Biology S1 T3
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
DNA (2)
a molecule that determines the characteristics of living things
deoxyribonucleic acid
Watson-crick model
Created in 1953 by james watson and francis crick to describe its structure
nucleotides, and what they're made up of (2)
- Basic units of DNA molecule
- phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar and one of four nitrogen rich bases
nucleotide organisation
organisation of nucleotides creates a double helix
uprights of ladder are alternating sugar and phosphate groups
nitrogen rich bases form the rungs
nitrogen rich bases + how they pair (4)
adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine
- different chemical structures and shapes that complement each other
- can only pair up in one way, a characteristic known as complementary base pairing
(A-T, C-G)
chromosomes (2)
long, thin, thread like structures found in the nuclei of all cells in the human body that contain a nucleus
(some chromosomes found in mitochondria)
- one very long DNA molecule wrapped around in proteins
chromosome number (4)
body cells -> 46 chromosomes, half from mother, half from father
gametes have only half as many chromosomes as body cells
out of the 46, two are sex chromosomes, x and y (XX is female, XY is male
other 44 are autosomes, grouped into 22 pairs, these pairs are made up of homologous chromosomes
homologous chromosomes (3)
same length
structure called the centromere in the same position (the point on a chromosomes that connects two chromatids)
genes for particular characteristics at the same location along their length
genes + difference between one gene and the next (3)
sections of DNA arranged along a chromosomes
difference determined by
- order of bases along the DNA strand
- number of bases in that section of DNA
genetic code (2)
order of the bases along the DNA strand
- each gene codes for a specific protein
proteins (1)
- create the structures and perform actions needed for cells to survive, grow and function
proteins may be
- structural (collagen and keratin)
- enzymes (lactase and amylase)
- regulatory (growth hormone and insulin)
replication
process of copying DNA
