StemUp: OCR A A level Biology 2.1.3 + 2.1.4 Nucleotide, nucleic acids and enzymes
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
What are nucleotides and what are they used to make? (2)
- Monomers
- That are used to make nucleic acids (their polymers)
What components make up a nucleotide? (3)
- Pentose sugar
- Nitrogenous base
- Phosphate group
What is the role of DNA? (!)
Stores genetic information
What is the role of RNA? (1)
Uses the instructions from DNA's genetic material to produce proteins
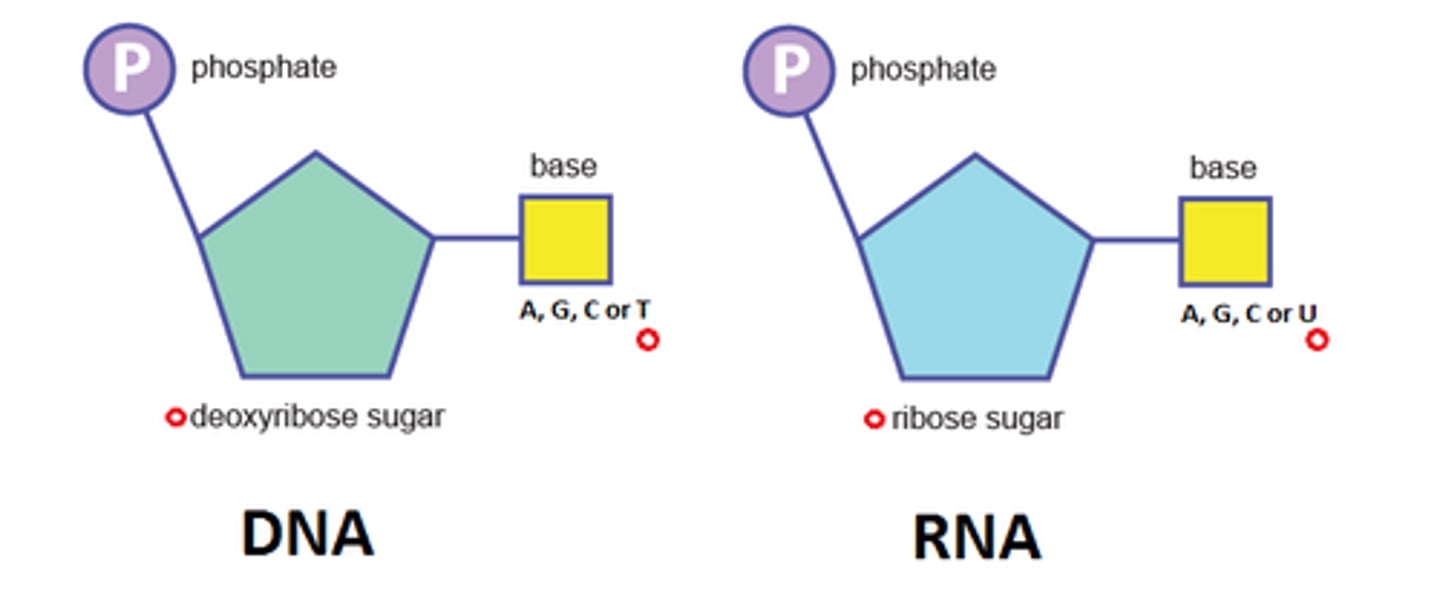
What does DNA's nucleotides contain? (3)
- Deoxyribose sugar
- Nitrogenous base (A, T, C, or G)
- Phosphate group
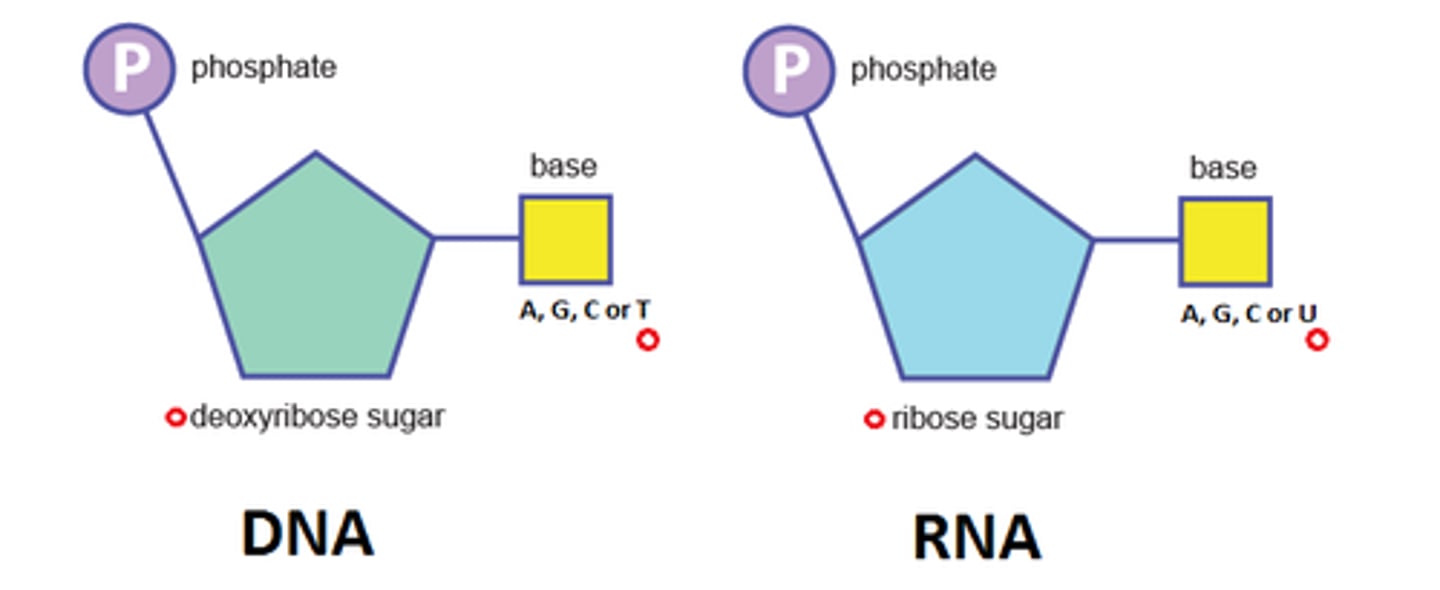
What does RNA's nucleotides contain? (3)
- Ribose sugar
- Nitrogenous base ((A, U, C, or G)
- Phosphate group
What are purines and pyrimidines? (2)
Purines = Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines = Cytosine (C), Thymine (T), and Uracil (U)
What are the key differences between DNA and RNA? (3)
- DNA is double-stranded, RNA is single-stranded.
- DNA contains deoxyribose, RNA contains ribose.
- DNA contains thymine, RNA contains uracil.
How are nucleotides joined together? (3)
- By phosphodiester bonds
- Formed by condensation reactions
- Between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the pentose sugar of another
What is the sugar-phosphate backbone? (2)
