Biology STAAR Review
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
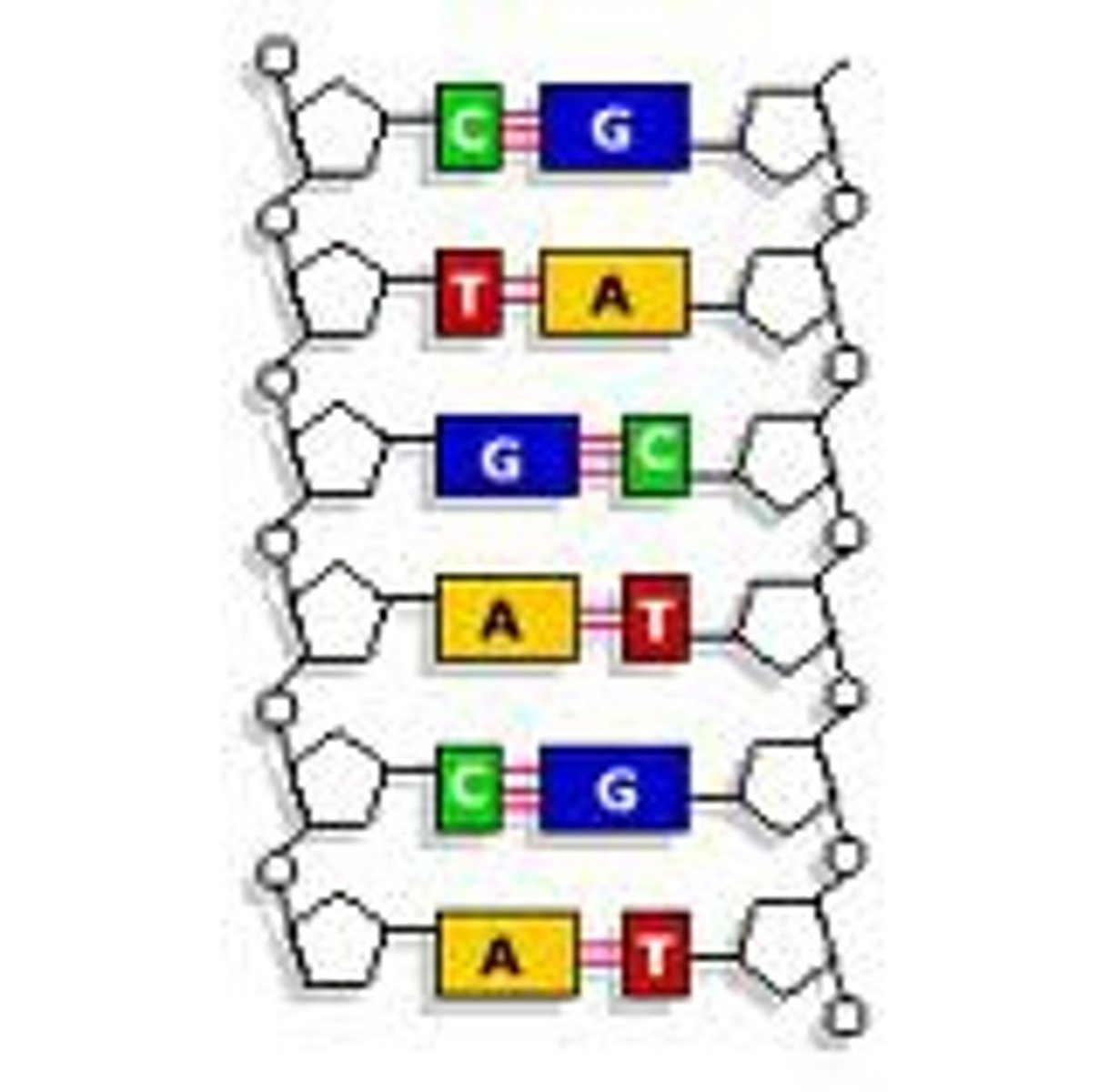
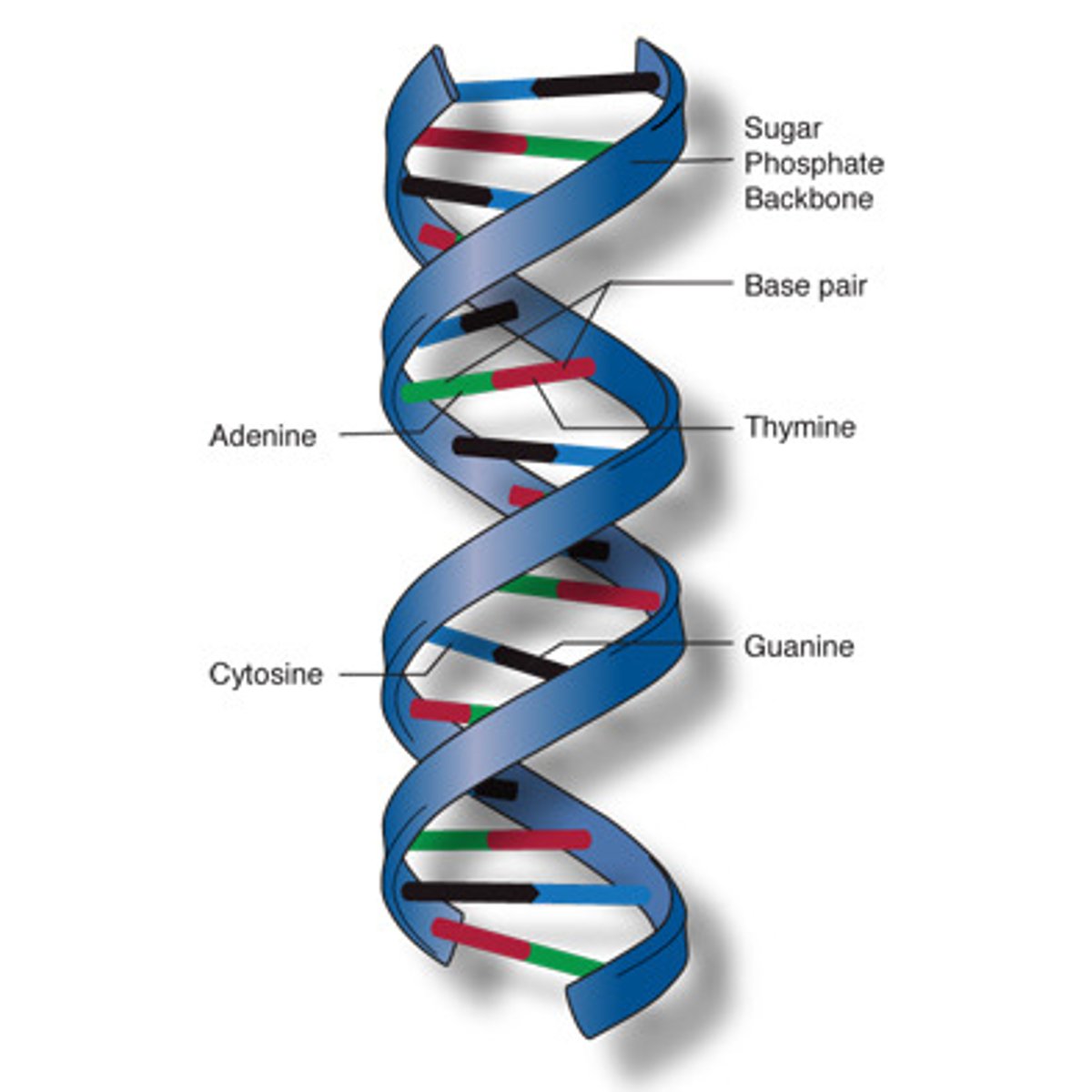
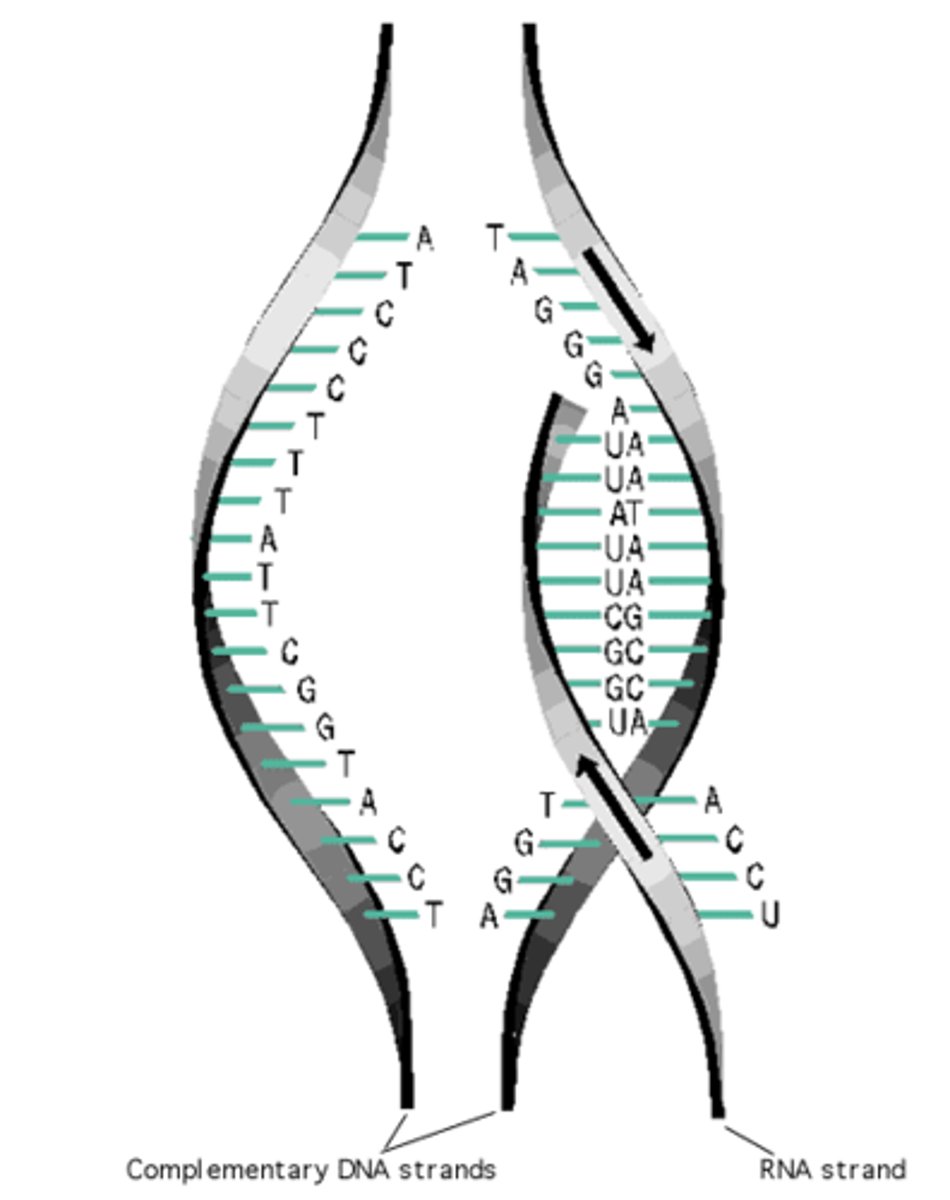
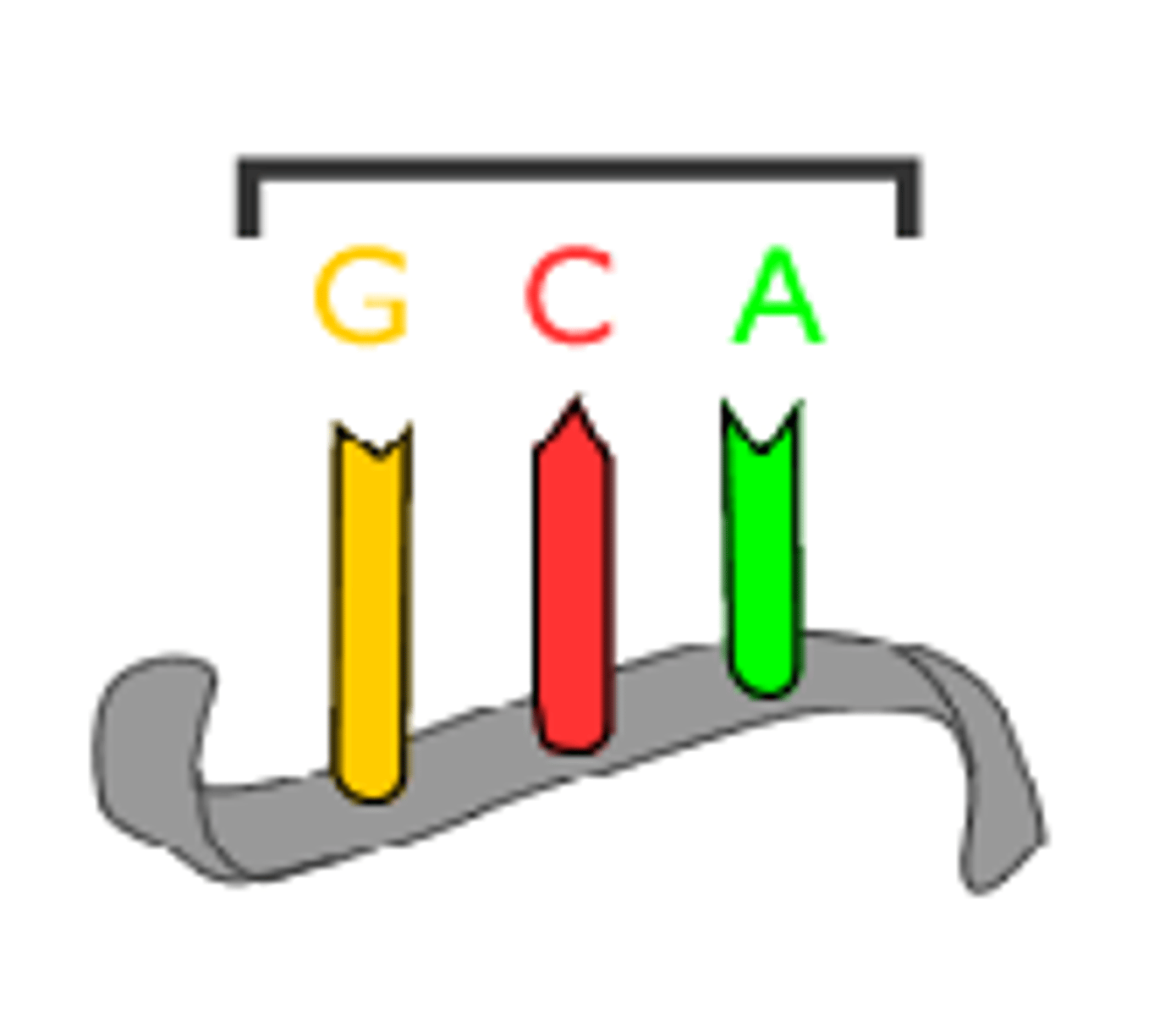
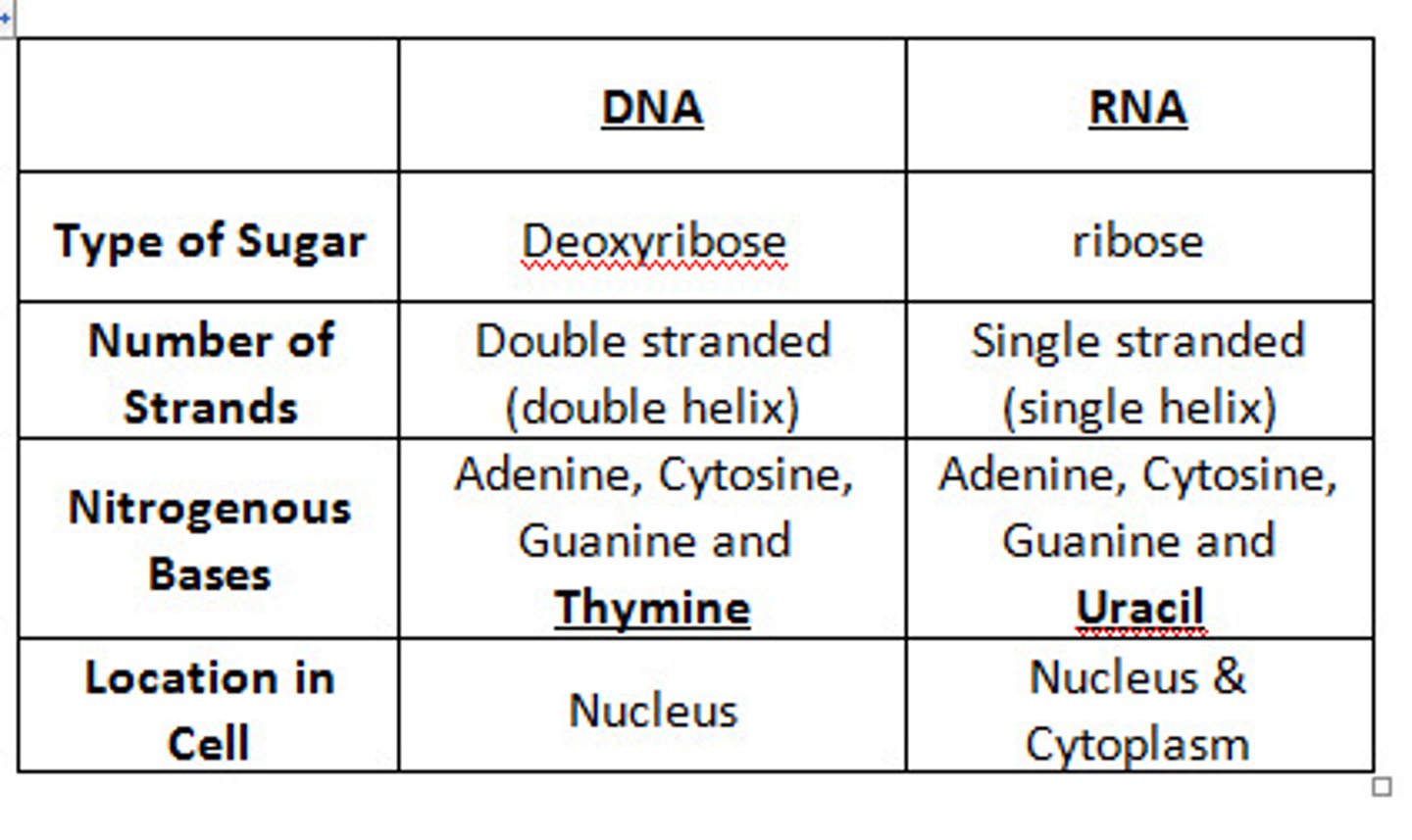
Base-Pairing Rules
DNA: A-T & C-G; RNA: A-U & C-G.
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance in all living cells.
DNA
Double-stranded molecule containing GCAT nucleotides.
RNA
Single-stranded molecule containing GCAU nucleotides.
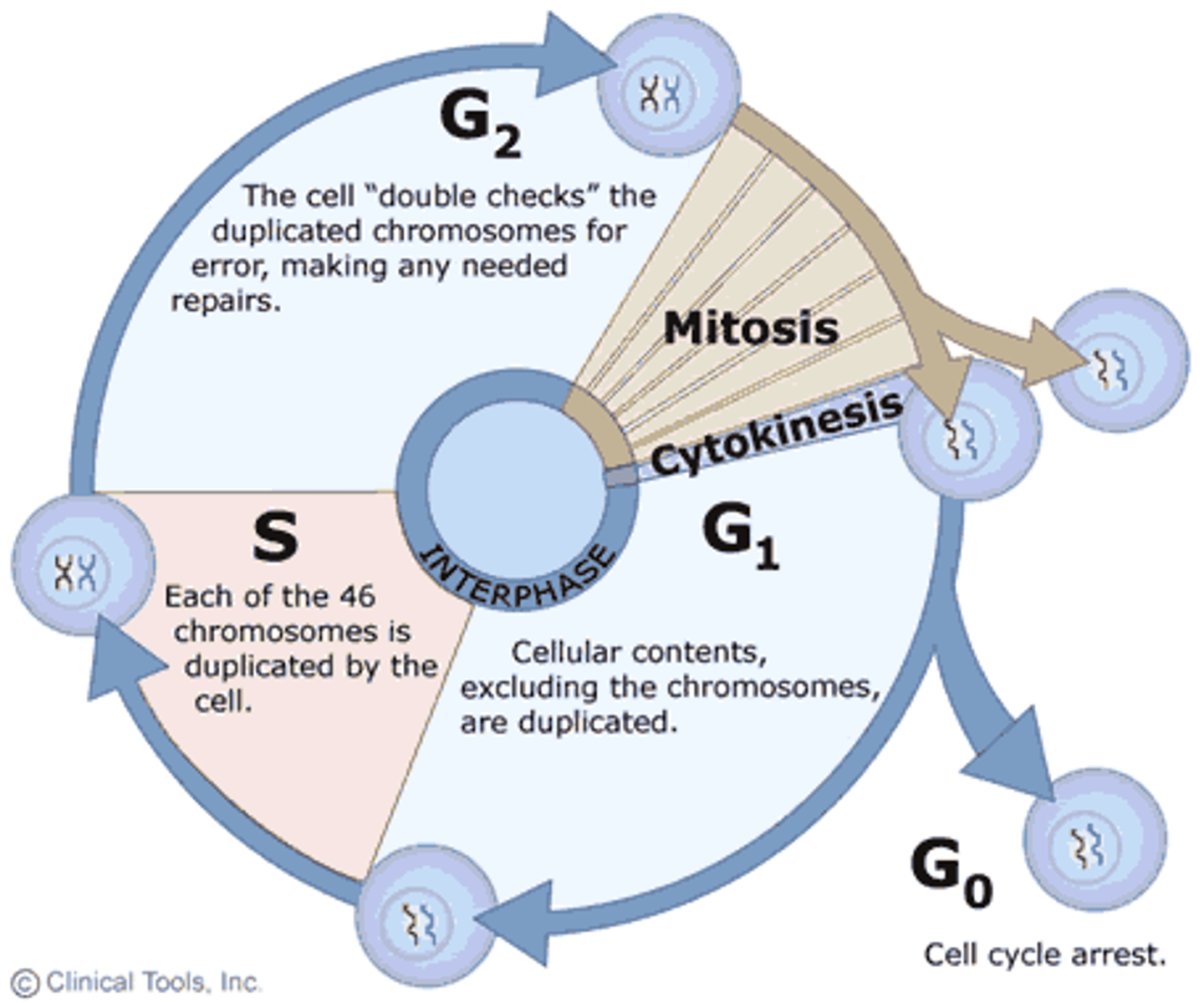
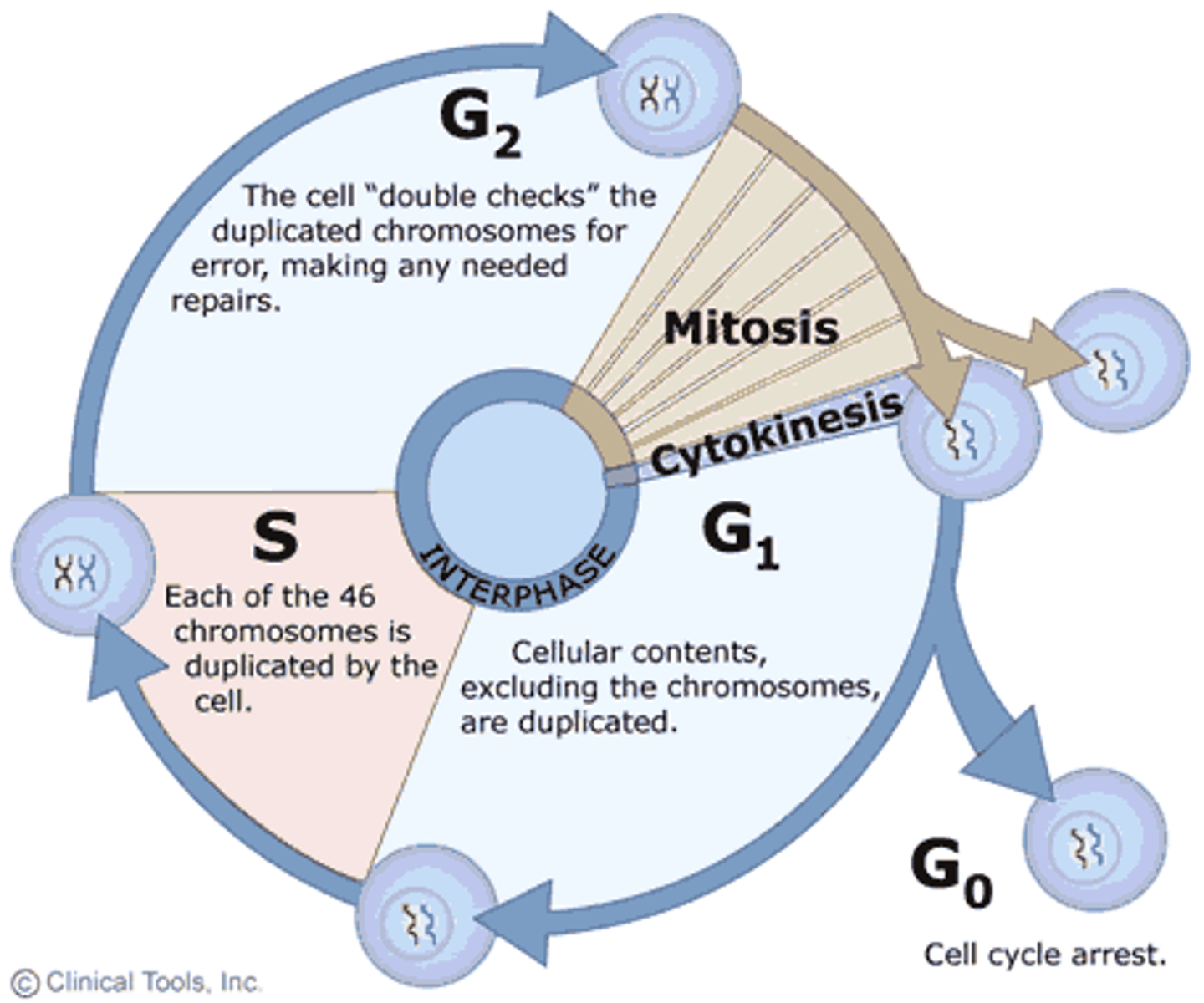
S Phase
Phase of cell cycle where DNA replicates.