why is DNA replication needed? (2)
the two new daughter cells contains the same genetic information, or DNA, as the parent celll. if it does not coccur, the cell cycle will not move forward into the next stage and will die
replication step 1 ( 2)
- strands of double helix seperate from eachother,
- bases are then exposed.within the nuclei there are individual nucleotides that are not yet part of the DNA chain
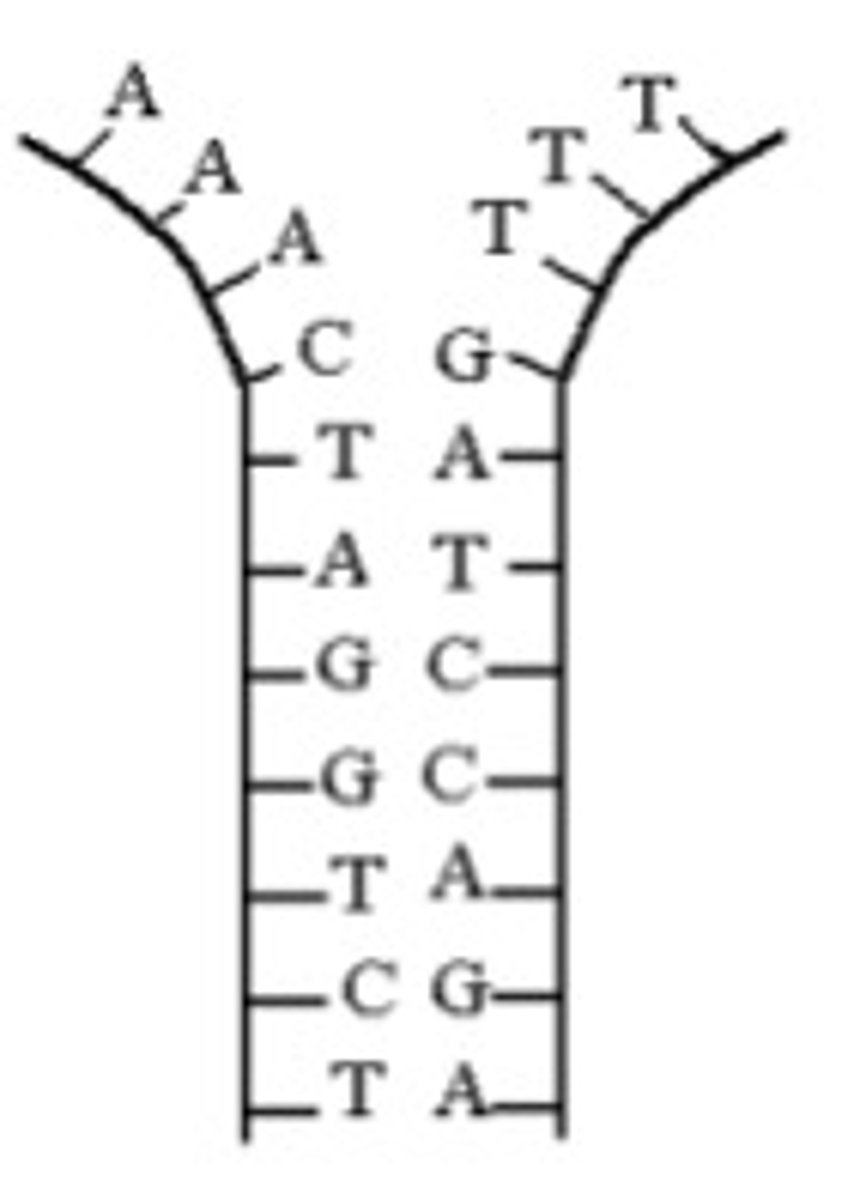
replication step 2 (2)
1) nucleotides pair up with exposed bases using complementary base pairing
2) sugar and phosphate molecules bond with neighbouring nucleotides
3) and new strands of DNA are formed, identical to parent dna
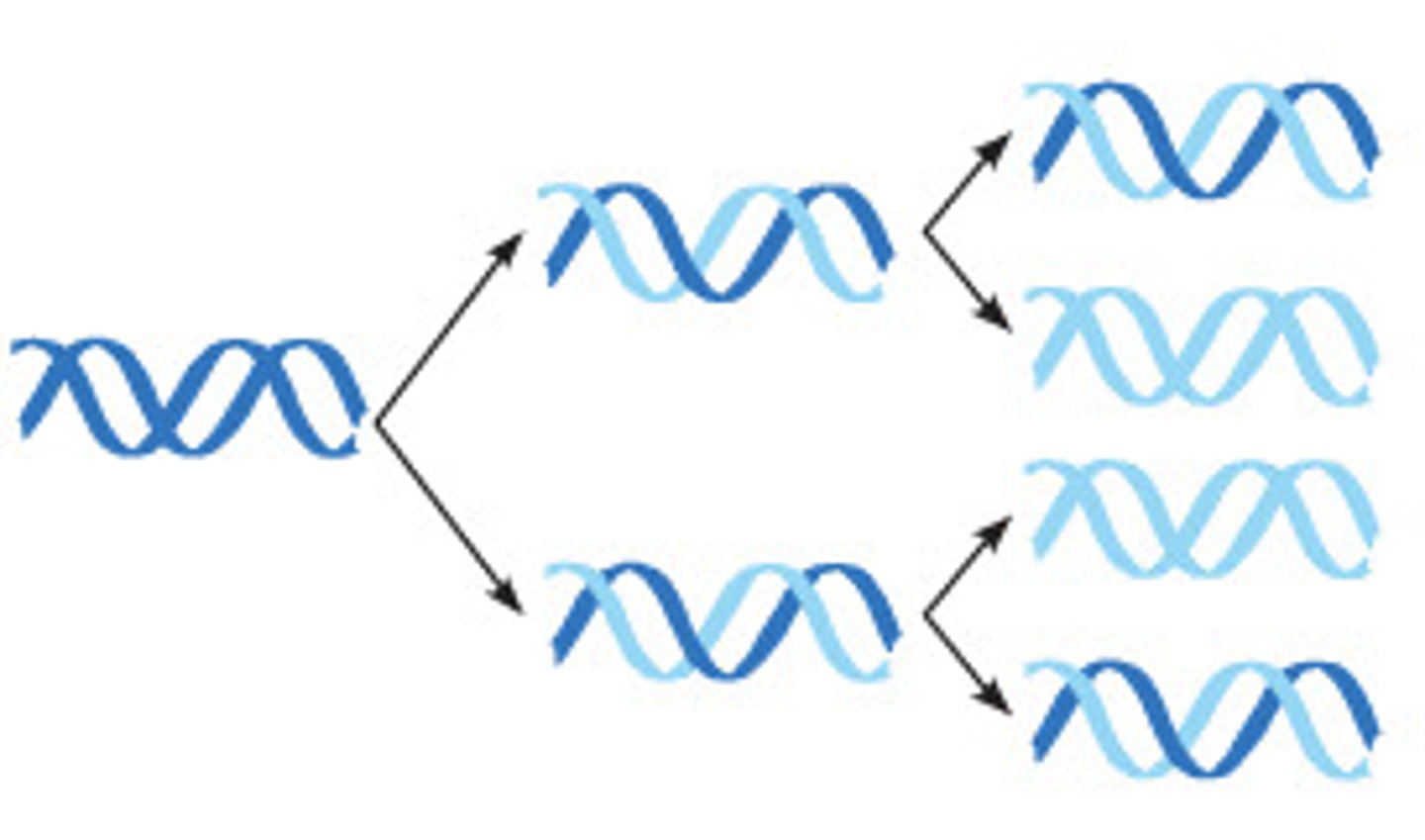
chromosomes after replication
each replicated chromosomes has the two identical DNA molecules which are now chromatids
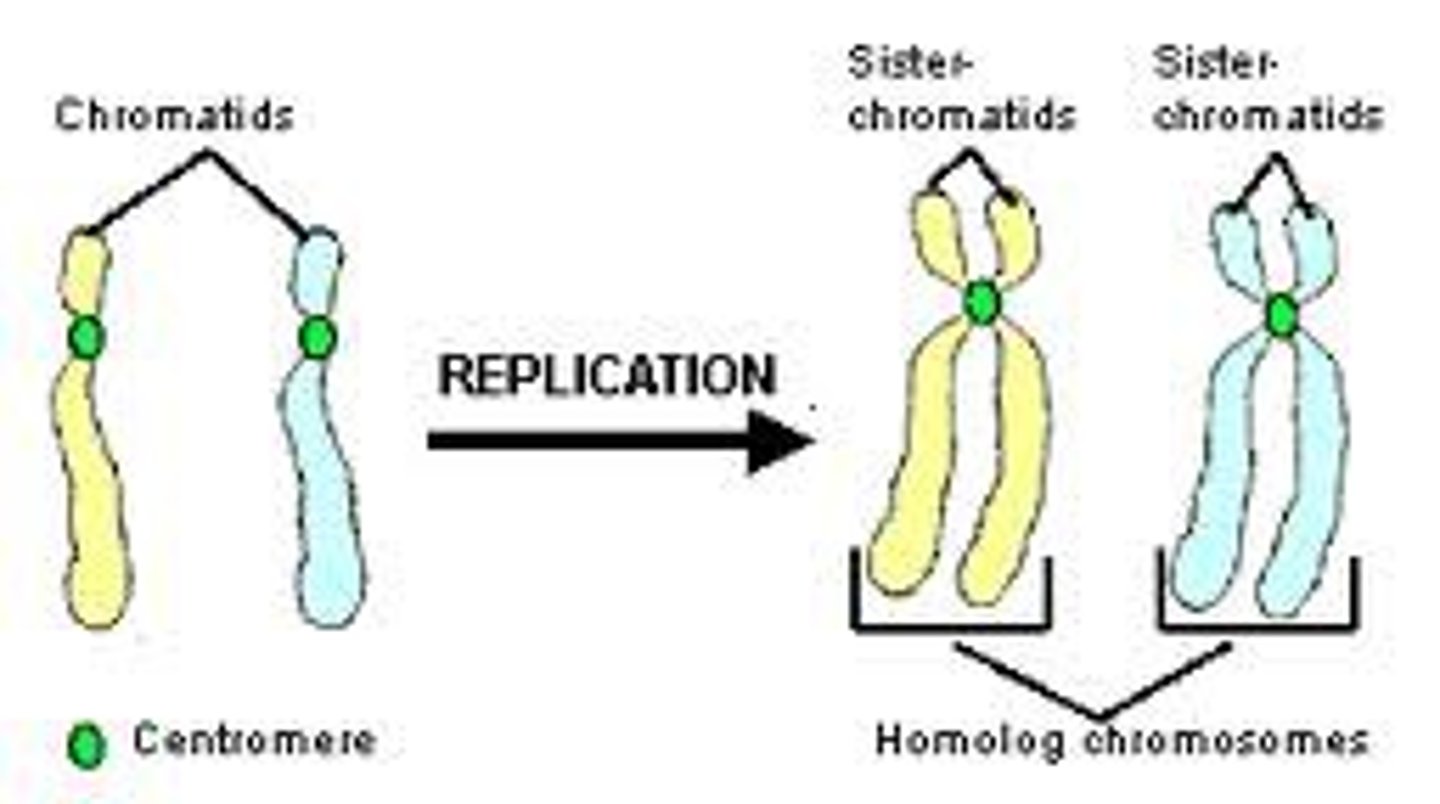
chromatids
two identical chromosomes that split and contain the same genetic material
centromere
Area where the chromatids of a chromosome are attached
in the period between divisions
DNA replicates.
asexual reproduction
- offspring are produced without any union of gametes
- produced through mitosis of particular cells
gametes (2)
sex cells
- ova
produced in the ovaries of the female reproductive system
- sperm produced in the testes of th male reproductive system
chromosomes number in gametes? why?
half the diploid chromosomes.
if each parent passed on a complete set of genetic info, offspring would have 4n chromosomes, next gen would have 8n etc.
by halving number of chromosomes in gametes, the number of chromosomes from generation to generation is kept constant at 2n
one chromosome from each homologous pair must en dup in each gamete that is produced, therefore, the gametes have 23 chromosomes in total
female sex chromosomes
XX, homologous pair
male sex chromosomes
XY, not homologous by behave as a pair in meiosis
sexual reproduction (4)
- creates variation in population, so they can adapt to changes in environment
role of male and female reproductive systems to ensure that
- male and female gametes meet
- fertilisation takes place
- the new individual has the best chances
where does meiosis occur in females
