ADHD Medicinal Chemistry
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What percentage of the population have ADHD?
3%
(Controversial figure: some studies claim 1 in 5 people have ADHD)
Describe how ADHD is diagnosed
Diagnosis in ADHD is difficult because
- there are not any biological markers for it
- there are not any biological tests for it
Therefore we have standardised rating scales with input from patient and other individuals such as family and close friends.
However, there is room for a lot of errors to creep in through these tests
What are some theories for ADHD in some individuals?
- Differences in monoamines particularly noradrenaline and dopamine between individuals with ADHD and those without.
Why the monoamine levels are different in individuals with ADHD, we don't know right not.
- We are looking at different volumes in the brain and connectivity. We understand that these systems are involved but we don't know the specifics at an individual level
What do NICE guidelines recommend for ADHD treatment?
- Offer medication if changes to the person's environment hasn't helped
- Methylphenidate can be offered or lisdexamphetamine for 6 weeks
- If that doesn't' work then use dexamphetamine to adults whose symptoms are improving but cannot tolerate long half life of lisdexamphetamine/ methylphenidate.
- If cannot tolerate stimulant, give non-stimulant.
What percentage of people with ADHD respond positively to medication?
Around 75% of people with ADHD respond positively to the medication
Give examples of stimulant ADHD medication
Methylphenidate
Amphetamines e.g. Lisdexamphetamine
What is the mechanism of action for methylphenidate?
- It inhibits the reuptake of dopamine (DA) and noradrenaline (NA).