- Chain of sugars and phosphates
- That form the structure of a polynucleotide
How can polynucleotides be broken down? (1)
By the hydrolysis of the phosphodiester bonds
What does the structure of ADP contain? (3)
- Adenine
- Ribose
- x2 phosphate groups
What does the structure of ATP contain? (3)
- Adenine
- Ribose
- X3 phosphate groups
How is energy released from ATP? (3)
- Energy is released when ATP is hydrolysed
- To form ADP and a phosphate molecule
- Catalysed by ATP hydrolase
What can the inorganic phosphate from ATP hydrolysis do? (2)
- Phosphorylates other compounds
- Making them more reactive
How is ATP synthesised? (2)
- Condensation of ADP and inorganic phosphate groups
- Catalysed by ATP synthase
How are the two DNA polynucleotide strands joined together? (2)
- By hydrogen bonds
- Between the nitrogenous bases
What is complementary base pairing in DNA? (4)
- A pairs with T
- C pairs with G
- 2 hydrogen bonds form between A and T
- 3 hydrogen bonds form between C and G
Describe the structure of DNA (3)
- Consists of two antiparallel polynucleotide strands
- That coil to form a double helix
- With hydrogen bonds between the two polynucleotide strands
How do you start the process of purifying DNA? (2)
- Break up the cells in the sample using a blender
- Homogenisation
What does the detergent solution do during DNA purification? (3)
- Detergent breaks down cell membranes.