ovaries, producing haploid eggs
where does meiosis occur in males
testes, producing haploid sperm
ovaries
releases eggs (ova)
female sex hormones oestrogen and progesterone
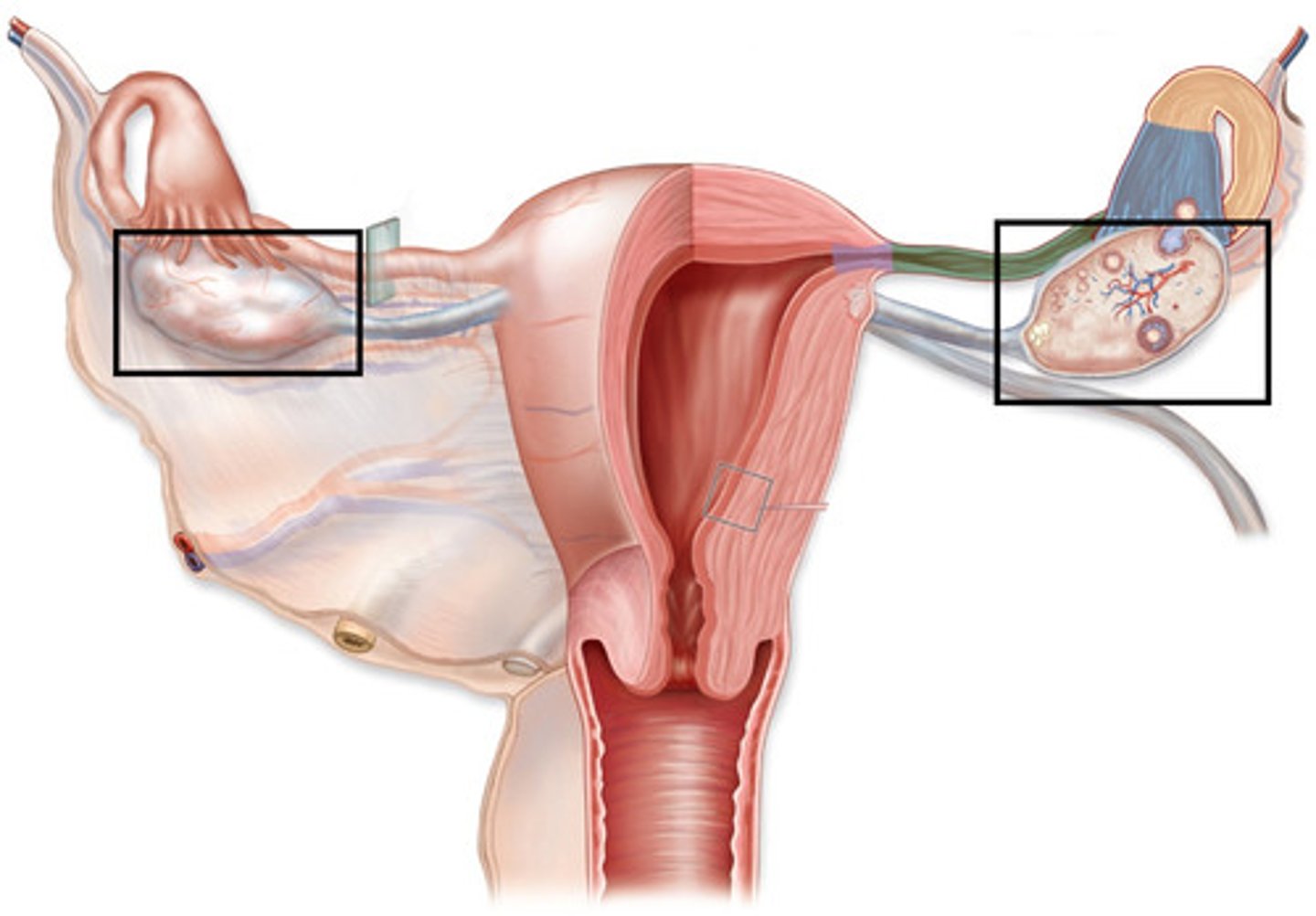
cervix (3)
small opening to the uterus
stretches duriing childbirth
allows passageway fo
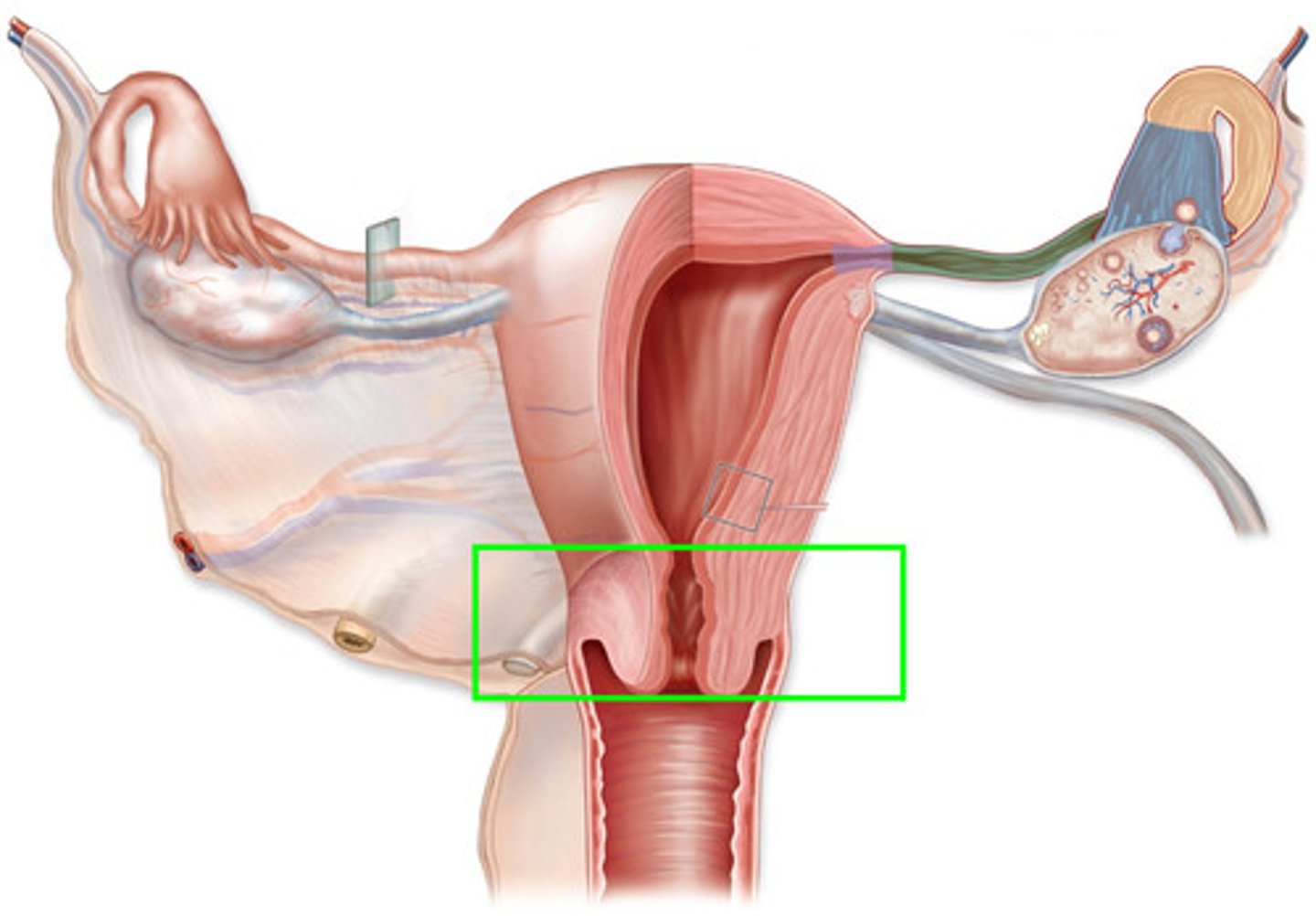
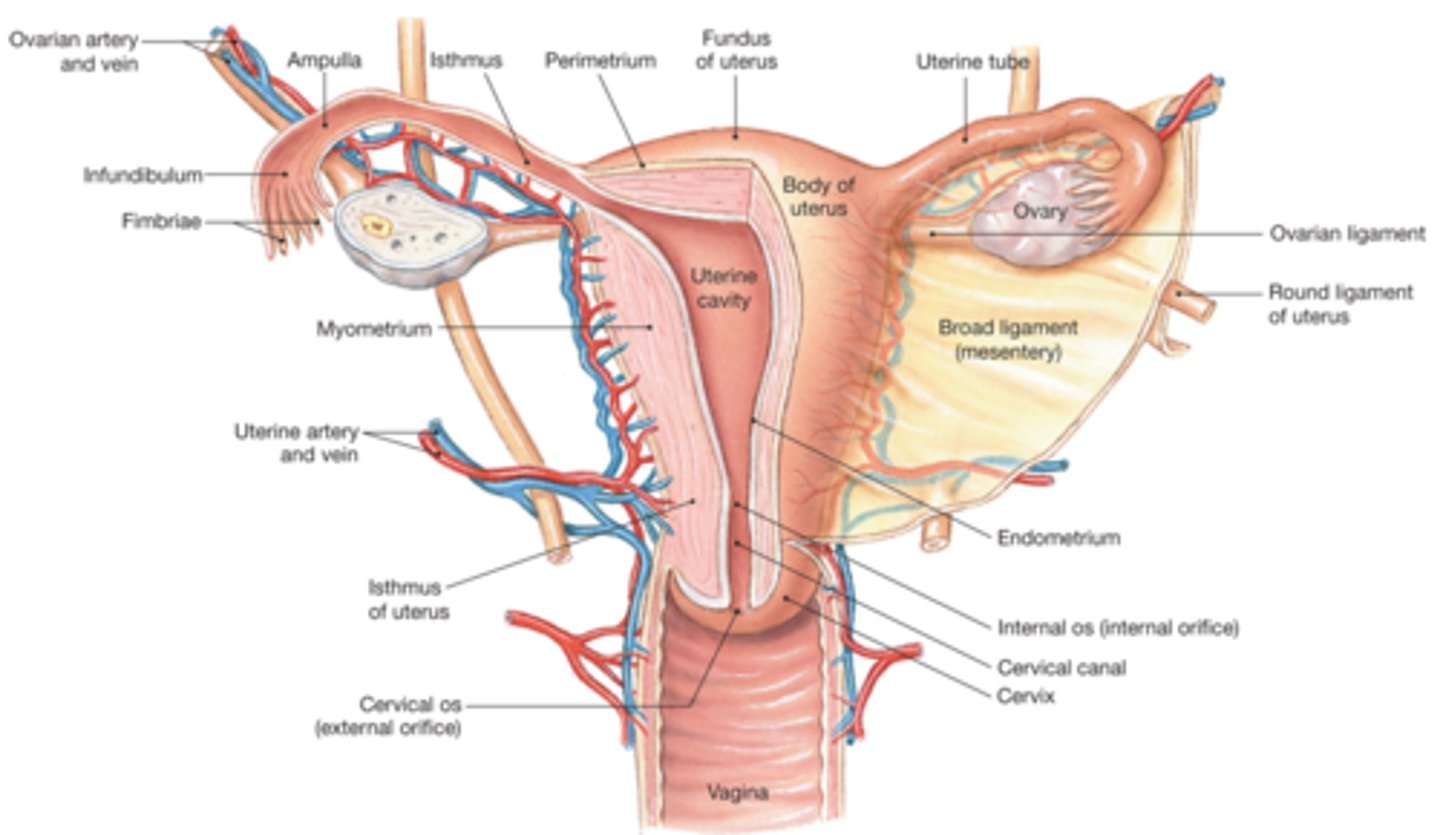
fallopian tube/oviduct(2)
tubes connecting ovaries to uterus
fertilisation occurs here

uterus/womb (2)
the fertilised egg implants itself in the lining of the uterus to continue growing
baby grows and develops for 9 months of preg
vagina (2)
penis enters here during sexual intercourse
sperm must swim from here to fallopian tubes if fertilisation is to occur
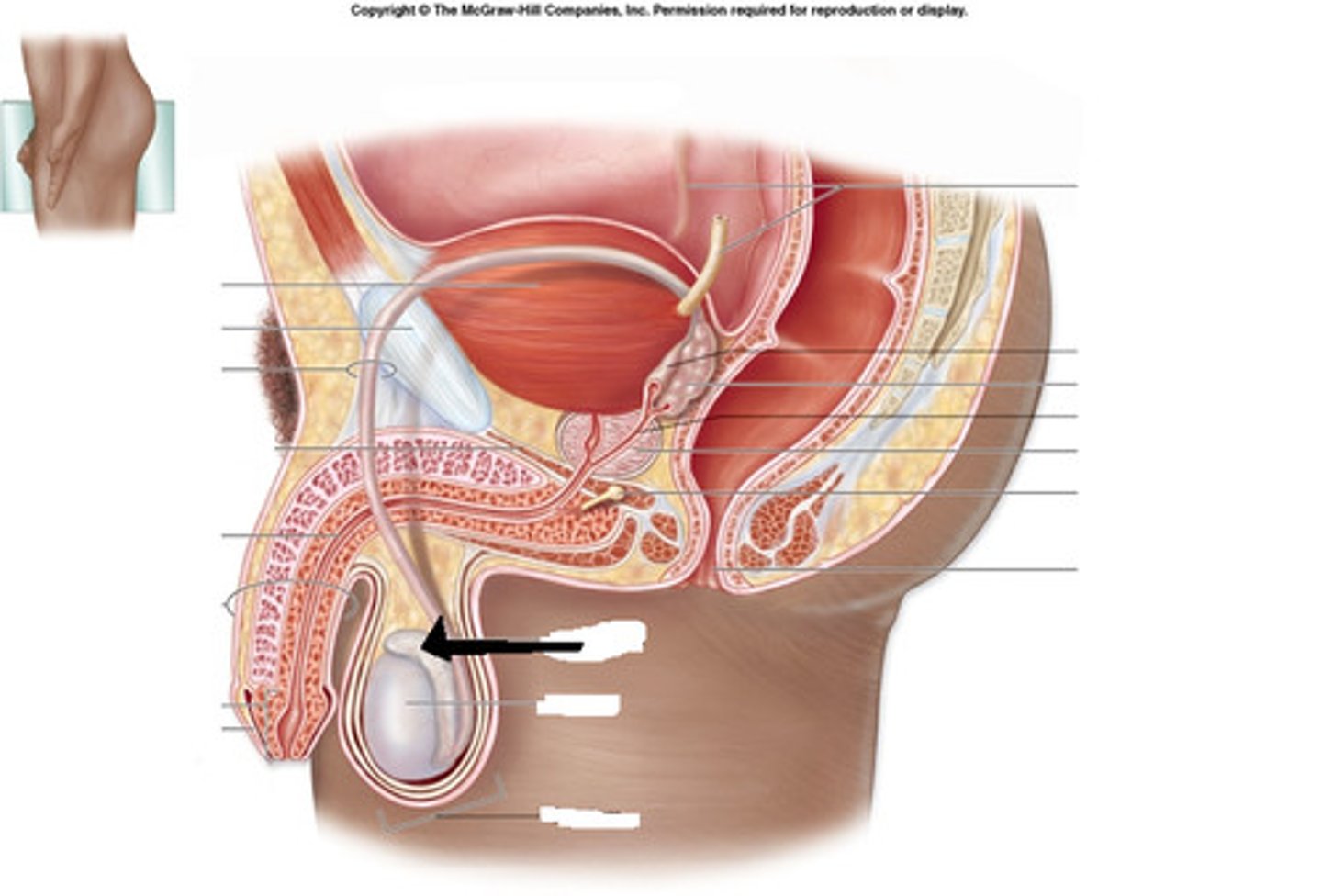
penis (2)
sponge like tissue that fills with blood when male is sexually aroused
tissue expands and is harder than before, causing an erection
urethra (2)
tube running from the length of the penis
empties bladder of urine
allows the passage of semen
testicles/testis (2)
made up of tightly coiled tubes called seminiferous tubules where sperm form and mature
produce male sex hormone testosterone
sperm duct (vas deferens)
connects testes to the penis
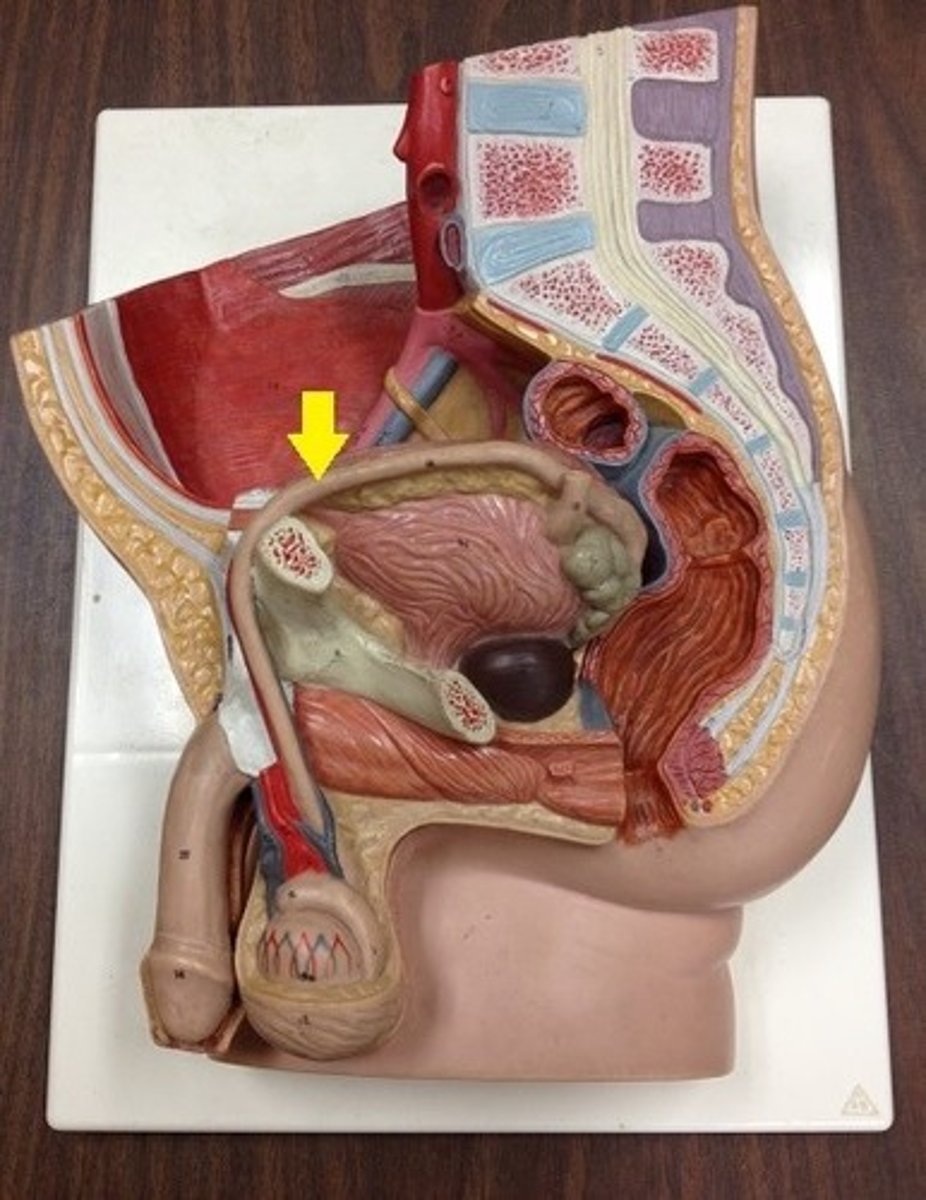
bladder
stores urine
epididymis
coiled tubes at the top of the testis in which sperm are stored
prostate gland, cowpers grand and seminal vesicle
add fluids to sperm to make semen (under bladder)
ureters
deliver urine from the kidneys to the bladder
(tube behind bladder
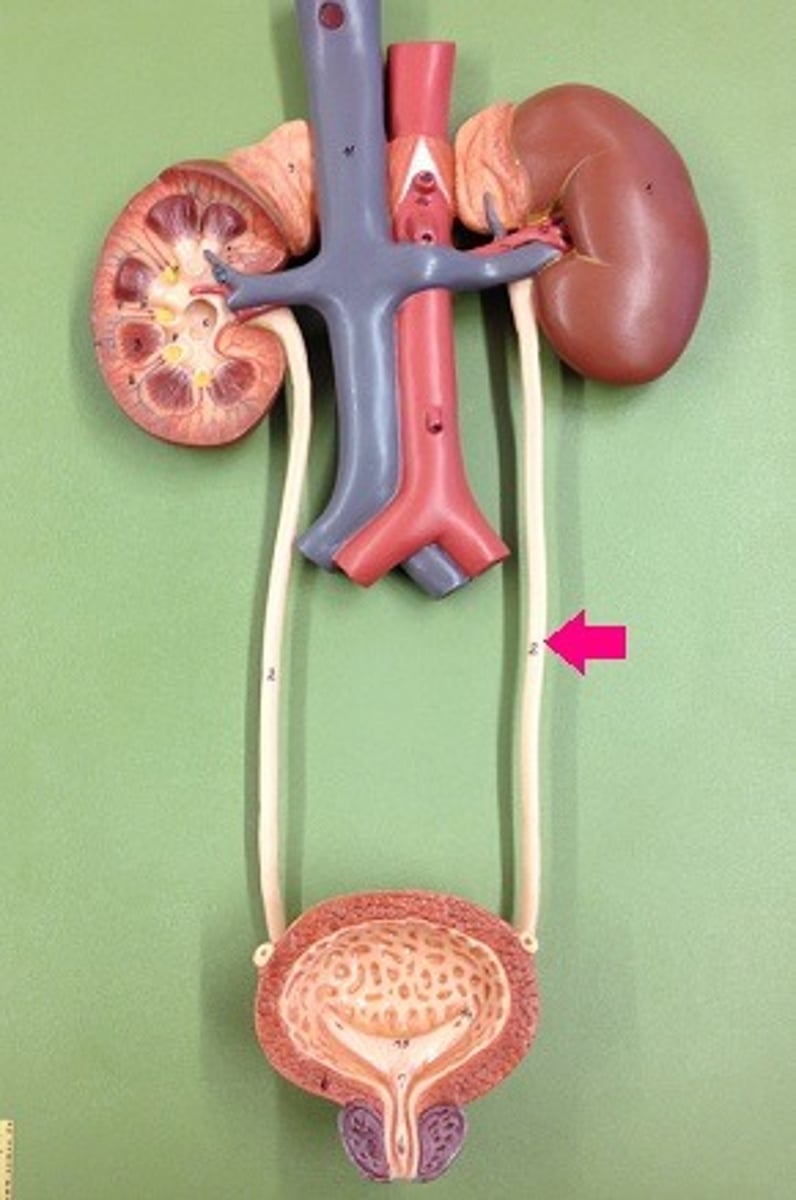
scrotum
sac holding the testes
fertilisation
when a single egg and a sperm fuse in an animal, fertilisation takes place and new offspring are created
fertilisation / chromosome number and division
each gamete carries a haploid number of chromosomes resulting in a diploid off spring. cells then divide by mitosis to develop into a new individual
internal fertilisation
male deposits sperm cells inside the female, usually on land
external fertilisation
the male deposits sperm cells onto the ovum, as the female lays them
usually in water
internal factors (4)
few offspring
sexual reproduction
