social psychology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:10 AM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
1
New cards
who published the first study on social psych?
Norman Triplett (1898)
2
New cards
what was the first study on social psych about and what did it find?
the effect of competition on performance and it found that people do better on familiar tasks in the presence of others
3
New cards
who published the first textbooks on social psych (independently)?
william mcdougall and e.h. ross (1908)
4
New cards
who was the first to suggest that social approval infulences behavior?
Verplank
5
New cards
who created the reinforcement theory (1950’s)?
verplank, pavlov, thornedike, hull, and skinner
6
New cards
what does reinforcement theory say?
behavior is motivated by the anticipated rewards
7
New cards
what is albert banduras most well known theory?
social learning theory
8
New cards
what does social learning theory say?
behavior is learned through immitation
9
New cards
who created role theory (1970’s)?
bindle
10
New cards
what does role theory say?
people know the roles they are suppose to fill and behavior can be attributed to adopting these roles
11
New cards
what other theories influence social psych the most?
cognitive theory
12
New cards
what does cognitive theory say that influences social psych?
perception, judgement, memories, and decision making influence behavior and arousal
13
New cards
what are attitudes?
cognitions, beliefs, feelings, and behavioral predispositions
typically opinion statements (likes/dislikes of people/things/ideas)
typically opinion statements (likes/dislikes of people/things/ideas)
14
New cards
what does consistency theory say?
people prefer consistency and will/wont change based upon this preference
15
New cards
who created balance theory?
fritz heider
16
New cards
what does balance theory say?
the way 3 elements relate results in balance (all 3 fit together 1 or 3 positive) or stress (no balance, 0 or 2 positives)
17
New cards
what are the 3 elements of balance theory?
P = person we are talking about
O = other person
X = thing/idea/other person
O = other person
X = thing/idea/other person
18
New cards
balance theory figures
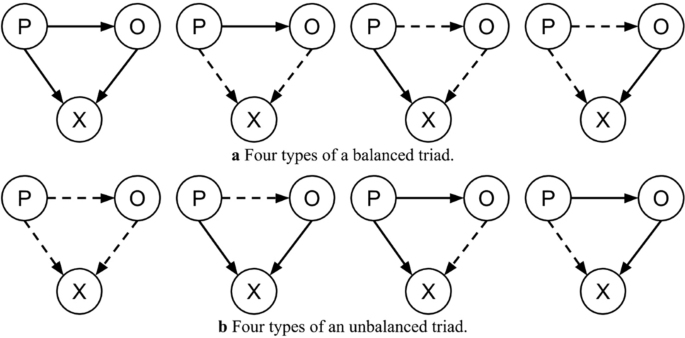
19
New cards
who created cognitive dissonance theory and social omparison theory?
leon festinger
20
New cards
what does cognitive dissonance theory say?
conflict you feel when your attitudes aren’t in synch with your behavior
the greater the dissonance, the greater the pressure to reduce it
when behavior can be justified by means of external inducements ($), there is no need to change cognitions
minimal justification effect
two types of cognitive dissonance
two main principles
the greater the dissonance, the greater the pressure to reduce it
when behavior can be justified by means of external inducements ($), there is no need to change cognitions
minimal justification effect
two types of cognitive dissonance
two main principles
21
New cards
what are the two types of cognitive dissonance?
free choice - making a choice between desirable options and post-decision dissonance and spreading of alternatives
forced compliance - forced to behave inconsistently with beliefs
forced compliance - forced to behave inconsistently with beliefs
22
New cards
what are the two principles of cognitive dissonance?
1) if there is pressure to do/say something, there is a tendency to chin beliefs
2) the greater the pressure, the less likely to change
2) the greater the pressure, the less likely to change
23
New cards
what is the minimal justification effect?
when external justification is minimal, dissonance is reduced by changing cognitions
24
New cards
who created the self-perception theory?