- Salt binds to the DNA causing it to clump together
- Heat stops enzymes from breaking down the DNA
What are the final steps in DNA purification? (5)
1. Filter the solution and transfer to a clean test tube
2. Add protease enzymes to break down proteins
3. Add RNase to break down RNA
4. Slowly dribble cold ethanol down the side to form a layer on top of the DNA mixture.
5. Leave the tube for a few minutes and the DNA will form a white precipitate which can be removed with a glass tube
What is semi-conservative replication? (2)
- Each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one new strand
- Ensuring that there is accurate replication of genetic information
What enzyme breaks the bonds between DNA strands during replication? (2)
- DNA helicase
- Which breaks the hydrogen bonds between the two polynucleotide strands
How are new strands of DNA formed? (4)
1. Free-floating DNA nucleotides join the exposed bases on each template strand
2. By complementary base pairing (A with T, C with G)
3. DNA polymerase joins the nucleotides together
4. Forming the sugar-phosphate backbone
What can occur randomly during DNA replication? (2)
- Random, spontaneous mutations can occur
- Altering the DNA base sequence
What is a mutation? (2)
- Change in the DNA base sequence
- Can result in no effect, an altered amino acid sequence, or a non-functional protein
What is the genetic code? (3)
- The order of bases on DNA
- Consisting of triplets of bases (codons)
- Each coding for a specific amino acid
What is a gene? (1)
Section of DNA that codes for a particular polypeptide
What are introns and exons? (2)
- Introns = Non-coding sections of DNA.
- Exons = Coding regions of DNA
What does it mean that the genetic code is non-overlapping? (2)
- Each triplet is read once
- Triplets don't share bases
What does it mean that the genetic code is degenerate? (2)
- More than one triplet can code for the same amino acid,
- Reducing the effect of mutations
What does it mean that the genetic code is universal? (1)
The same specific base triplets code for the same amino acids in all living things
What is the role of start and stop codons? (2)
- Start and stop codons
- Determine where protein synthesis starts and stops
Where do transcription and translation occur? (2)
- Transcription = occurs in the nucleus
- Translation = occurs at ribosomes in the cytoplasm
What happens during transcription? (1)
The DNA strand is transcribed into pre mRNA
What happens to pre-mRNA after transcription before translation? (2)
- Pre-mRNA is spliced
- To remove their introns (non-coding DNA)
What happens during translation? (2)
- Amino acids are assembled
- To form a polypeptide chain
What is mRNA? (3)
- Made in the nucleus
- 3 adjacent bases are called a codon
- Carries the genetic code from the DNA to the cytoplasm
What is tRNA? (3)
- Found in the cytoplasm
- Has an amino acid binding site at one end and an anti-codon at the other
- Carries amino acids to the ribosomes.
What is rRNA? (2)
- Forms the two subunits of the ribosome along with proteins
- Helps catalyse the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids during protein synthesis
What happens during transcription? (5)
1. Hydrogen bonds between complementary bases break, and the DNA helix uncoils.
2. RNA polymerase uses one strand of DNA (the antisense strand) as a template to make the mRNA molecule.
3. Free RNA nucleotides line up by complementary base pairing, and adjacent nucleotides are joined by phosphodiester bonds, catalysed by RNA polymerase.
4. When RNA polymerase reaches a stop codon, it detaches from the DNA.
5. The mRNA moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm through a nuclear pore.
What happens first in translation? (1)
mRNA attaches to a ribosome
What is the role of tRNA in translation? (2)
- tRNA molecules carry amino acids to the ribosome
- tRNA attaches to mRNA by complementary base pairing between the codons of the mRNA and the anti-codons of tRNA
How are amino acids joined during translation? (3)
1. Two tRNA molecules attach to the mRNA one at a time
2. The amino acids are joined by a peptide bond
3. Catalysed by rRNA
What happens after the first tRNA detaches? (2)
1. A third tRNA molecule binds to the next codon on the mRNA
2. A peptide bond is formed between the second and third amino acids, and the second tRNA molecule detaches
How does the process of translation continue? (1)
With the formation of a polypeptide chain as amino acids are added
When does translation stop? (2)
- When a stop codon is reached
- On the mRNA
What are enzymes? (2)
- Biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions
- Without being used up in the reaction
What types of reactions do enzymes catalyse? (2)
- At a cellular level, e.g., respiration.
- At the whole organism level, e.g., digestion in mammals.
What are intracellular enzymes and give one example & it's function? (2)
- Enzymes that work inside cells.
- Example: Catalase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen
What are extracellular enzymes and give two examples & their functions? (3)
- Enzymes that work outside cells
- Example: Amylase, found in saliva, catalyses the breakdown of starch into maltose
- Example: Trypsin, secreted into the small intestine, catalyses the breakdown of polypeptides.