good parental care and protection
offspring has high chance of survival to adults hood
external factors (4)
many offspring
broadcast spawning
poor parental care and protection
offspring have a low chance of survival into adulthood
advantages of sexual reproduction, what creates variation
creates variation among species, crossing over creates variation
thing to note about this
four gametes produced by gametes are all different
same number of chromosomes therefore same set of genes with information about the same characteristics. however specific information in many of the genes is slightly different
example of difference
in a homologous pair, one chromosome holds infor for blue eyes while the other specifies info for brown eyes. when 4 gametes are formed, half will have the information for blue eyes and half will have info for brown eyes
infertility
the inability to conceive a child after one year (or 6 months if older than 35)
risk factors in females
pcos, uterine fibroids or blocked fallopian tubes
risk factors in males
decreased sperm count and mobility, alcohol use, age, medicines
diagnosing infertility
hysterosalpingography and laproscopy
hysterosalpingography
use of x rays
checks for blcokages
use of special dye
non-surgical
laproscopy
checks for disease/physical problems
no dye used
surigical procedure
uses laproscope
endometriosis
endometrial tissue located outside the uterus
uterine fibroids
a non-cancerous tumour that grows in and around the womb.
polycystic ovarian syndrome
endocrine disorder associated with chronic anovulation
treatments of infertility
zift and ivf
zift
Zygote intra fallopian transfer
an embryo is implanted into fallopian tube
ivf
In vitro fertilisation
embryo is implanted into the uterus
medicines for infertility
human menopausal gonadotroping (hMg) and follicule stimulating hormone (FSH)
hMg
for women who dont ovulate. the hormone is injected and stimulates ovaries to begin ovulation
fsh
hormone which is injected as a treatment and causes ovaries to begin the process of producing ova. often used in conjuction with ivf
mitosis
produces two daughter cells that are identical to the parent cell.
involved in growth and repair of the body.
