Biochemistry Amino Acid
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Ala, A
Alanine
Arg, R
Arginine
Asn, N
Asparagine
Asp, D
Aspartic Acid
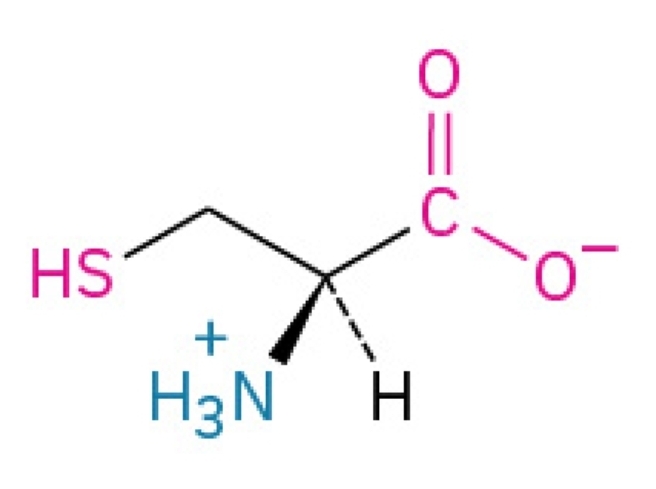
Cys, C
Cysteine
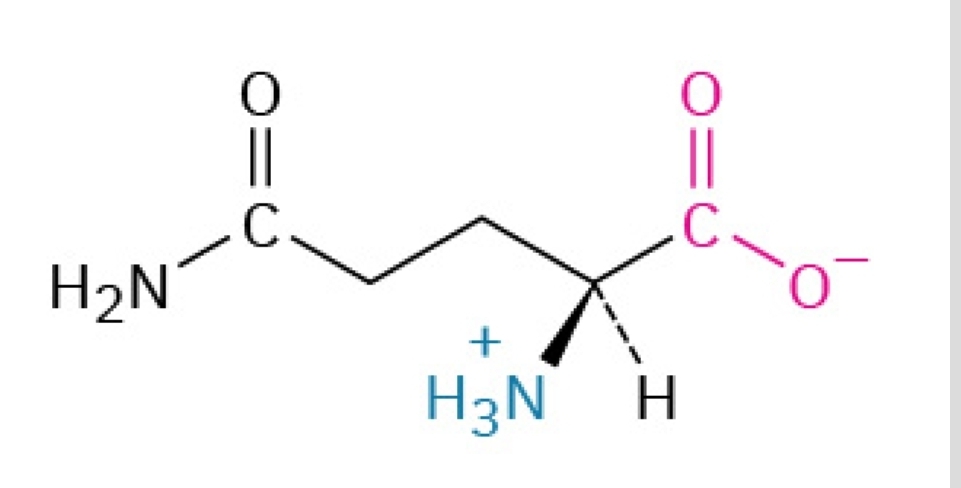
Gln, Q
Glutamine
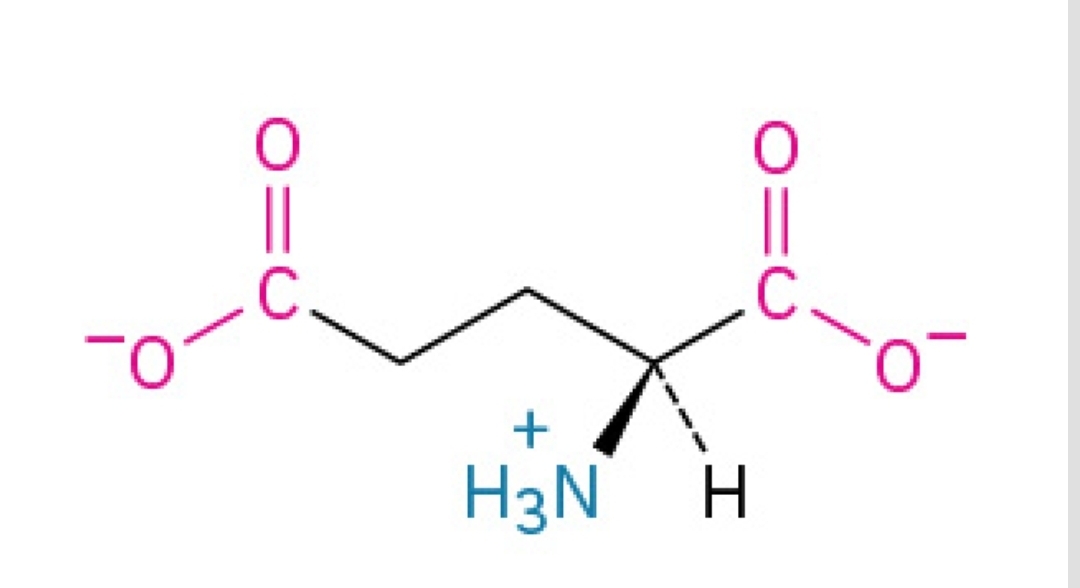
Glu, E
Glutamic Acid
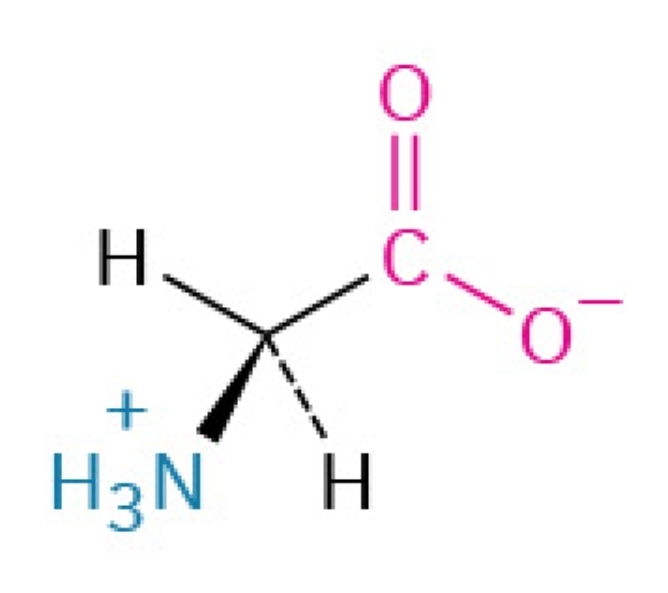
Gly, G
Glycine
His, H
Histidine
Ile, I
Isoleucine
Leu, L
Leucine
Lys, K
Lysine
Met, M
Methionine
Phe, F
Phenylalanine
Pro, P
Proline
Ser, S
Serine
Thr, T
Threonine
Trp, W
Tryptophan