Describe the structure of enzymes (2)
- Globular proteins with an active site
- The active site has a specific shape determined by the enzyme's tertiary structure
How are enzymes specific? (2)
- Their active site only binds to substrate molecules with a complementary shape
- Forming an enzyme substrate complex
What is activation energy? (2)
- The minimum energy required for a reaction to occur
- Enzymes lower the activation energy, allowing reactions to occur at lower temperatures
How do enzymes lower activation energy? (2)
1. By reducing repulsion between molecules, making it easier for substrates to bond (in the case of joining)
2. By putting strain on the bonds in substrates, making it easier for them to break apart (in breakdown reactions)
Describe the lock and key hypothesis (3)
Theory suggests:
- Active site is rigid
- Only exactly complementary substrates can bind
- To form enzyme-substrate (ES) complexes
Describe the induced hypothesis (3)
- The active site changes shape slightly as the substrate binds
- Providing a better fit
- After the reaction, the products are released, and the active site reverts to its original shape
Describe how temperature affects enzyme activity (3)
1. Initially, as temperature increases, kinetic energy increases, molecules move faster, and the rate of enzyme-substrate collisions increases, speeding up the reaction
2. At optimum temperature, the rate of reaction is at its maximum
3. Beyond the optimum temperature, bonds in the enzyme's tertiary structure break, the active site changes shape, and the enzyme becomes denatured
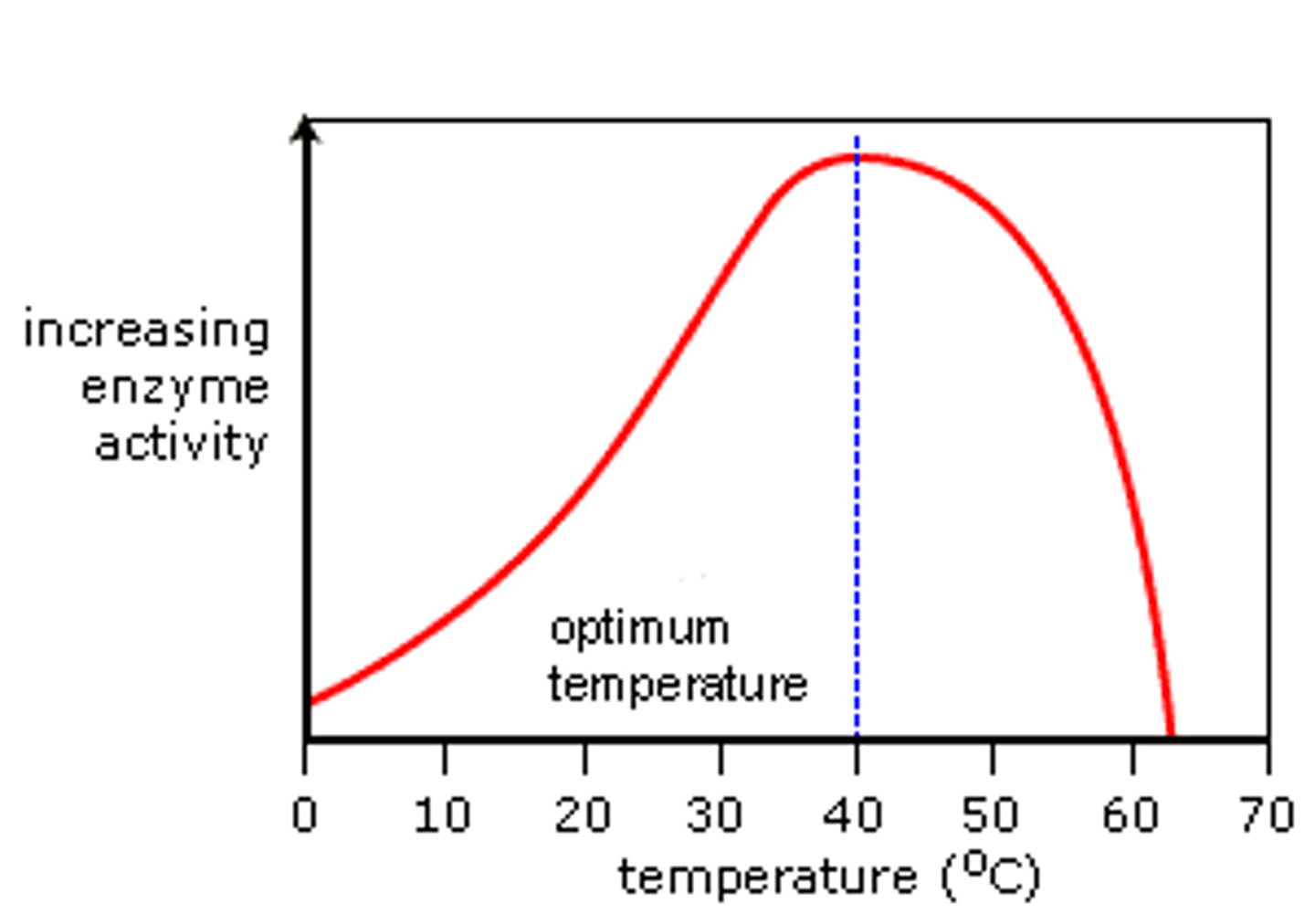
What is the temperature coefficient (e.g. Q10)? (2)
- Q10 shows how much the rate of reaction changes when the temperature is raised by 10°C
- Q10 = 2 means the rate doubles with a 10°C increase, and Q10 = 3 means the rate trebles
What happens to an enzyme when it denatures due to temperature? (3)
- The enzyme's active site changes shape
- The substrate is no longer complementary,
- So enzyme-substrate complexes can no longer form
Describe how pH affects enzyme activity (4)
- Enzymes have an optimum pH.