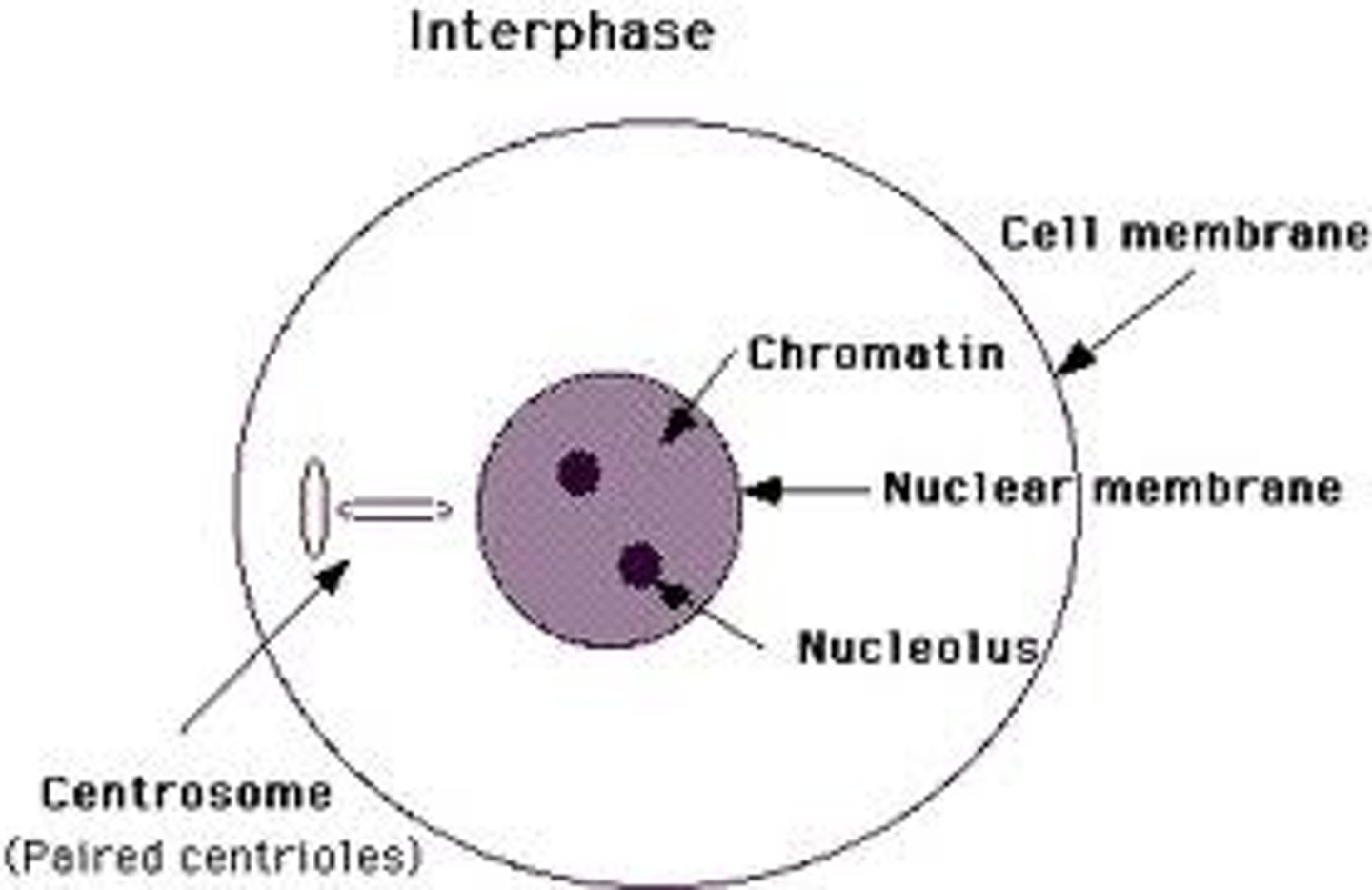
interphase
period between nuclear divisions. DNA replicates, thus the amount of dna doubles between divisions
Prophase
centrioles become visible, moving to poles
nuclear membrane breaks down
chromosomes become visible
spindle fibres form

metaphase (2)
chromosomes line up on the spindle fibres at the equator of the cell
centromere of the chromosomes attach to the spindle fibres
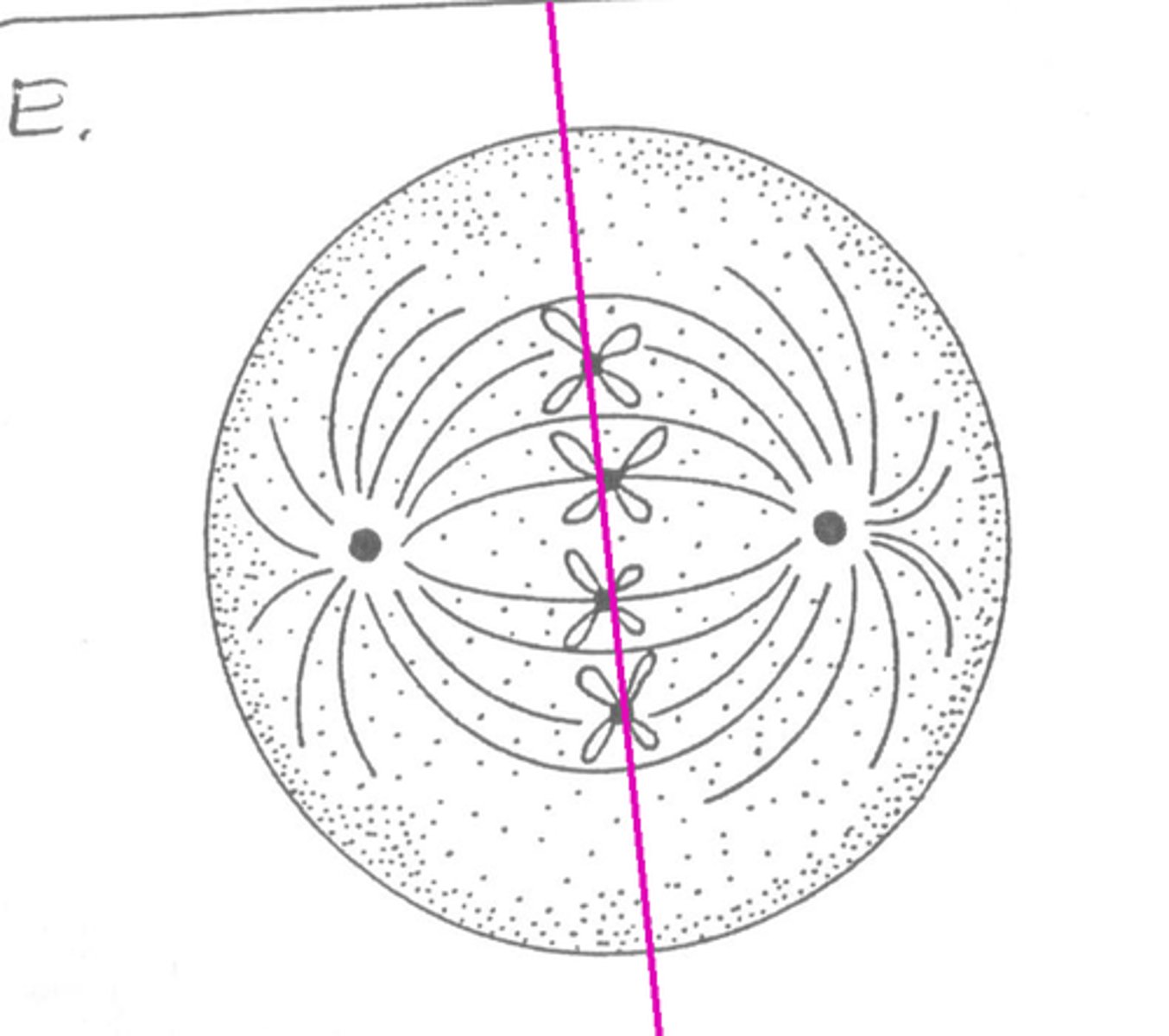
anaphase (2)
chromatids seperate as spindle fibres contract, now considered as seperate chromosomes. pulled to poles of the cell