Tyr, Y
Tyrosine
Val, V
Valine
Alanine
Non-polar, hydrophobic, nonessential amino acid
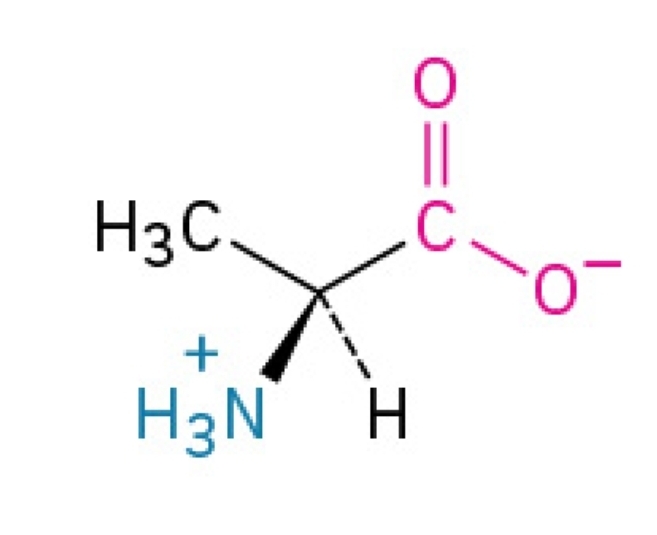
Arginine
Basic, hydrophilic, nonessential amino acid
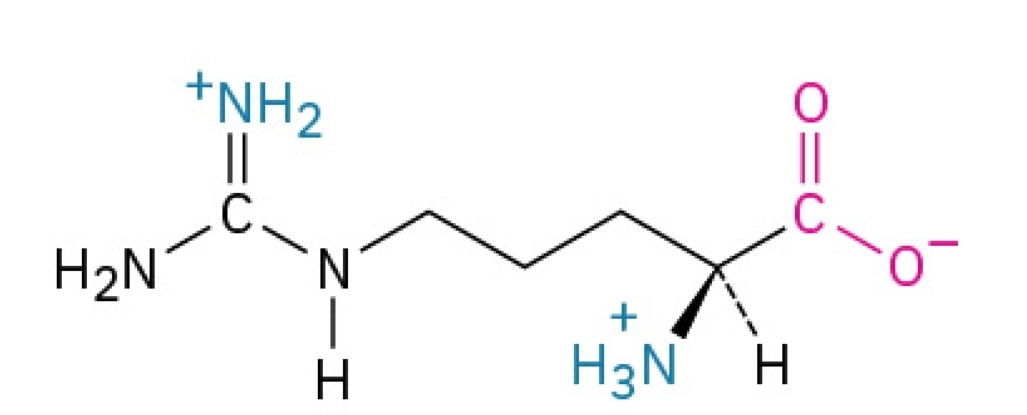
Asparagine
Polar, hydrophilic, nonessential amino acid
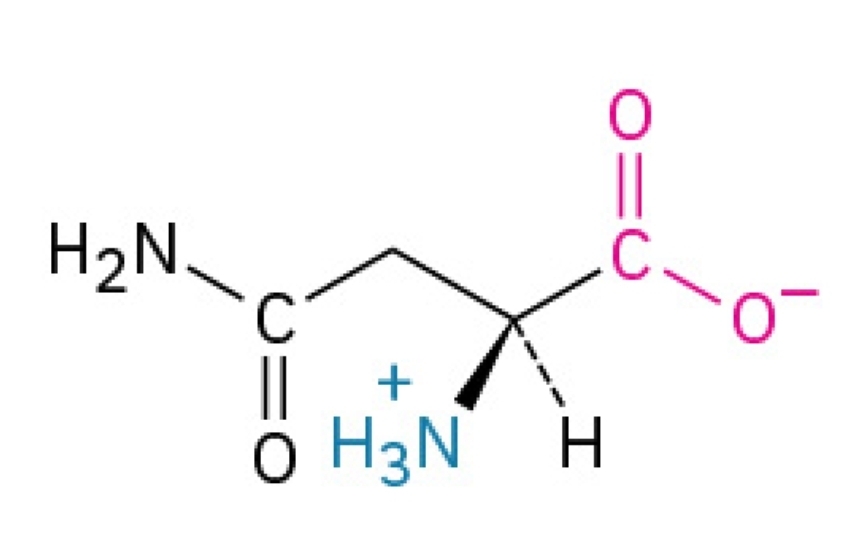
Aspartic Acid
Acidic, hydrophilic, nonessential amino acid
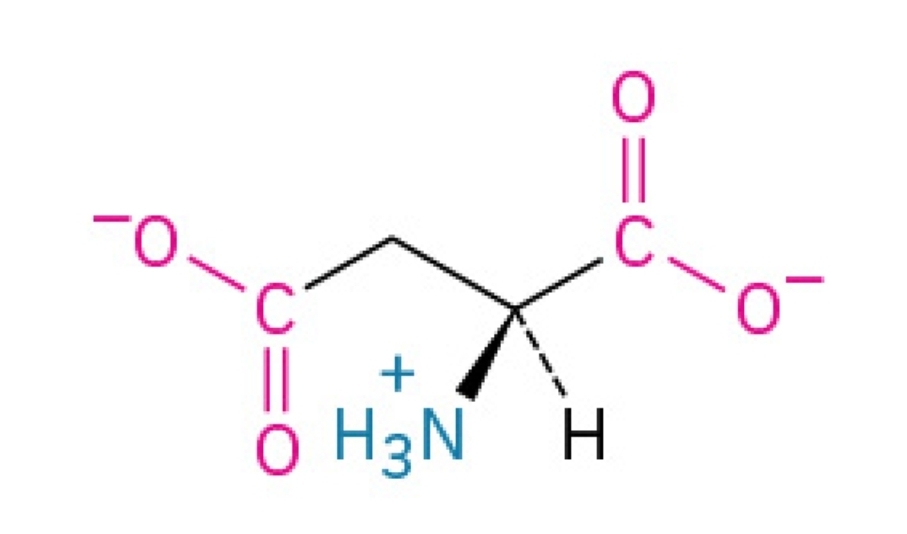
Cysteine
Polar, hydrophilic, nonessential amino acid
Glutamine
Polar, hydrophilic, nonessential amino acid
Glutamic Acid