- pH changes break hydrogen and ionic bonds in the enzyme's tertiary structure
- Altering the active site's shape
- The substrate is no longer complementary, and the enzyme is denatured
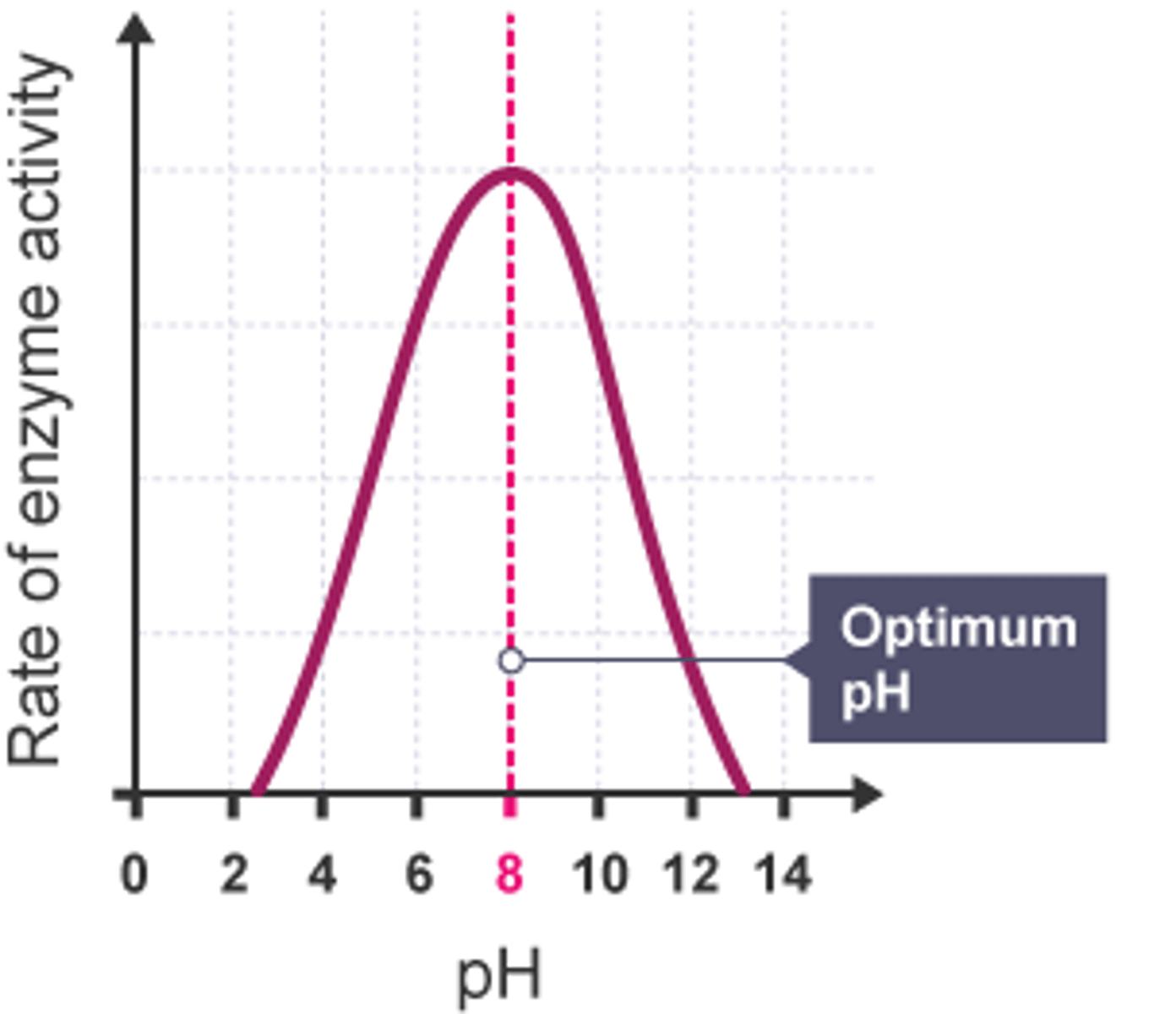
How does enzyme concentration affect the rate of reaction? (3)
1. Increasing enzyme concentration increases the chance of successful collisions and the formation of enzyme-substrate (ES) complexes, increasing the reaction rate
2. If the substrate is limited, the reaction rate will eventually plateau, and adding more enzyme will have no effect
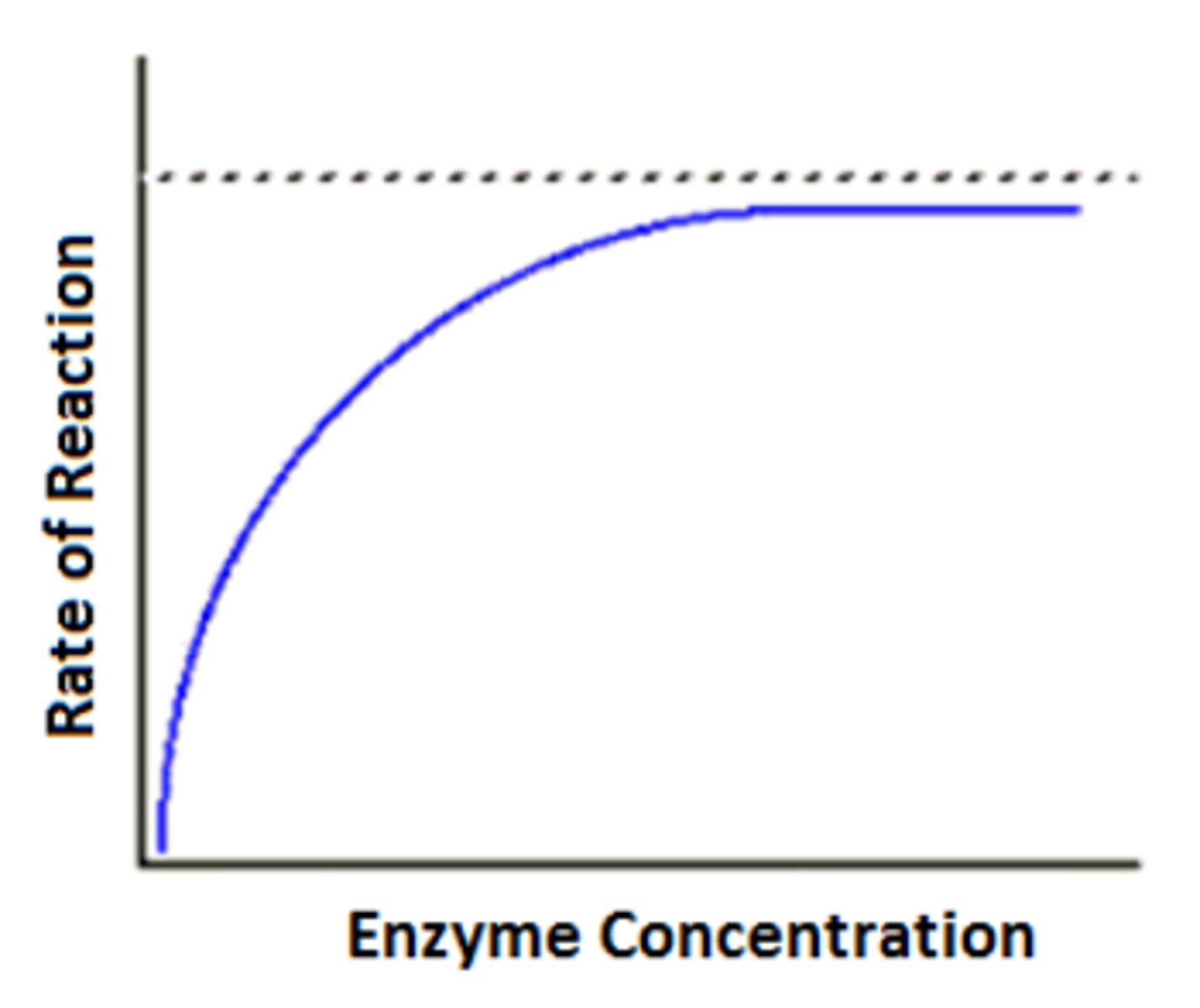
How does substrate concentration affect the rate of reaction? (3)
1. Increasing substrate concentration increases the chance of successful collisions, increasing the formation of ES complexes and the reaction rate
2. At saturation point, all active sites are occupied, and the reaction rate reaches a maximum
3. Substrate concentration decreases over time unless more is added, so the reaction rate decreases over time
How can you measure the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction? (2)
1. Measure how fast the product appears (e.g., oxygen production by catalase breaking down hydrogen peroxide)
2. Measure how fast the substrate disappears (e.g., using the iodine starch test to time starch breakdown by amylase)
How can you investigate the effect of temperature on catalase activity? (7)
1. Set up tubes containing the same volume and concentration of hydrogen peroxide and buffer solution
2. Place tubes in water baths at different temperatures (e.g., 10-40°C)
3. Leave the tubes for 5 minutes to reach the set temperature