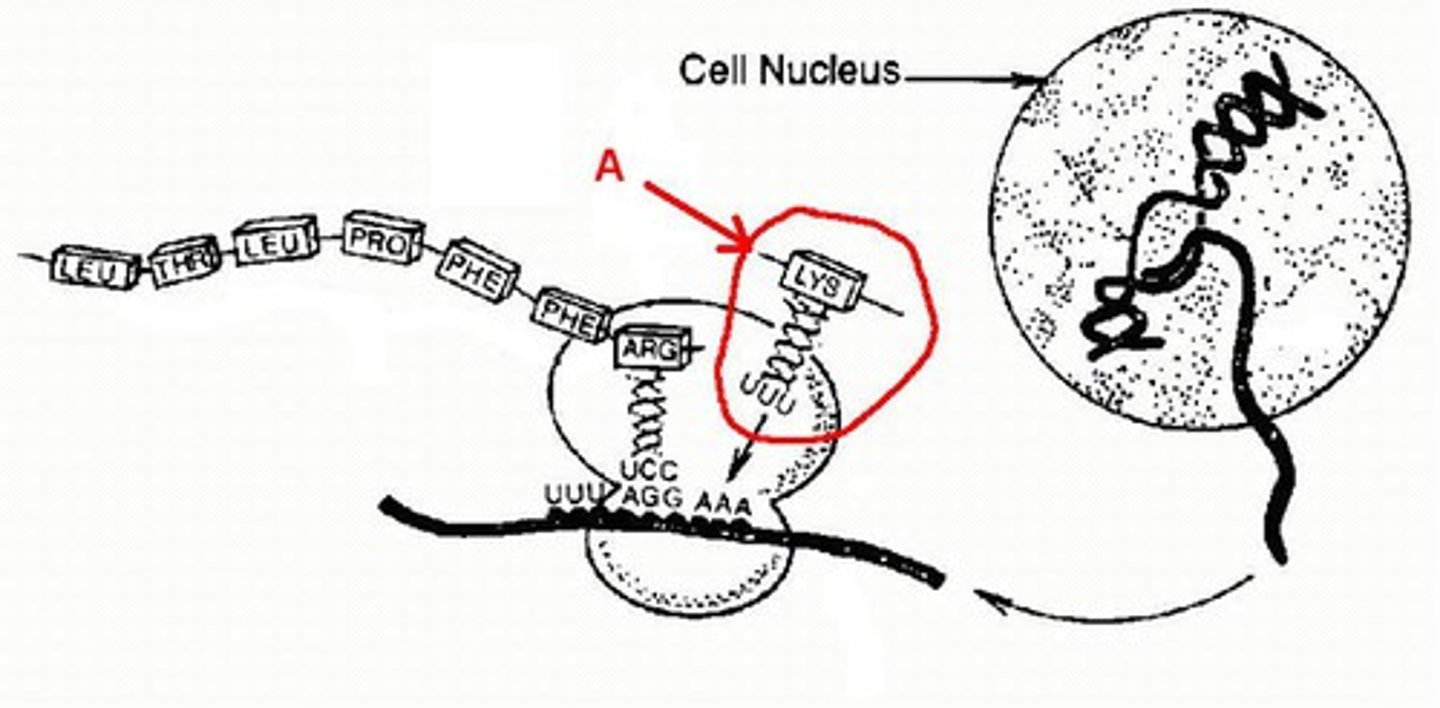
Transcription
Process of converting DNA to mRNA. Happens in Nucleus.
Translation
Process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA. Happens in Ribosome.
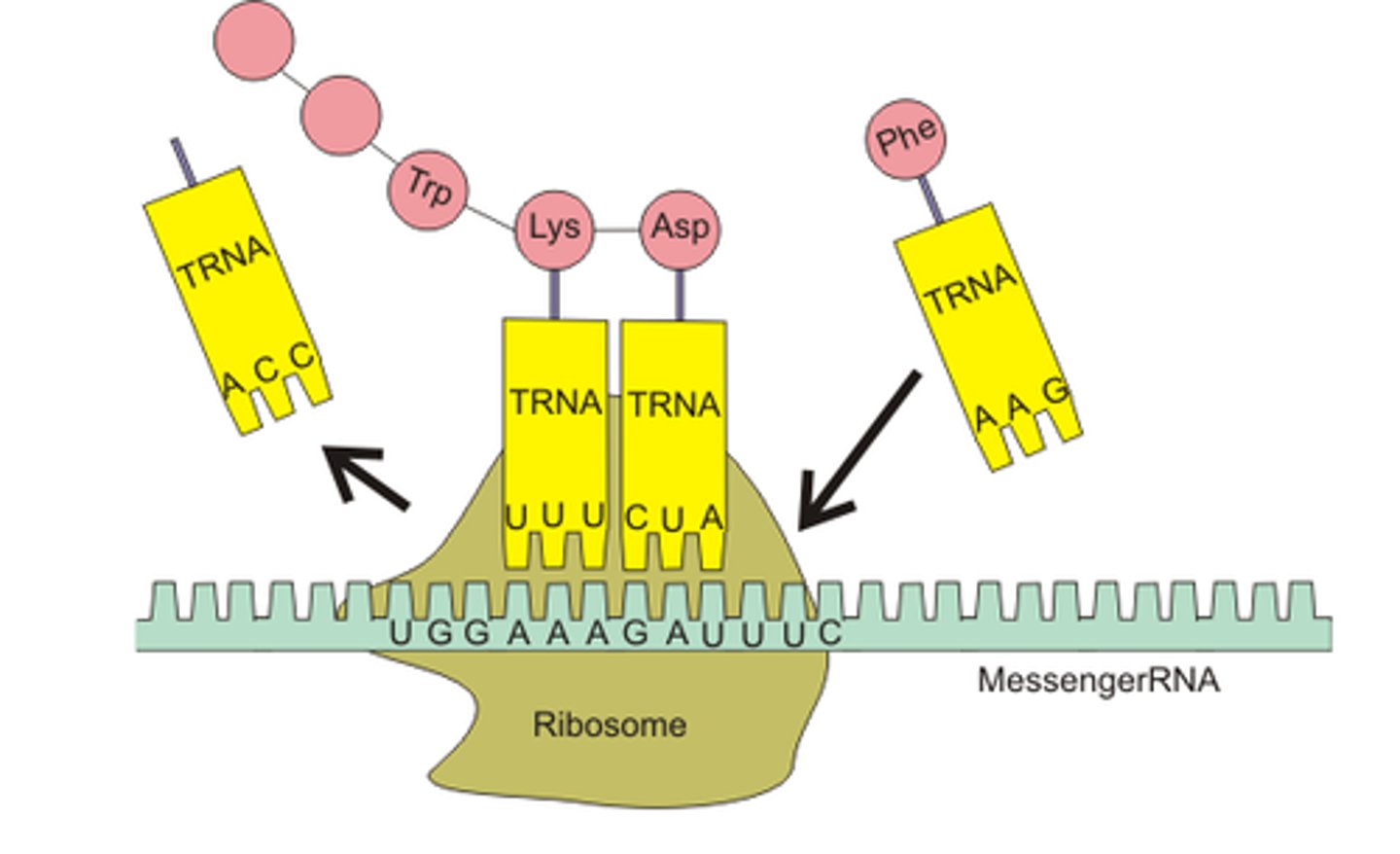
Codon
Three mRNA bases coding for an amino acid.
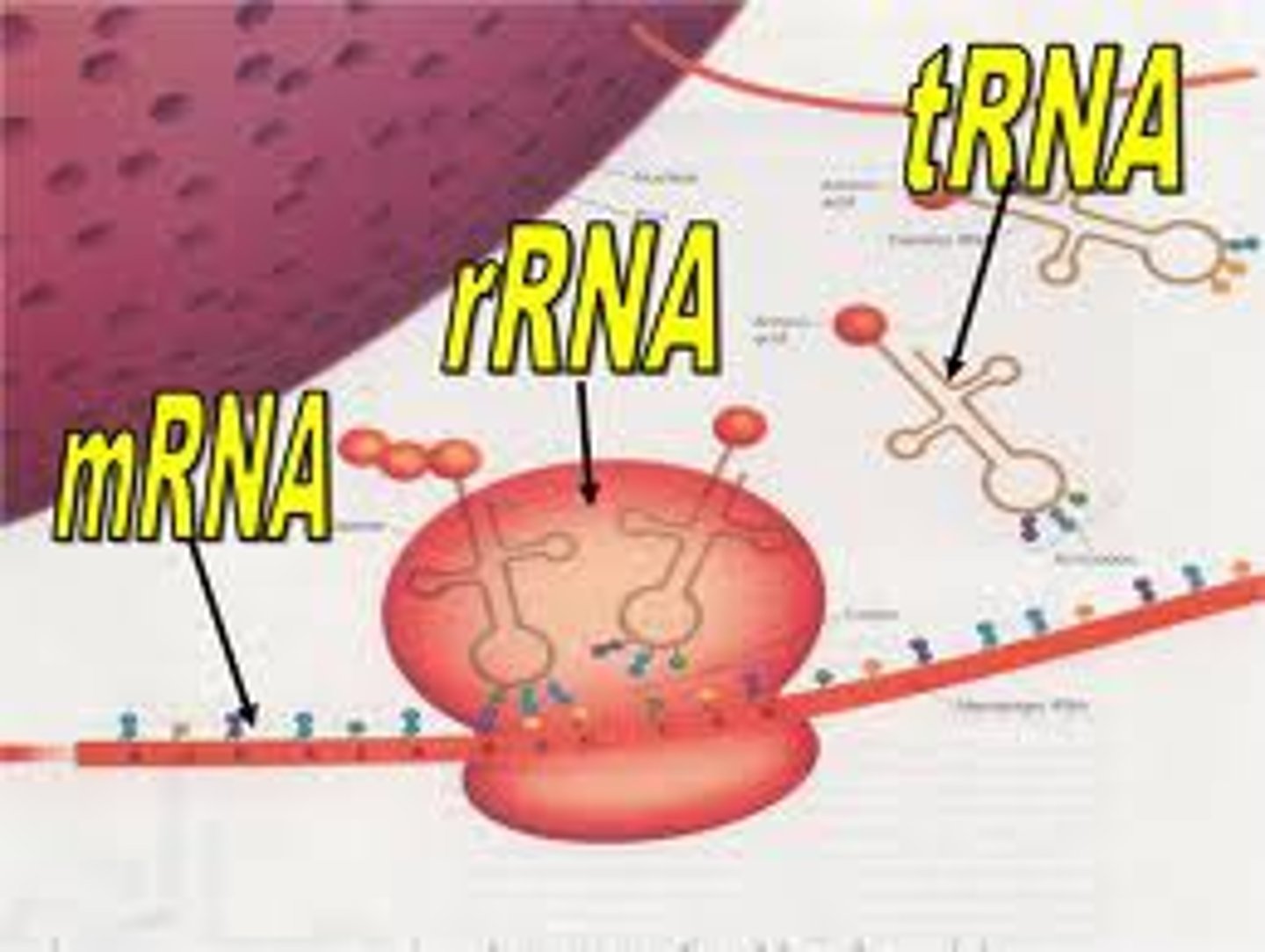
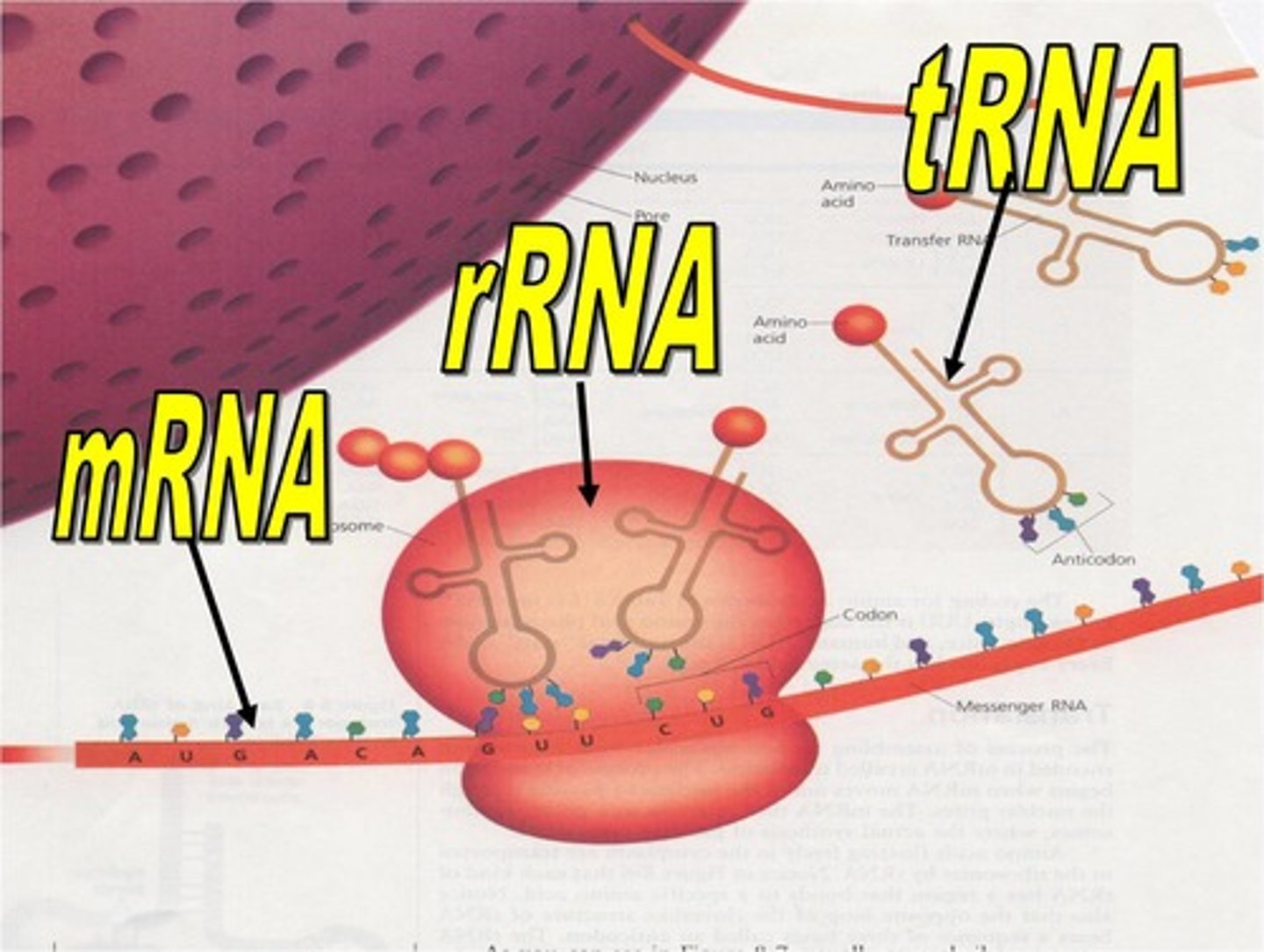
mRNA
Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosome.
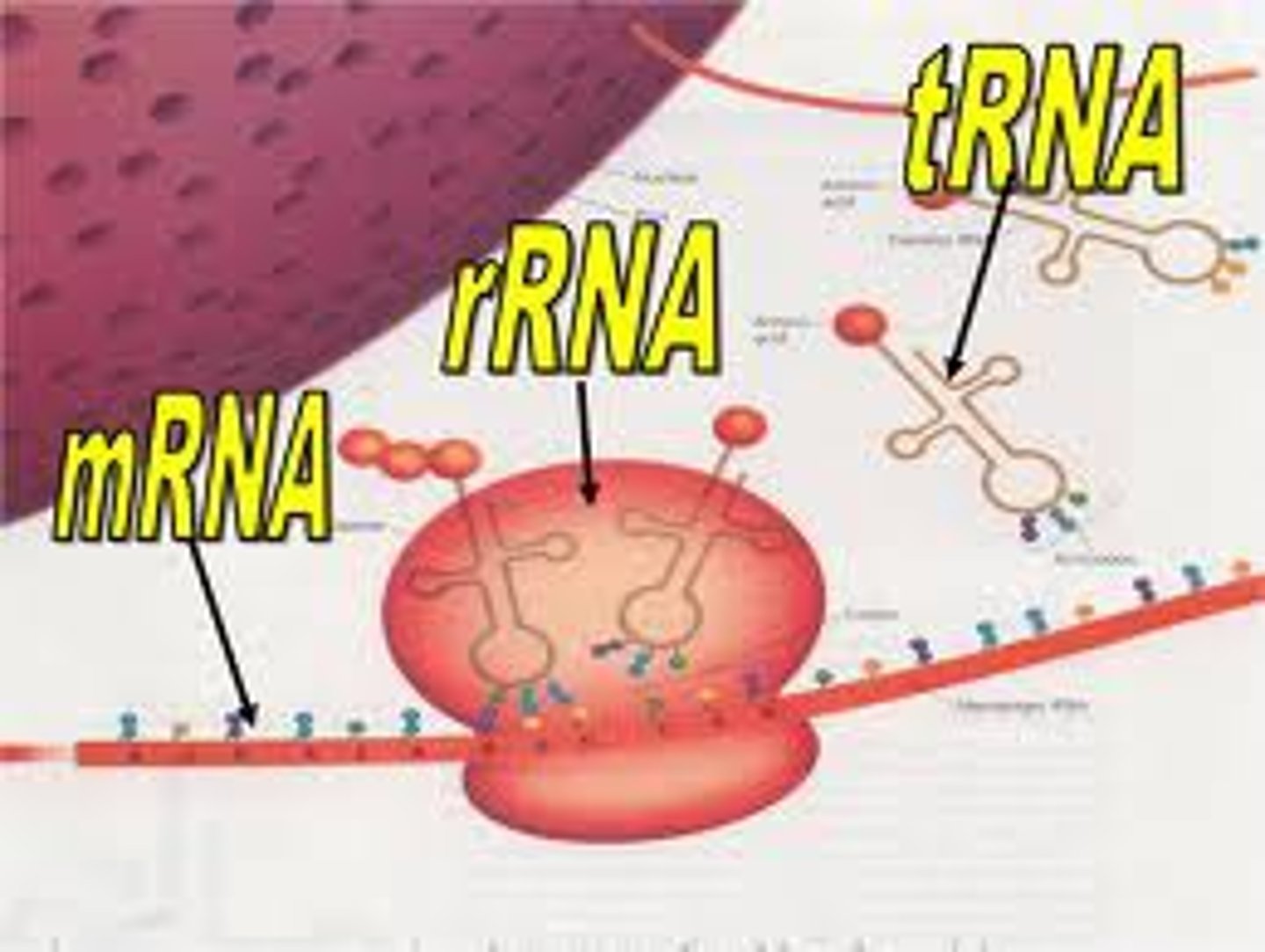
tRNA
Delivers amino acids to ribosome for protein synthesis.
rRNA
Structural component of ribosomes.
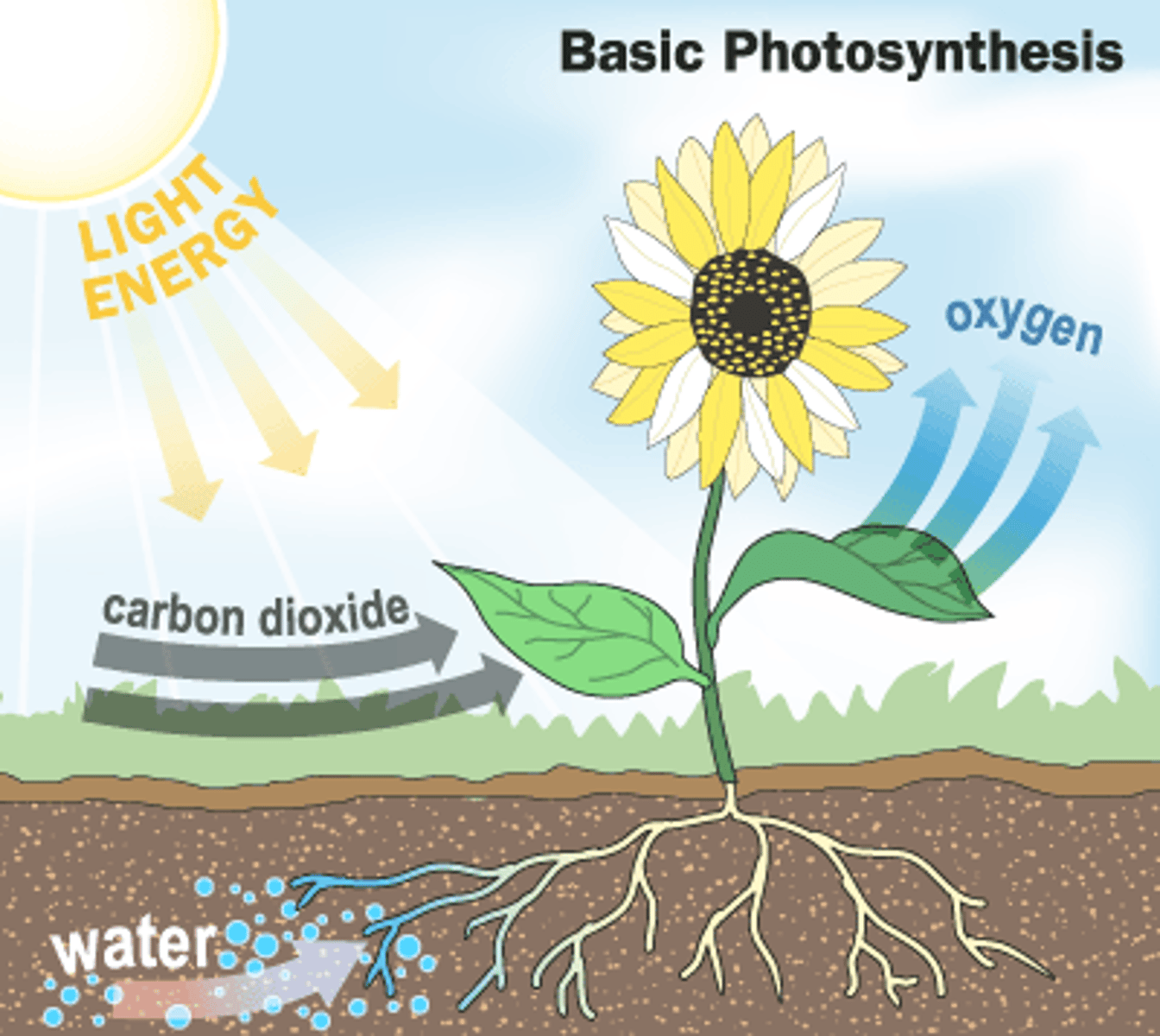
Photosynthesis
Converts sunlight into glucose and oxygen. Happens in Chloroplast.
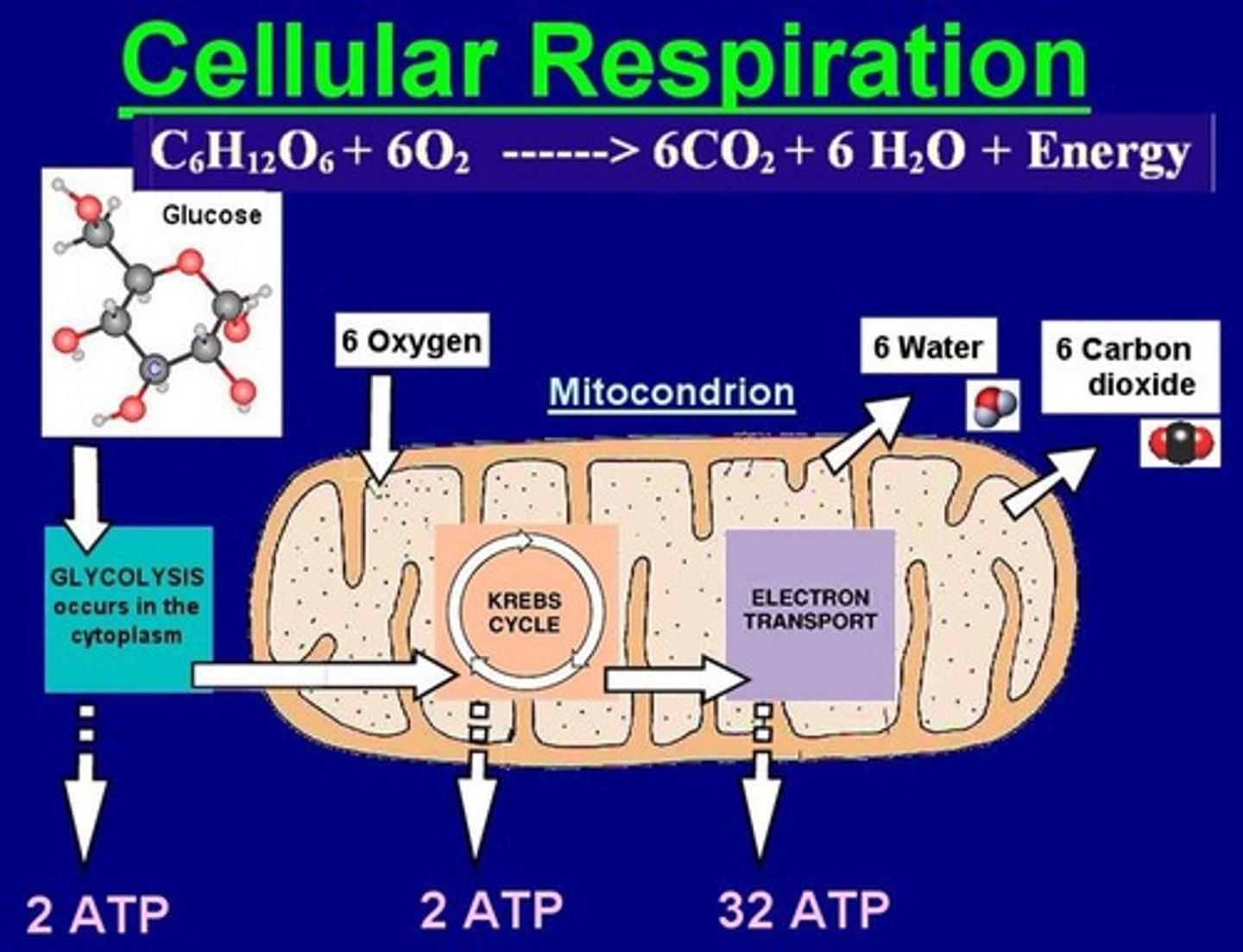
Cellular Respiration
Process converting glucose and oxygen into ATP. Happens in Mitochondria.
Chemical Reactions
Reactants transform into products.
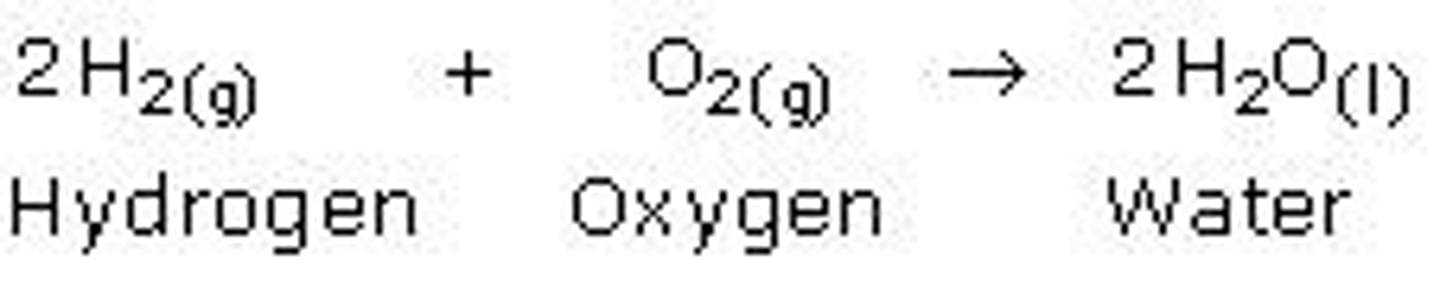
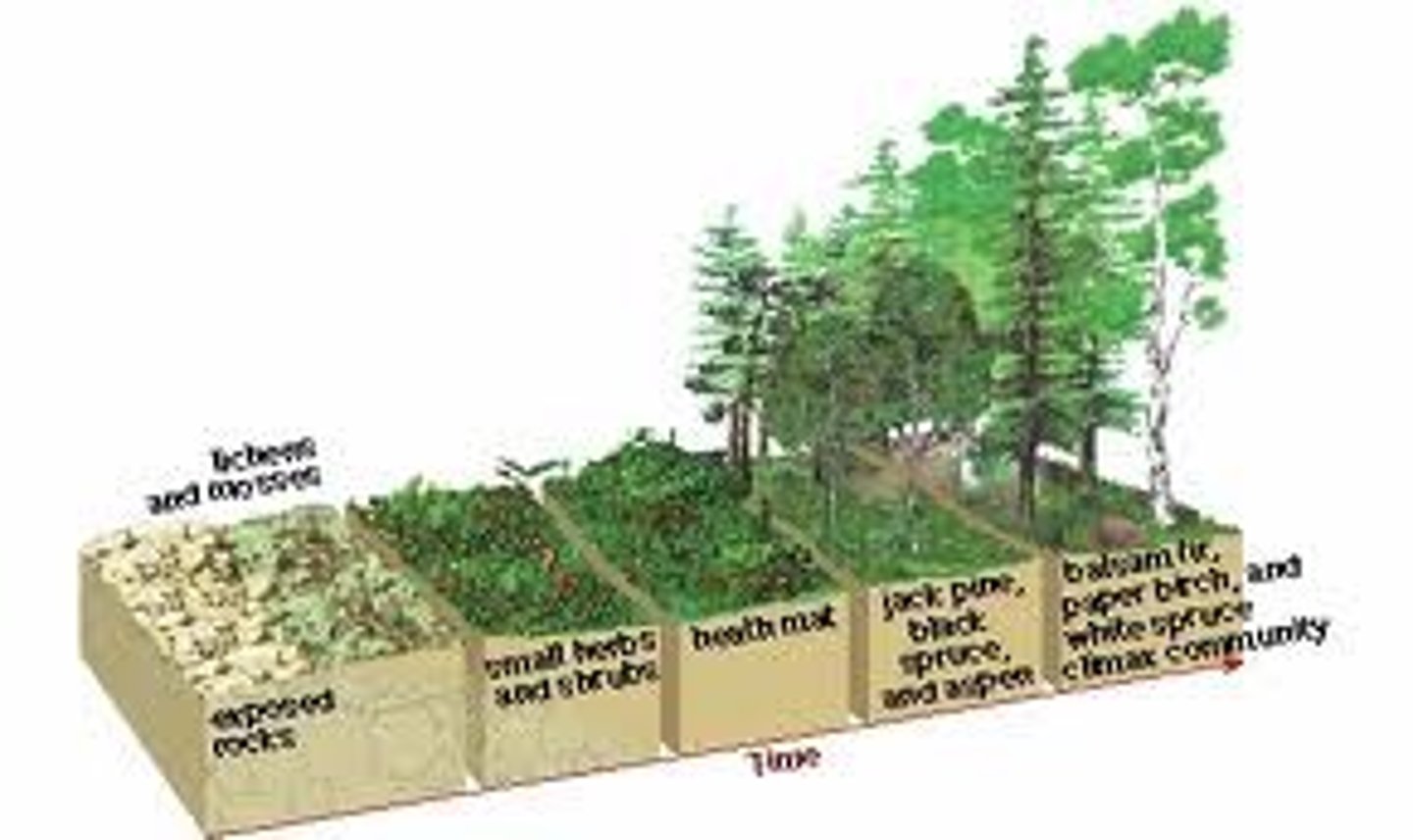
Primary Succession
Ecosystem development starting from bare rock.
