Chp. 12 Weather Theory
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
Air is made up of
78% nitrogen
21% oxygen
1% other gasses
what is the first layer and how high up is it?
Troposphere, up to 20,000ft
The stratosphere is how high?
160,000ft (50km)
Cariolis force/effect
caused by the rotation of the earth
What rate does temperature decrease?
rate of 2c every 1,000 ft gained in altitude
What rate does pressure decrease?
Pressure decreases 1hg every 1000 attitude gained
What’s anticyclonic circulation?
High to low pressure creates clockwise winds
clockwise aka anticyclonic circulation indicates
dry, stable, descending air movement
Cyclonic circulation
low to high pressure creates counterclockwise winds
cyclonic circulation aka counterclockwise indicates:
moist, unstable ascending air, poor conditions (clouds and precipitation)
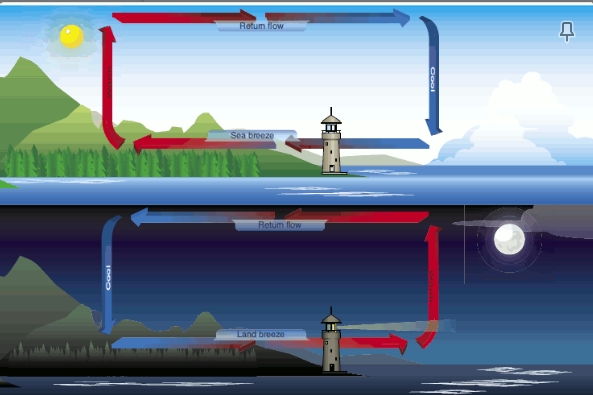
Onshore winds are known as
sea breeze
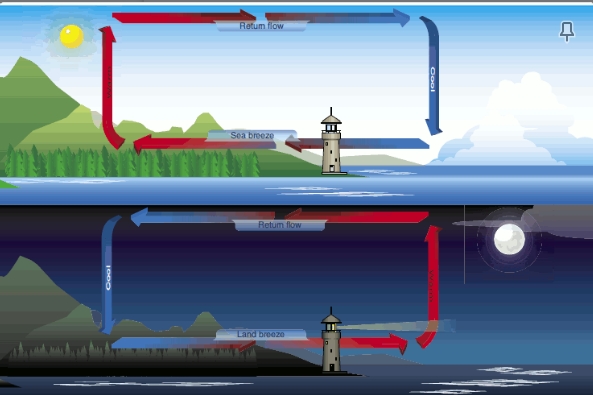
offshore winds are known as:
Land breeze
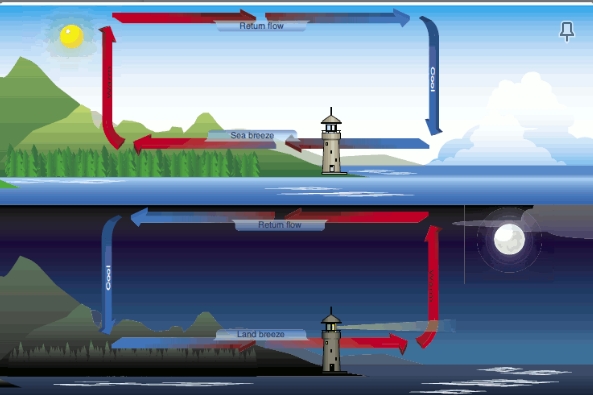
sea breeze occurs when:
the land is hot, air rises towards the sea and cold air from the sea pushed onto the land
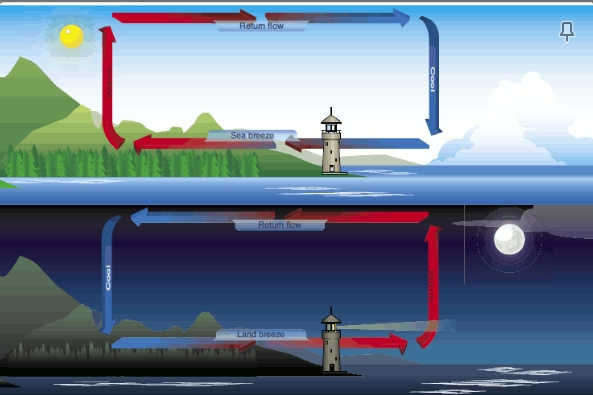
land breeze occurs when:
at night when the land is cooler, cooler dense air pushes into the sea
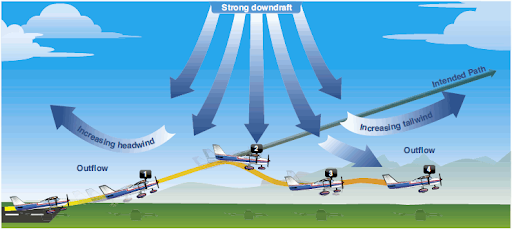
microburst is a type of
wind shearing
what is wind shearing?
