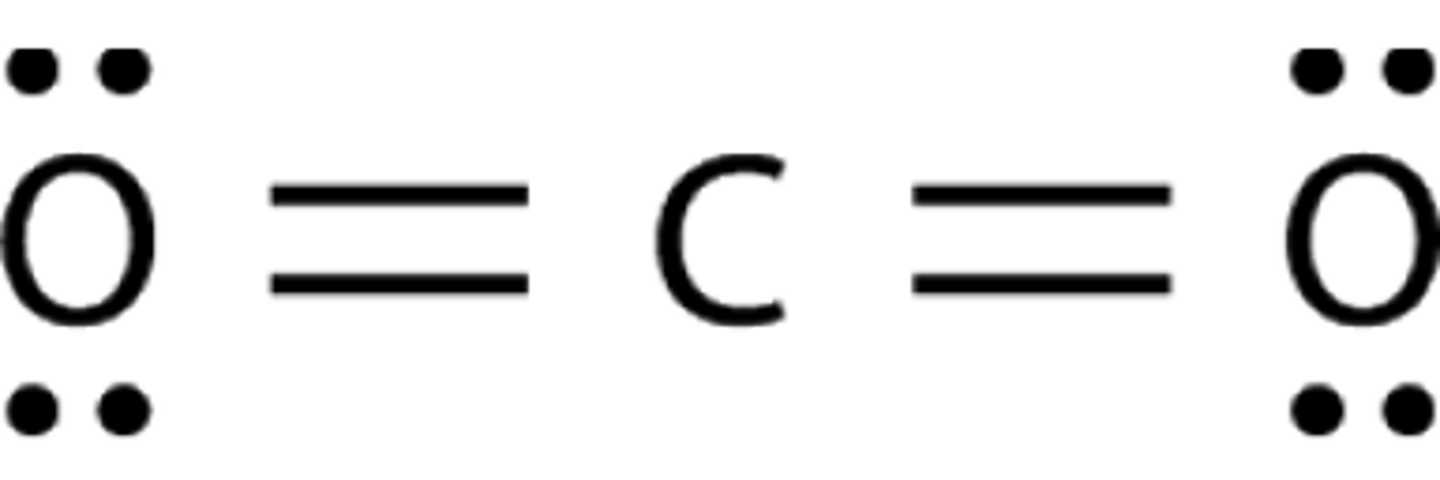
Explain why SO₂ and SO₃ have polar bonds, but only SO₂ has polar molecules.
For a molecule to be polar, it must have polar bonds and it must have asymmetry in its shape, such that the dipoles do not cancel out
SO₂ and SO₃ both have S=O bonds, which are polar because O is more electronegative than S.
SO₂ has a non linear shape, so its dipoles do not cancel, resulting in a polar molecule
However, the trigonal planar shape of SO₃ is symmetrical, resulting in the dipoles cancelling, so the molecule is non-polar overall.