Secondary Succession
Ecosystem recovery starting from soil.
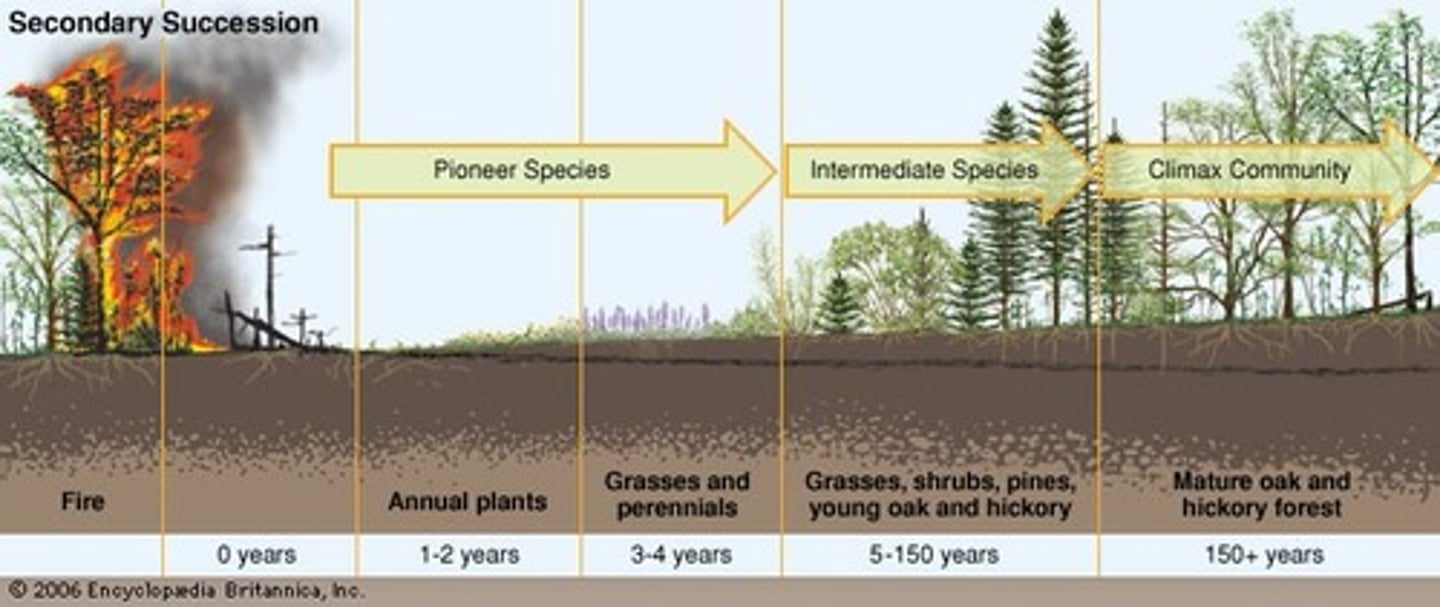
Trophic Levels
Producer --> Primary Consumer --> Secondary Consumer --> Tertiary Consumer
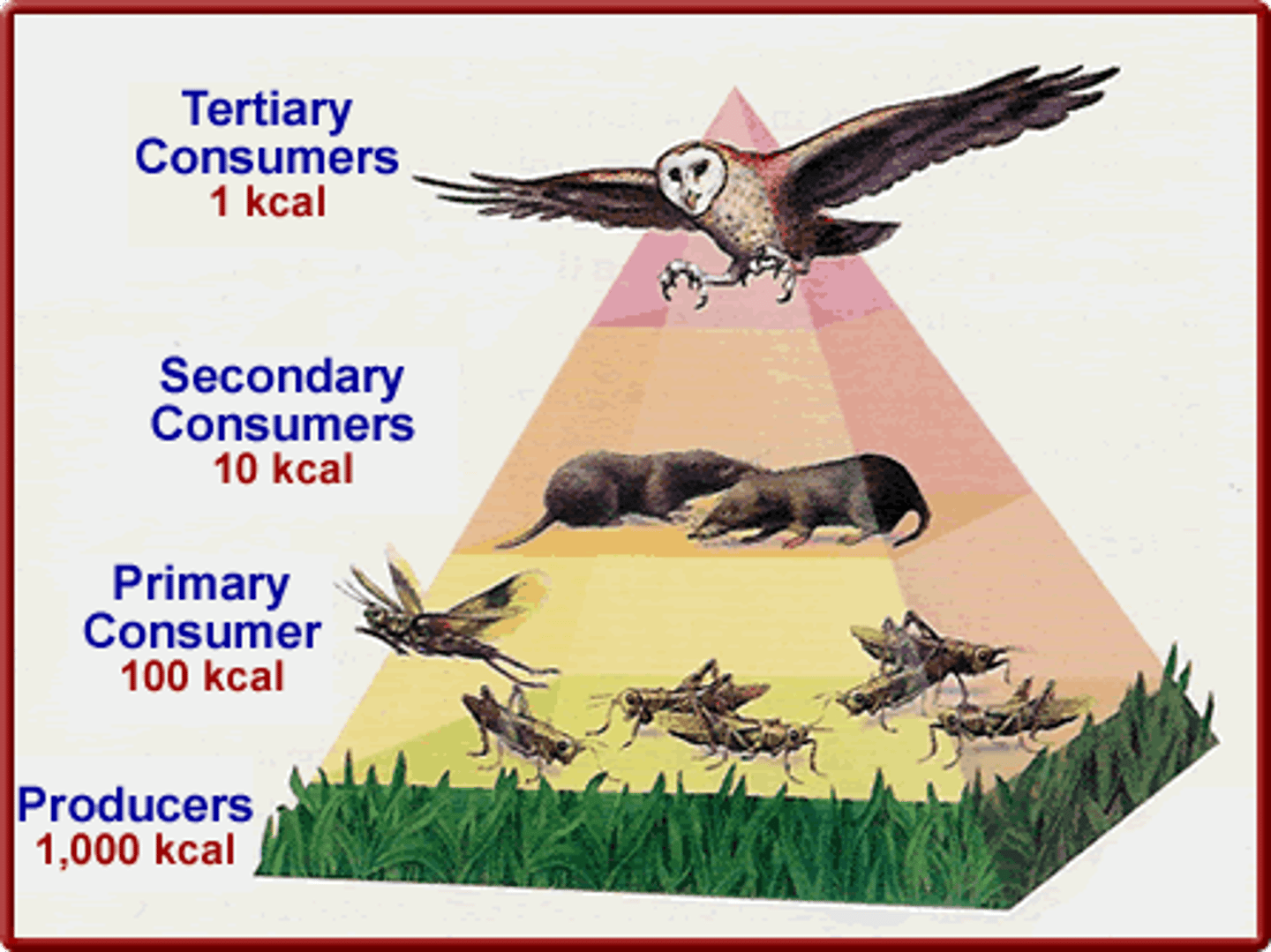
10% Rule
Only 10% of energy transfers between trophic levels. 90% lost as heat.
Fitness
Ability to produce more offspring than competitors.
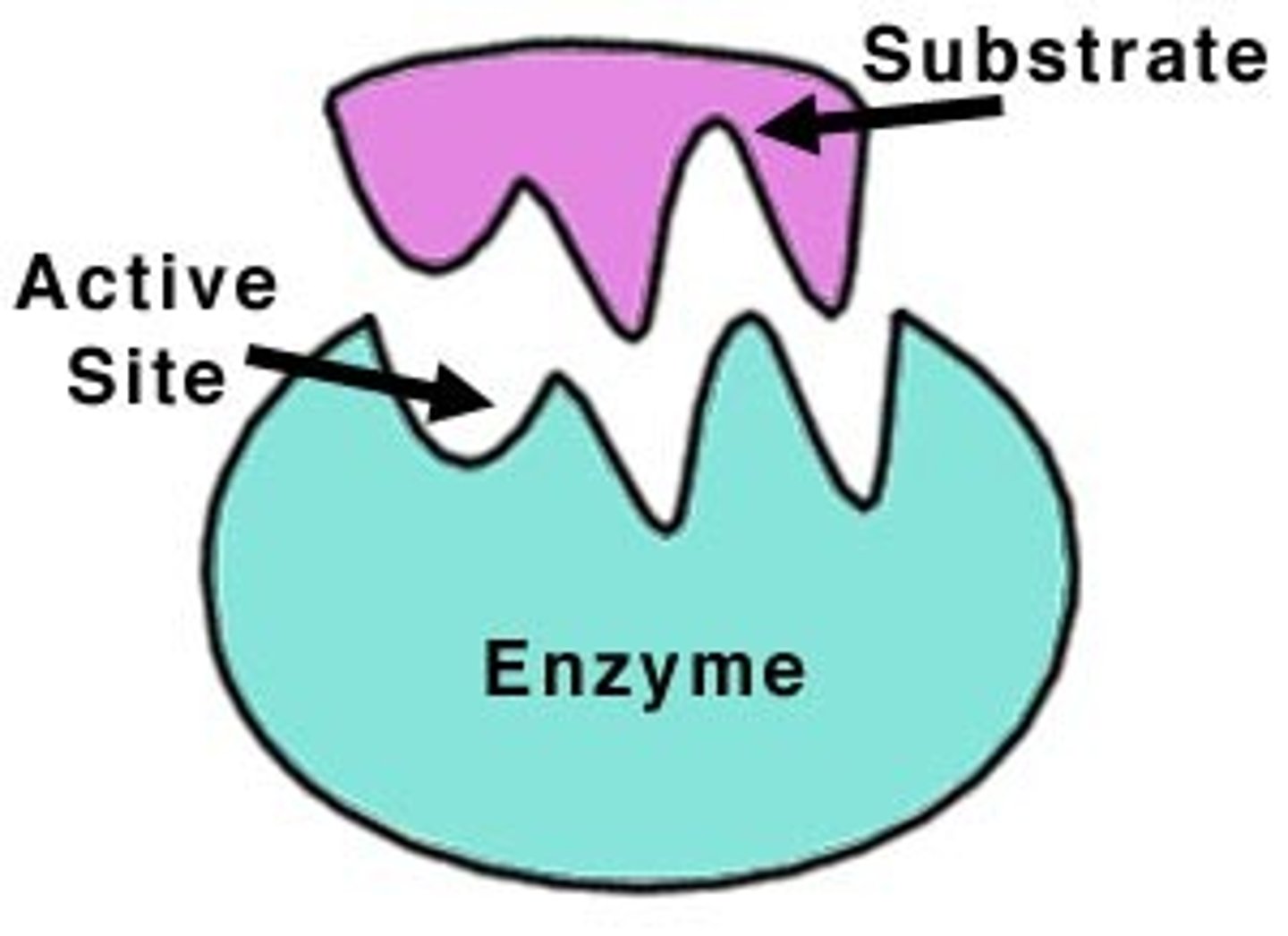
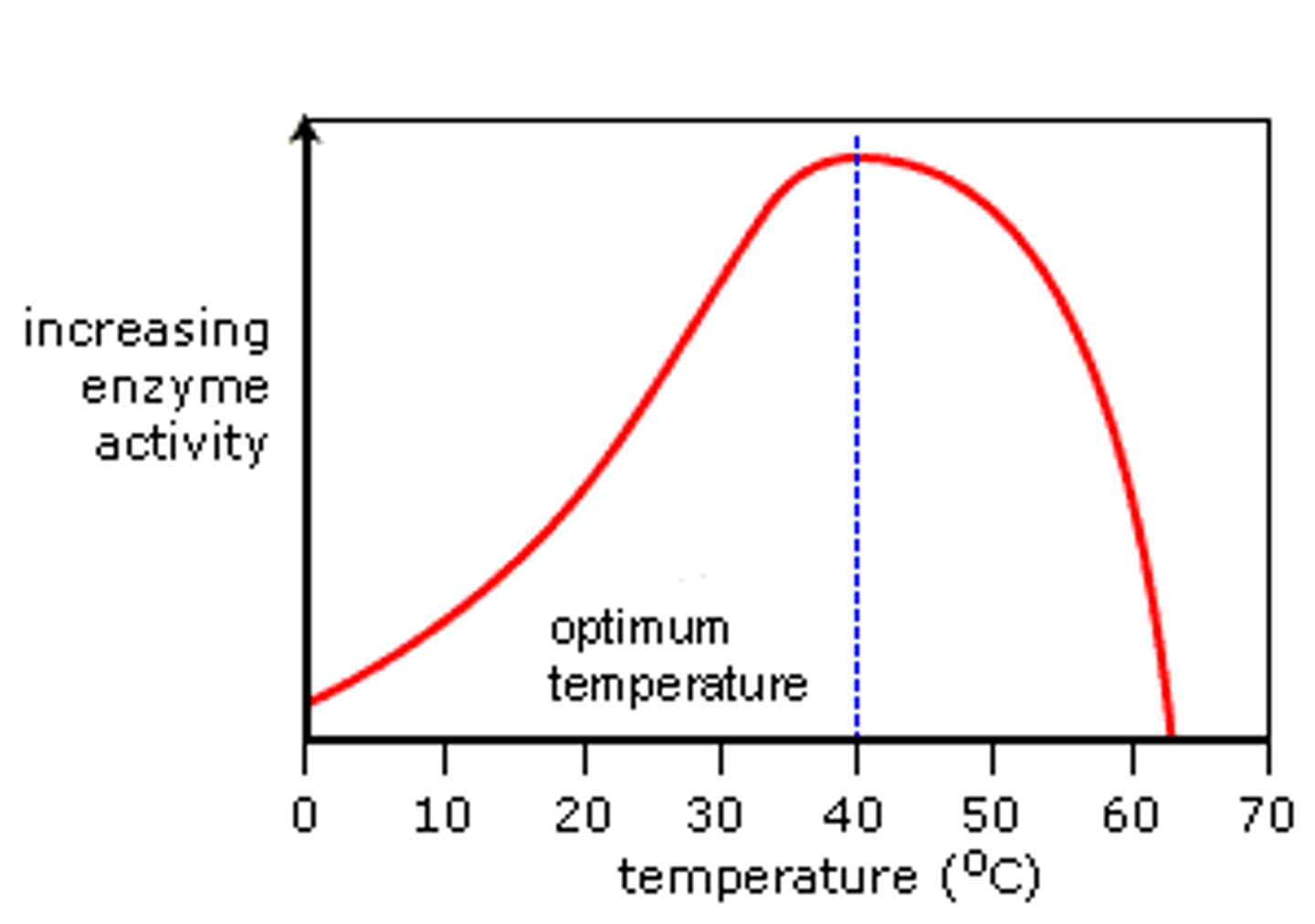
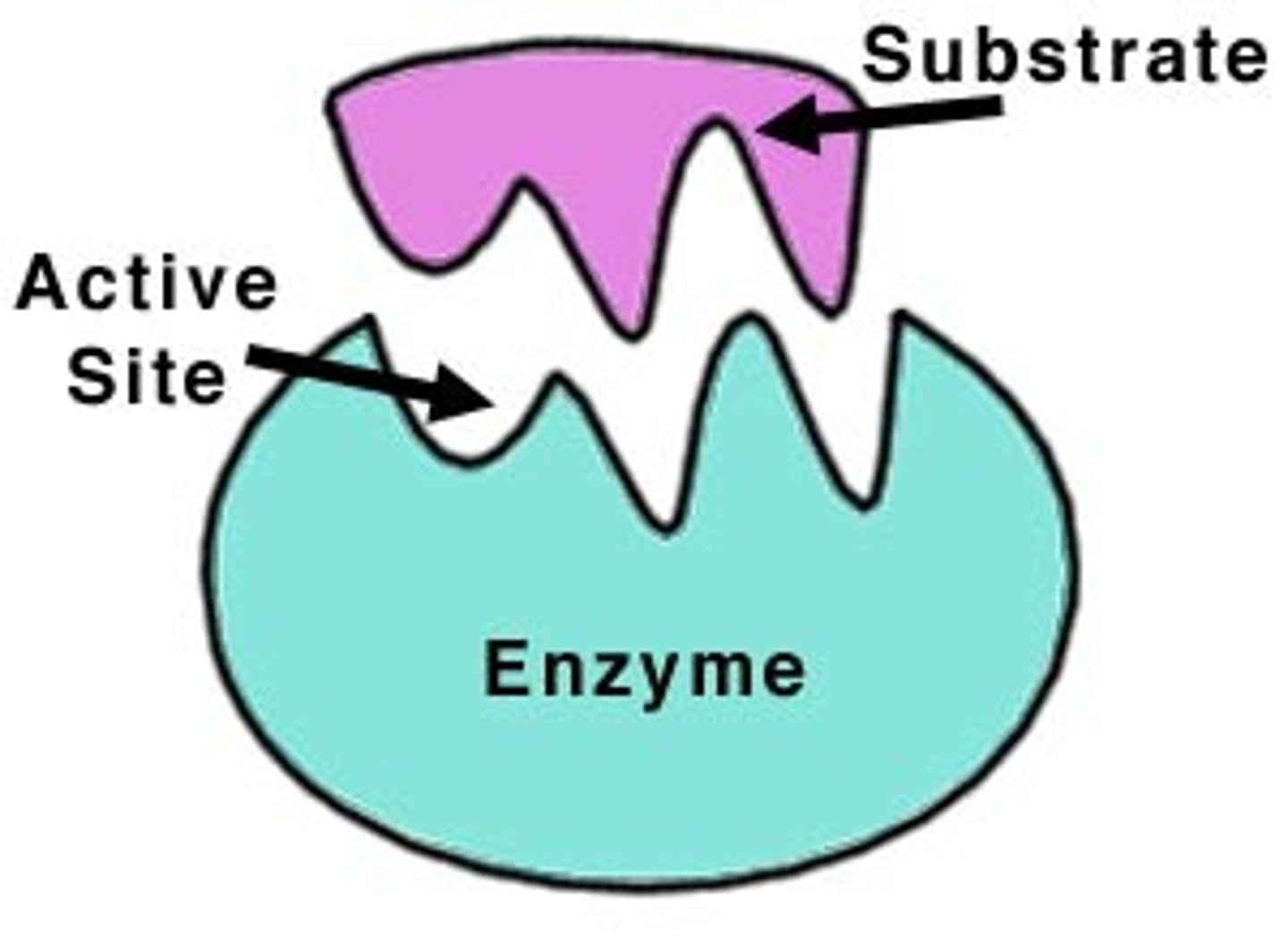
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy
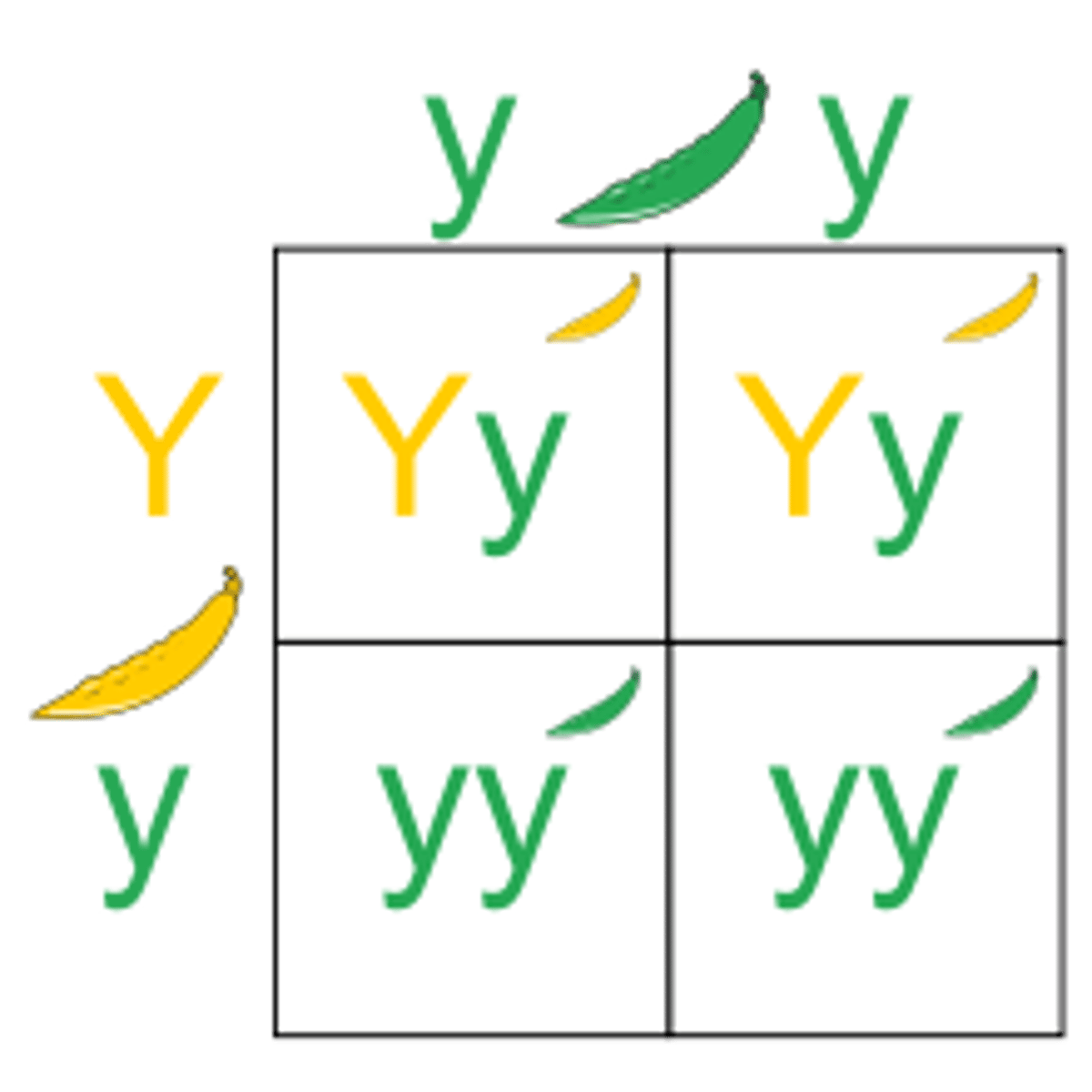
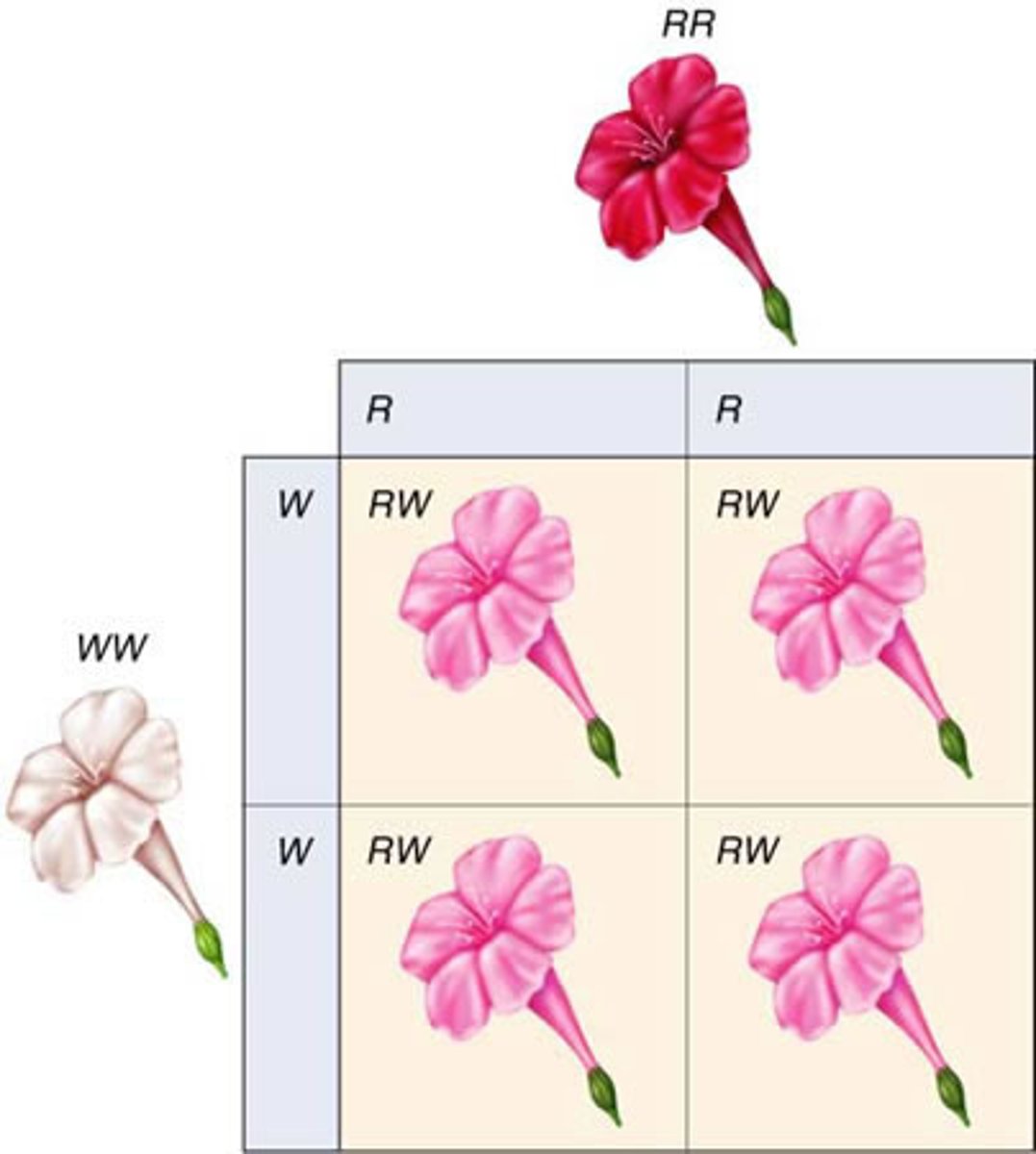
Punnett Square
Tool for predicting genetic trait inheritance.
Homozygous Dominant
Genotype with two dominant alleles (BB).