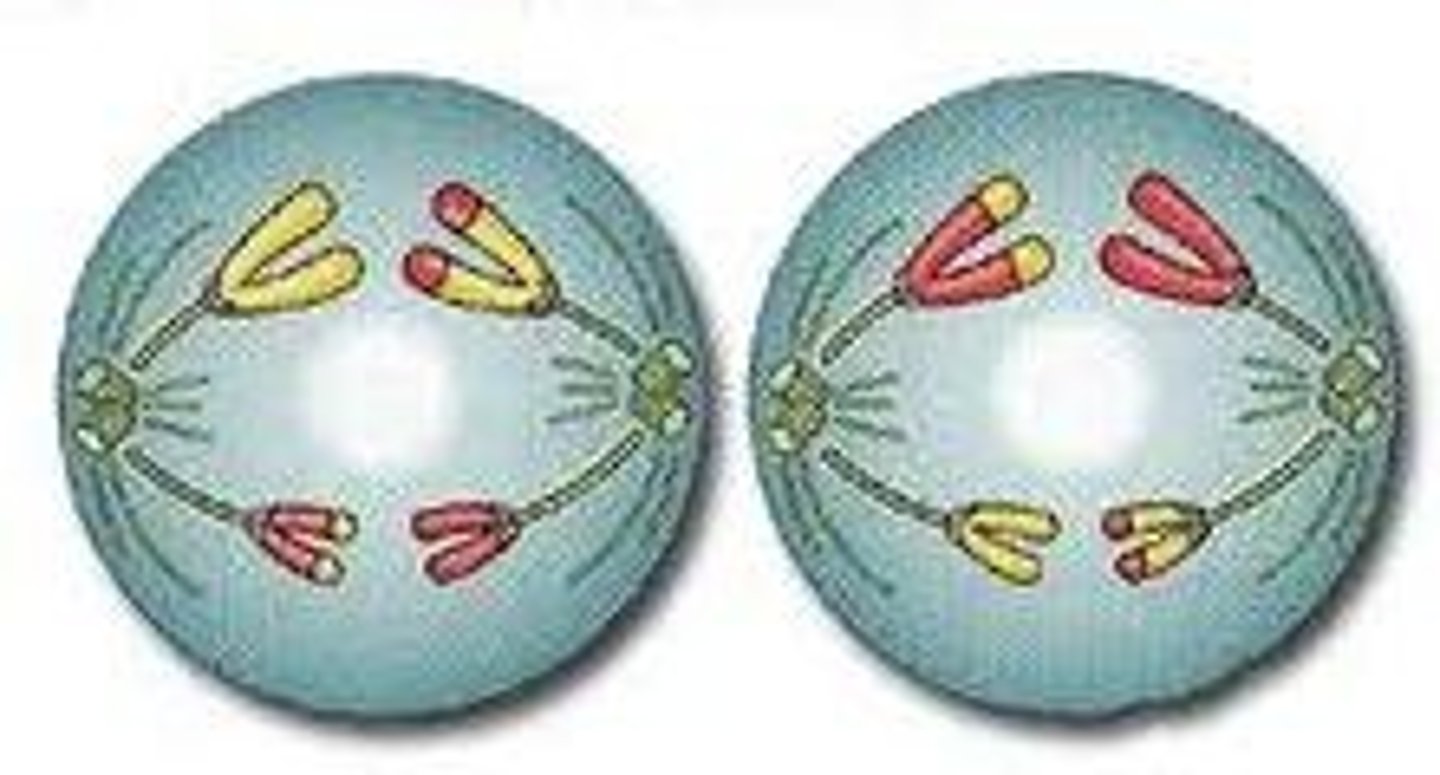

telophase (5)
spindle disappears
nuclear membrane forms
chromosomes uncoil, lengthen and become thinner
cytoplasm divides, as does the remainder of the cell
cell membrane reforms to produce two daughter cells
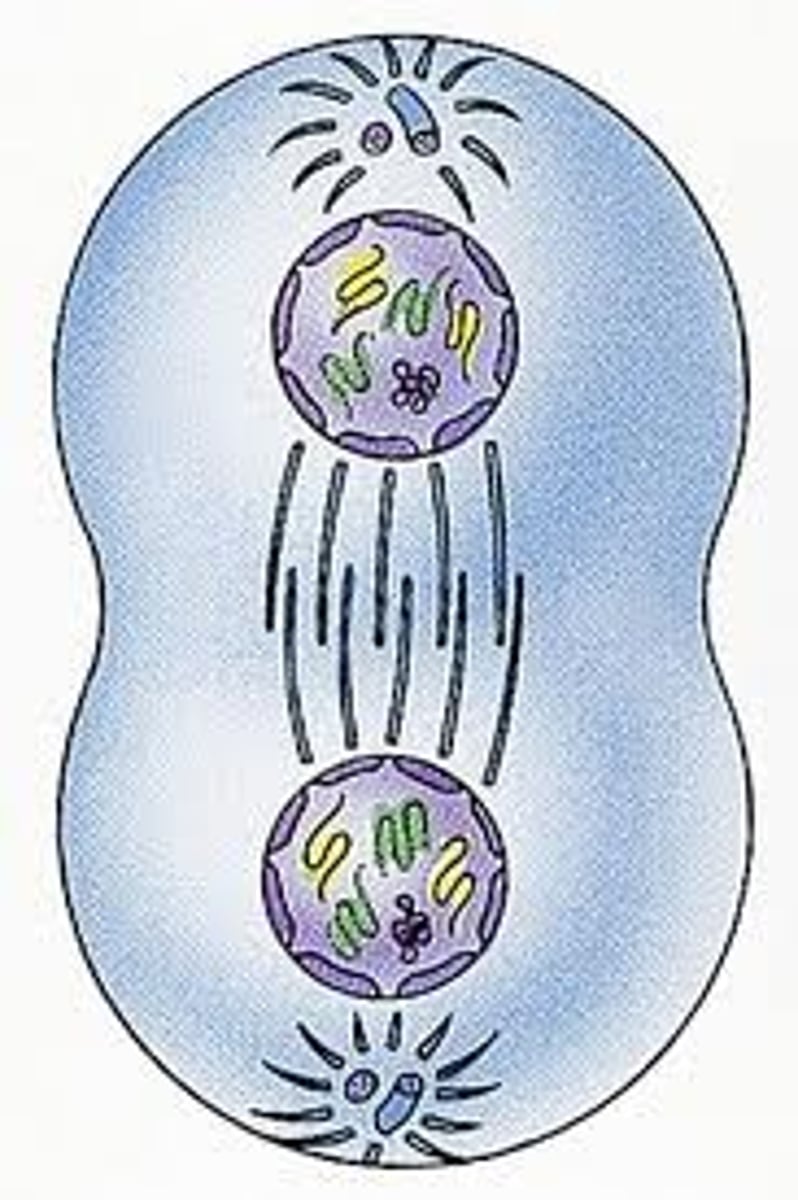
cytokinesis (2)
division of nucleus is complete. cytoplasm then divides and the result is two identical daughter cells.
daughter cells grow in size in prep for next round, become specialised cells
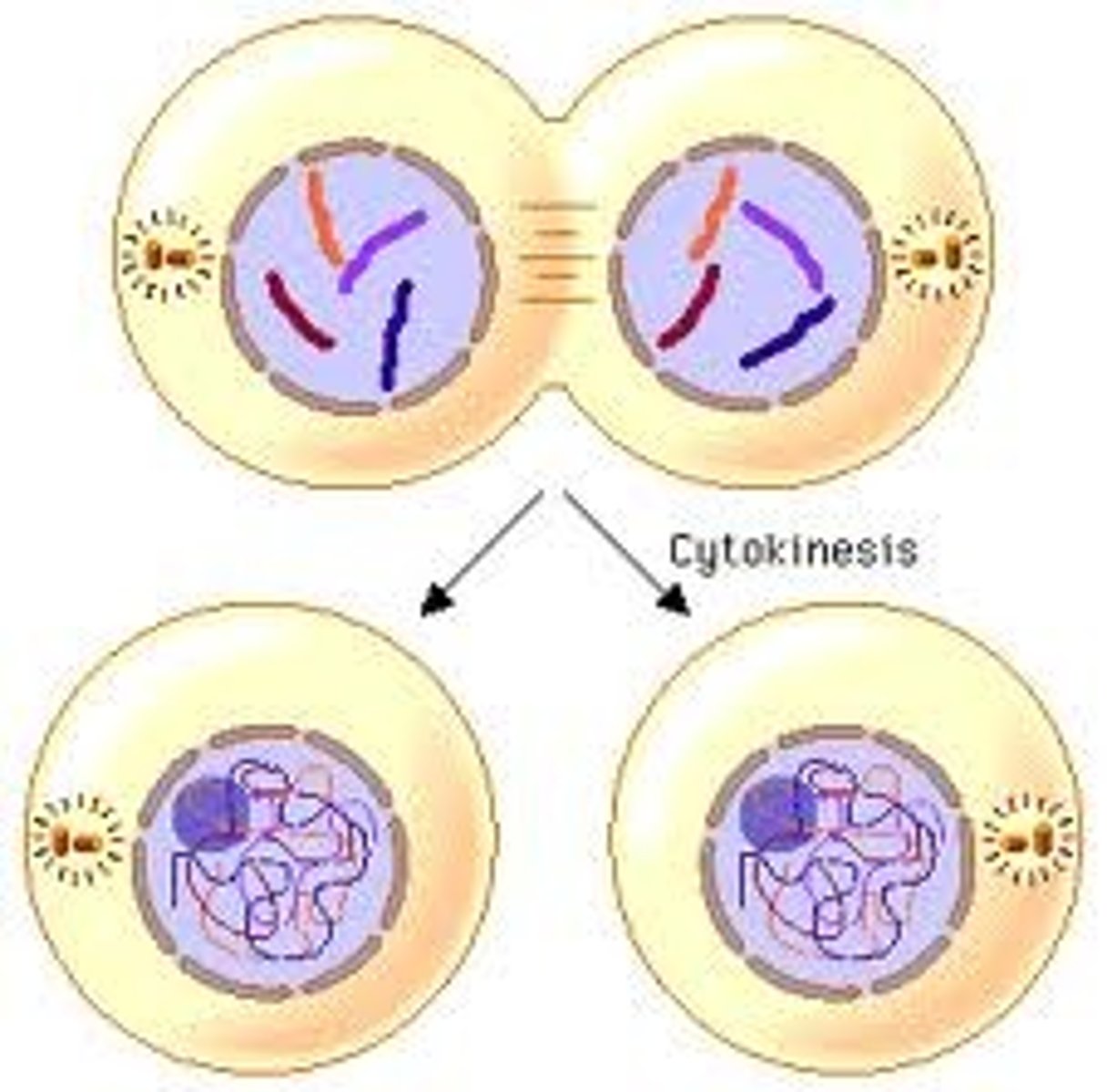
meiosis
produces gametes with haploid number of chromosomes