Wind changes direction or speed suddenly over a short distance
How long does a microburst last?
5-15mins
why are microburst the most dangerous wind shearing?
can cause a faulty take off, first you’re climbing rapidly than a downward push and lastly an increase in tailwind
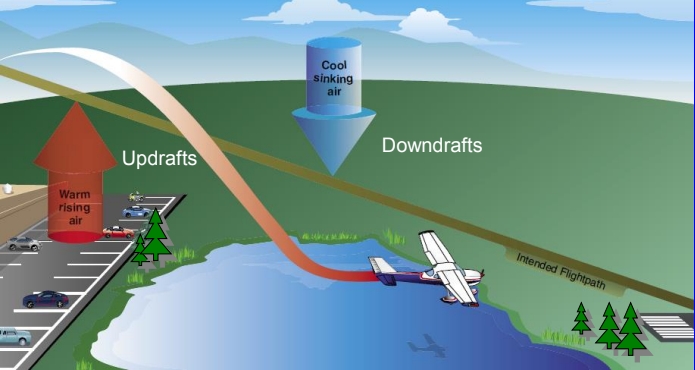
convection currents are:
pockets of high and low air
Why are convection currents more transparent over ______?
water because water has a different temperature
Stable atmosphere makes:
is dry air that makes vertical movement difficult
Unstable atmosphere
is moist warm rising air whose small vertical movements are large and can create turbulence with good surface visibility
convective turbulence mountains
aircraft is carried smoothly up the windward side of the mountain, but dangerous turbulence awaits the other side, tends to push aircraft into the side of the mountain
what to do during maneuvering speed (Va)(Velocity always) during turbulence:
don’t try to correct turbulence try and keep neutral
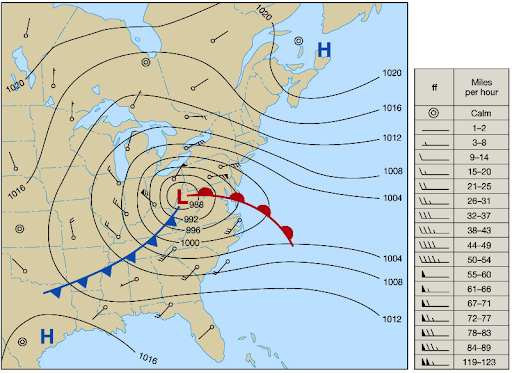
Isobar
lines drawn to depict wind behavior a few thousand feet up
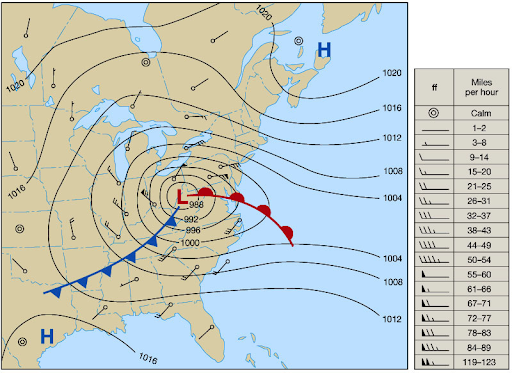
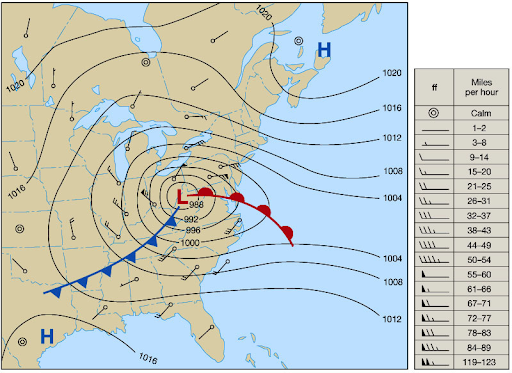
What do closer and isobars mean?