Daryl Bem
25
New cards
what does self-perception theory say?
when an attitude is weak/ambiguous, you observe your own behavior and attribute an attitude to yourself
you infer your attitude based on your behavior
does not hypothesize dissonance - initial attitude is irrelevant and no discomfort is produced by the behavior
over justification effect
you infer your attitude based on your behavior
does not hypothesize dissonance - initial attitude is irrelevant and no discomfort is produced by the behavior
over justification effect
26
New cards
carl hovelands model
deals with attitude change as part of communicating a message with intent to persuade someone
3 components: communicator, communication, and situation
arguing against your self interest can cause significant change in attitude
credible sources are most efficient
sleeper effect and two sided messages
3 components: communicator, communication, and situation
arguing against your self interest can cause significant change in attitude
credible sources are most efficient
sleeper effect and two sided messages
27
New cards
what is the sleeper effect?
credible sources loose impact and uncredible sources gain impact over time
28
New cards
two sided messages
messages that include arguments for and against a position
29
New cards
what is the elaboration model of persuasion?
two routes of persuasion:
1. central route - issue is very important to us, we follow argument closely and evaluate the argument. strong arguments > weak arguments
2. peripheral route - issue is not that important to us, we don’t really pay attention, and strength of argument does not matter
1. central route - issue is very important to us, we follow argument closely and evaluate the argument. strong arguments > weak arguments
2. peripheral route - issue is not that important to us, we don’t really pay attention, and strength of argument does not matter
30
New cards
who created the elaboration model of persuasion?
Petty and Cacioppo
31
New cards
what is the theory of resistance to persuasion?
analogy of inoculation (william mcguire)
32
New cards
analogy of inoculation
people can be inoculated to persuasion: 1. expose a weakened argument 2. refute argument
cultural truism - unquestioned beliefs
belief perseverance - hold beliefs even after they are proven false
reactance - freedom is pressured so person acts in a way to reassert a sense of freedom
cultural truism - unquestioned beliefs
belief perseverance - hold beliefs even after they are proven false
reactance - freedom is pressured so person acts in a way to reassert a sense of freedom
33
New cards
what does social comparison theory say?
we are drawn to affiliate because of a tendency to evaluate ourselves in relationships to other people
3 principle:
1. people prefer to evaluate themselves by objective, nonsocial means and compare to others when this isn’t possible
2. the fewer similarities and tendencies, the lower tendency to make the comparison
3. if discrepancies exist with opinions and abilities, we tend to change position to move towards the group
3 principle:
1. people prefer to evaluate themselves by objective, nonsocial means and compare to others when this isn’t possible
2. the fewer similarities and tendencies, the lower tendency to make the comparison
3. if discrepancies exist with opinions and abilities, we tend to change position to move towards the group
34
New cards
what did stanley schachter say about the social comparison theory?
the greater the anxiety, the greater the desire to affiliate
anxious people prefer the company of other anxious people (anxiety and need to compare self may play a role here)
anxious people prefer the company of other anxious people (anxiety and need to compare self may play a role here)
35
New cards
what is the reciprocity hypothesis?
we tend to like people who like us and tend to dislike those who dislike us
we take into account another persons evaluation of us
gain loss principle
we take into account another persons evaluation of us
gain loss principle
36
New cards
who created the gain loss principle?
aronson and linder
37
New cards
what does the gain loss principle say?
an evaluation that changes will have more of an impact than an evaluation that remains constant
we will like someone more if their evaluation of us increases and does not stay the same
we will like someone more if their evaluation of us increases and does not stay the same
38
New cards
what does the social exchange theory say?
a person weighs the rewards and cost of interaction
when rewards outweigh costs the greater the interaction (max. rewards, min. cost)
equity theory
when rewards outweigh costs the greater the interaction (max. rewards, min. cost)
equity theory
39
New cards
what does equity theory say?
we consider our own rewards and the other persons rewards and prefer them to be equal, there will be instability if inequal
40
New cards
affiliation and attraction with individual characteristics
correlation between affiliation and similarity of intelligence, attitude, education, age, religion, SES, etc.
