Fibrillar Proteins
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Describe what the extracellular matrix is and the main components?
The “ground substance” in connective tissues between cells
Components:
Collagens: provide the tensile strength of the tissue
Elastic Fibers: provide the resilience of the tissue
Proteoglycans: provide the resilience of the tissue
Hyaluronan: provide the resilience of the tissue
Glycoprotein: mediate adhesive interactions between other matrix molecules or between cells and matrix molecules
What synthesize the ECM? What does the ECM do? What are cell surface receptors and what do they do? What happens when the tissue is damaged?
Resident cells
provide an optimal environment for the cells.
Cells bind to extracellular matrix molecules through cell surface receptors.
These receptors allow the cells to sense changes in ECM and respond accordingly.
If tissue = damaged, primary response of cells = restore integrity of tissue by re-synthesizing ECM
When does the ECM get remodeled by cells? How are ECM remodeled? How are these molecules regulated?
Remodeling and Degradation when:
tissue differentiation (matrix composition changes)
cell migration (cells have to move through the matrix)
Remodeling Mechanism:
the cells secrete matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs, Zn2+) that degrade the matrix proteins.
Regulation:
Cells also secrete TIMPs (tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases) that inhibits MMPs
extent of tissue remodeling dependent on ratio of MMPs and TIMPs
How do cancer cells invade surrounding tissues?
Cancer cells secrete large amounts of MMPs to invade the surrounding tissue.
What is collagen and describe its structure
The main fibrillar proteins in connective tissues
triple helical structure
heavily cross-linked → very stable
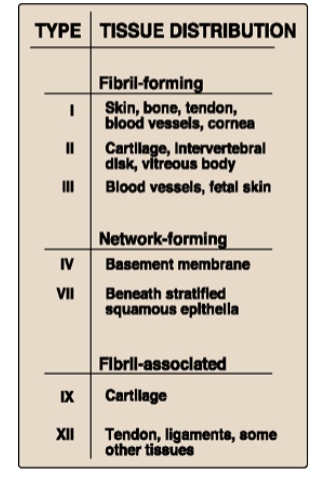
What are the three major groups of collagen? Describe where they are?
Fibril forming (I-III)
Network forming (forms meshes) (IV)
Fibril-associated (associates with Type I, II, III) (V, VI)
When is the propeptide of collagen removed extracellularly?
removed extracellularly by proteolytic digestion after three procollagen chains are assembled into a triple helical structure.
Describe Collagen’s chain
3 α chains (can be identical or different)
The long helical part of the chains is composed of Gly- Proline - Hydroxypoline;
favor triple helix formation
Describe the synthesis of collagen
Synthesis of procollagen chains occurs in RER
Certain proline and lysine residues → hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine (co-translational modification!)
Some hydroxylysine residues are also glycosylated.
3 pro-alpha chains assemble
Intra/Inter disulfide bonds form at C-term.
The triple helix forms in the rough ER
formation proceeds from C to N terminus.
held together by hydrogen bonds
Hydroxyproline stabilizes triple helix formation.
Propeptides are cleaved off after procollagen is secreted into the extracellular space.
enzyme = N and C procollagen peptidases
Then, collagen monomers assemble into fibrils.
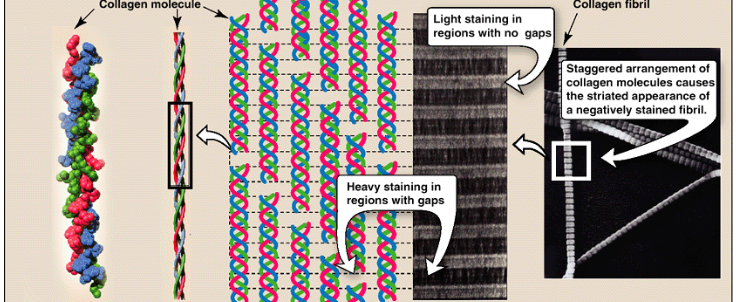
How are collagen fibrils formed? Stabilized? How are they viewed under the electronic microscope
formed from collagen’s triple helix units that associate in a staggered manner.
stabilized by covalent crosslinking between collagen triple helices.
staggered assembly produces characteristic striated pattern of collagen when viewed under electron microscope
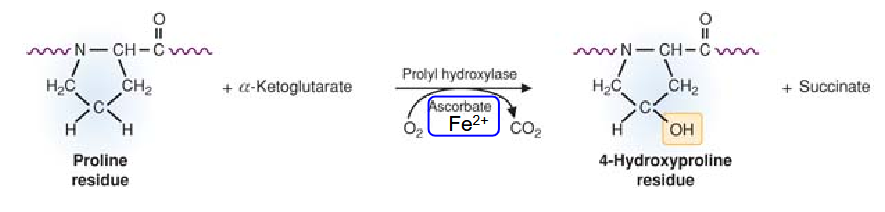
What is the triple helix stabilized by? Describe the synthesis of this
stabilized by hydrogen bonds and hydroxyproline.
produced by prolyl hydroxylase.
requires Fe2+ and vitamin C (ascorbate) as cofactors.
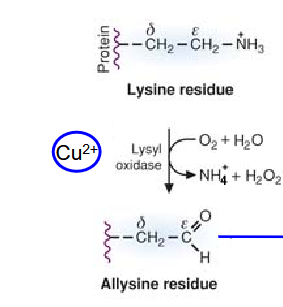
What participates in the cross linking of collagen chains? How is this produced?