- Therefore, DA and NA neurotransmitter remains in the synaptic cleft for longer and there is s higher concentration of monoamine neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft.
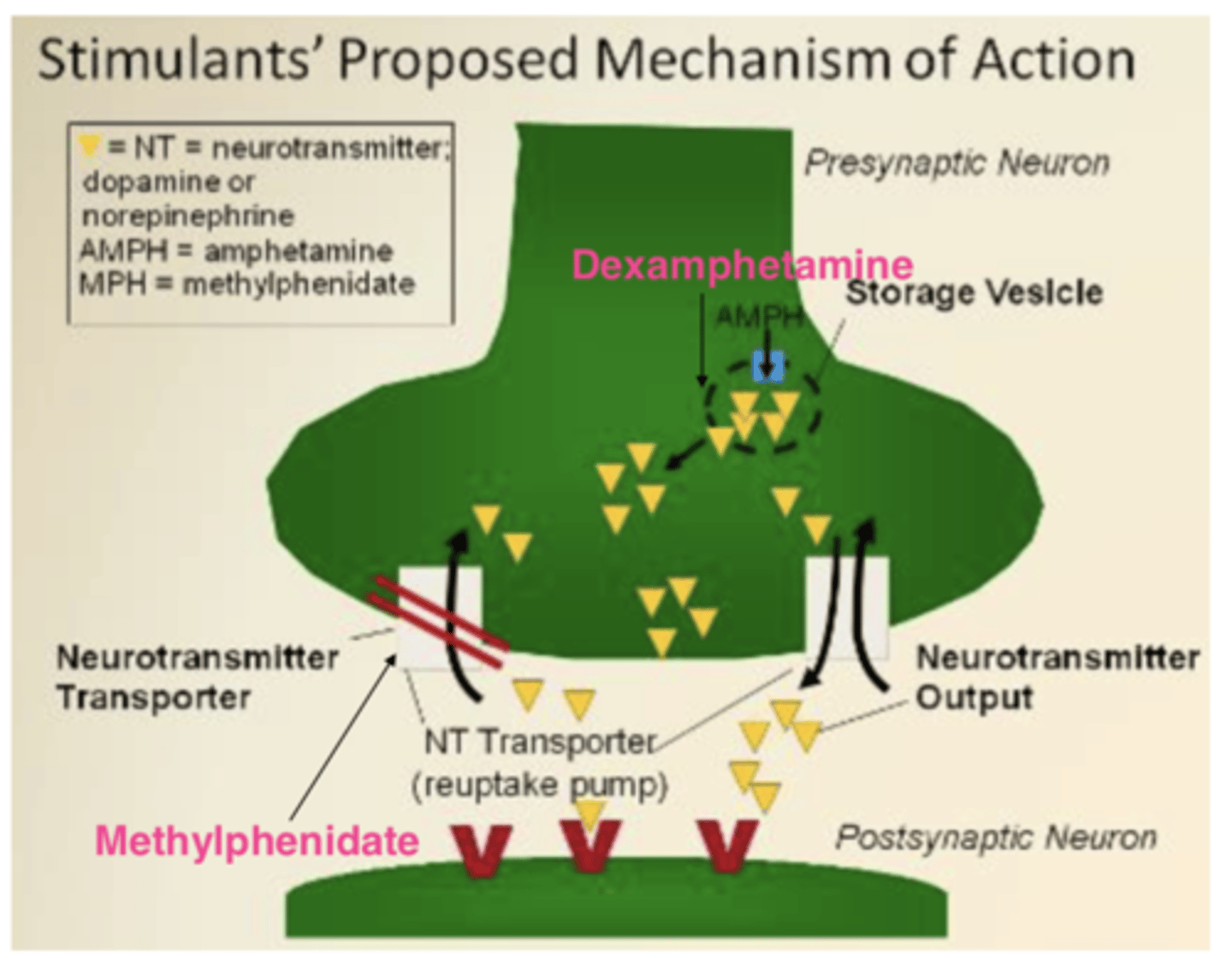
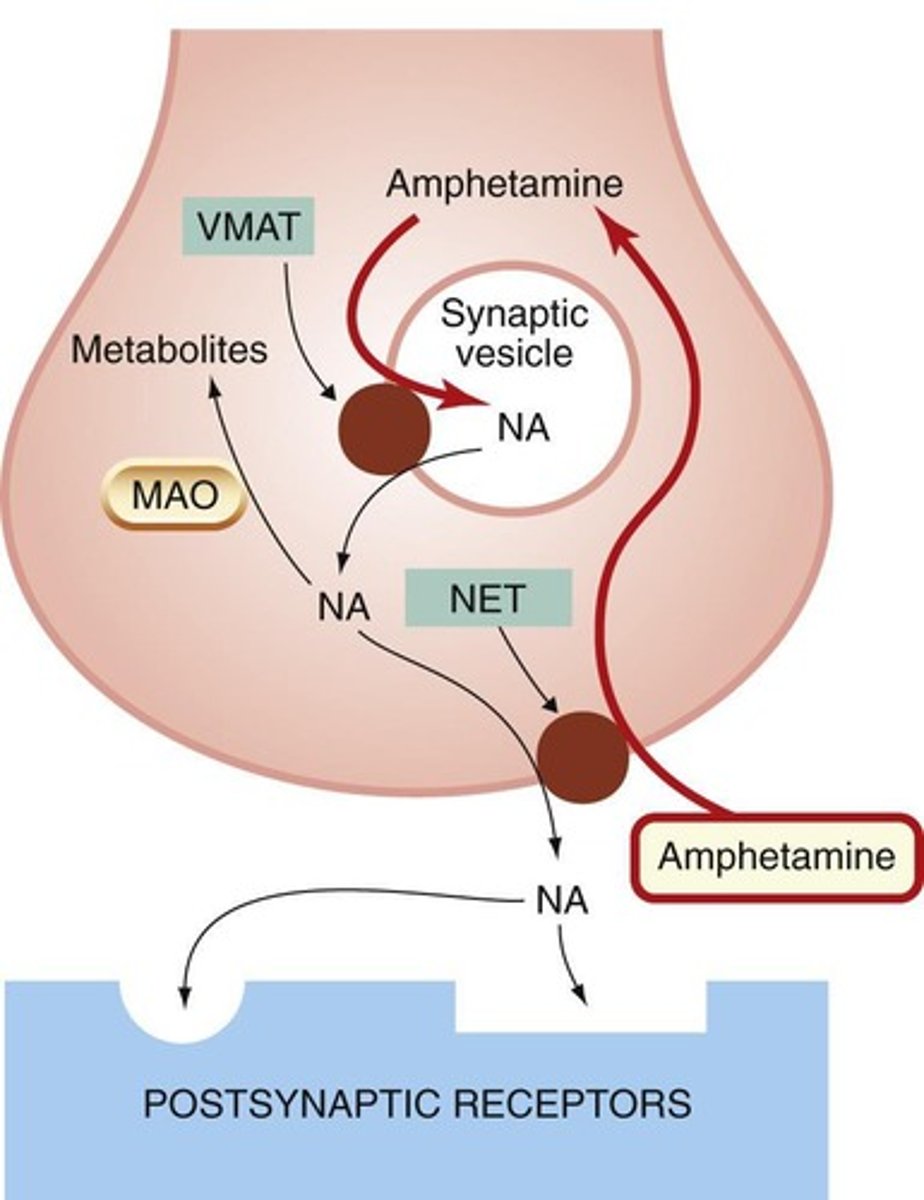
What is the mechanism of action for amphetamines?
It is a dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor and increases dopamine release.
This leads to a higher concentration of monoamine in the synaptic cleft.
Give examples of non-stimulant ADHD medication
Atomoxetine
Clonidine
Guanfacine
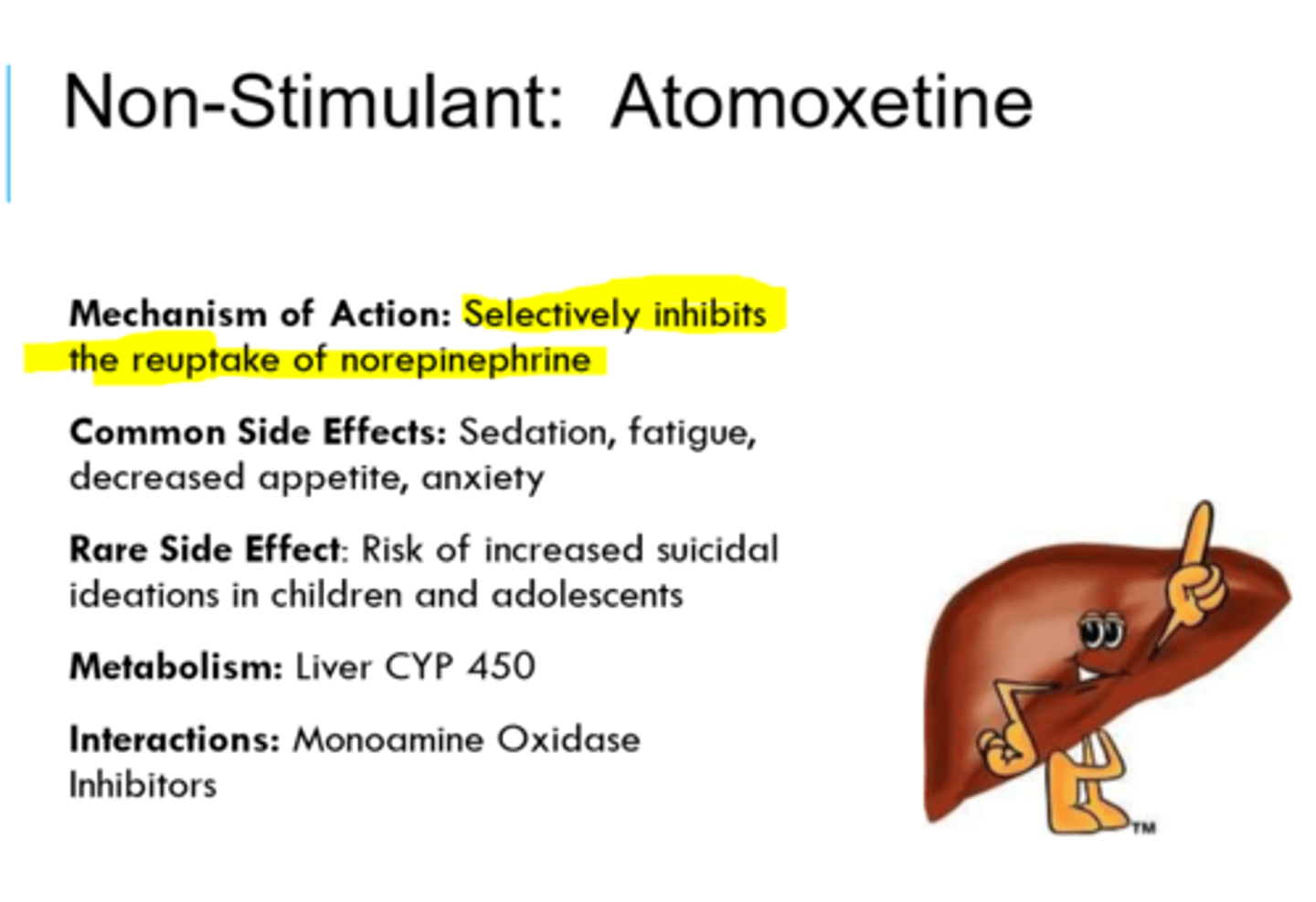
What is the mechanism of action for atomoxetine?
It is a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor.
- Useful for when stimulant medications are contraindicated
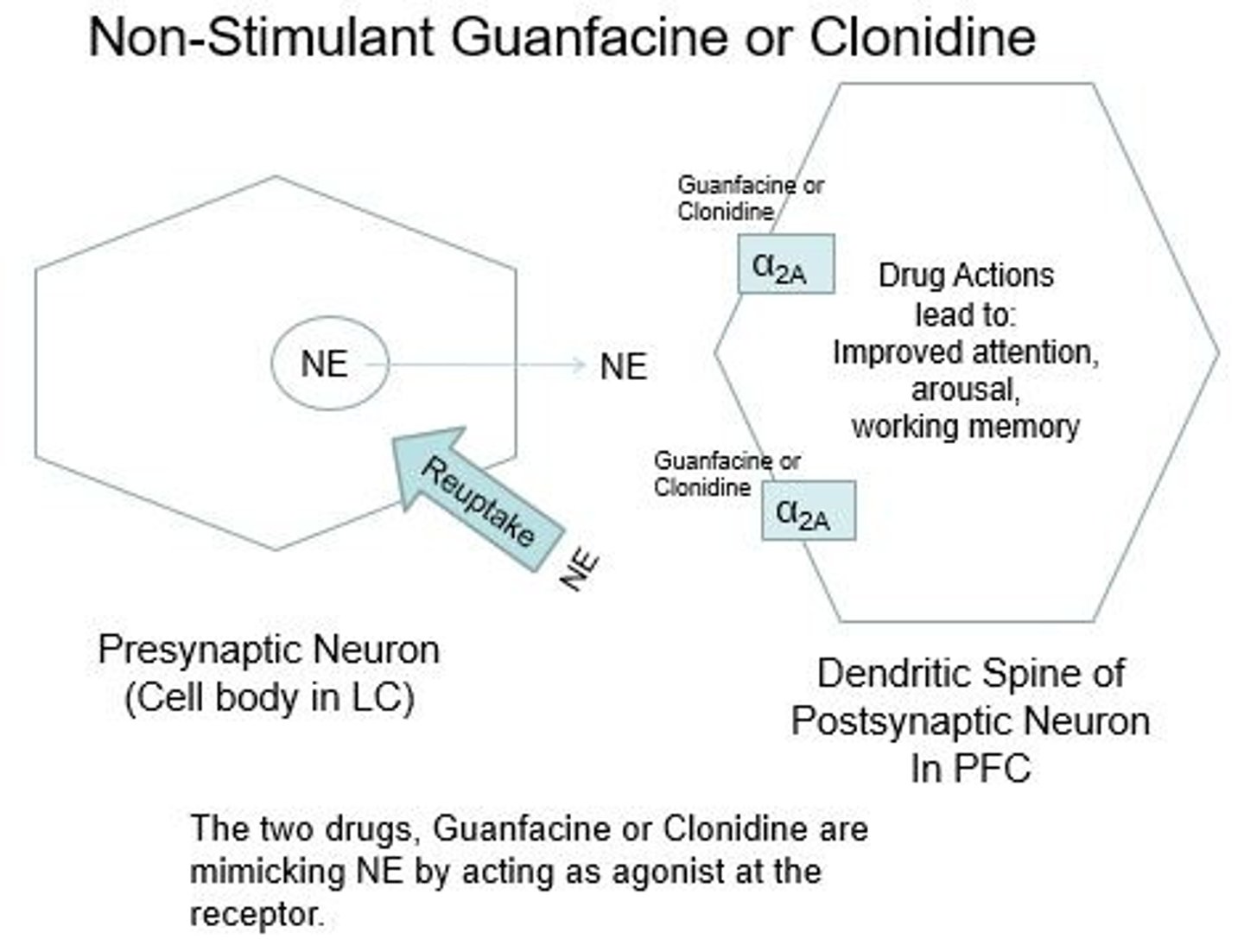
What is the mechanism of action for guanfacine and clonidine?
They are norepinephrine receptor agonists (a2-adrenoceptor agonists)