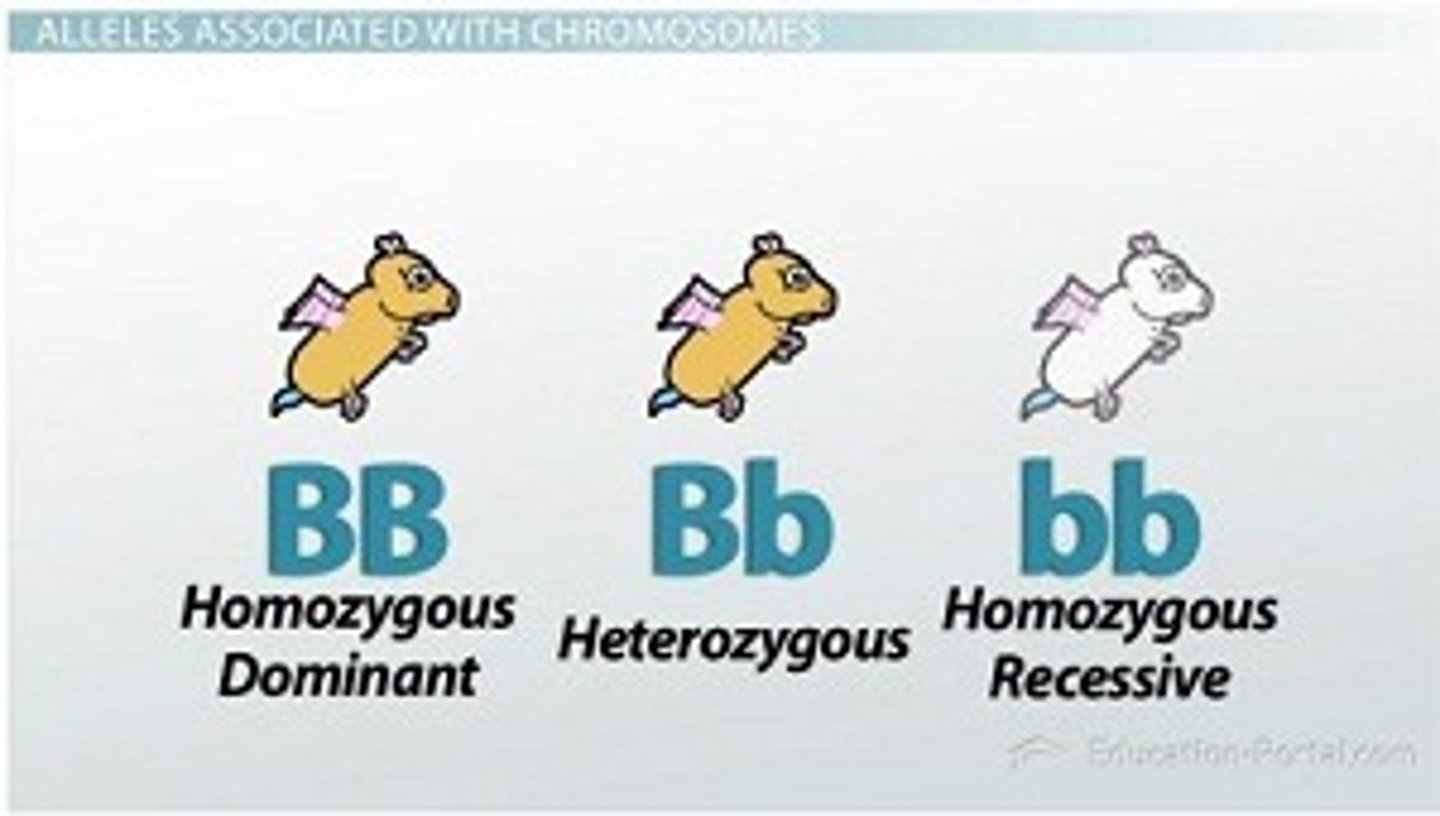
Homozygous Recessive
Genotype with two recessive alleles (bb).
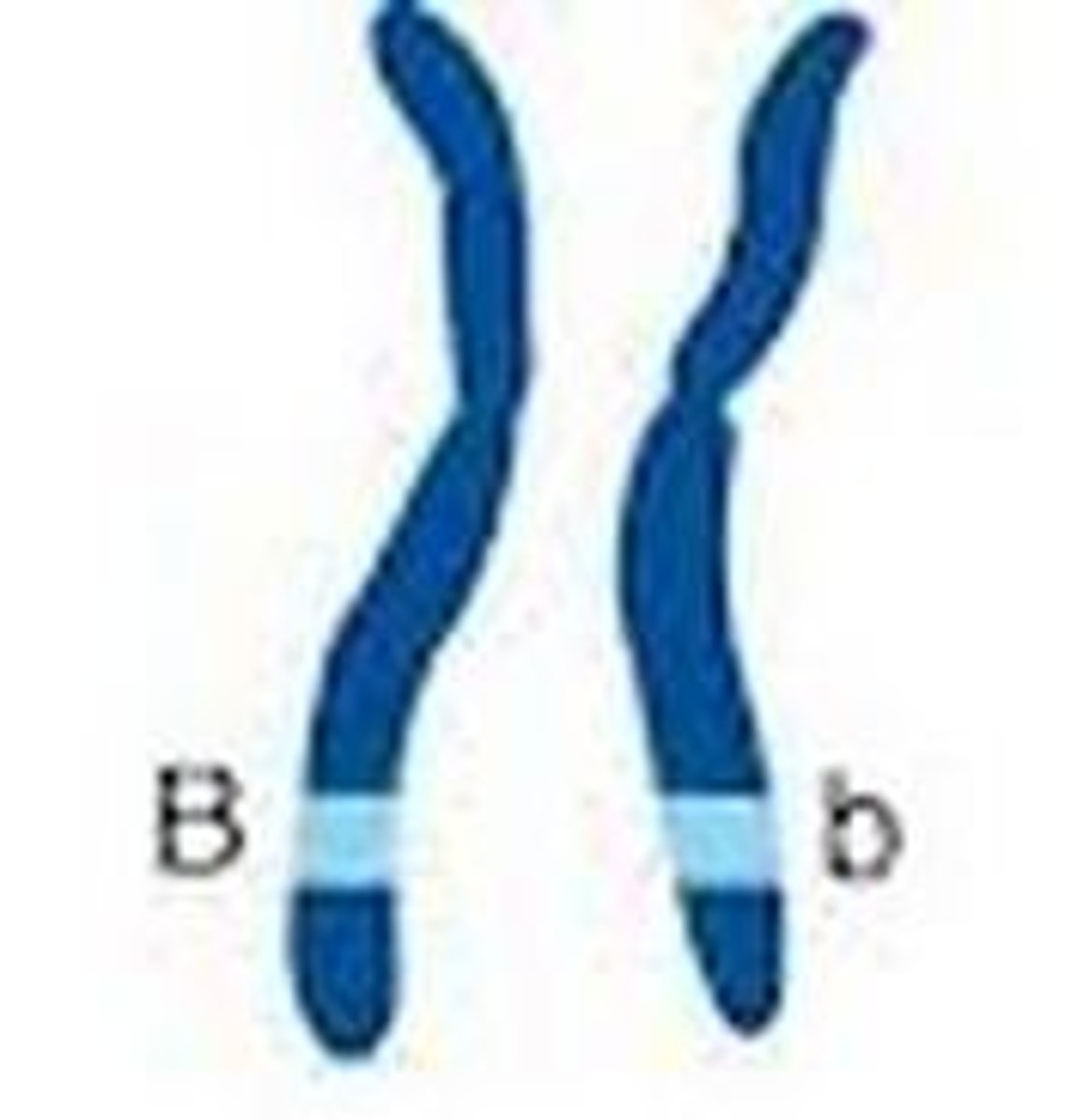
Heterozygous
Genotype with one dominant and one recessive allele (Bb).
Codominance
Both dominant traits expressed simultaneously (spots & stripes).
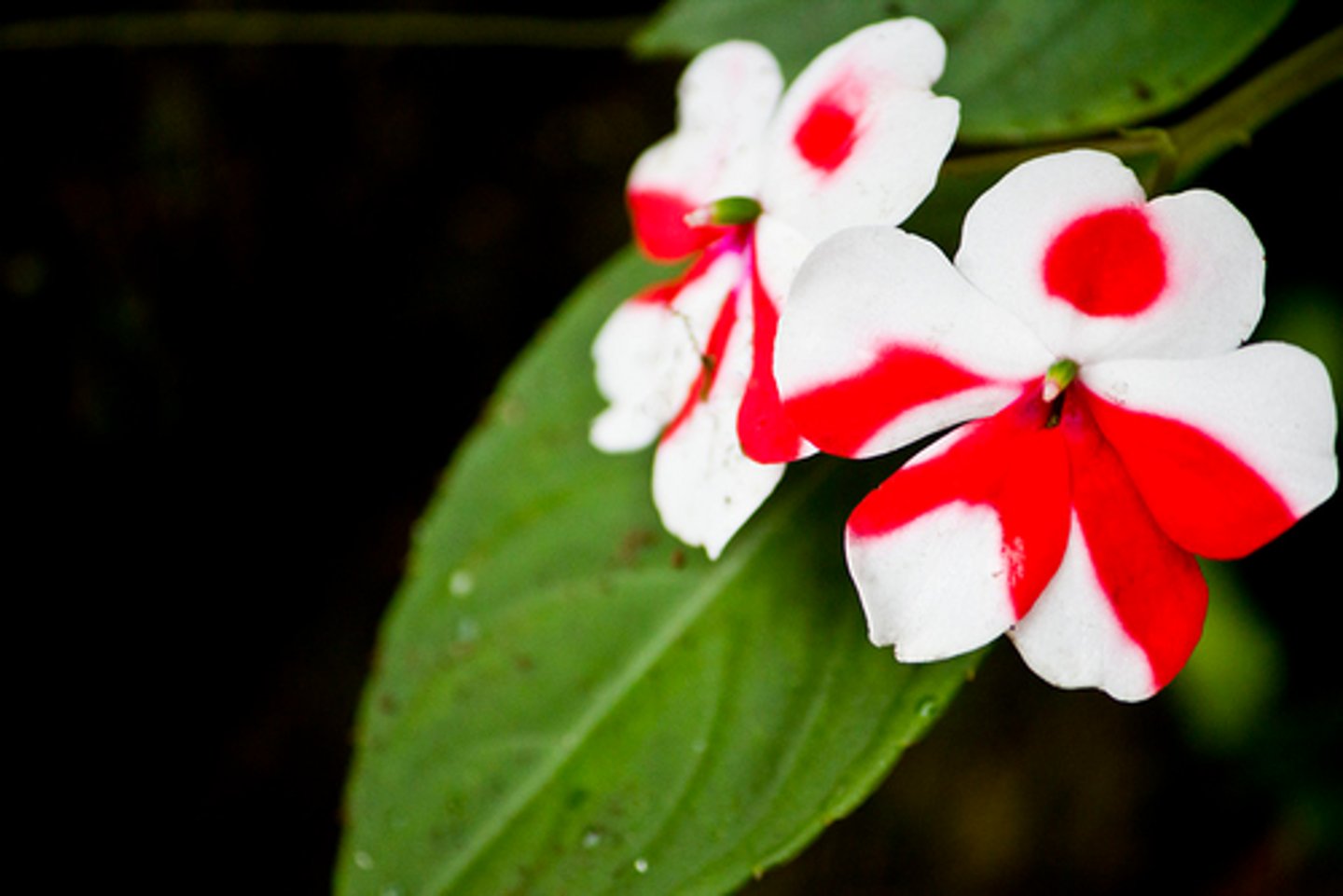

Incomplete Dominance
Blending of two dominant traits (Red + White = Pink).
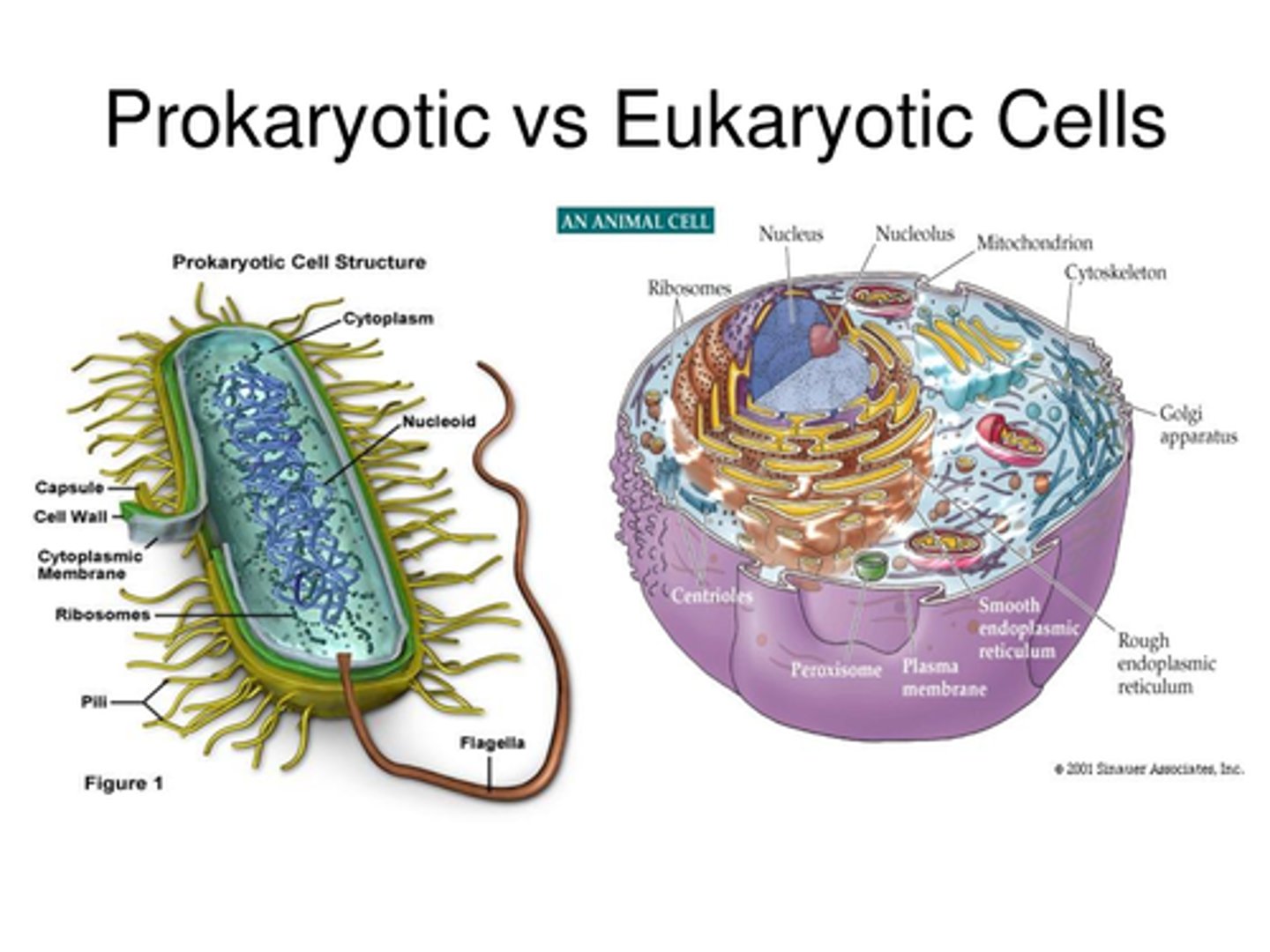
Prokaryotic Cells
Cells without a nucleus, primarily bacteria.
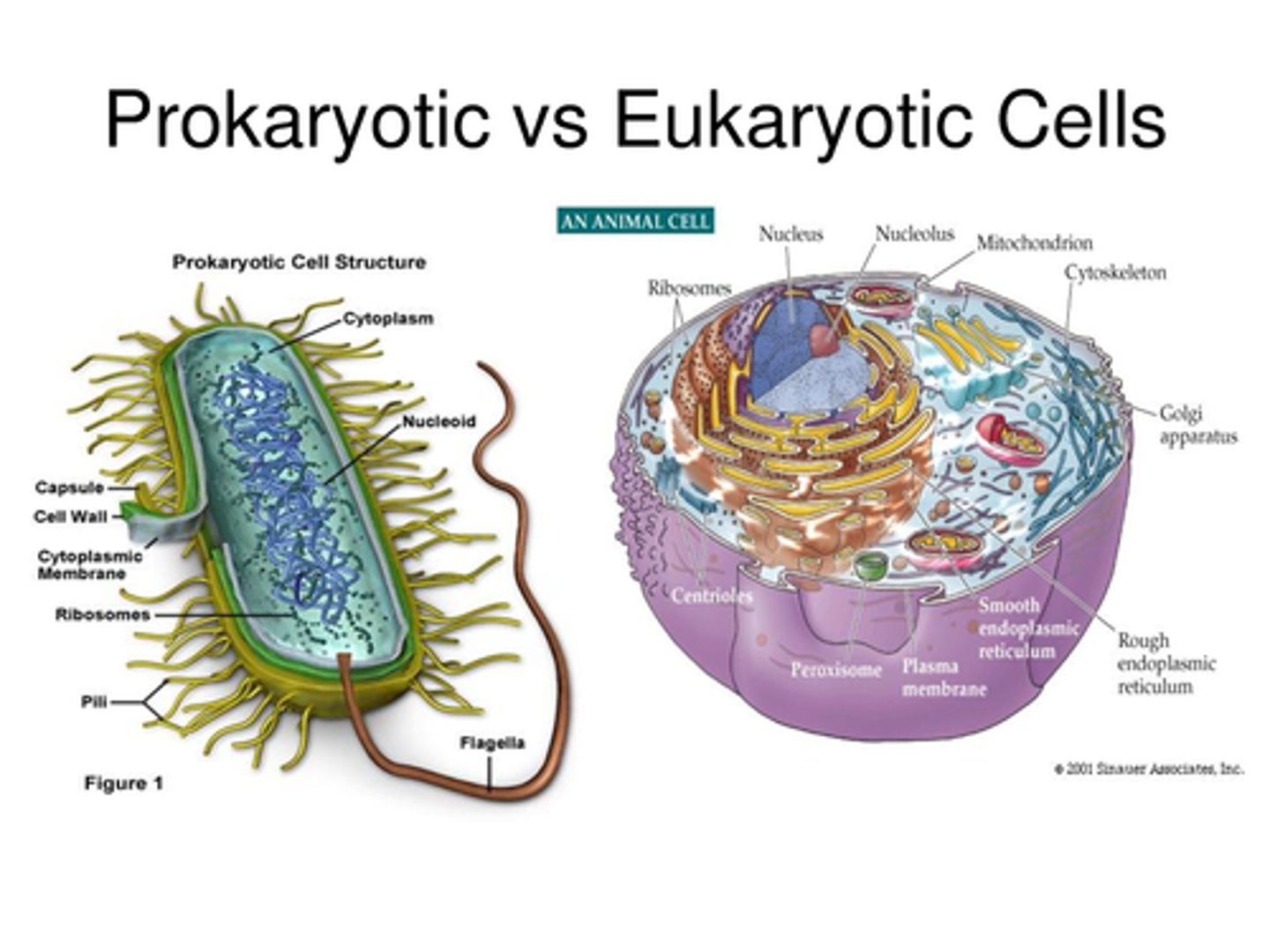
Eukaryotic Cells
Cells with a nucleus, all cell types except bacteria.
Somatic Cells
Regular body cells for growth and repair.
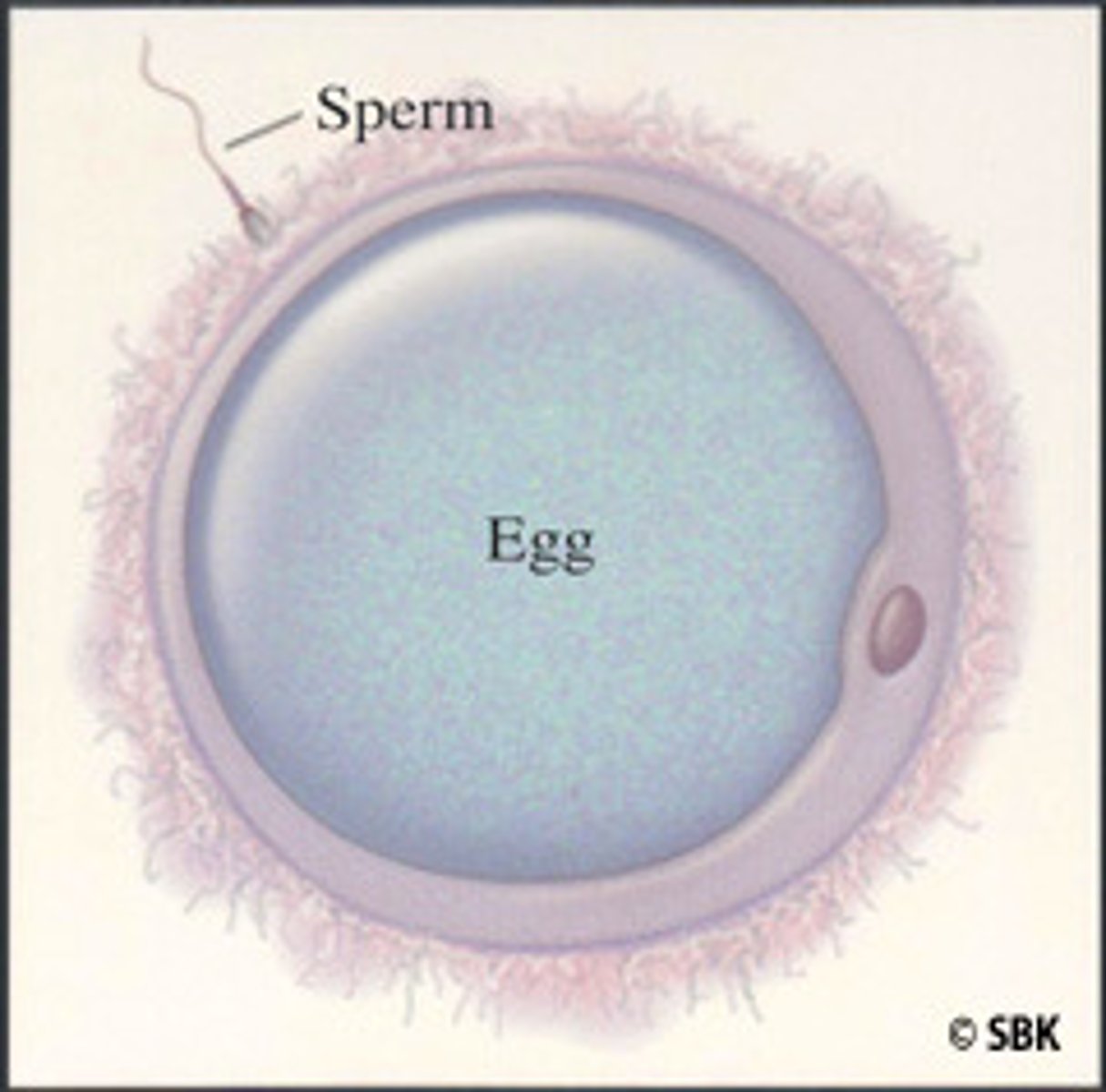
Gametes
Sperm & egg cells carrying half the chromosome number
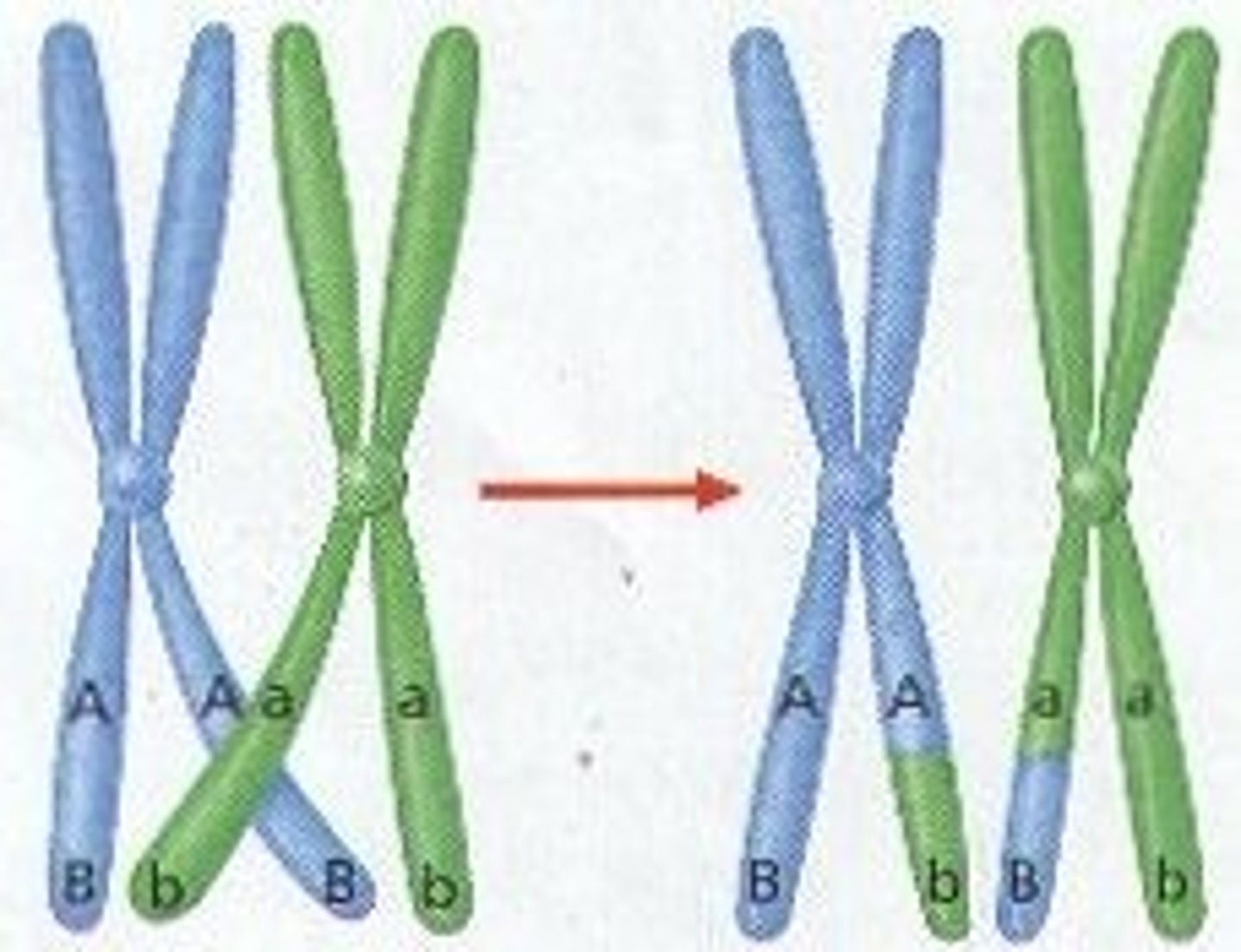
Crossing Over
Gene exchange between chromosome pairs. Increases Genetic Diversity.