need complementary - people choose relationships so they mutually satisfy each others needs
potency of physical attractiveness - attractiveness stereotype says we attribute positive qualities and desirable characteristics to attractive people
spatial proximity - tend to develop a greater liking to someone who lives closer because they are more accessible and there is an increased intensity of initial reaction
mere exposure hypothesis (Zojanc) - based on familiarity, repeated exposure leads to increased liking
need complementary - people choose relationships so they mutually satisfy each others needs
potency of physical attractiveness - attractiveness stereotype says we attribute positive qualities and desirable characteristics to attractive people
spatial proximity - tend to develop a greater liking to someone who lives closer because they are more accessible and there is an increased intensity of initial reaction
mere exposure hypothesis (Zojanc) - based on familiarity, repeated exposure leads to increased liking
41
New cards
what is the potency of physical attractiveness?
attractiveness stereotype says we attribute positive qualities and desirable characteristics to attractive people
42
New cards
what is spatial proximity?
tend to develop a greater liking to someone who lives closer because they are more accessible and there is an increased intensity of initial reaction
mere exposure hypothesis (Zojanc) - based on familiarity, repeated exposure leads to increased liking
mere exposure hypothesis (Zojanc) - based on familiarity, repeated exposure leads to increased liking
43
New cards
what did john darley and bibb latane study? what did they fine?
bystander intervention
two factors in deciding whether or not to help: social influence and diffusion of responsibility
two factors in deciding whether or not to help: social influence and diffusion of responsibility
44
New cards
what was the experiments john darley and bibb latane did regarding bystander intervention?
smoke experiment (social influence): participants did not respond if they didn’t think the fire was real
seizure experiment (diffusion of responsibility): 100% reported when they thought they were alone, 85% when 2 others, and 62% when 4 others
seizure experiment (diffusion of responsibility): 100% reported when they thought they were alone, 85% when 2 others, and 62% when 4 others
45
New cards
social influence with bystanders
if others arent acting in emergency then they wont either
pluralistic ignorance - leading others to define event as nonemergency
pluralistic ignorance - leading others to define event as nonemergency
46
New cards
diffusion of responsibility with bystanders
the more people that are present, the less likely the individual is to offer help
if alone, 100% of responsibility is on individual
if alone, 100% of responsibility is on individual
47
New cards
who created the empathy-altruism model?
Batson
48
New cards
what is the empathy-altruism model?
when in a situation where others may need help, people may feel distress or empathy which determines the helping behavior
49
New cards
empathy
ability to vicariously experience the emotions of others
50
New cards
what experiment did batson do? what did he find?
people watched others getting shocked and there were 2 conditions: easy escape (chance to leave after 2 shocks) or difficult escape (had to stay for 10 shocks)
after 2 shocks the participants filled out how distressed they were
easy escape participants reported more distress and left
difficult escape participants reported more empathy and helped
after 2 shocks the participants filled out how distressed they were
easy escape participants reported more distress and left
difficult escape participants reported more empathy and helped
51
New cards
what is the frustration-aggression hypothesis?
when people are frustrated they act aggressively
the strength of aggression correlates with strength of frustration
the strength of aggression correlates with strength of frustration
52
New cards
what did banduras social learning theory say about aggression?
aggression is learned through modeling and reinforcement
believes aggression is selectively reinforces - people act aggressively because they expect a reward
bobo doll experiment
believes aggression is selectively reinforces - people act aggressively because they expect a reward
bobo doll experiment
53
New cards
what is the most influential theory on aggression?
bandura’s social learning theory
54
New cards
who did the major conformity and obedience studies?
mazafer sherif, soloman asch, and stanley milgram
55
New cards
what did sherif’s conformity study find?
the autokinetic effect on subjects estimated change so that group agreed on amount of movement
individuals conform to the group and judgement converges on the same group norm
individuals conform to the group and judgement converges on the same group norm
56
New cards
what did asch’s conformity study find?