Hydroxylysine
produced by lysyl hydroxylase
requires Fe2+ and vitamin C (ascorbate) as cofactors.

Describe how the covalen crosslinking within collagen fibers are created?
formation of oxidized lysine and hydroxylysine
Oxidation of lysine and hydroxylysine catalyzed by lysyl oxidase.
Cu2+ as cofactor
Takes place in ECM
The allysine (or hydroxyallysine) residue will react with
lysine/hydroxylysine/allysine/hydroxyallysine residues to
create covalent crosslinks between collagen chains
Describe the assembly of Type IV Collagen Network
main basement membrane collagen
In the extracellular space, two type IV triple helices attach at their C- terminal, forming a dimer
Dimers associate through their N- terminal ends to form tetramers and eventually a large network
Describe the pathology of Scruvy and the symptoms
Caused by lack of fruits and vegetables in the diet.
Prolyl and lysyl hydroxylases are not efficient (require Vitamin C).
The collagen triple helix is less stable and crosslinking is also reduced.
General connective tissue disease.
Symptoms
Bruises on skin (especially on legs)
Bleeding gums, loose teeth
Delayed wound healing
Bone and joint abnormalities (especially in infants)
Describe the pathology of Osteogenesis Imperfecta (OI) and the symptoms
Types I, II, III, IV = Type I collagen mutations.
Type I : Reduced number of collagen fibrils
Types II, III and IV OI: Defective collagen fibrils
Severity can range from perinatal lethal to mild predisposition to fractures
Characteristic symptoms:
Increased incidence of fractures
Short stature
Grey or brown teeth that wear down easily (dentinogenesis imperfecta)
Blue sclera
Describe the pathology of Achondrogenesis Type 2 and the symptoms
Mutation in type II collagen
Dwarfism, short stature
Defective cartilage formation and bone ossification
Death before birth or shortly after birth
Describe the pathology of Kyphoscoliotic Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS)and the symptoms; other types?
Loss-of-function mutations in lysyl hydroxylase
progressive scoliosis (abnormal curving of the spine)
hyperextensive skin
delayed wound healing, easy bruising, thin scars
joint hypermobility
increased risk of vascular rupture
Other types:
vascular type EDS: mutation in type III
classic type EDS: mutation in Type V collagen
Describe the pathology of Alport Syndrome and the symptoms
mutations in Type IV collagen genes
Affects glomerular basement membranes → renal failure
X-linked or autosomal recessive
Main symptoms
Hematuria (appearance of red blood cells in urine)
Proteinuria (increased protein in urine)
Renal insufficiency
Anterior lenticonus (conical shape of the lens)
Sensorineural hearing loss (mutation affects the basement membrane of the organ of Corti in the cochlea of the inner ear)
NOTE: Memorizing tech: “The AIRPORT (sounds like alport) was giving out KIDNEY BEANS (renal failure) in the BASEMENT (basement membrane)
Describe the pathology of Collagen Related Myopathies and the symptoms
Type VI collagen connects the skeletal muscle basement
membrane to the fibrillar collagen network.Mutations in type VI collagen lead to muscle weakness.
Severity of the disease depends on the type of mutation.
What is Elastin? What does it allow? How is it synthesized? What happens in extracellular space? What does correct assembly require?
major component of elastic fibers
allows tissues to stretch and contract
Widespread localization
synthesized in the ER and secreted as monomers by the cells
In the extracellular space, lysine residues are oxidized by lysyl oxidase, then form crosslinks between elastin monomers
Correct assembly of elastic fibers requires microfibrils formed by fibrillins
What is Marfan Syndrome? Symptoms?
Defective microfibril formation of elastic fibers
Via mutations in fibrillin-1
Skeletal
Very tall stature,
Disproportionally long limbs, fingers, and toes
Hyperflexible joints
kyphoscoliosis
Oculars
Disclocation of the lens of the eyes (ectopia lentis)
Cardiovascular
Dilation of the aorta
Heart valve problem
Describe the receptors cells use to interact with the ECM
(function? Binds what? Why this is important?)
integrins (αβ dimer)
anchors cells to ECM
bind to collagens and glycoproteins, such as fibronectin or laminin.
Integrin-laminin interactions important for formation of basement membranes.
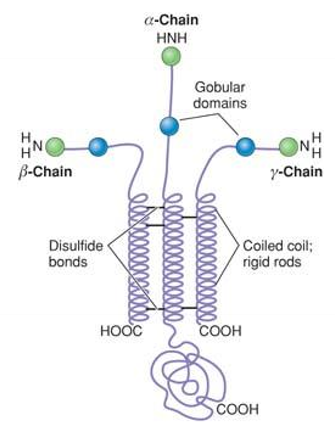
What are laminins? Structure? Synthesis? Interaction?
Basement membrane proteins (characteristic cross-shape)
Heterotrimers (α, β and γ chains); stabilized by disulfide bond
Multiple variants of the individual chains exist.
synthesis: ER; assembly: Golgi
Interact with basement membrane proteins and integrins (cell receptor)
What is Junctional Epidermolysis Bullosa caused by? What does it affect? and the symptoms?
mutations in certain laminins and integrins.
Affects basement membrane of epidermis and mucosal membranes.
Main symptom:
fragile skin → extreme blistering
What Laminin 2 (Merosin)-Related Muscular Dystrophy caused by and the symptoms?
Mutations in the α2 chain of laminin impair interaction between basement membrane and skeletal muscle cells.
It leads to moderate to severe muscle weakness depending on type of mutation.