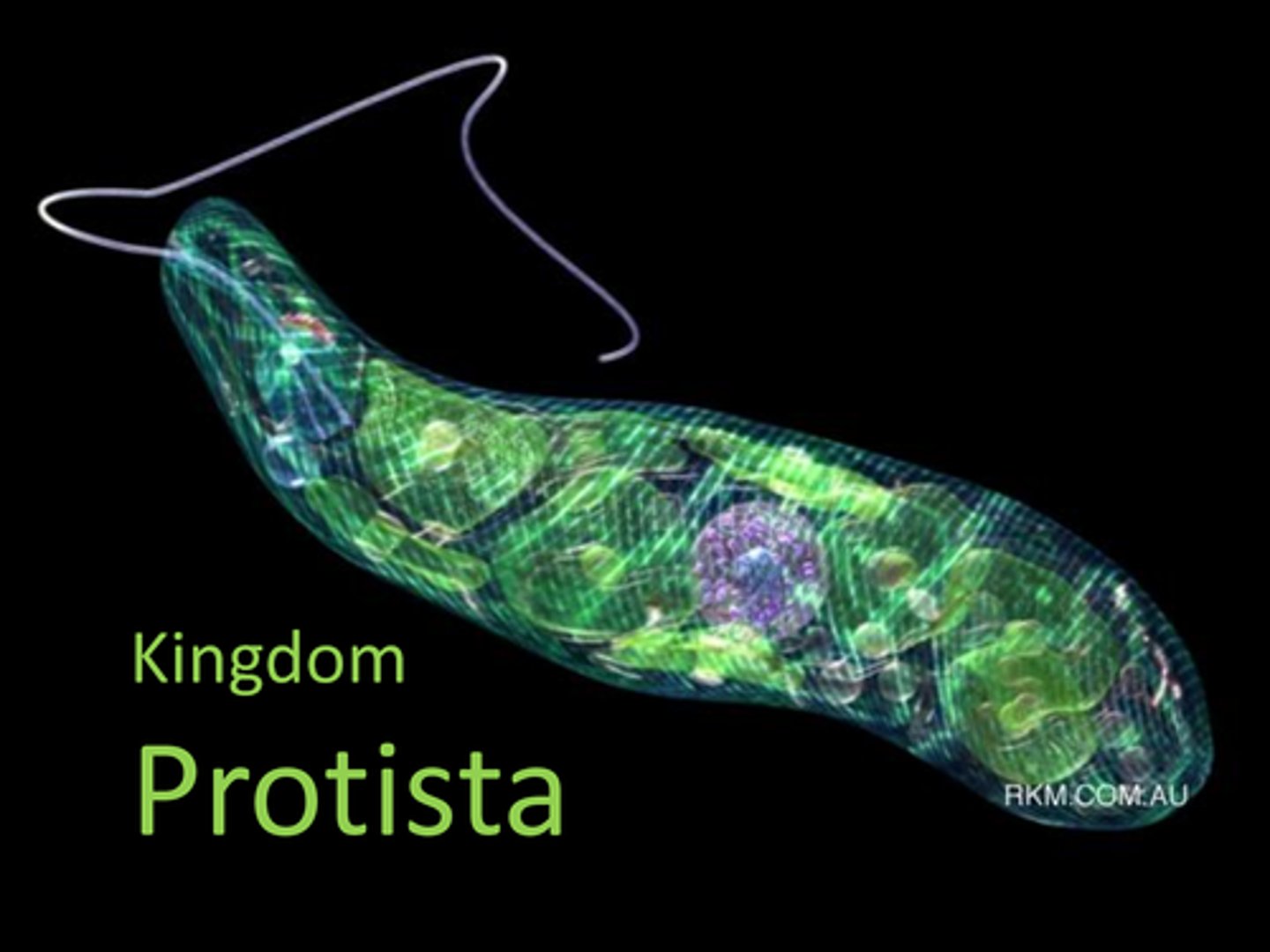
Protists
Eukaryotic, often single-celled organisms.
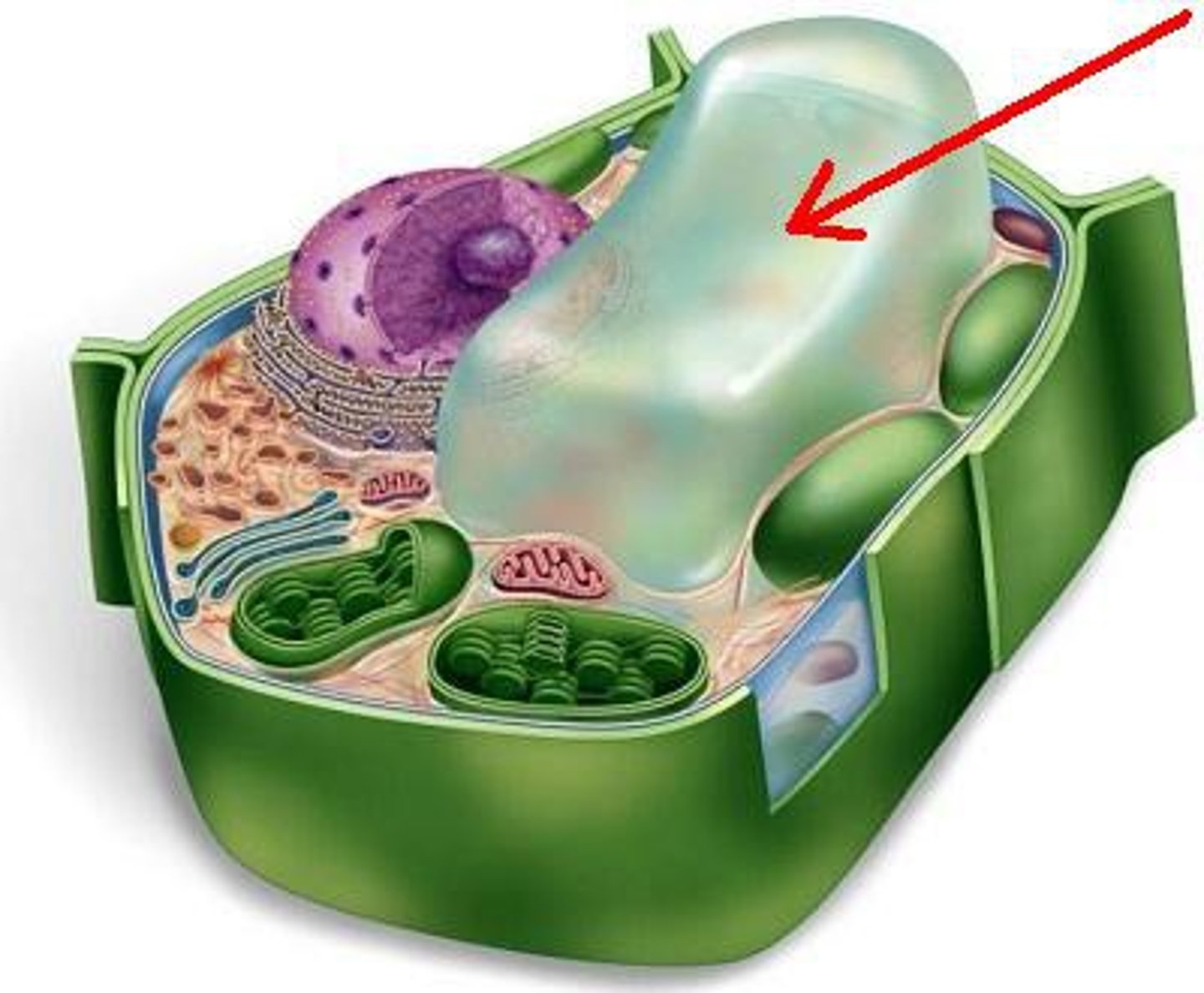
Plant Cells
Contain chloroplasts, cell walls, and vacuoles.
Fungi
Heterotrophic consumers with chitin cell walls.
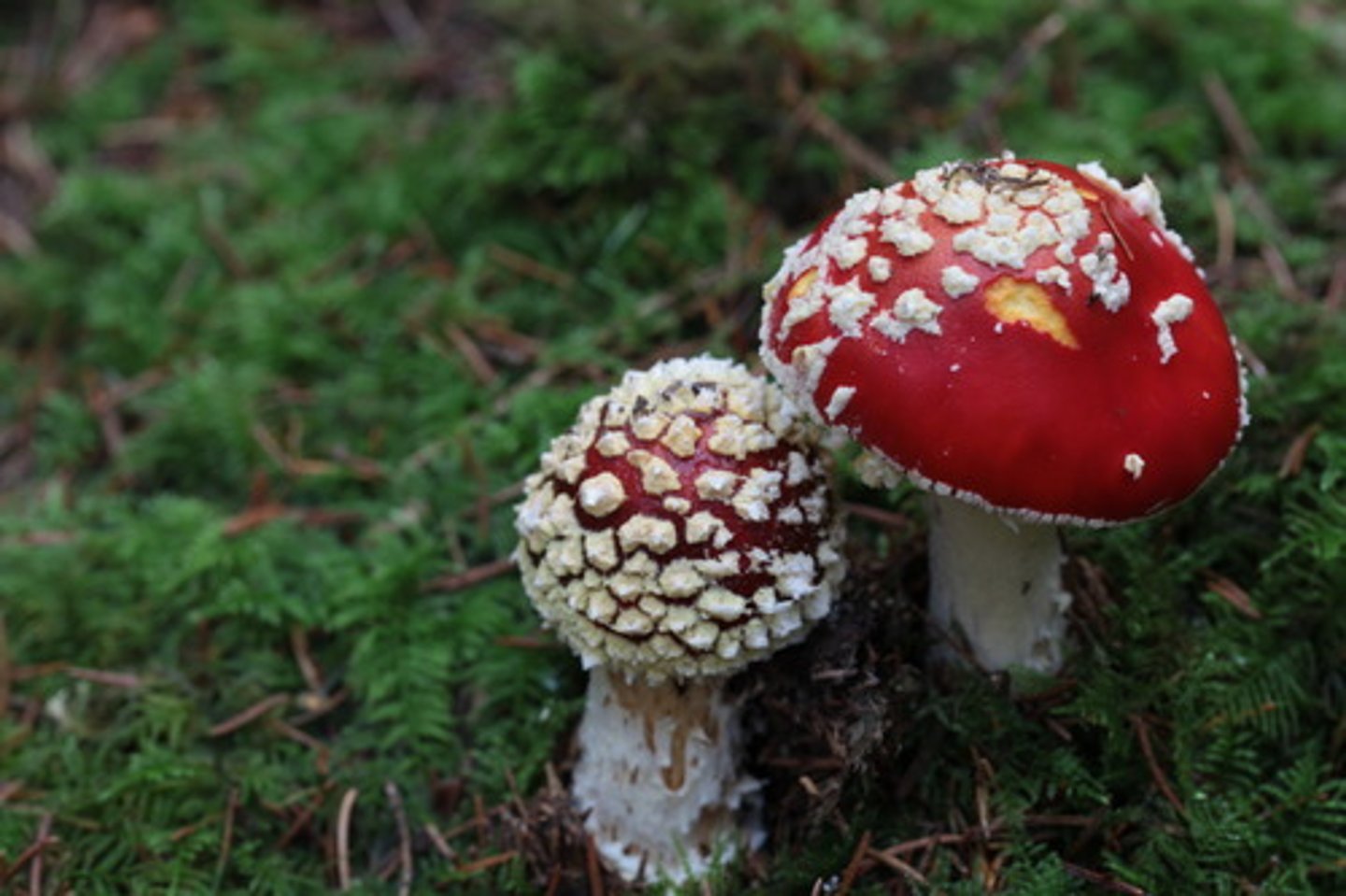

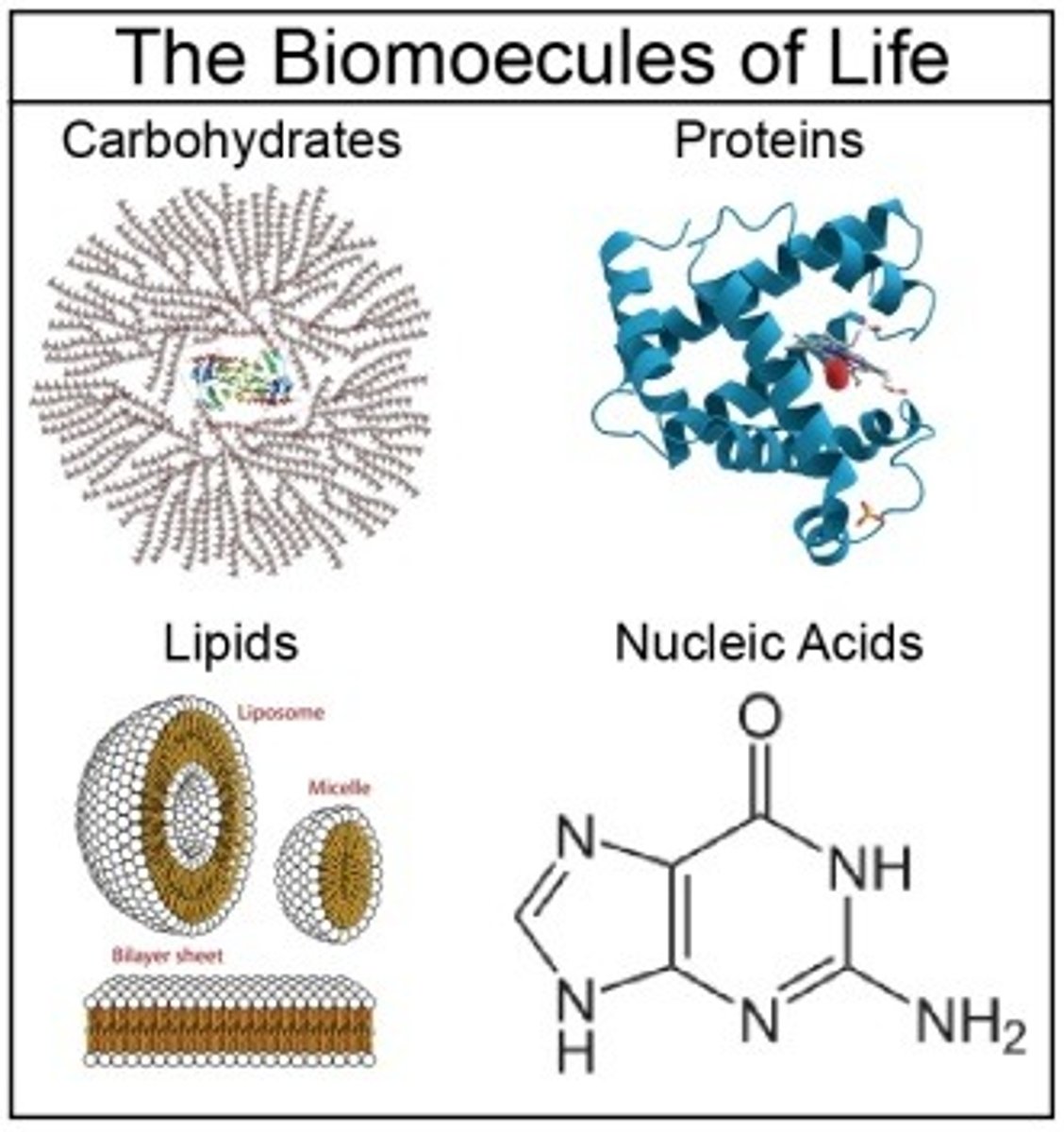
Biomolecules
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids.
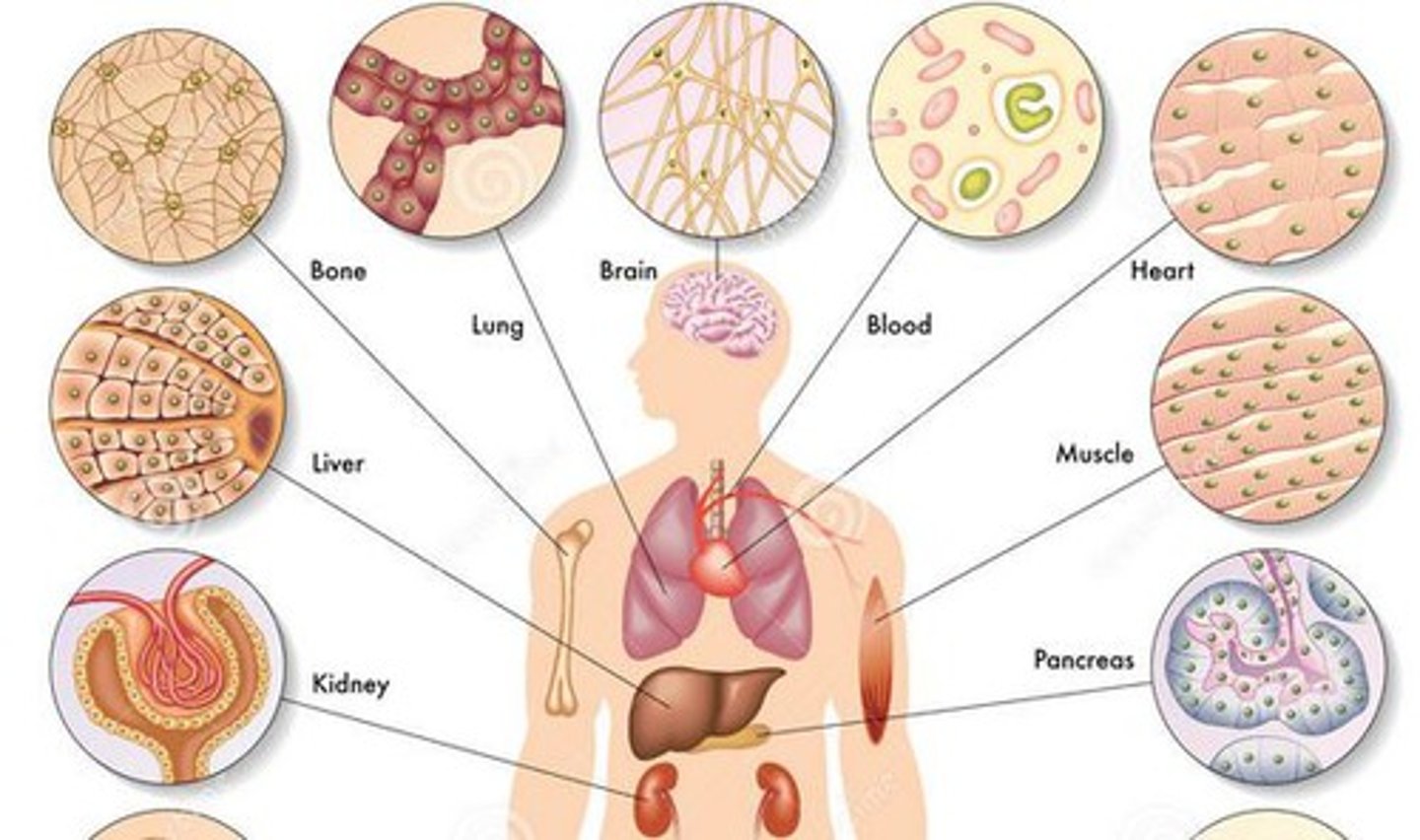
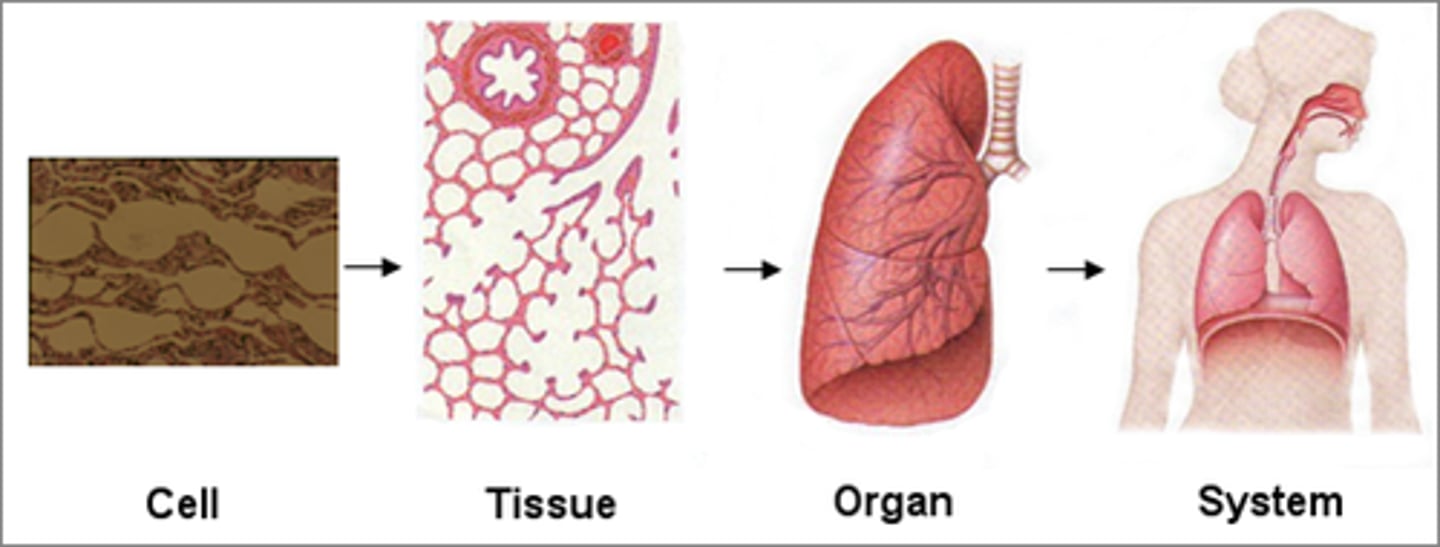
Body Organization
Hierarchy: cell → tissue → organ → system --> organism.
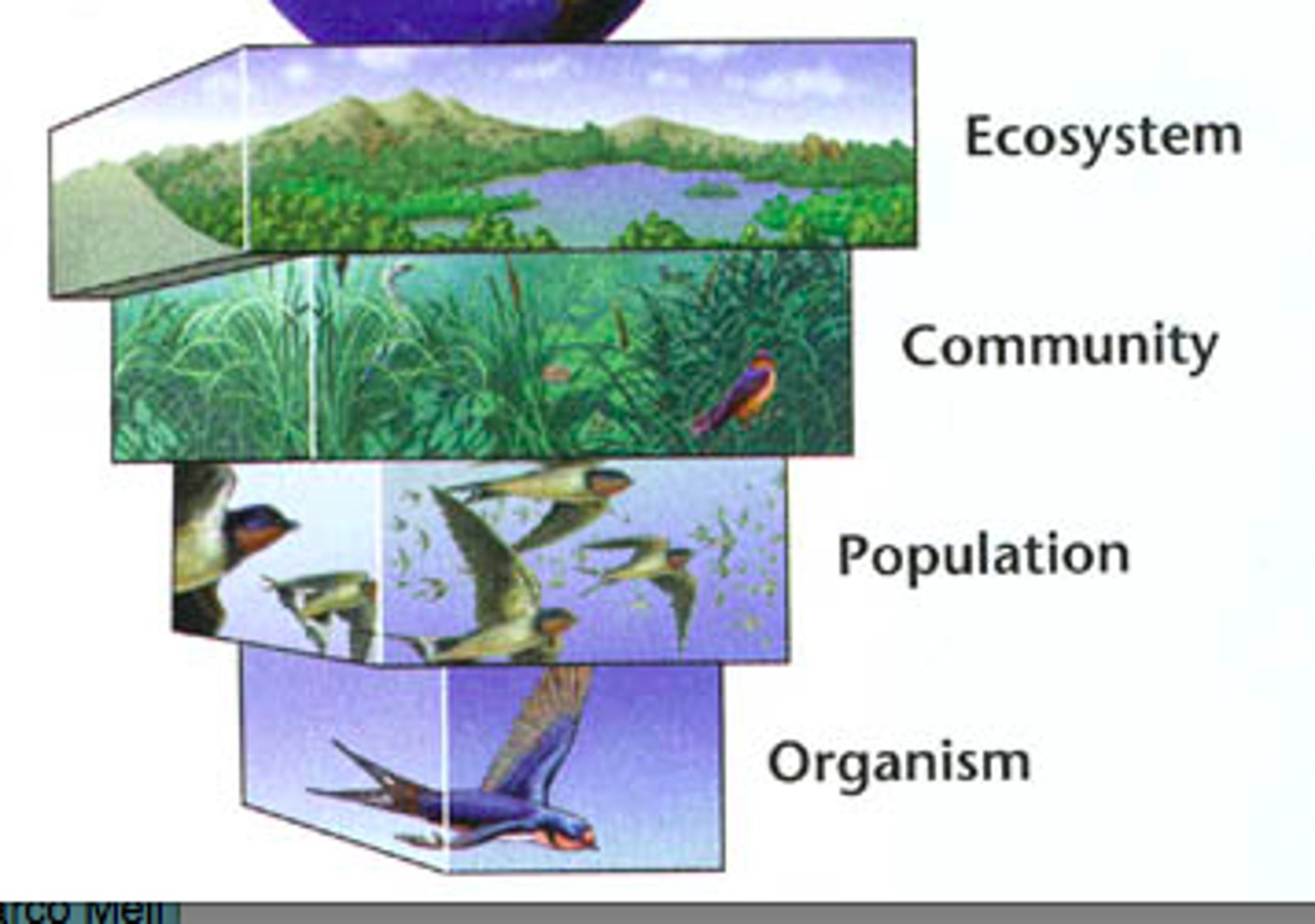
Ecosystem Organization
Hierarchy: organism → population → community → ecosystem.
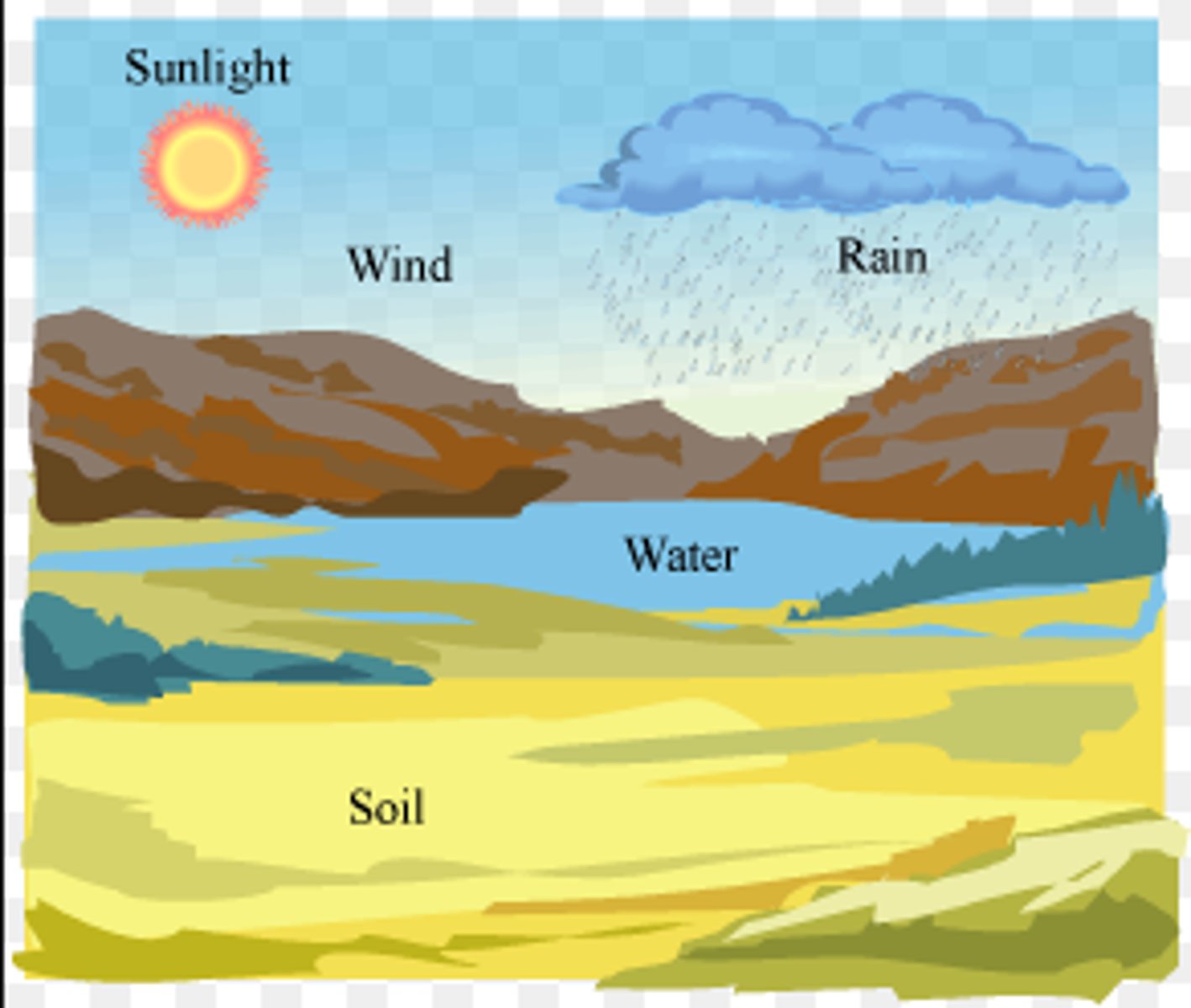
Biotic Factors
Living components of an ecosystem.