length of line study found alone subject got the line length wrong
57
New cards
conformity
yielding to group pressure without explicit demand
58
New cards
what did milgram’s obedience study find?
the effects of punishment on learning and obedience to authority
found the drive to obey was greater than the drive not to hurt others
when confederates defied, so did participants
had confederates deliver shock and participants did entire experiment
found the drive to obey was greater than the drive not to hurt others
when confederates defied, so did participants
had confederates deliver shock and participants did entire experiment
59
New cards
what is the foot in door effect?
compliance with a small request increases the likelihood of compliance with a larger request
60
New cards
what is the door in the face effect?
refusing a large initial request increases the likelihood to agree to a second, smaller effect
61
New cards
compliance
changes in behavior as result of pressure
62
New cards
what influences self perception?
other peoples views, social roles, and group memberships
63
New cards
what was the clark and clark doll preference study? what did they find?
ethnic self-concept of black and white kids
majority preferred white doll
showcased negative effects of racism
majority preferred white doll
showcased negative effects of racism
64
New cards
what has research since the clark and clark doll preference study shown?
black kids hold positive view of ethnicity
65
New cards
dimensions of personal identity
several factors determine which identity is enacted in particular situation
66
New cards
hierarchy of salience
the more salient, the more conformity
67
New cards
what is albert banduras self-efficacy?
individuals belief in their ability to execute behavior
those with strong efficacy exert more effort on harder tasks
judgement based on previous performance, vicarious experiences, social persuasion, and psychological and emotional states
those with strong efficacy exert more effort on harder tasks
judgement based on previous performance, vicarious experiences, social persuasion, and psychological and emotional states
68
New cards
social perception
the way we form impressions about characteristics of a certain group/individual
69
New cards
primary effect
occasions when the first impressions are more important than subsequent impressions
70
New cards
recency effect
the most recent info we have about someone is most important
71
New cards
what is attribution theory? who created it?
fritz heider
tendency to infer the cause of other people’s behavior
we attempt to discover cause and effect in events
two causes - situational (external and related to surroundings; threats, peers, money) or dispositional (related to features of person whose behavior is being considered; attitude, personality)
bias towards dispositional causes
tendency to infer the cause of other people’s behavior
we attempt to discover cause and effect in events
two causes - situational (external and related to surroundings; threats, peers, money) or dispositional (related to features of person whose behavior is being considered; attitude, personality)
bias towards dispositional causes
72
New cards
what is the fundamental attribution bias?
tendency to look for personality flaws in situations rather than looking for situational influences
73
New cards
what is the halo effect?
tendency to allow a general impression of someone influence other, more specific evaluations of the person
this is why people are often inaccurate in evaluations of people they believe are generally good/bad
this is why people are often inaccurate in evaluations of people they believe are generally good/bad
74
New cards
what is the belief in a just world?
belief that good things happen to good people and bad things happen to bad people
a strong belief in a just world increases victim blaming because it doesn’t allow for innocent victims
a strong belief in a just world increases victim blaming because it doesn’t allow for innocent victims
75
New cards
the presence of others can…
improve or worsen performance
76
New cards
what did theodore newcombs study find?
over time, students increasingly accept norms of community
66% of parents voted republican, 62% of freshman, 43% of sophomores, and 15% of juniors and seniors
66% of parents voted republican, 62% of freshman, 43% of sophomores, and 15% of juniors and seniors
77
New cards
what did edward hall study?
proxemics
how culture governs how far away from one another we stand
how culture governs how far away from one another we stand
78
New cards
proxemics
study of how individuals space themselves in relation to others
79
New cards
what is zojoncs theory?
increased arousal in presence of others which consequently enhances emission of a dominant response (mistakes or correct acts)
80
New cards
what is social loafing?
tendency for people to put forth less effort when part of a group
81
New cards
what did philip zimbardo find when he studied anonymity?
people are more likely to commit antisocial acts when they feel anonymous within the social environment because there is a diminished restraint of unacceptable behavior
82
New cards
what is deindividualization?