4. Add the same volume and concentration of catalase to each tube
5. Measure oxygen production in 60 seconds using a stopwatch
6. Repeat 3 times and calculate the mean volume of oxygen produced
7. Calculate the mean rate of reaction (cm³/second)
What is the role of a negative control in the experiment of investigating temperature on catalase activity? (1)
- Shows that the enzyme alone is not producing oxygen
How can you investigate the effect of pH on enzyme activity? (1)
Use buffer solutions with different pH levels for each tube
How can you investigate the effect of substrate concentration? (1)
Use different concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, made by serial dilutions
How can you investigate the effect of enzyme concentration? (1)
Use different concentrations of catalase in each tube
What is the key principle for controlling variables in enzyme experiments? (1)
Only one variable should be changed at a time in the experiment
What is a cofactor? (2)
- A non-protein compound required for an enzyme's activity
- There are three types: coenzymes, activators, and prosthetic groups
What are coenzymes? (3)
- Organic cofactors that do not bind permanently
- They participate in the reaction and are changed by it, acting as carriers of chemical groups between enzymes
- Most coenzymes are derived from vitamins (e.g., NAD from niacin, which acts as a hydrogen acceptor)
What are activators? (4)
- Inorganic metal ions
- That temporarily bind to the enzyme and alter its active site
- Making the reaction more feasible
- They do not directly participate in the reaction and are not used up