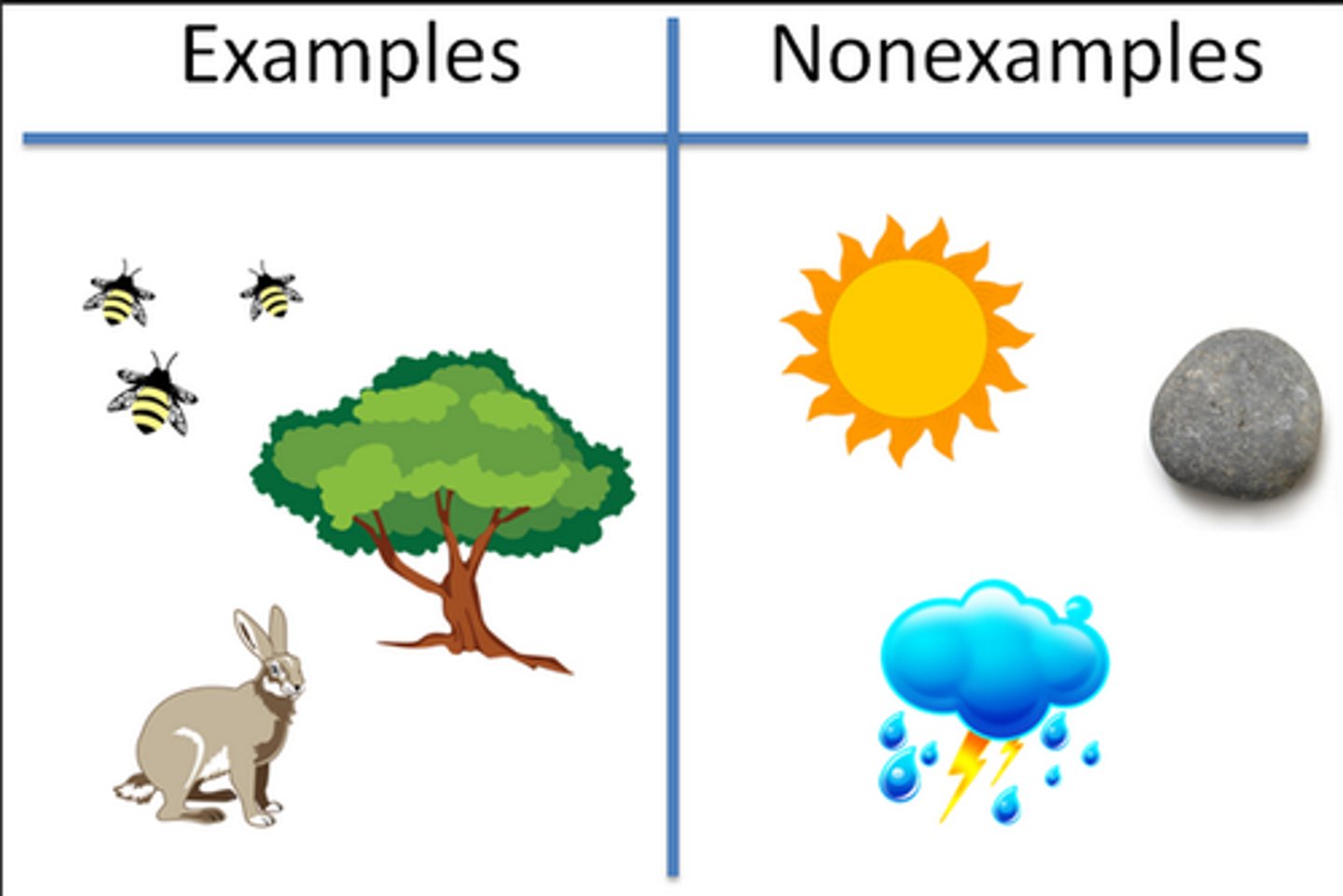
Abiotic Factors
Non-living components of an ecosystem.
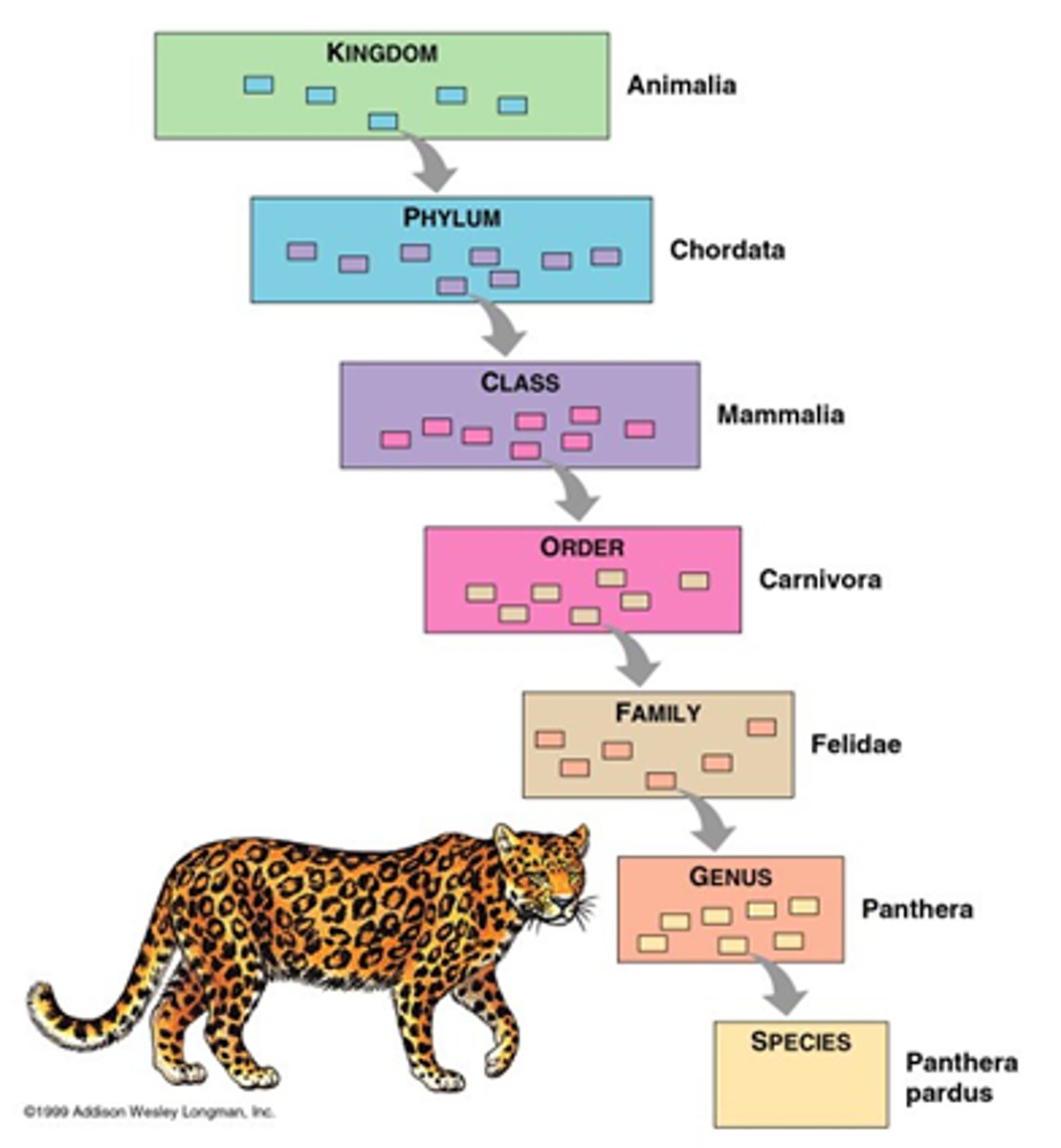
Taxonomy
Classification of organisms into hierarchical groups.
Scientific Name
Genus name + species name. For organism identification. Avoids confusion with other species.

Evolution
Change in frequency of a population's gene pool.
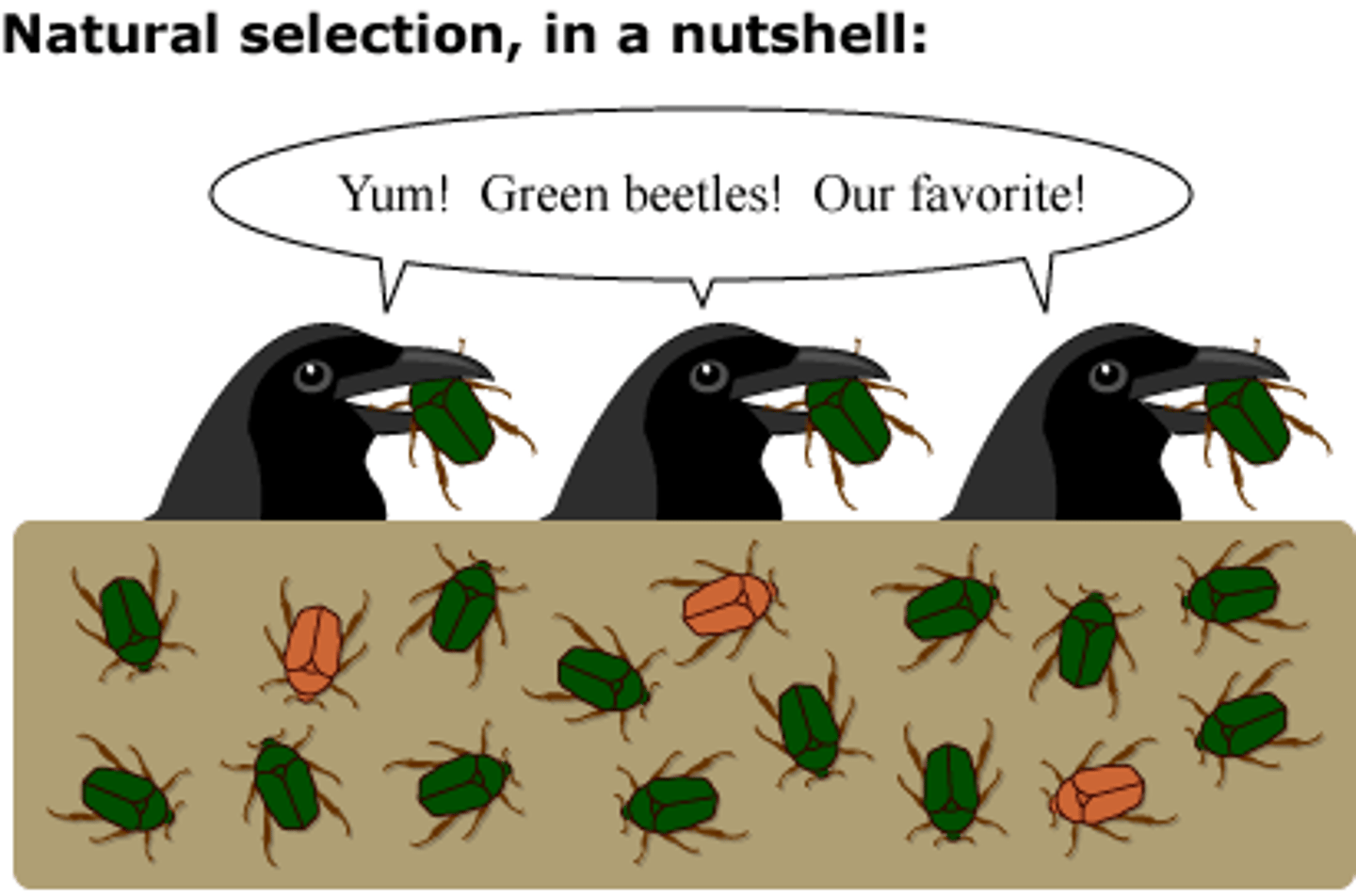
Natural Selection
Survival of organisms better adapted to environment.
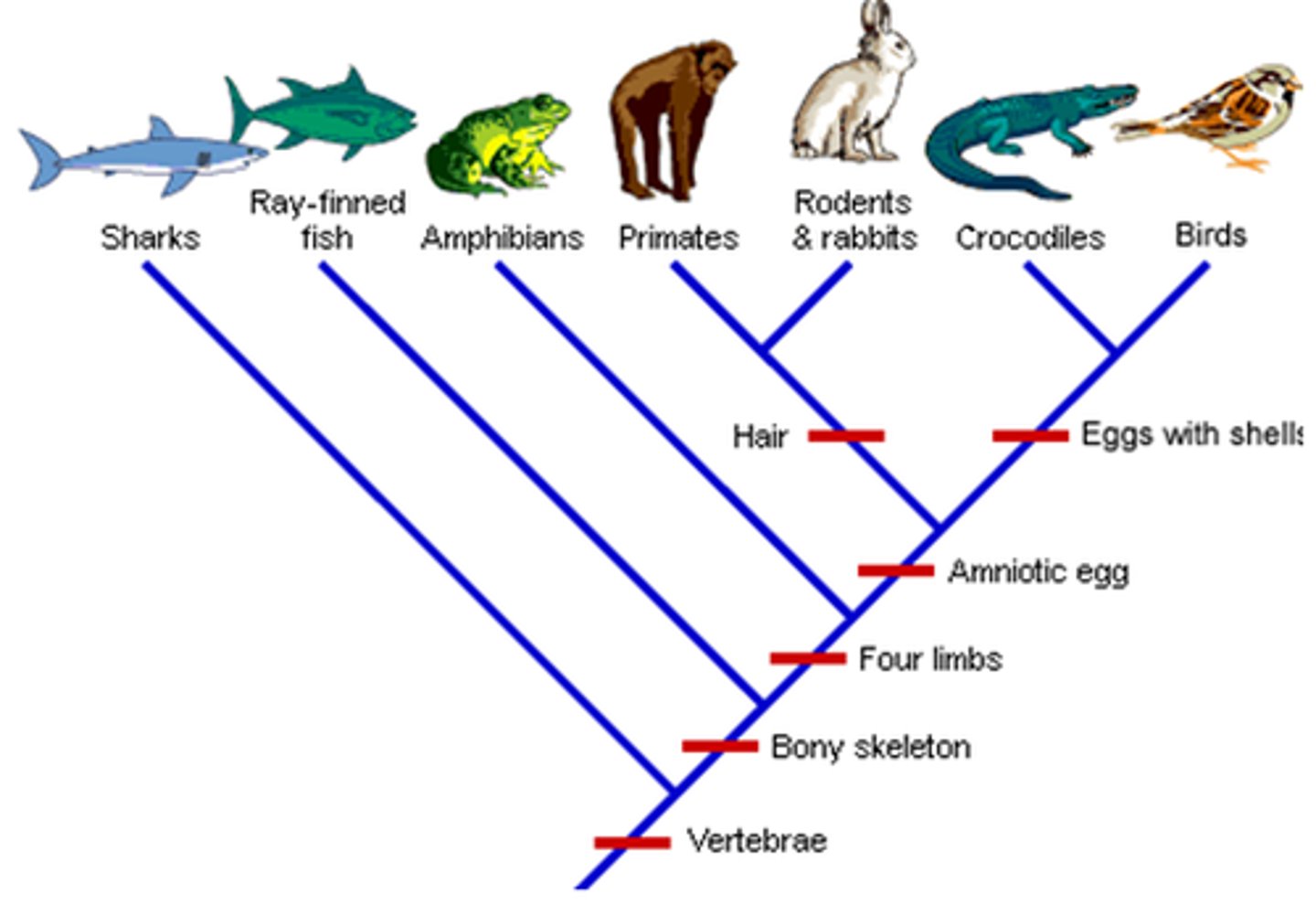
Cladogram
Diagram showing evolutionary relationships.
Symbiosis
Relationships between different species in nature.
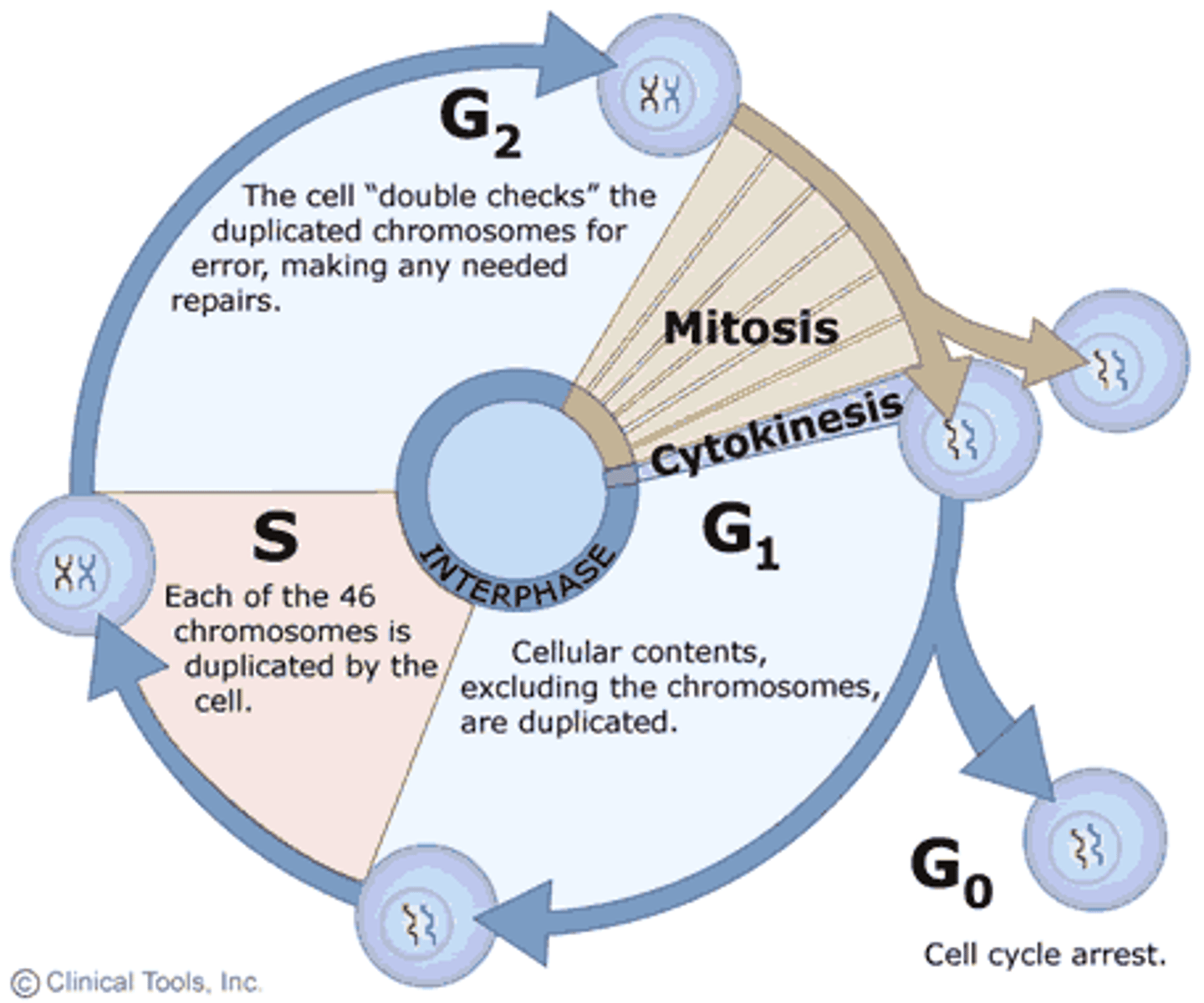
Cell Cycle
Includes Interphase (G1, S, G2) Mitosis & Cytokinesis
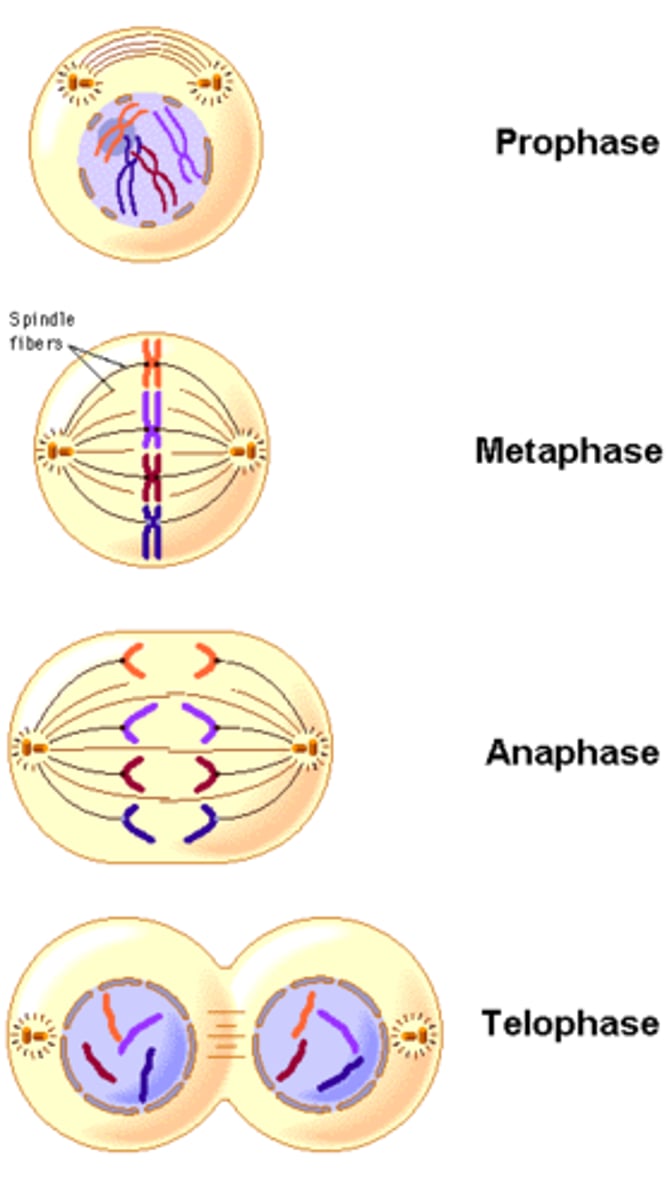
Mitosis
Cell division process with Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase & Telophase.
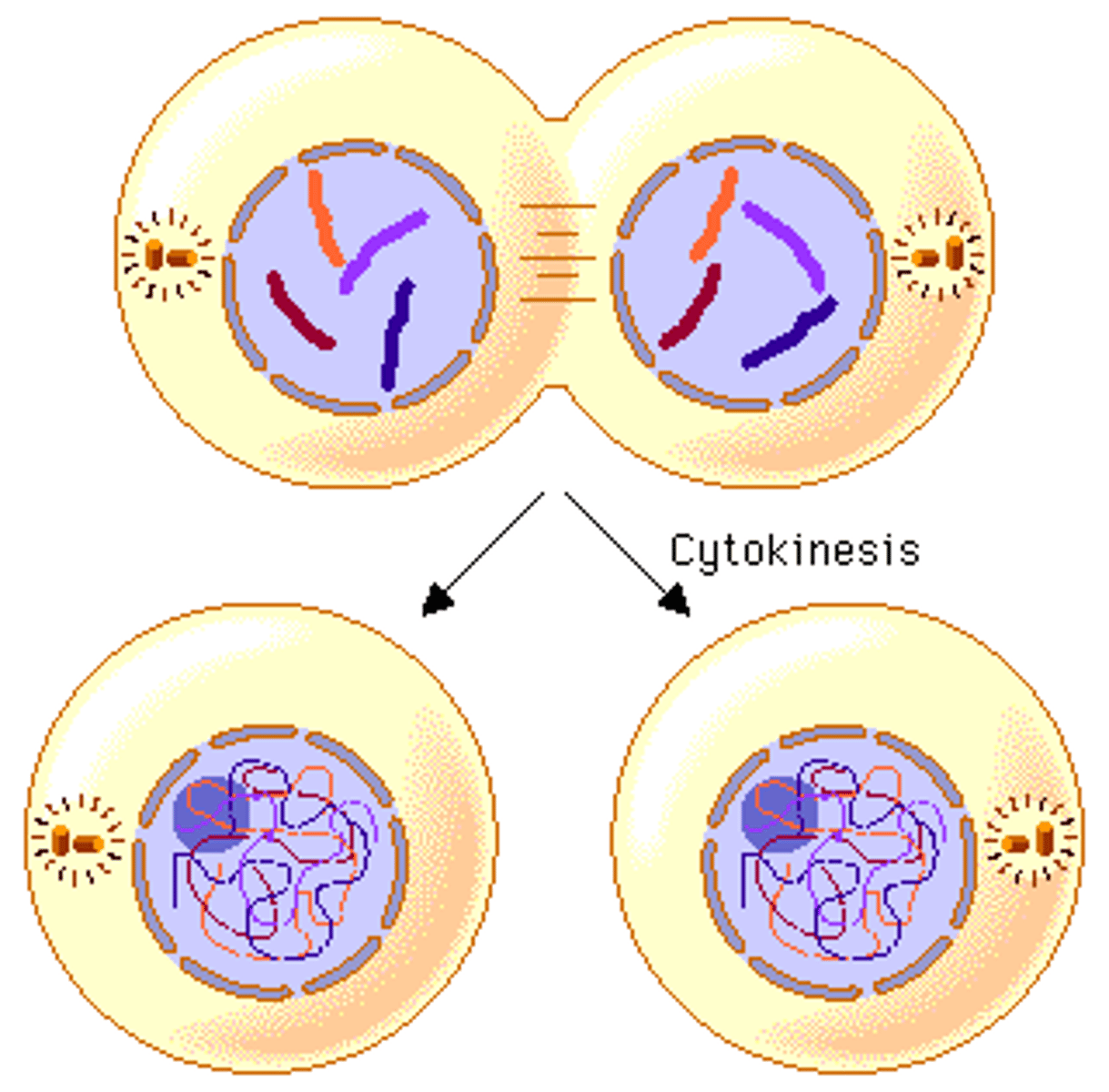
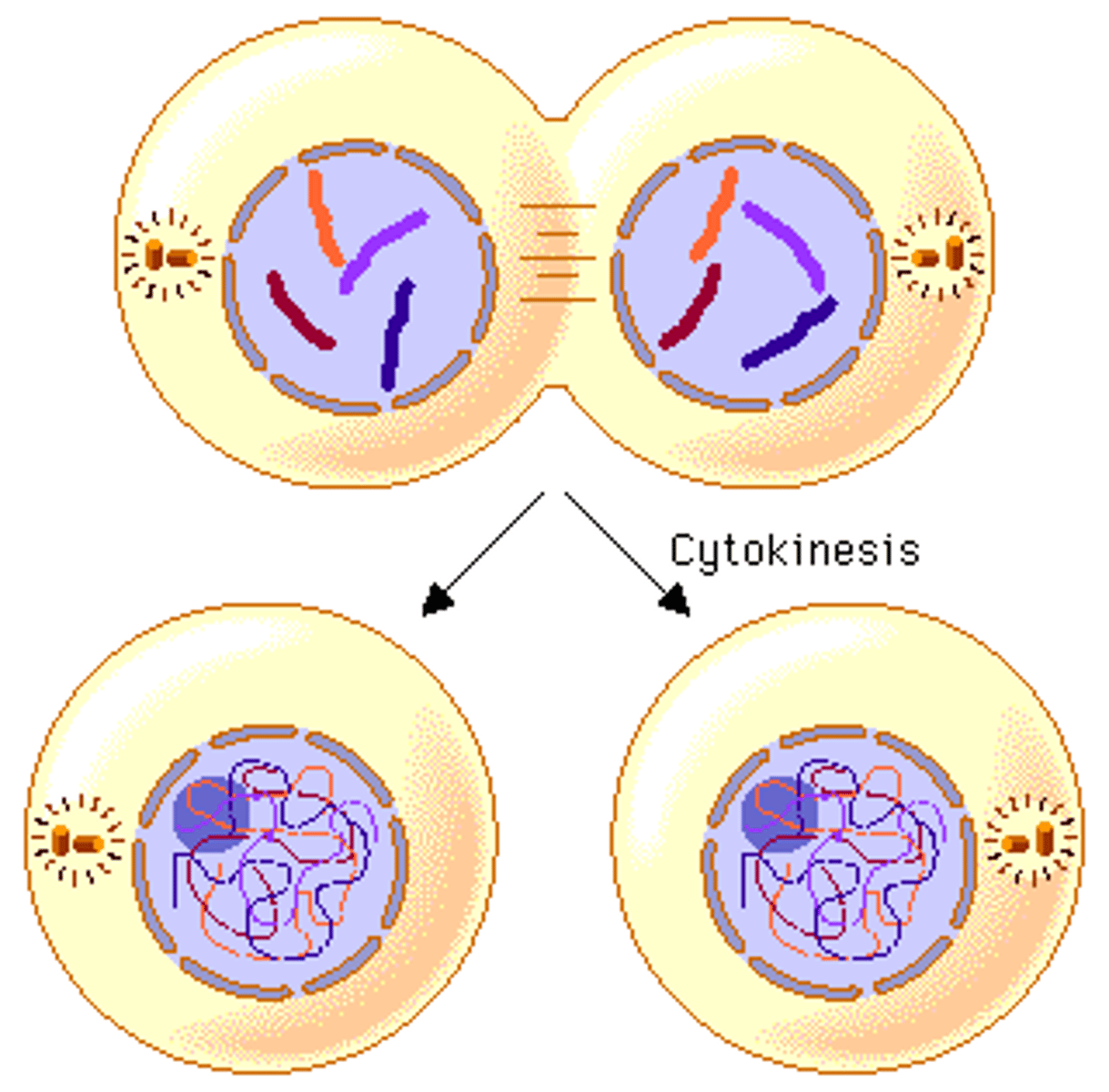
Cytokinesis
Final separation of cells after mitosis.