loss of self-awareness and personal identity
83
New cards
what is often a factor in group decision making?
group think
84
New cards
what is group think?
the group decision making strives for consensus and does not consider discordant info
85
New cards
what is the risky shift?
group decisions are often riskier than individual decisions
86
New cards
what is the value hypothesis of the risky shift?
risky shifts occur in situations where riskiness is valued culturally
87
New cards
what did james stoner study?
group decisions
gave couples a dilemma (about pregnancy) and found that decisions shifted towards caution and away from risk
found that this shift may be determined by the nature of the risk
gave couples a dilemma (about pregnancy) and found that decisions shifted towards caution and away from risk
found that this shift may be determined by the nature of the risk
88
New cards
what is group polarization?
the tendency for a group discussion to enhance the initial tendencies towards riskiness or caution
89
New cards
what do leaders possess and do that followers do not?
special qualities and they engage in more commuication
90
New cards
what can increase some ones perceived leadership?
increased amount the person speaks (even artificially)
91
New cards
what did kurt lewis study?
the effects of leadership styles
laisse-faire: less efficient, organized, and satisfying
autocratic: more hostile, aggressive, dependent, work
democratic: more satisfying, cohesive, and work ethic and motivation
laisse-faire: less efficient, organized, and satisfying
autocratic: more hostile, aggressive, dependent, work
democratic: more satisfying, cohesive, and work ethic and motivation
92
New cards
Aronson & Linder
Asch
Bandura
Bem
Clark & Clark
Asch
Bandura
Bem
Clark & Clark
gain & loss principle
conformity
social learning theory
self-perception theory
doll preferences
conformity
social learning theory
self-perception theory
doll preferences
93
New cards
Darley & Latane
Eagly
Festinger
Hall
Heider
Hovland
Eagly
Festinger
Hall
Heider
Hovland
non-helping factors (social influence and diffusion of responsibility)
gender differences and conformity (gender roles)
cognitive dissonance theory and social comparison theory
interpersonal distance
balance theory & attribution theory
attitude change
gender differences and conformity (gender roles)
cognitive dissonance theory and social comparison theory
interpersonal distance
balance theory & attribution theory
attitude change
94
New cards
Janis
Lerner
Lewin
McGuire
Milgram
Newcomb
Lerner
Lewin
McGuire
Milgram
Newcomb
group think and group decisions (why they go wrong)
belief in a just world
leadership styles
psychological inoculation
obedience (shock) & stimulus overload theory
political norms
belief in a just world
leadership styles
psychological inoculation
obedience (shock) & stimulus overload theory
political norms
95
New cards
Petty &Cacioppo
Schachter
Sherif
Zajonc
Zimbardo
Schachter
Sherif
Zajonc
Zimbardo
elaboration likelihood model of persuasion (route of persuasion)
relationship between anxiety and affiliation
autokinetic effect (robbers cave)
mere exposure effect & social facilitation effect
prison simulation
relationship between anxiety and affiliation
autokinetic effect (robbers cave)
mere exposure effect & social facilitation effect
prison simulation
96
New cards
cooperation
people act together for mutual benefit
97
New cards
competition
person acts for their benefit so they can obtain a goal that has limited availability
98
New cards
what is the prisoners dilemma?
experiment that investigated people choice to cooperate or compete
99
New cards
prisoners dilemma figure
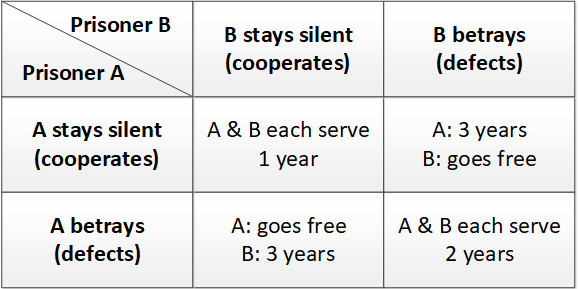
100
New cards
who did the robbers cave experiment?
Muzafer Sherif