steep pressure and strong winds moving faster
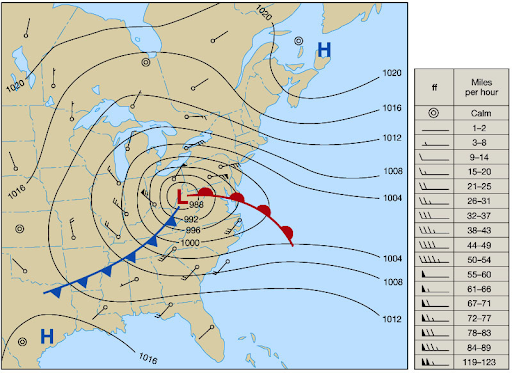
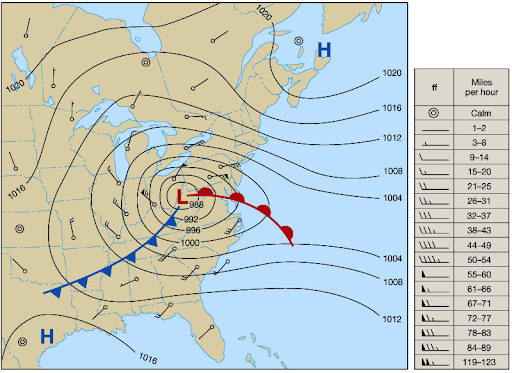
Inversion is
temperature rising with altitude
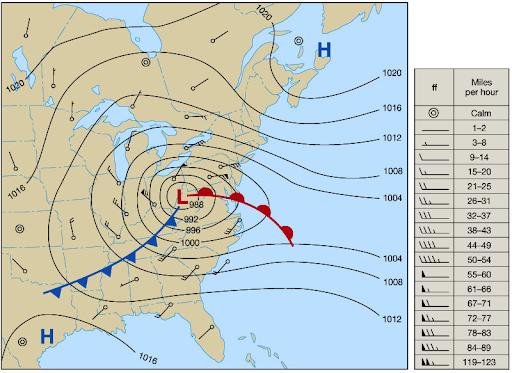
Inversion acts as:
smooth and shallow layer close to the ground acting as a lid for temperature
When does surface based temperature inversion occur?
in clear cool nights, because the night cools the ground
what is frontal inversion?
when warm air spreads over cool air or cool air forced under warm air
Dew point
is the temperature in which the air can no longer hold any more moisture
Broken clouds are:
⅝-⅞ clouds cover the sky
Overcast is:
entire sky is covered in clouds
air masses are:
regions or areas where the air remains stagnant for a period of days
Virga
when rain falls through the atmosphere but evaporates prior to striking the ground
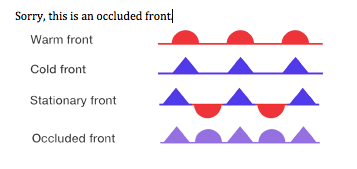
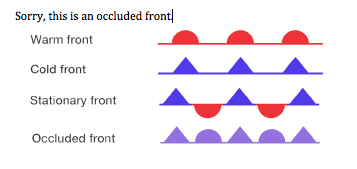
Front
boundary layer of two types of air mass
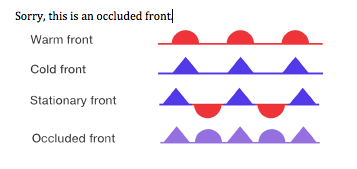
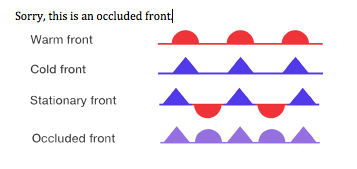
Warm front
hot mass of air replaces a cold body of air pushing the cold body out of the area. The warm air often contains high humidity and as it lifts temperature drops and condensation forms
Signs of warm fronts:
cirriform/stratiform clouds, along with fog, light to moderate forms of precipitation, in summer months cumulonimbus clouds likely to form
During warm front:
stratiform clouds, little drizzle,
After warm front:
stratocumulus clouds exist and sometimes hazy conditions
Cold front
Cold, dense, stable air replaces a body of warm air
the cold air pushes the warm air up creating clouds
Are cold or warm fronts faster and why:
Cold fronts because they stay low to the ground and act like a plow
Indicators of cold fronts:
high dew point, falling barometric pressure, depending on the intensity heavy rain, thunder, lightning, hail, or tornado forms
During cold front:
lack of visibility with winds, gusty temperature and dewpoint drop
After cold front passage
cumulus clouds, decrease in precipitation, temp remains cool
Tailwind
moving with air creating higher speed
headwind
moving against the air lower speed
convective currents
uneven heating of the air above objects on the ground like rocks and hills can be the cause of turbulence
Stable atmosphere indicators:
stratiform clouds, smooth air, poor visibility
what is actual lapse rate used for?