Why may drug abusers turn to stimulants?
As pharmacists we should consider that people who abuse stimulants may be self medicating for ADHD.
What are common adverse effects of stimulant medication?
More minor side effects; more common
- Decreased appetite
In a growing child, this may result in stunted growth (deficits in height/weight gain).
In adults, it can be seen through weight loss.
- Increased blood pressure or heart rate
- Sleep disturbance
Severe side effects; rarer
- Tics
- Seizures
- Psychotic symptoms
What are some problems with taking stimulants (non-pharmacological)?
- Some people don't want to take medication
- Some people may stop taking stimulants due to the side effects
- Some people don't see them as effective; don't see benefits of the medication
- Some people may experience stigma (due to being labelled with a condition)
- There is an element of trial and error. It is not guaranteed that medication will work. May not want to try different options
What drug used for ADHD treatment is a prodrug?
Lisexamphetamine
Why was lisdexamphetamine developed?
We wanted a prodrug as the immediate release (dexamphetamines) have a shorter duration of action.
Therefore the effects of the medication are short lived and multiple doses must be taken daily to maintain plasma concentration within the therapeutic window.
- This is the rational for prodrug or slow release/ extended duration of action.
There have been some people which have developed extended release formulations of amphetamines - provides activity over 12 hours (once daily dosing).
How is lisdexamphetamine activated
Hydrolysis by an aminopeptidase.
Lisdexamphetmaine has an amide bond and therefore can be broken down by peptidases
This produces D-amphetamine and L-lysine.