What are prosthetic groups? (3)
- Cofactors that are permanently attached to the enzyme.
- Example: Zn²⁺ is a prosthetic group for carbonic anhydrase
- Which catalyses the production of carbonic acid from water and carbon dioxide in red blood cells
What is an inhibitor? (2)
- A substance that slows down or stops a reaction
- By affecting the binding of the substrate to the enzyme
How do competitive inhibitors work? (2)
- They have a similar structure to the substrate and bind to the enzyme's active site
- Competing with the substrate and decreasing the enzyme's activity
How does substrate concentration affect competitive inhibition? (1)
Increasing substrate concentration reverses the effect by outcompeting the inhibitor
How does competitive inhibition affect product formation? (1)
The amount of product remains the same, but the rate of product formation decreases
How do non-competitive inhibitors work? (2)
- They bind to a site away from the active site (allosteric site)
- Changing the shape of the active site and preventing substrate binding
How does substrate concentration affect non-competitive inhibition? (1)
Increasing substrate concentration has no effect on non competitive inhibition
Draw the graphs of enzyme activity without, with a competitive inhibitor and with a non-competitive inhibitor (3)
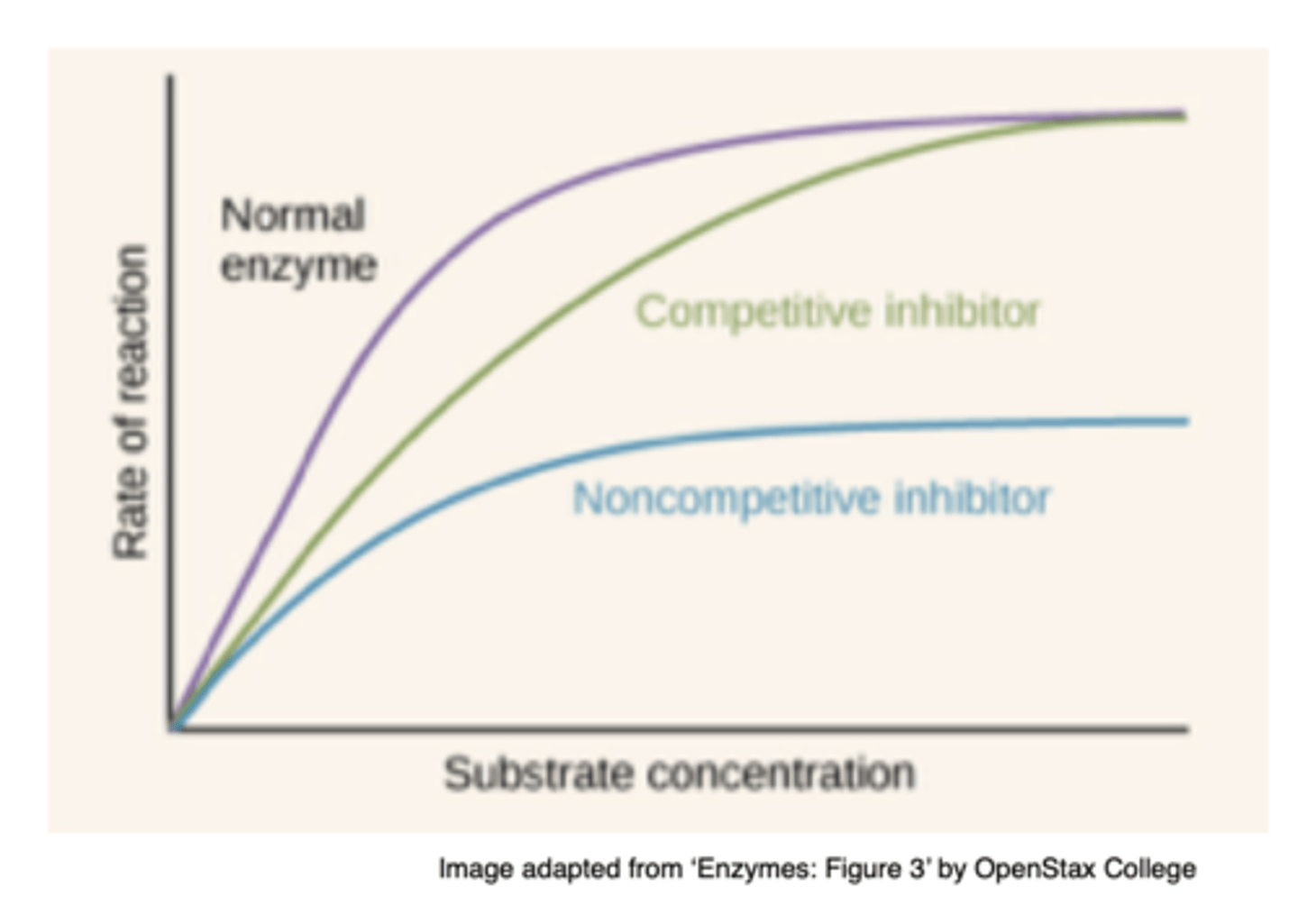
What are reversible inhibitors? (3)
- Bind to enzyme's active site through hydrogen bonds or weak ionic interactions
- So they do not bind permanently
- They can be competitive or non-competitive
What are irreversible inhibitors? (2)
- Form strong covalent bonds with the enzyme