to measure stability of the atmosphere
Sublimation
solid water (ice) to water vapor, bypassing liquid stage
Dew point
temperature which the air must be cooled to be saturated
Frost
Temperature of the Collecting Surface is at or below the Dew-point,
and the Dew-point is BELOW freezing.
Visibility is reported in
Statute Miles (SM)
Stratus
Uniform grayish clouds covering the entire sky, often associated with Drizzle or
Mist. NOTE: Moist stable air flowing up slope will form Stratus type clouds.
Cumulonimbus
Tallest of all clouds and can span all cloud layers. They may have large anvil-shaped tops and can produce lightning, heavy rain, hail, strong winds, severe or greater turbulence and tornadoes.
Towering Cumulus
Indicates Convective Turbulence = BAD FOR YOU!
Nimbus means
rain
Lenticular (Lens Shaped) clouds
appear stationary but can have high winds
Virgas dangerous because:
cold air causes quick sinking or downwardness
Radiation fog
Radiation fog forms in moist air over low, flat areas on clear, calm nights. Is known as ground fog if less than 20ft thick.
Advection fog
requires wind for formation.
Upslope fog
Moist, stable air force up Mountain Slopes
stream fog
Cold, dry air passes, over warm water. Low-Level turbulence, and icing are associated with steam fog.
frontal passage is
change in temp, wind direction, and pressure
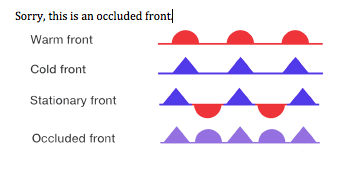
where do squall lines develope?
in front of a fast-moving cold front, usually clear rapidly but leave behind turbulence and cold temperatures
Stages of thunderstorm
cumulus stage the continues upward action, rain, and dissipation
Thunderstorms occur by
water vapor, unstable lapse rate, and lifting action
Lightning
always associated with thunderstorms
Clouds that form low to the ground, 65,000ft agl below
stratus, stratocumulus, nimbostratus, fog
they can change fast
What are the middle clouds you will find 65,000ft to 20,000ft agl?
altostratus, altocumulus
are composed of ice crystals and super cooled water droplets
What clouds will you find high above 20,000ft AGL?
cirrus, cirrostratus, cirrocumulus
are made of ice crystals and pose no real threat usually only form in stable air
What is the layer of the atmosphere that is between troposphere and stratosphere?
tropopause which changes based on the latitude and season of the year. It traps moisture associated weather of the troposphere and is often associated with the location of the jet stream which is possible clear air turbulence.
Where and how do cumulus clouds form?
They form low and vertically move up. They indicate that the air around and inside them is unstable and turbulent. They will later form into cumulonimbus clouds or thunderstorms. Cumulonimbus clouds contain a lot of unstable air and moisture and therefore can create lightening, wind gusts, wind shears, and hail.