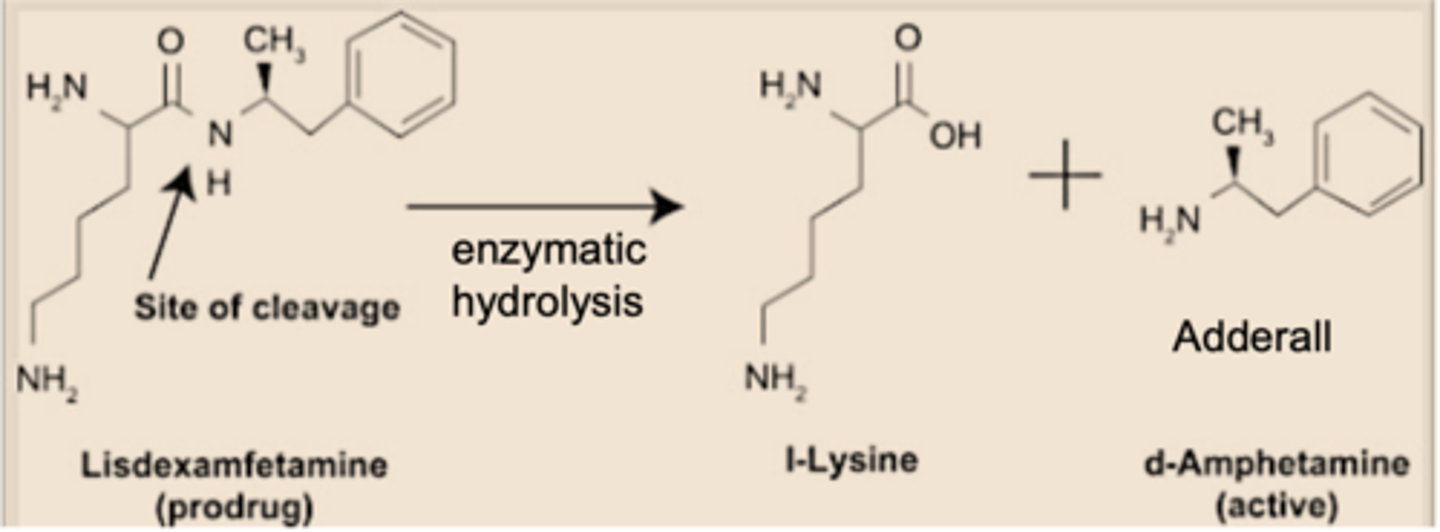
Why is an enzyme required for the hydrolysis of lisdexamphetamine?
An enzyme is needed because the carbonyl of an amide is not reactive. This means amides are stable. A Lewis acid is provided by the enzyme to make it more reactive to hydrolyse the amide bond.
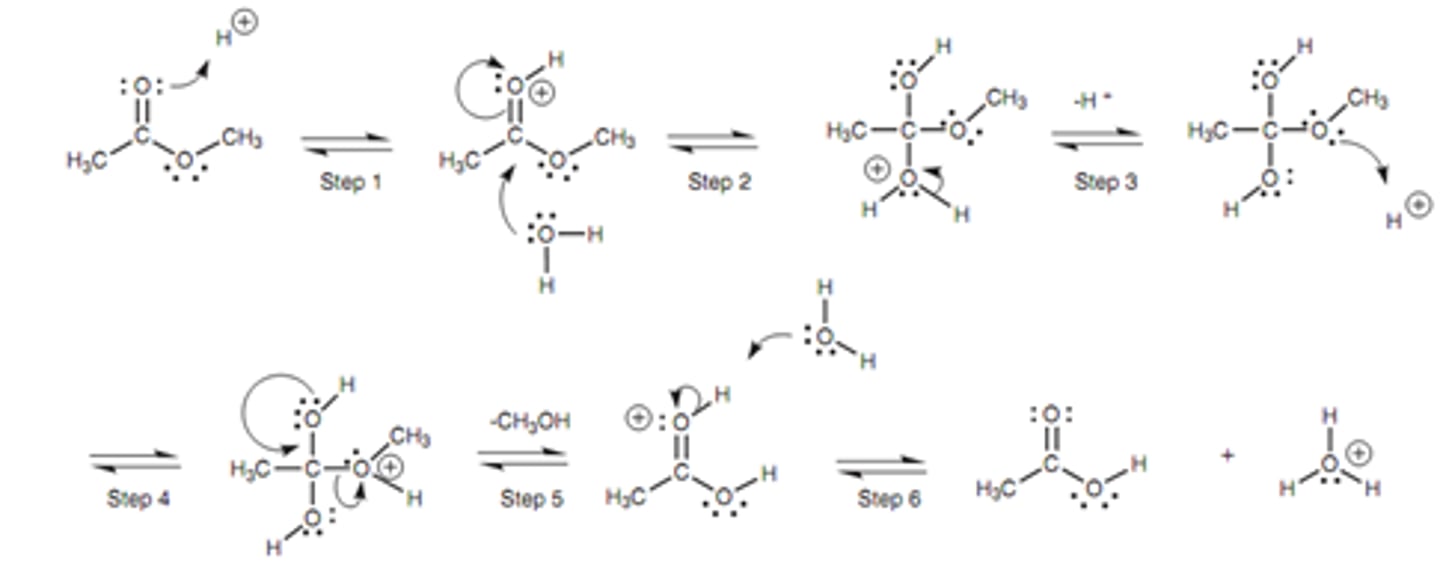
Draw the mechanism of aminopeptidase hydrolysis
(Same mechanism but with an amide bond rather than an ester bond)
Produces an amine and carboxylic acid
Rank carbonyl reactivity
Most to least reactive
- Acyl chloride
- Acyl chloride
- Ketone
- Ester
- Amide
How is lisdexamphetamine transported across the blood brain barrier?
Active transport
Lysine is attached to the amphetamine to make use of an active transport process.
Active transport is available in the brain for drugs which appear like/ are attached to glucose and amino acids. This is because, glucose and amino acids are accepted into the brain.
Amphetamines are a small molecule so it can be transported on the back of the lysine
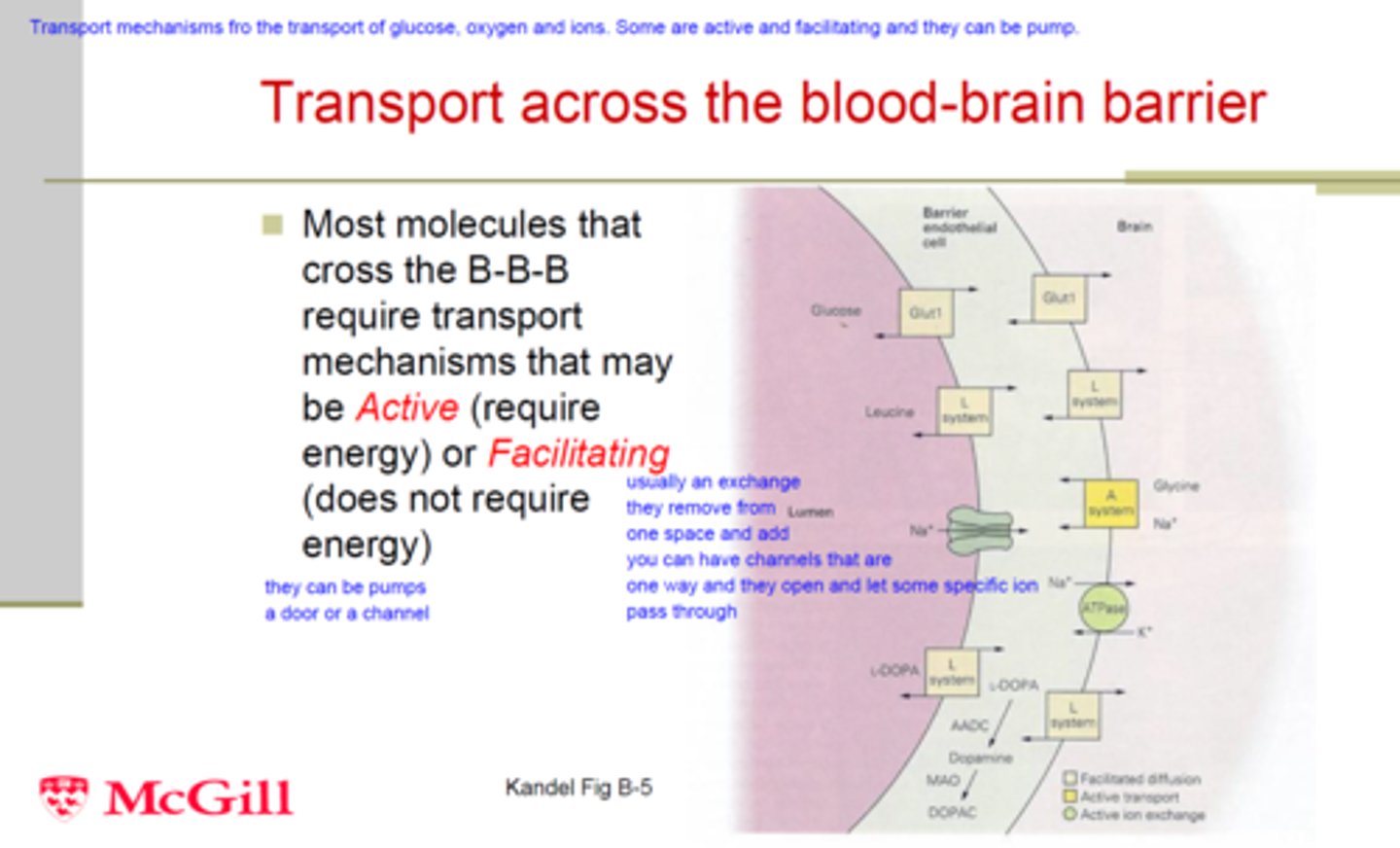