Acidic, hydrophilic, nonessential amino acid
Glycine
Polar, hydrophobic, nonessential amino acid
Histidine
Polar, hydrophilic, essential amino acid
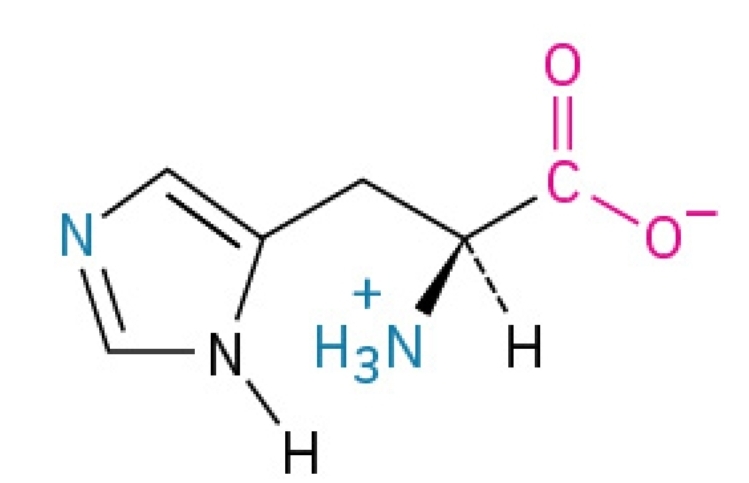
Isoleucine
Non-polar, hydrophobic, essential amino acid
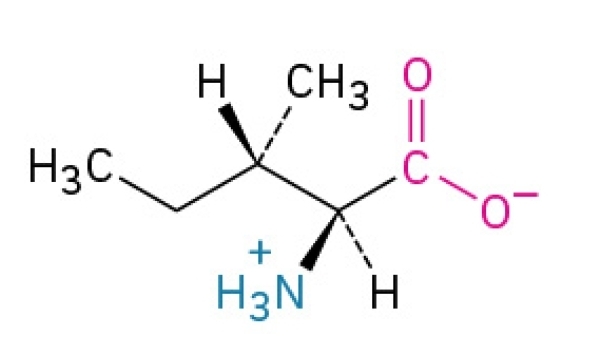
Leucine
Non-polar, hydrophobic, essential amino acid
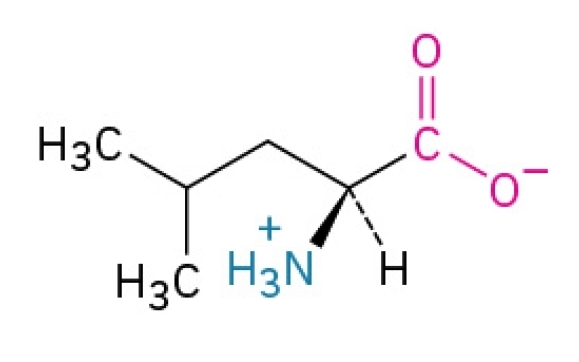
Lysine
Basic, amphipathic, essential amino acid
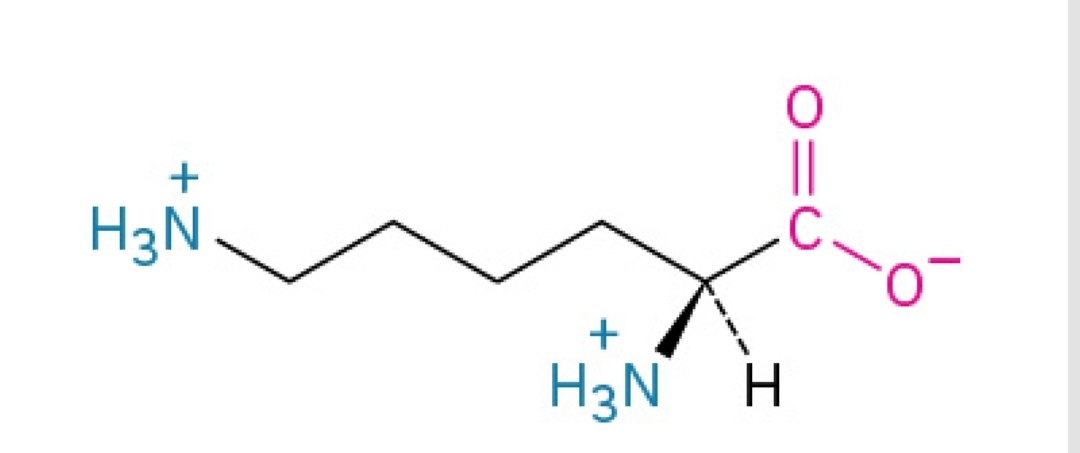
Methionine
Non-polar, amphipathic, essential amino acid
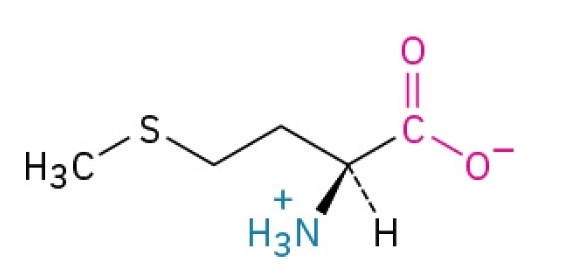