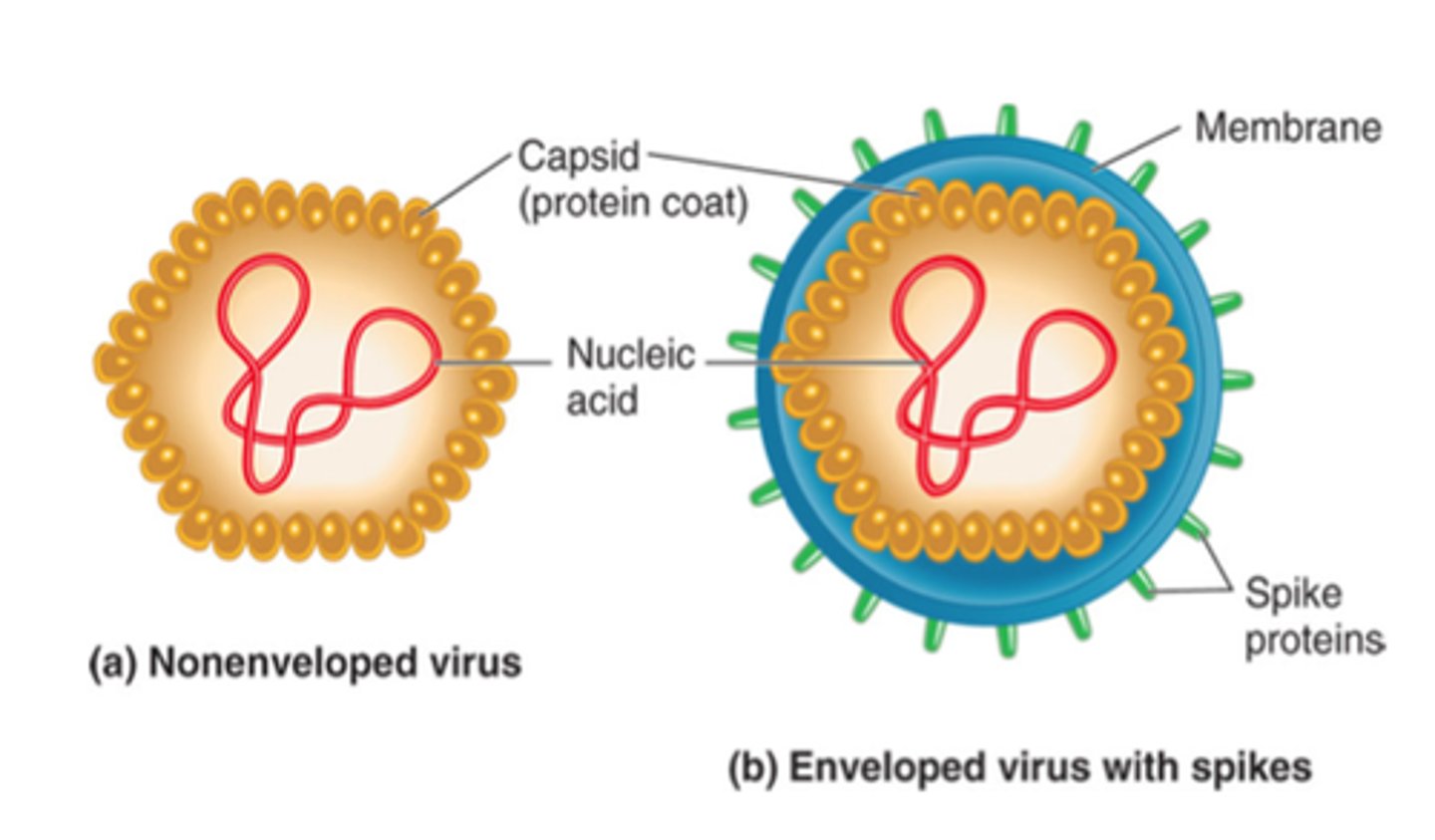
Viruses
Non-living entities requiring host cells to reproduce.
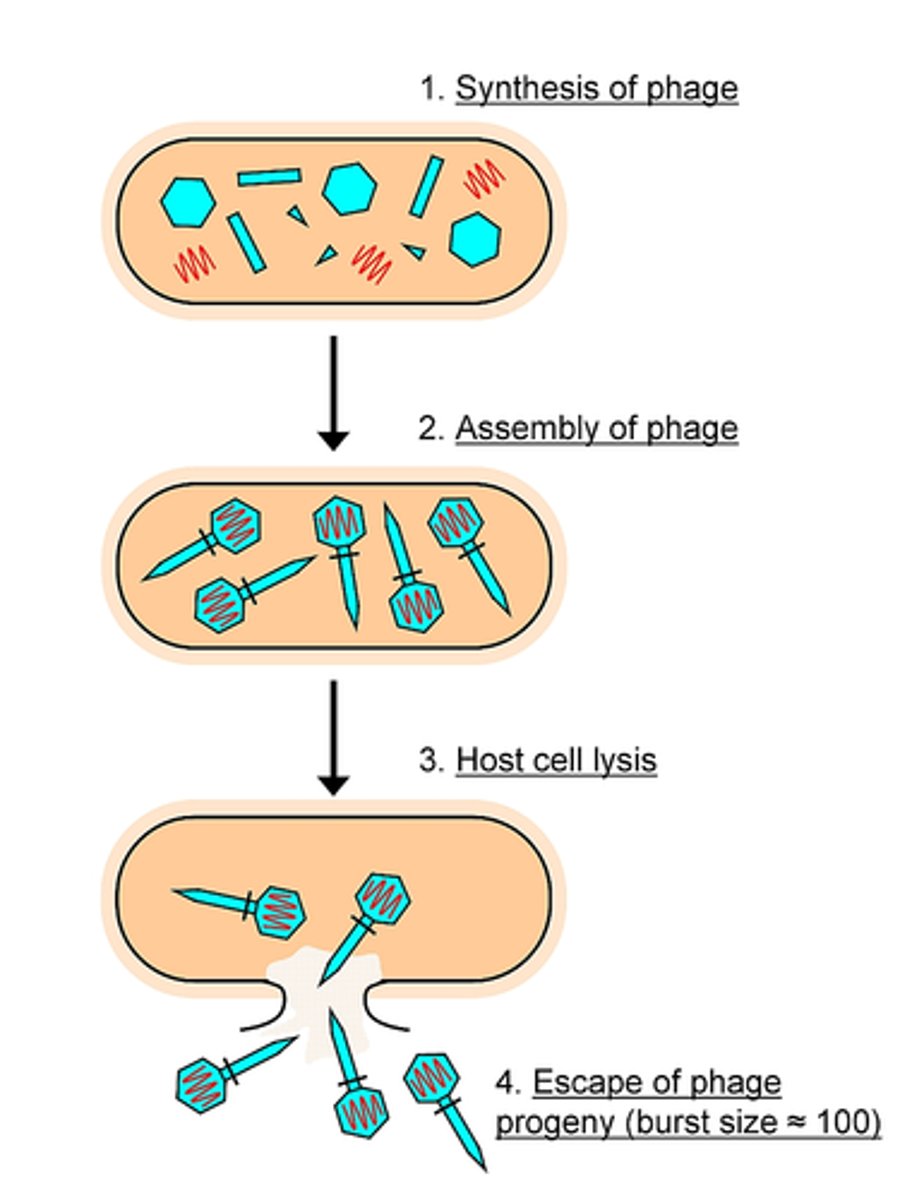
Lytic Cycle
Fast viral replication causing cell destruction.
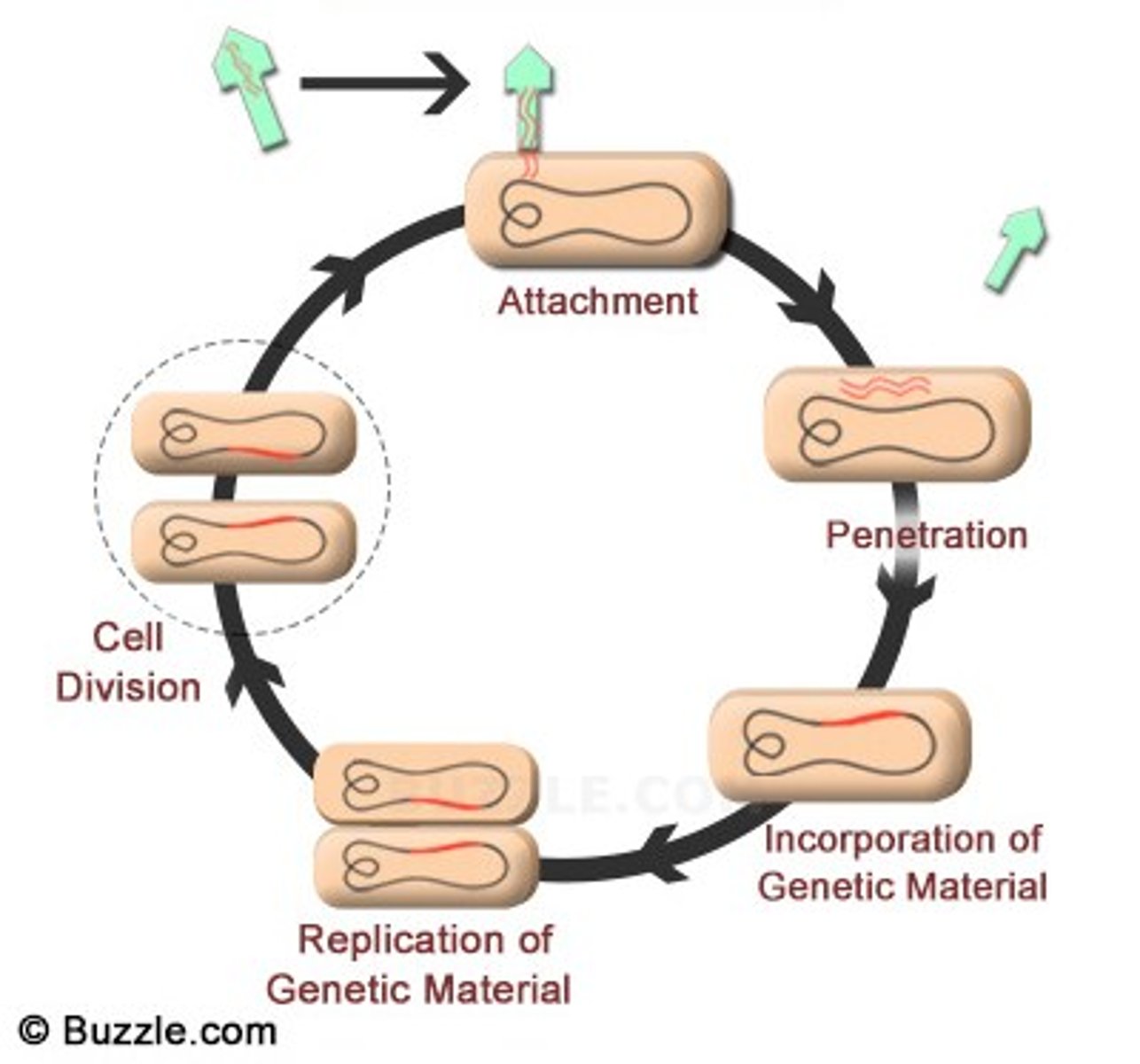
Lysogenic Cycle
Slow viral replication integrating into host DNA.
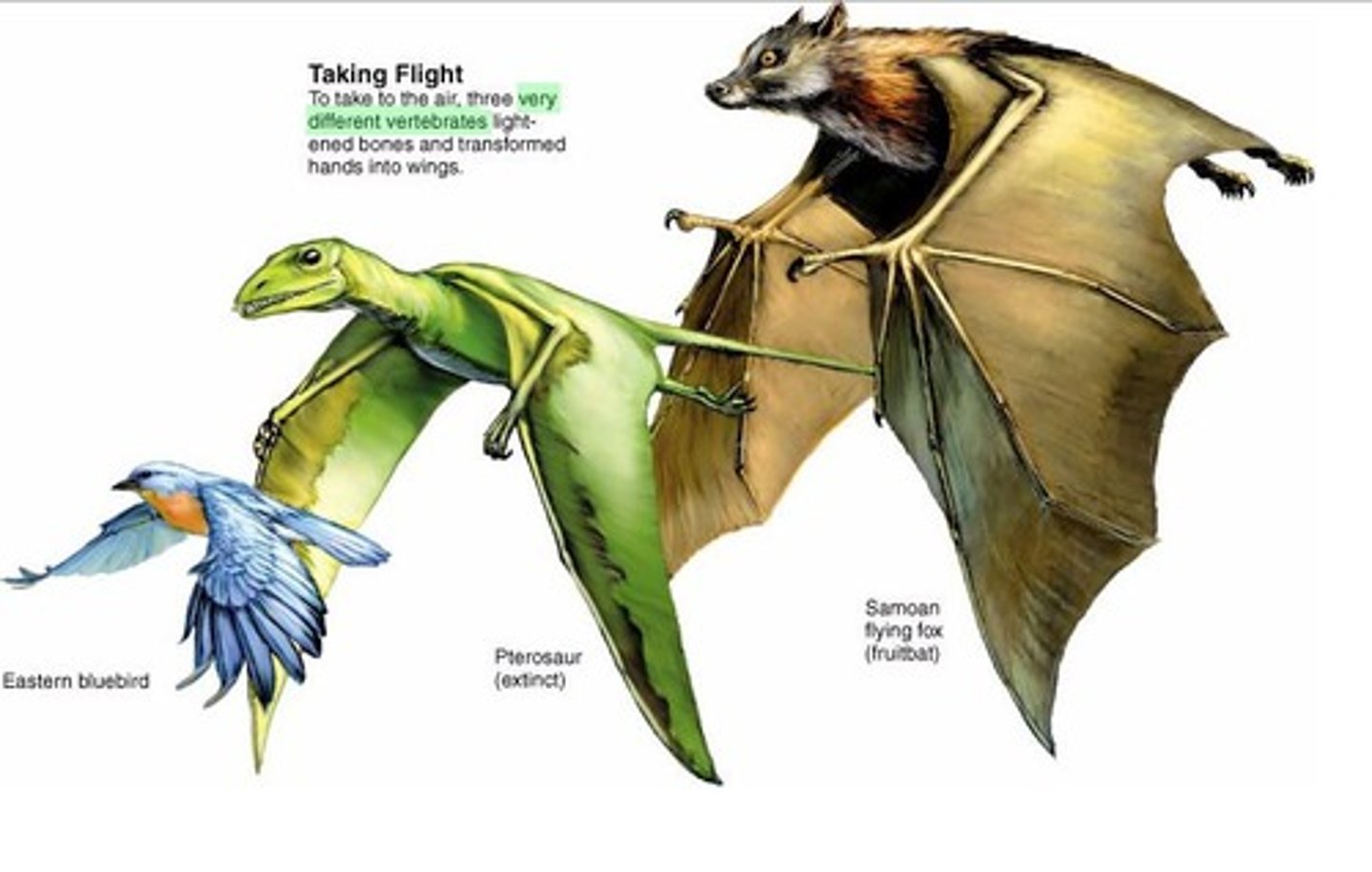
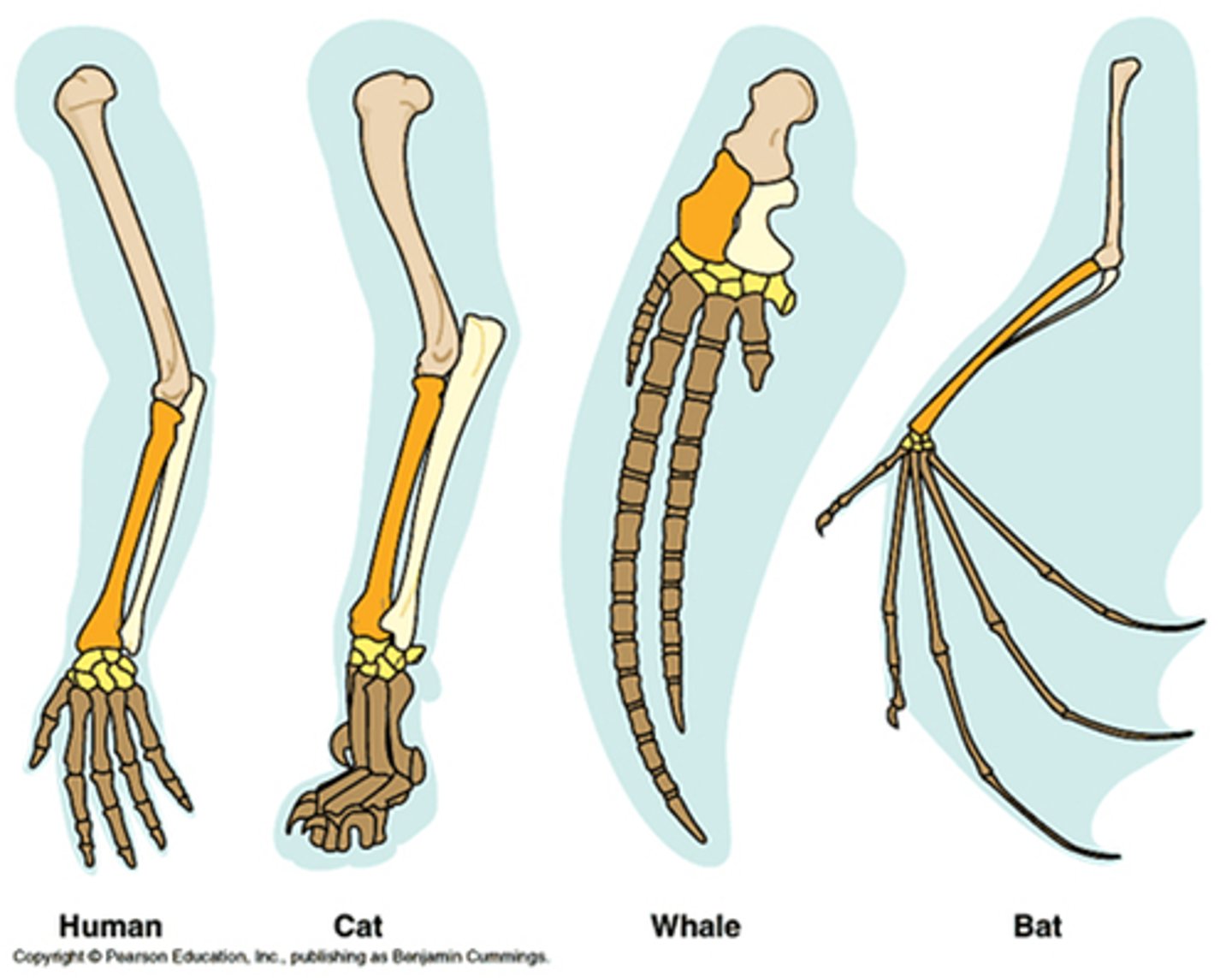
Homologous Structures
Similar structures with different functions indicating common ancestry. (Human arm & Bat wing)
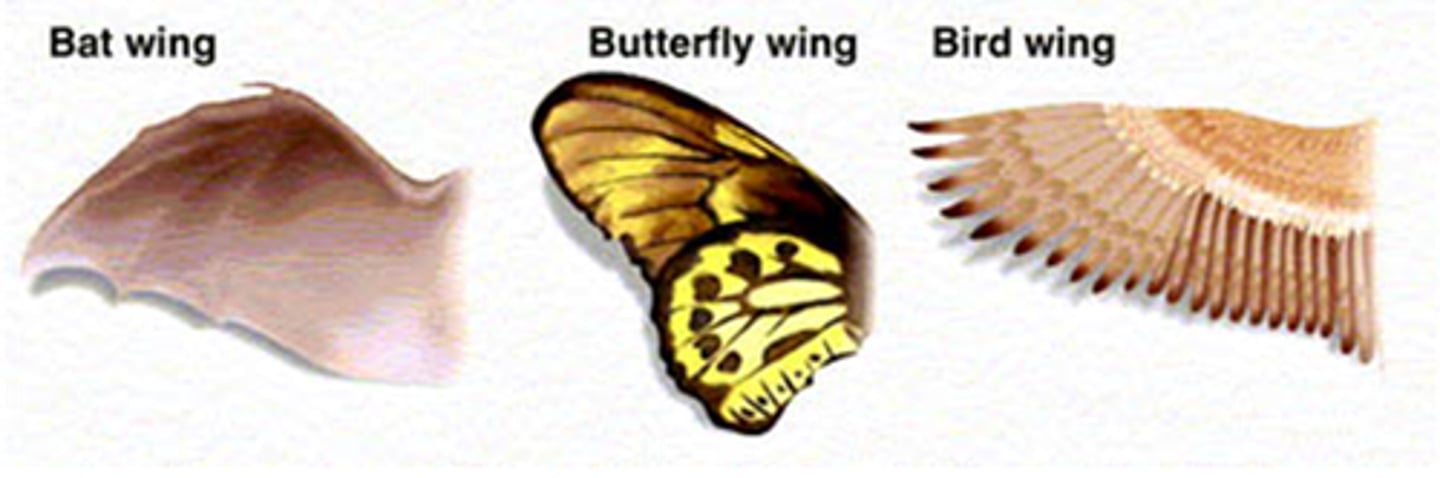
Analogous Structures
Structures in different organisms serving similar functions. (Bee wing & Bat wing)
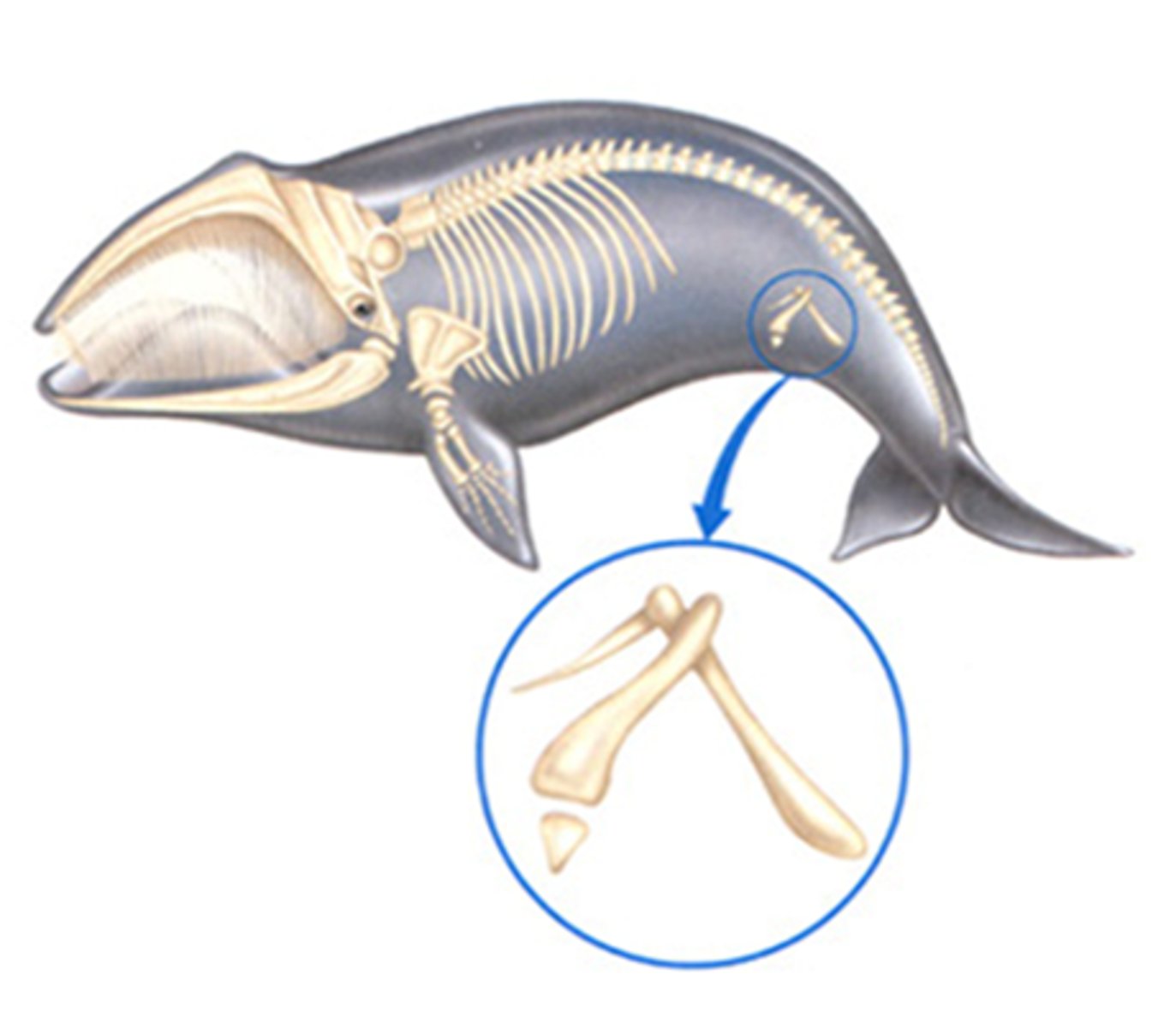
Vestigial Structures
Structures with no current function, but were important in the past. (Whale leg bone)
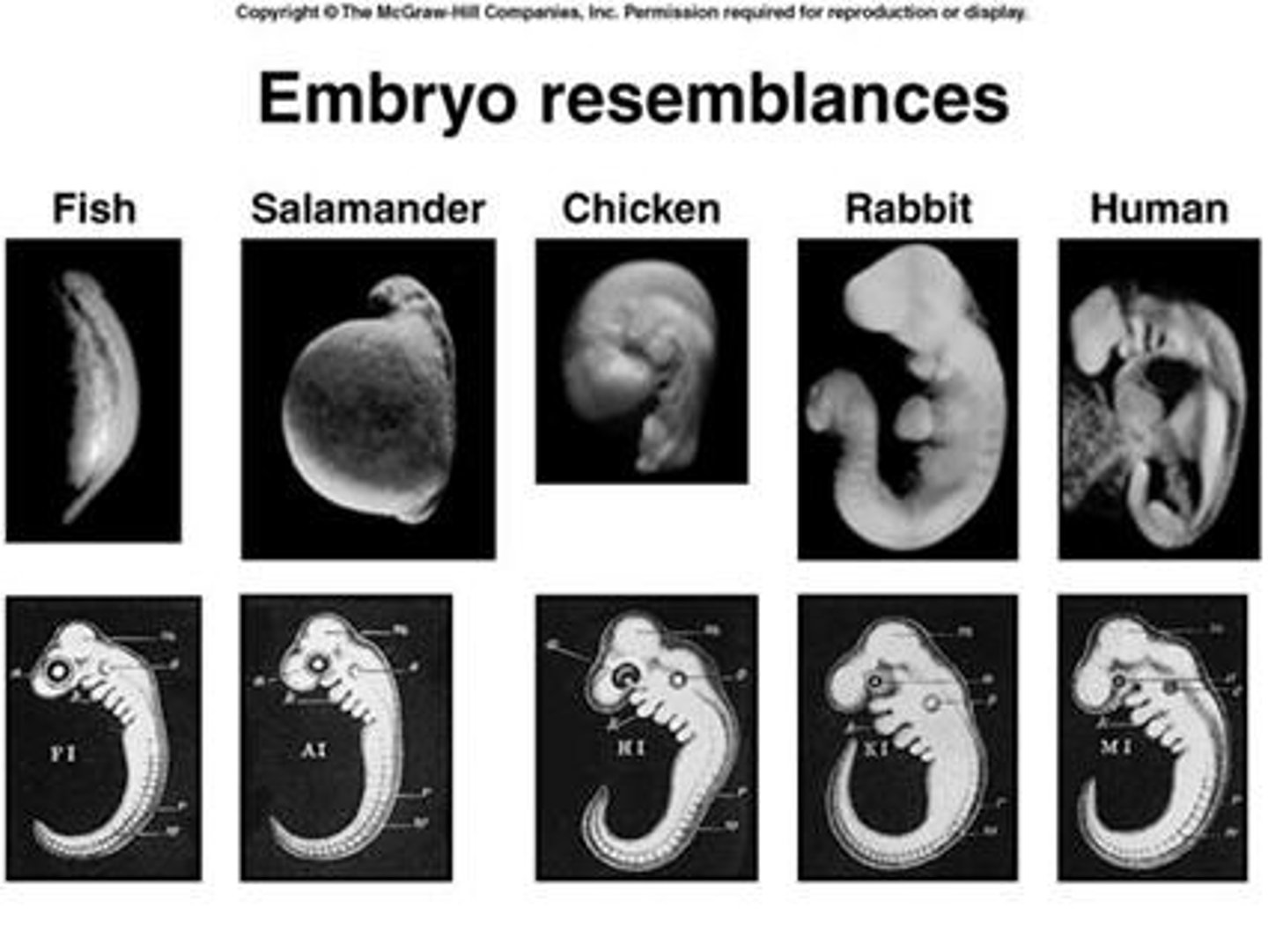
Embryology
Study of embryos indicating common ancestry.