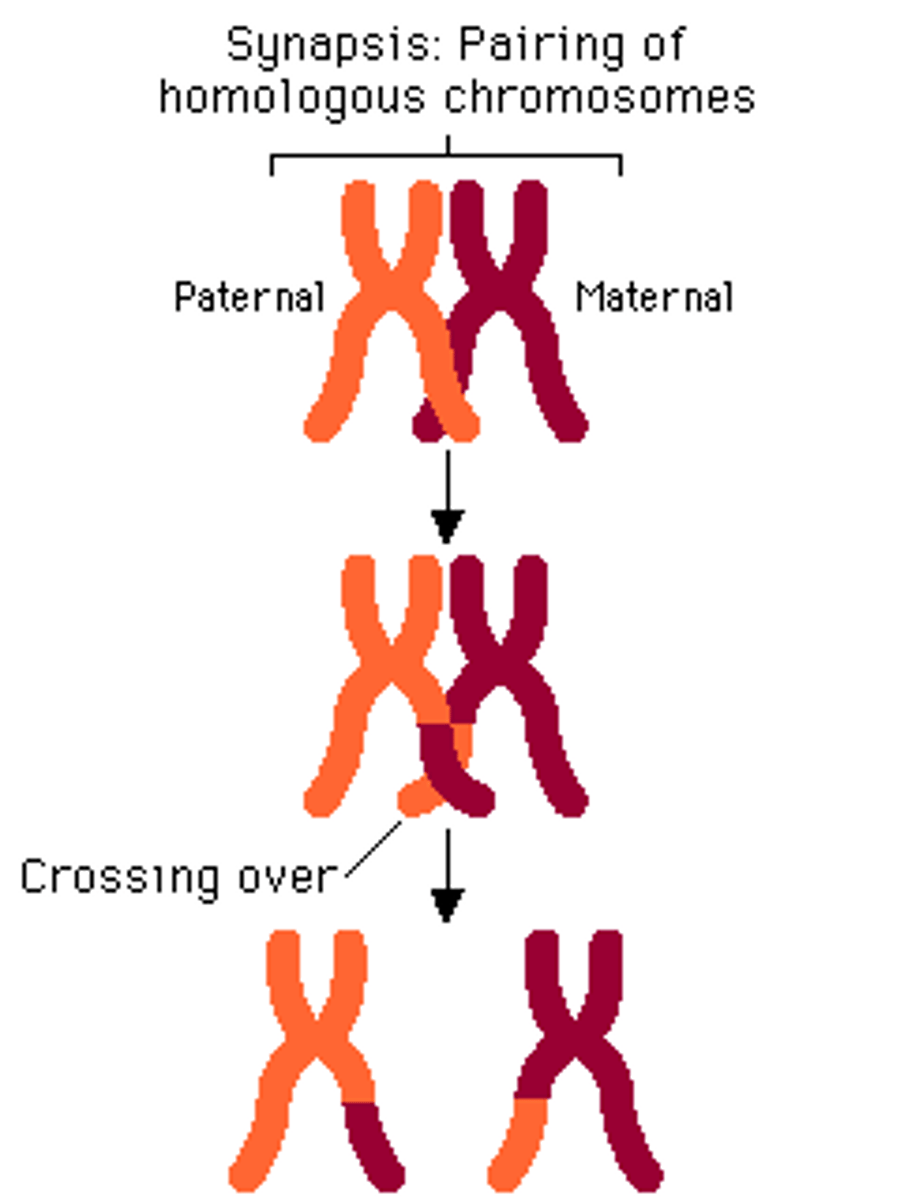
prophase 1
chromosomes appear and thicken
centrioles begin to form and move to poles
spindle fibres form
crossing over occurs
nuclear membrane disappears
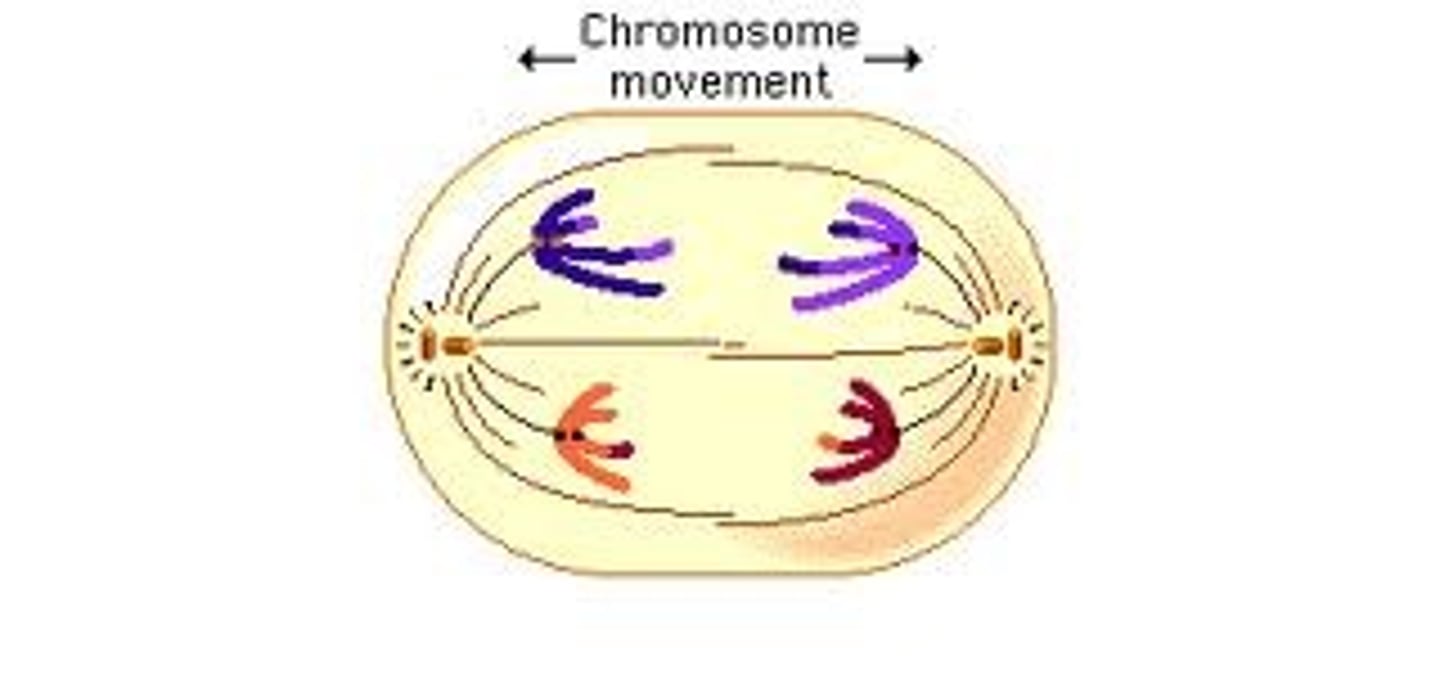
metaphase 1
chromosomes line up on the spindle fibres at the equator in homologous pairs
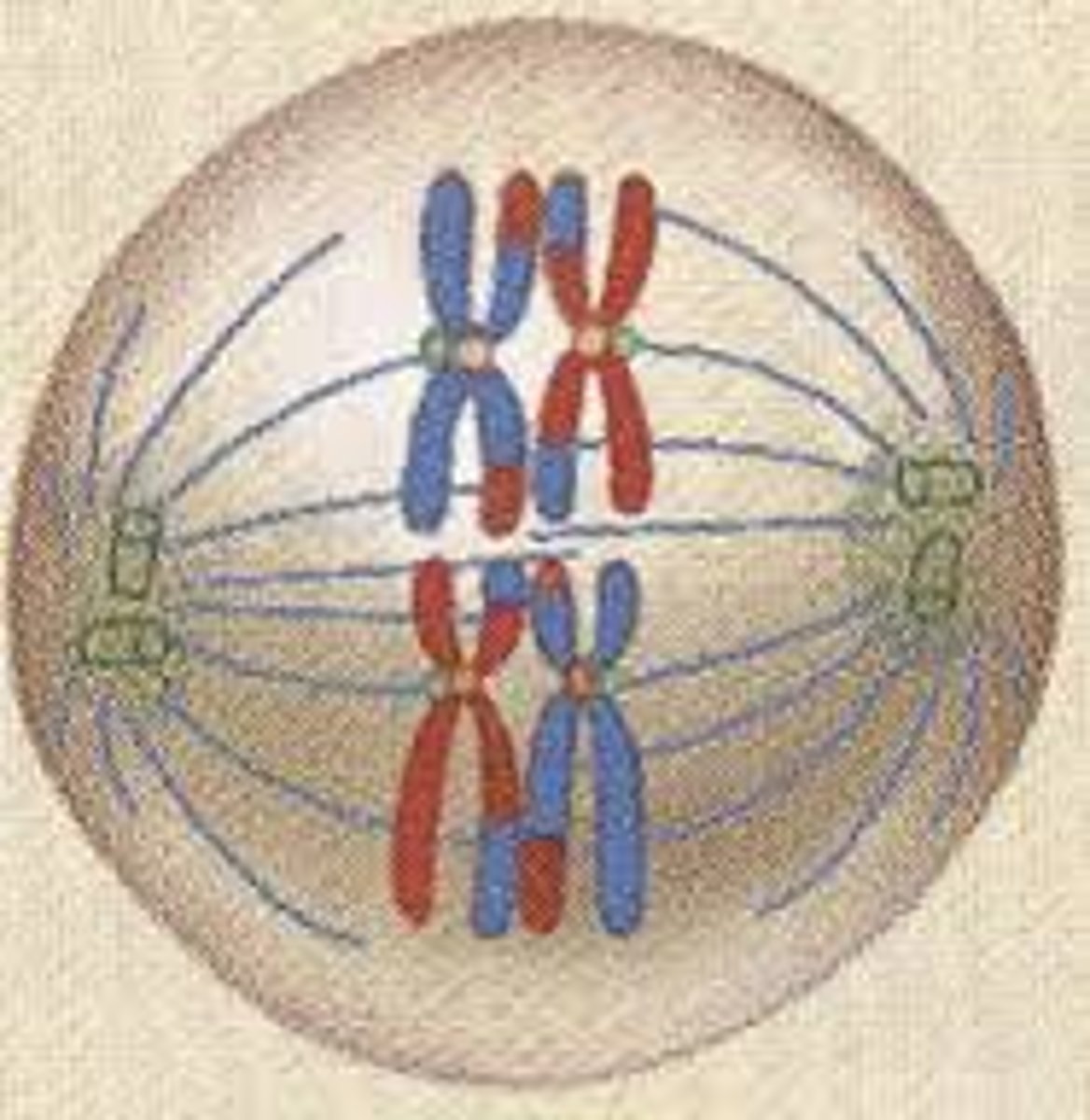
anaphase 1
homologous chromosomes move apart to the poles of the cell as spindle fibres contract
centromeres do not divide, chromatids remain in tact
telophase 1
cytoplasm divides,
nuclear membrane reforms to produce two daughter cells.