Phenylalanine
Non-polar, hydrophobic, essential amino acid
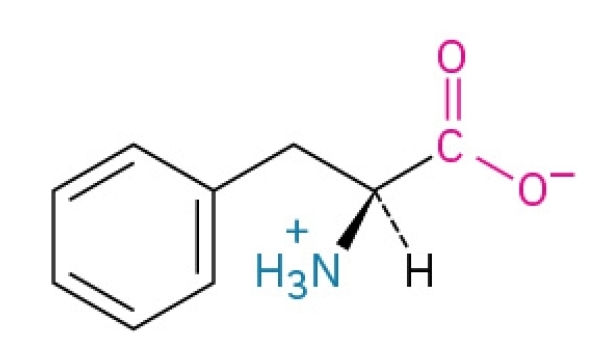
Proline
Non-polar, hydrophobic, nonessential amino acid
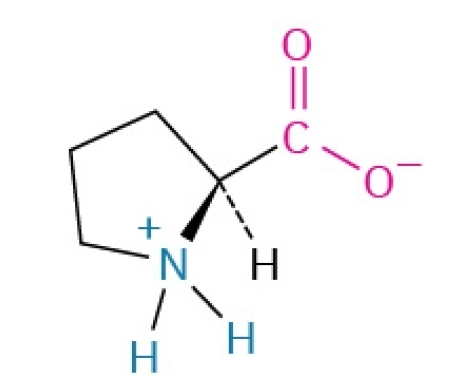
Serine
Polar, hydrophilic, nonessential amino acid
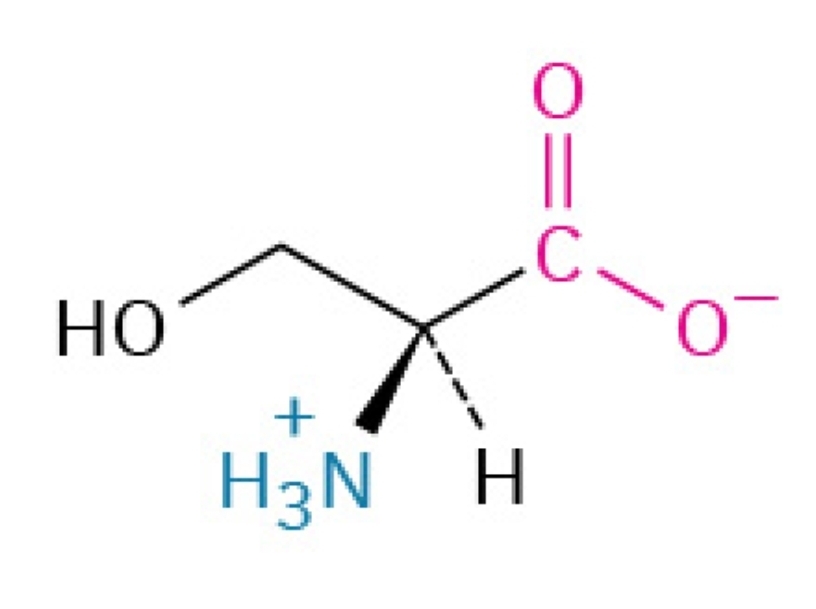
Threonine
Polar, hydrophilic, essential amino acid
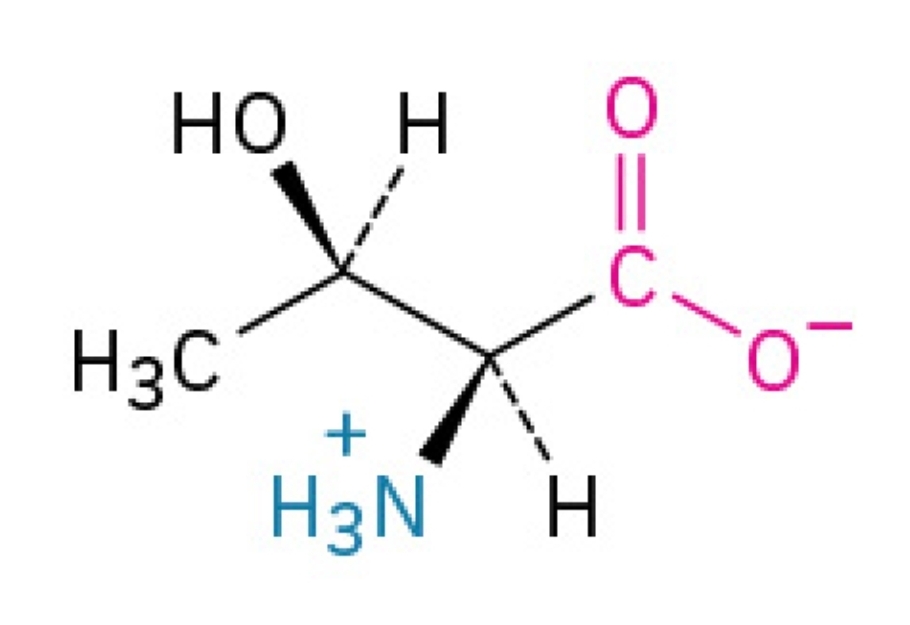
Tryptophan
Non-polar, amphipathic, essential amino acid
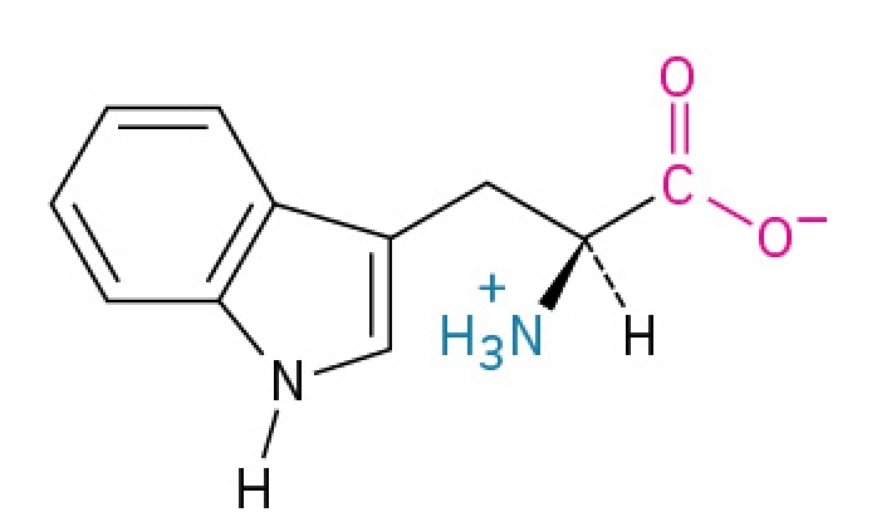
Tyrosine
Polar, amphipathic, nonessential amino acid