Nimbus clouds mean
rain bearing clouds
Fracto clouds
clouds that are scattered
source region
an area where weather has been stagnant for a few days
Cold air passing over warm air creates
poor visibility but not convective currents
Cirrus clouds
ringlets, fibrous high around 20,000 agl
what are squall lines?
lines of thunderstorms that usually occur in front of a cold front but can be found behind any front
Cold fronts vs warm fronts when they approach
cold fronts can approach in a few hours whereas warm fronts can be better predicted and can last for a few days
Wind shifts
low-pressure winds rotate counterclockwise, high-pressure winds rotate clockwise
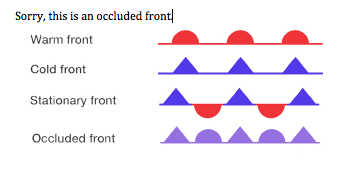
occluded fronts
fast moving cold front catches up to a slow-moving warm front
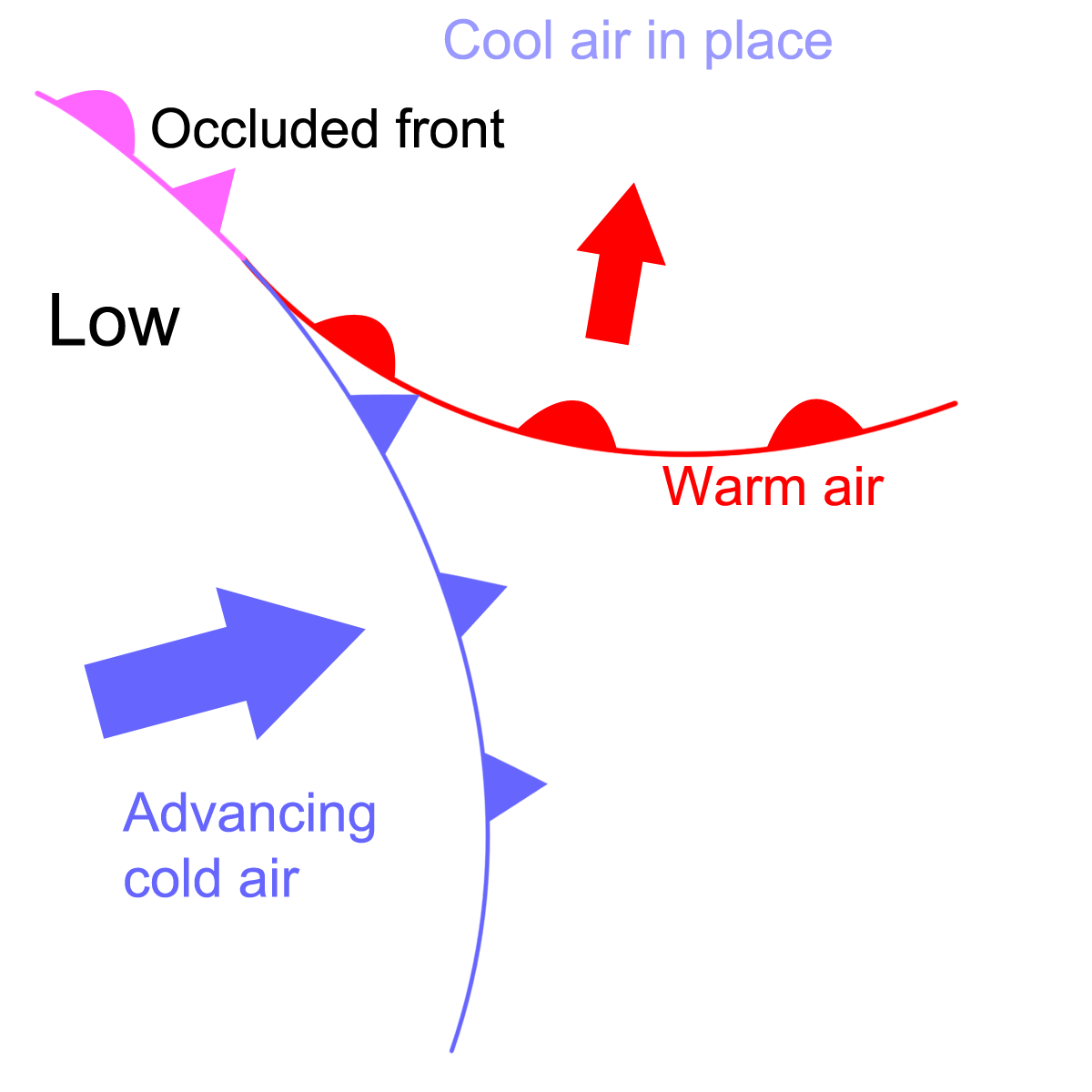
cold front occlusion
cold air is stronger than the warm air Infront of it forcing the warm air up
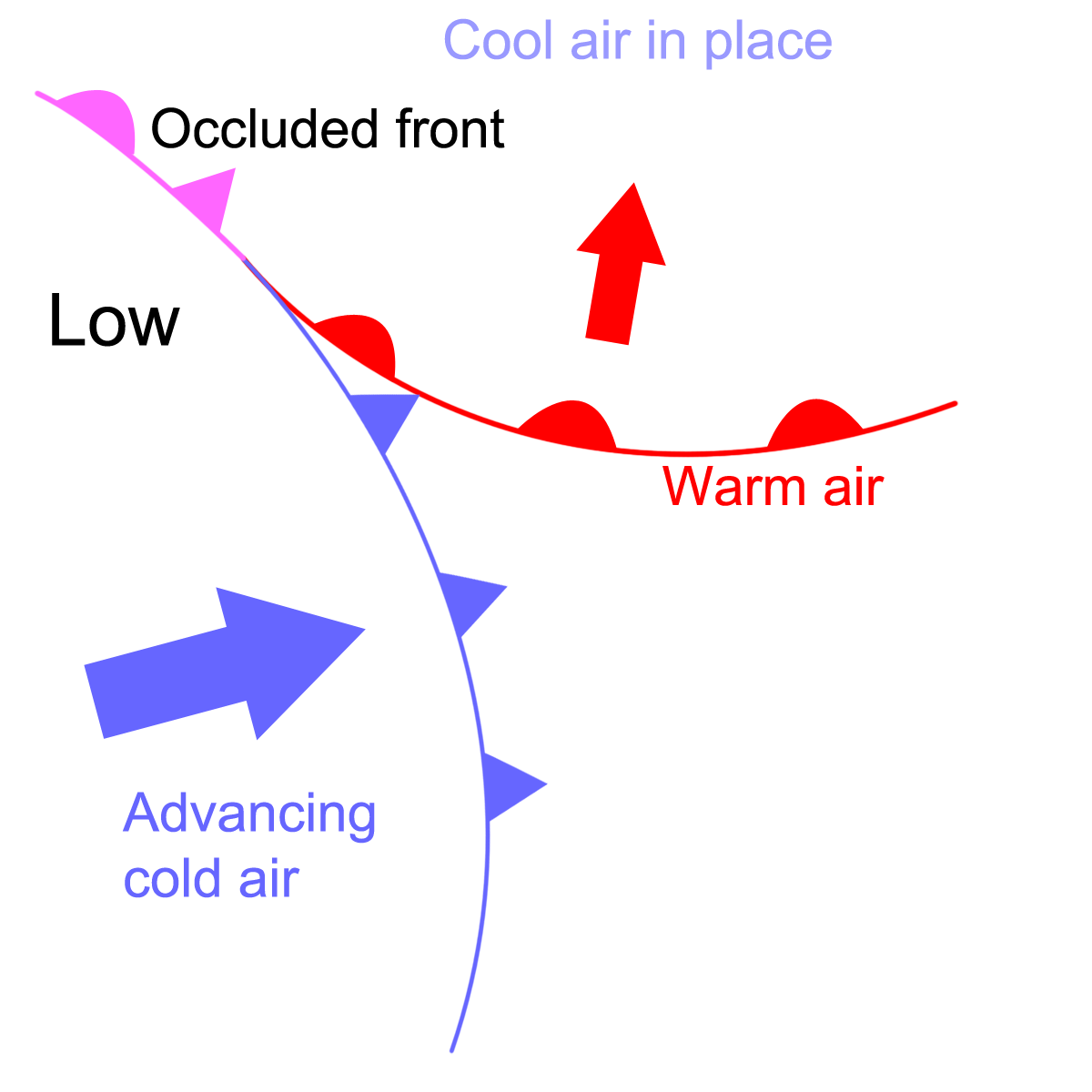
warm front occlusion
warm air is stronger than the cold air behind it so the cold air is forced over it. This creates more severe weather
Tornadoes
can form outside a squall line and is caused by the winds creating vortexes
Supercold water
water touching aircraft and immediately turning into ice
rotor clouds
clouds rolling over mountains
stationary front
warm and cold air stagnant