- Permanently affecting its activity
What are some examples of irreversible inhibitors? (2)
- Cyanide
- Heavy metal ions like mercury and silver
How do reverse transcriptase inhibitors work? (2)
- Inhibit the enzyme reverse transcriptase
- Preventing viral replication by stopping viral DNA replication
How does penicillin work as an enzyme inhibitor? (3)
- Inhibits transpeptidase
- Which weakens bacterial cell walls
- Causing the bacterial cell to burst and die
How does cyanide affect metabolic reactions? (2)
- Irreversible inhibitor of cytochrome oxidase
- Preventing respiration and causing cell death
What metabolic enzymes do malonate and arsenic inhibit? (2)
- Malonate inhibits succinate dehydrogenase
- Arsenic inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase, both of which catalyse respiration reactions
What is product inhibition? (1)
Occurs when an enzyme is inhibited by the product of the reaction it catalyses
What is end-product inhibition? (2)
- Occurs when the final product in a metabolic pathway inhibits an enzyme earlier in the pathway
- Regulating the pathway and controlling the amount of product made
Are product and end-product inhibition reversible?
- Yes
- When the level of product drops, the level of inhibition decreases, allowing the enzyme to function again
Why are some enzymes synthesised as inactive precursors? (2)
- To prevent them causing damage to cells e.g. proteases
- Which could damage proteins in the cells where they are made
How do inactive precursors become active? (2)
- Part of the precursor molecule inhibits the enzyme
- Once this part is removed, the enzyme becomes active