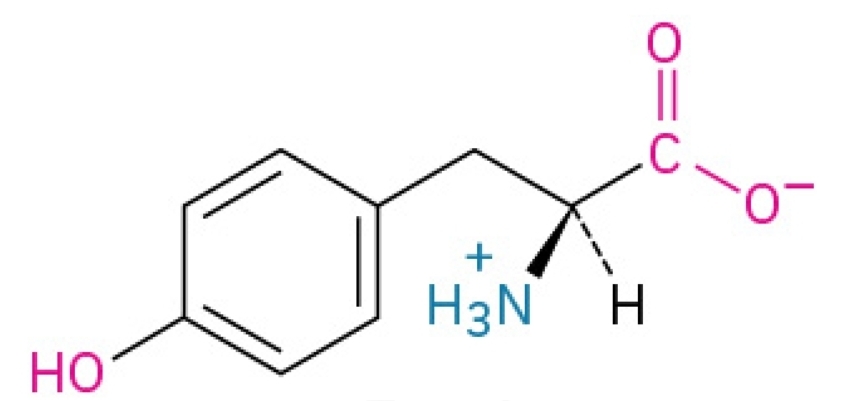
Valine
Non-polar, hydrophobic, essential amino acid
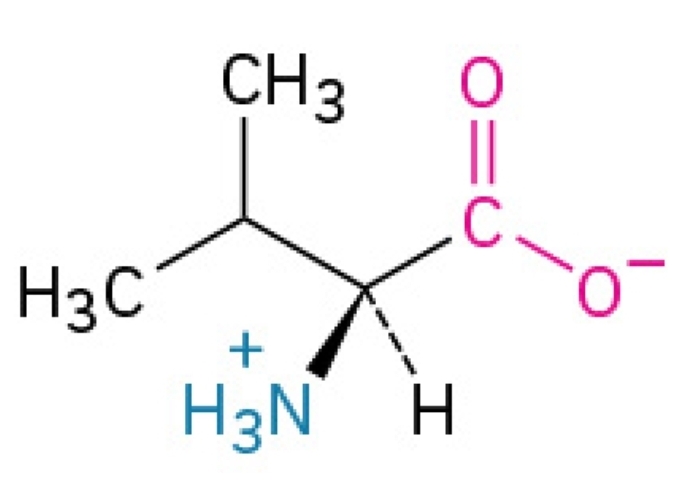
Cationic Form
This form of an amino acid occurs at low pH, where the amino and carboxyl group are protonated, resulting in a positively charged molecule (Gly1).
Zwitterionic Form
This form of an amino acid is the neutral state of an amino acid (Gly0) where the carboxyl group is deprotonated and the amino group is protonated, balancing the positive and negative charges in the molecule.
Anionic Form
This form of an amino acid occurs at high pH, where both the carboxyl group and the amino group are deprotonated, resulting in a negatively charged species (Gly2).
Isoelectric Point (pI)
This value is the pH at which an amino acid or peptide carries no net electric charge, resulting in a neutral state. It is calculated by averaging two pKa values of the side chains. For acidic and basic amino acids, these pKas are the two most acidic or basic values respectively.
Enantiomers
Nonsuperimposable mirror images of a molecule, are chiral, and present in all amino acids except Glycine.
L-enantiomer
Virtually all amino acids exist in what enantiomer form?
D- and L-enantiomer
What are the two forms of enantiomer amino acids can exist in?
Cysteine
Which amino acid contains a thiol group that can form disulfide bonds?
Serine
Which amino acid has a side chain that can form hydrogen bonds and is classified as polar?
Lysine
Which of the following amino acids contains a positively charged side chain at physiological pH?
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
What is the primary structure of a protein?