each cells is now haploid (n)
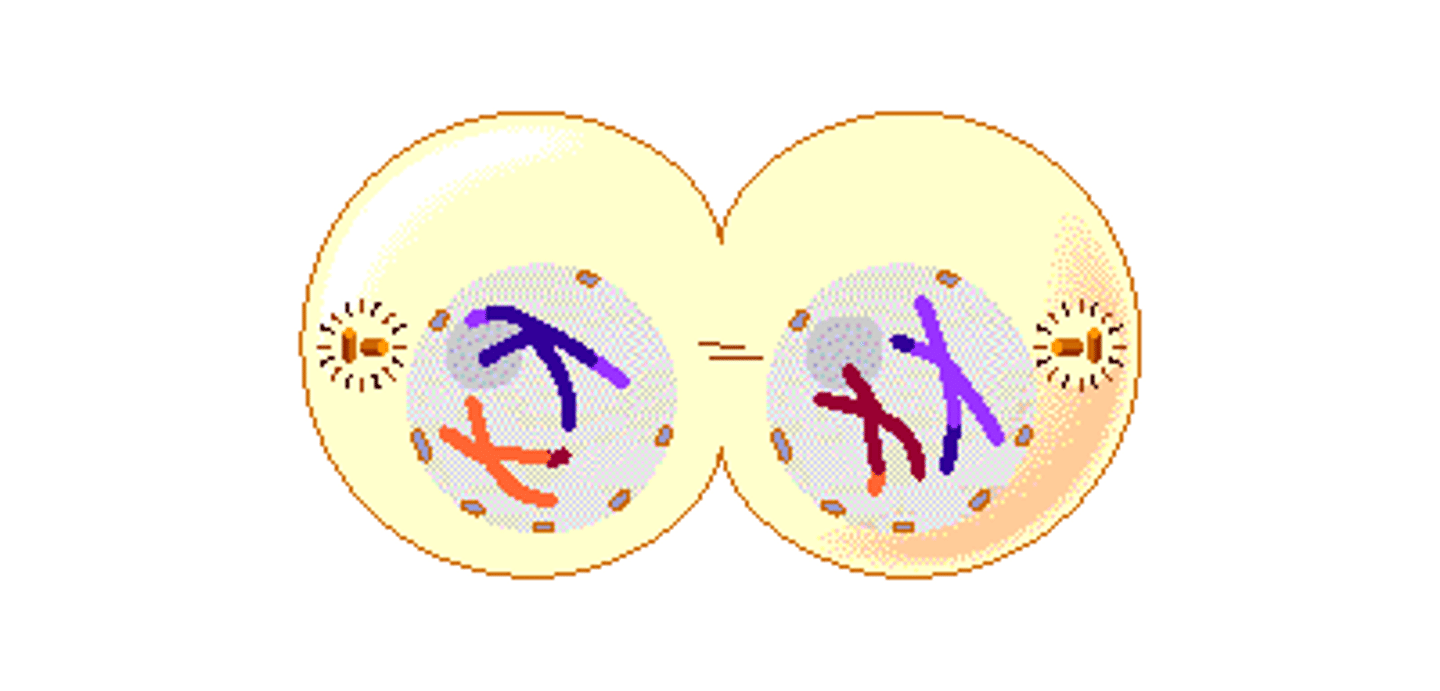
prophase 2
new spindles form at each end of original spindle at right angles.
chromosomes gradually move towards the equator

metaphase2
chromosomes line up on the spindle fibres at the equator of the cell
the centromere divide so that each chromatid is now a separate chromosome.
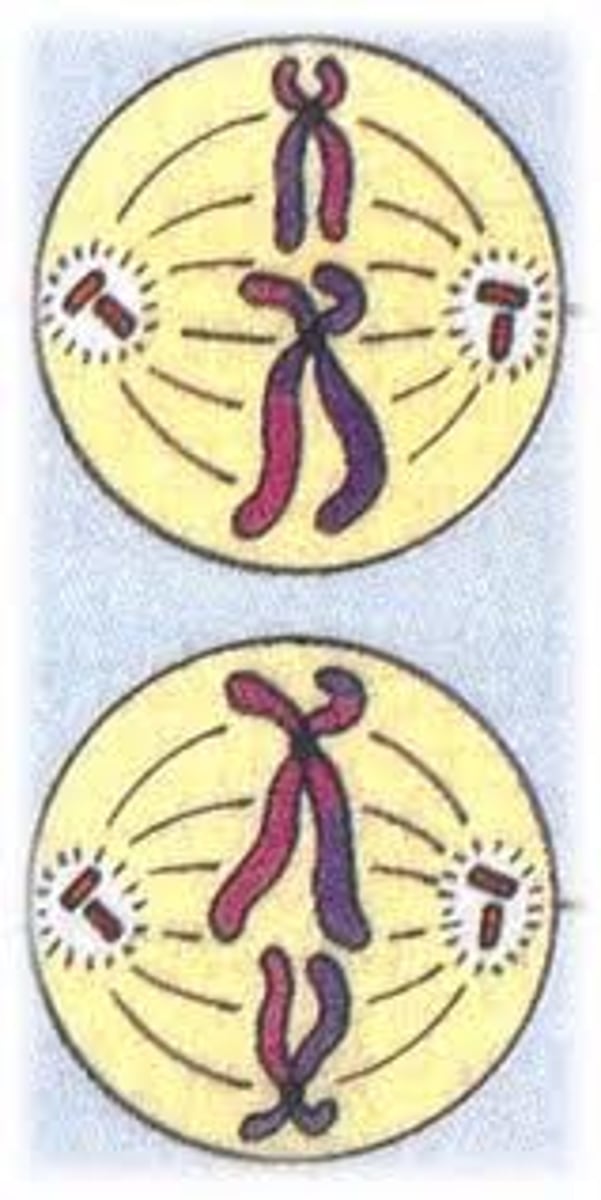
anaphase 2
chromatids separate
move to opposite poles of the cell
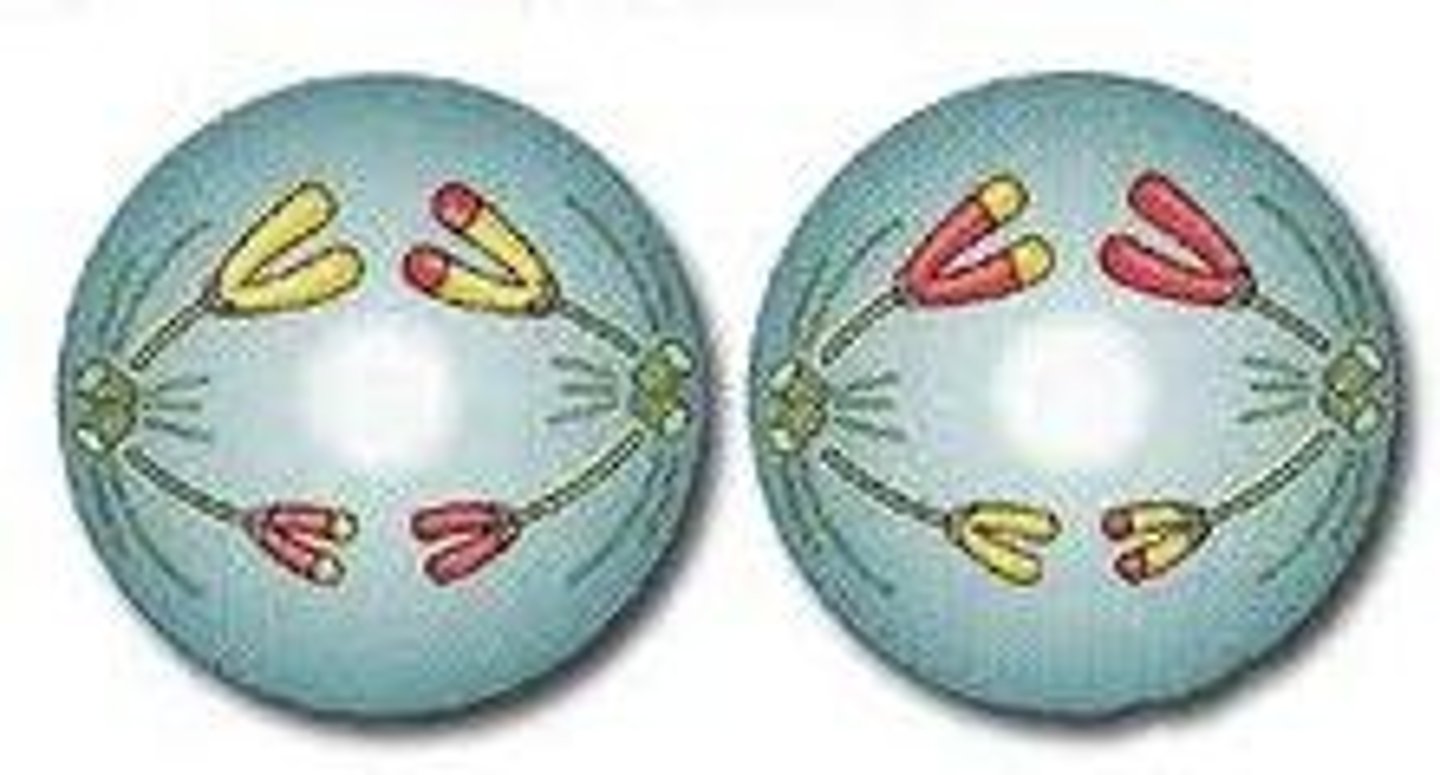

telophase 2
spindle disappears,
nuclear membranes form,
cytoplasm divides, as does the remainder of the cell.
cell membranes reform to produce four daughter cells with haploid number of chromosomes
embryo vs zygote
An embryo is the early stage of human development in which organs are critical body structures are formed. zygote is a single cell organism formed as a result of fertilisation