How do we know lisdexamphetamine is transported across the blood brain barrier via active transport?
- Lisdexamphetamine is highly aqueous and charged molecule, so it cannot be transported by passive transport
- Lysine will be a substrate for peptide transporters e.g. PEPT1 in the intestine
Where is lisdexamphetamine primarily absorbed?
Lisdexamphetamine is mainly absorbed by PEPT1 in the small intestines mainly.
What was the aim for with prodrug delivery with lisdexamphetamine?
By using the prodrug strategy, we hope that we get a longer duration of effect. It worked in the case of lisdexamphetamine.
Compare the pharmacokinetics between the prodrug lisdexamphetamine and dexamphetamine
The only difference between them is the slower onset of lisdexamphetamine compared to dexamphetamine.
- Lisdexamphetamine takes 1 hour longer to reach peak concentration (Cpeak) of active compound compared to dexamphetamine.
- If give just dexamphetamine (short-acting) and compare to prodrug lisdexamphetamine, the AUC is similar and the t ½ is the same.
Why does lisdexamphetamine have a longer duration of action than dexamphetamine if they both have the same t1/2 ?
The reason for slower onset and lower Cmax in lisdexamphetamine compared to dexamphetamine could be due to less tolerance than the immediate release preparation leading to an extended duration of action.
What is the duration of action of dextroamphetamine?
Dextroamphetamine (dexamphetamine): 4-6h
What is the duration of action of lisdexamphetamine?
Lisdexamfetamine (prodrug): 13h
What are the different durations of action for methylphenidate?
1. Methylphenidate (immediate release): 4h
2. Methylphenidate (extended release): 12h
3. Methylphenidate (delayed and extended release): 11h after 10-12h delay
Describe drug design properties for CNS delivery (in the context of ADHD medication)
- Relatively low Mw (no more than 250)
- Hydrogen bond donors, usually less than 2 but some break the rule e.g. guanfacine has 4
- Expect lipophilic Positive log P (all fit)
- PSA expected around 60 (none fit)
All bear some resemblance to D-amphetamine
Phenyl, amine, side chain.