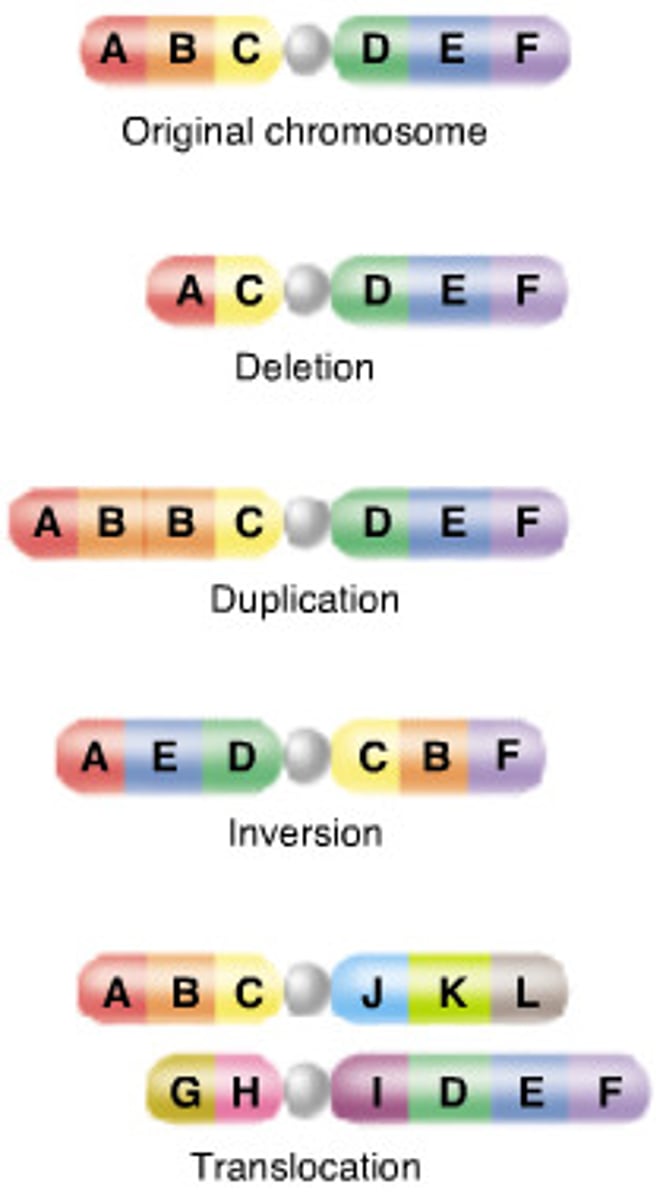
Types of Mutations
Substitution, deletion, insertions affecting genetic code.
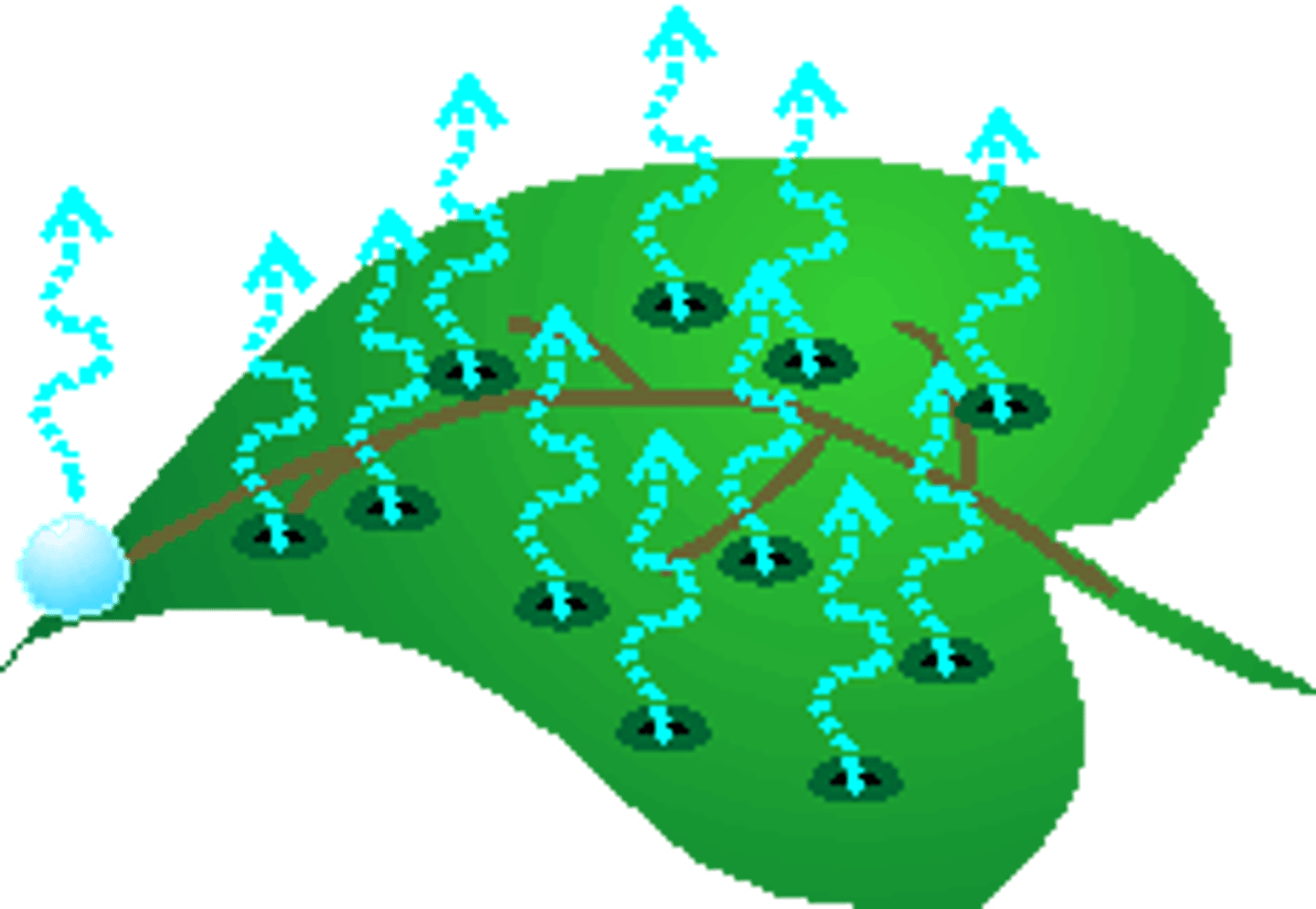
Transpiration
Water evaporation from stomata in leaves; sucks water up from roots
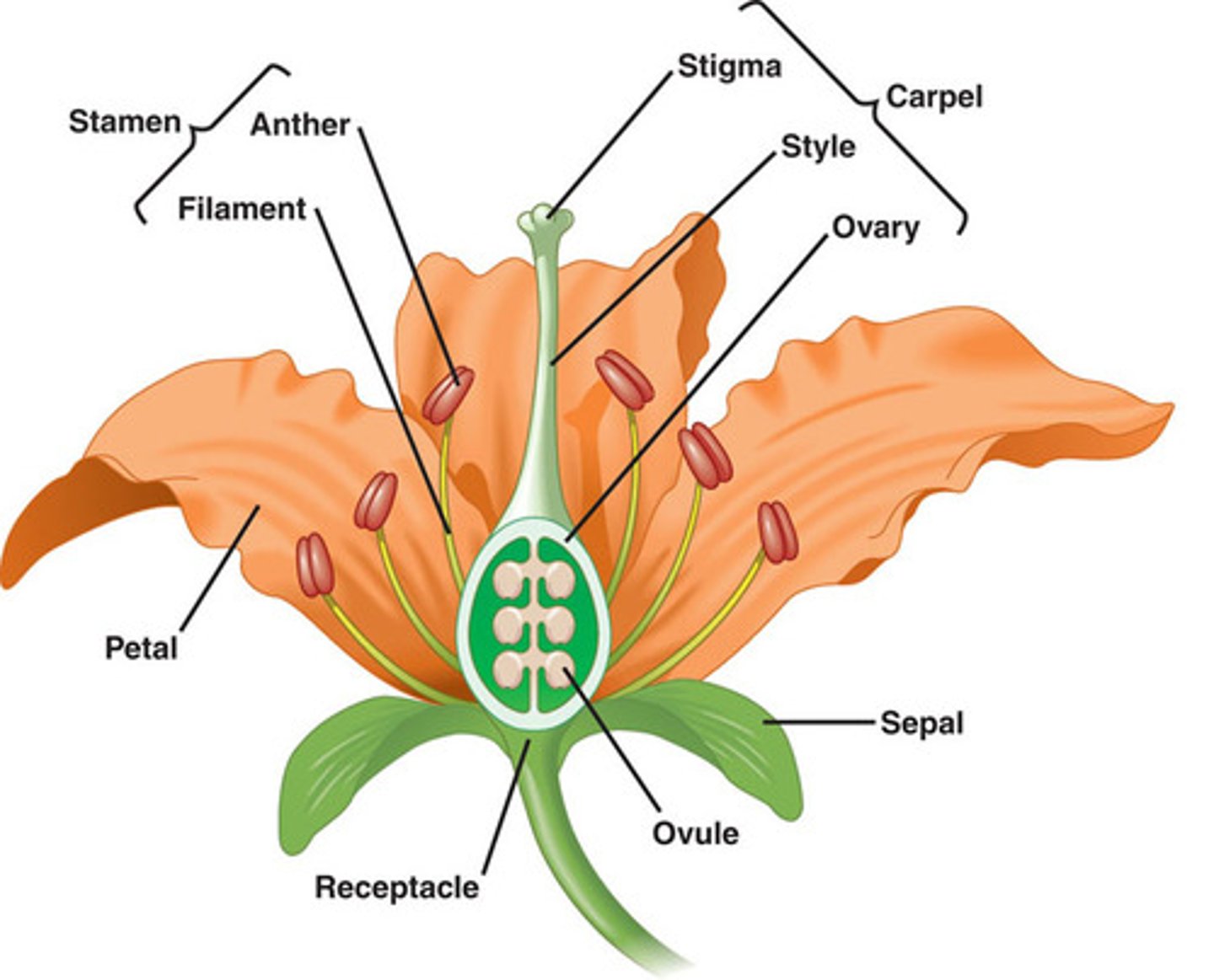
Plant Reproduction
Involves pistil and stamen for fertilization.
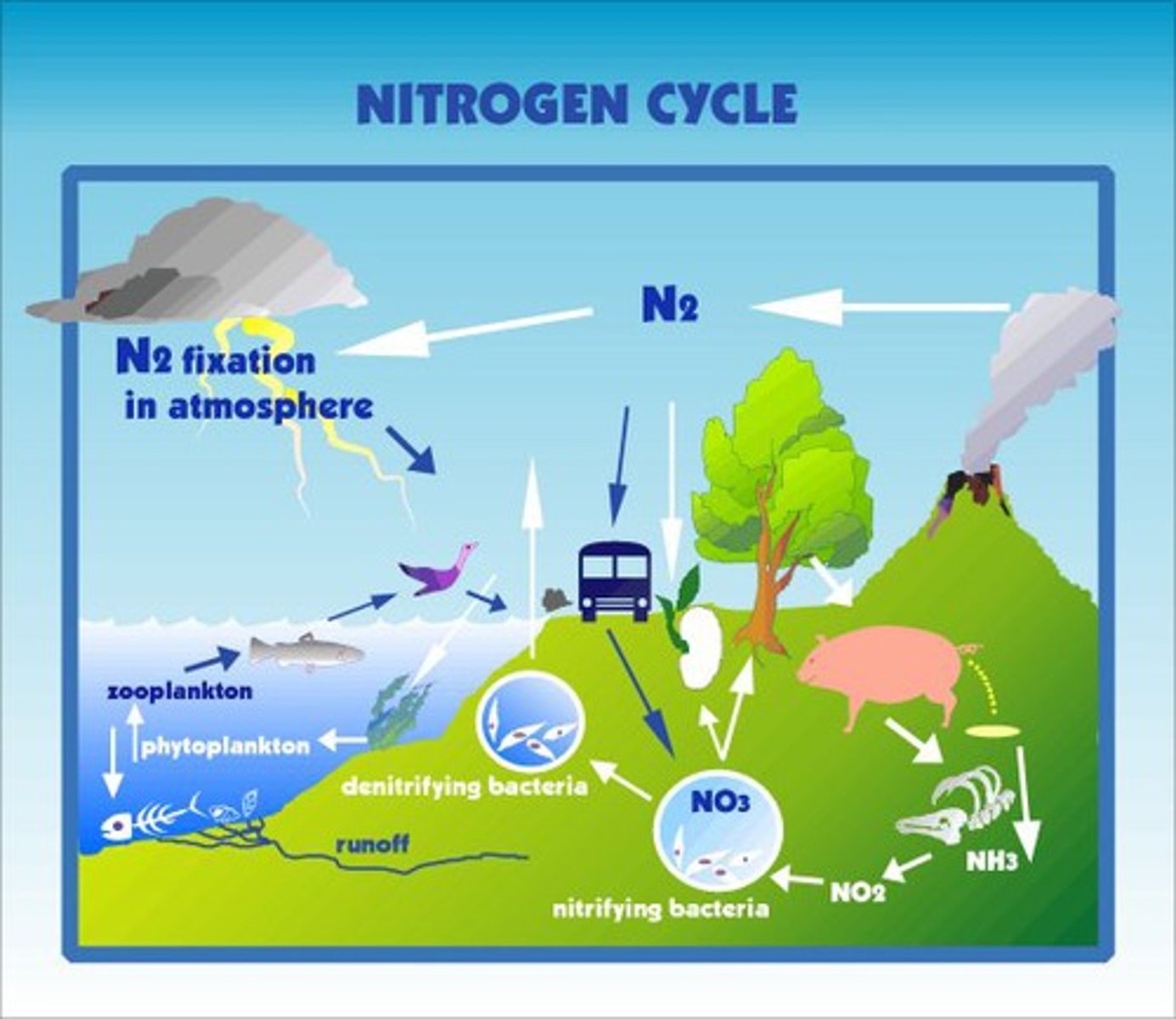
Nitrogen Cycle
Process of nitrogen fixation and denitrification.
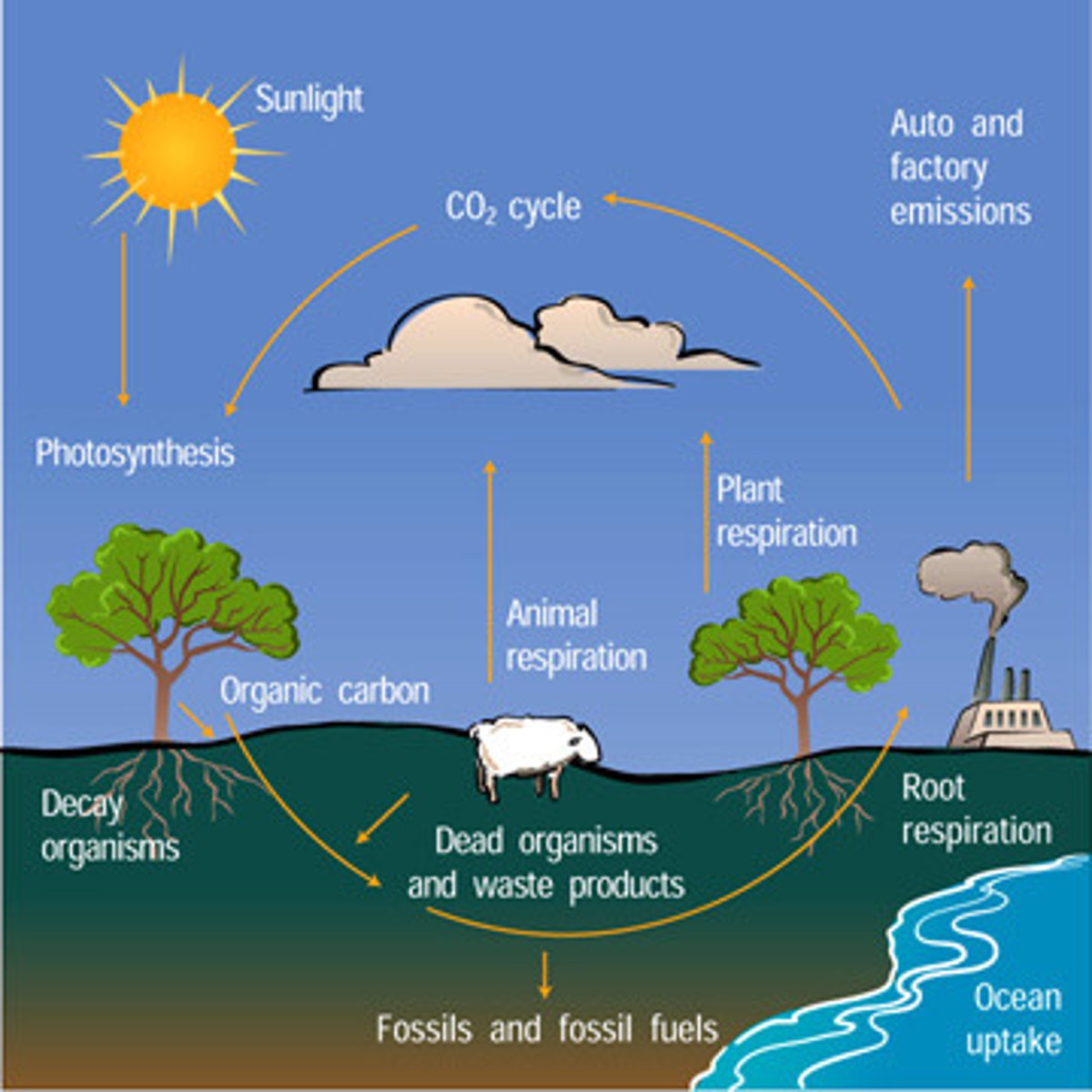
Carbon Cycle
Involves photosynthesis and decomposition of organisms.
Concentration Gradient
A force pushing molecules from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration
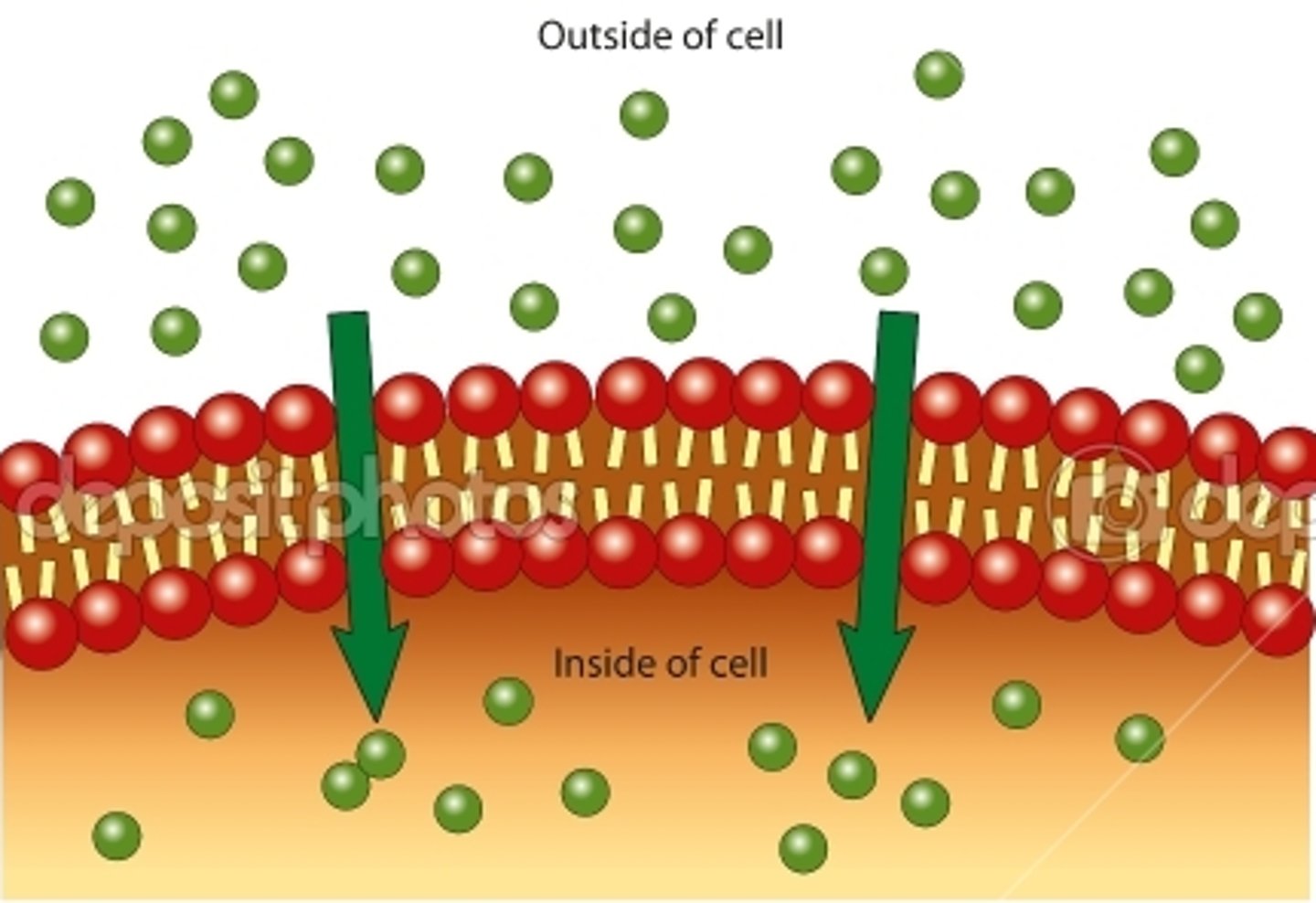
Passive Transport
Movement of molecules across cell membrane from high to low concentration without energy usage (AKA Diffusion)
Osmosis
Water diffusion across a semipermeable membrane.
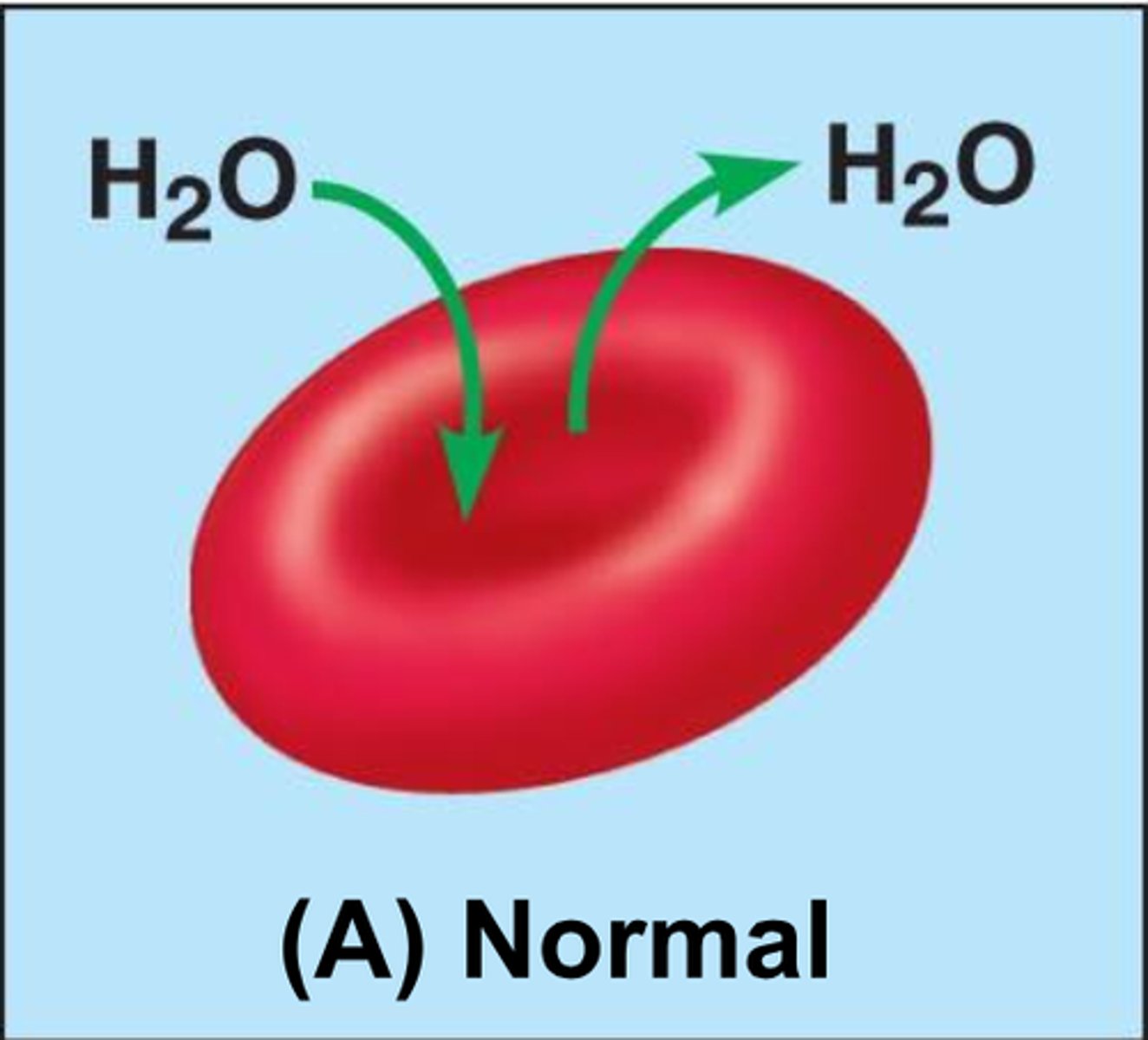
Hypotonic
Solution causing cell swelling because water enters the cell.
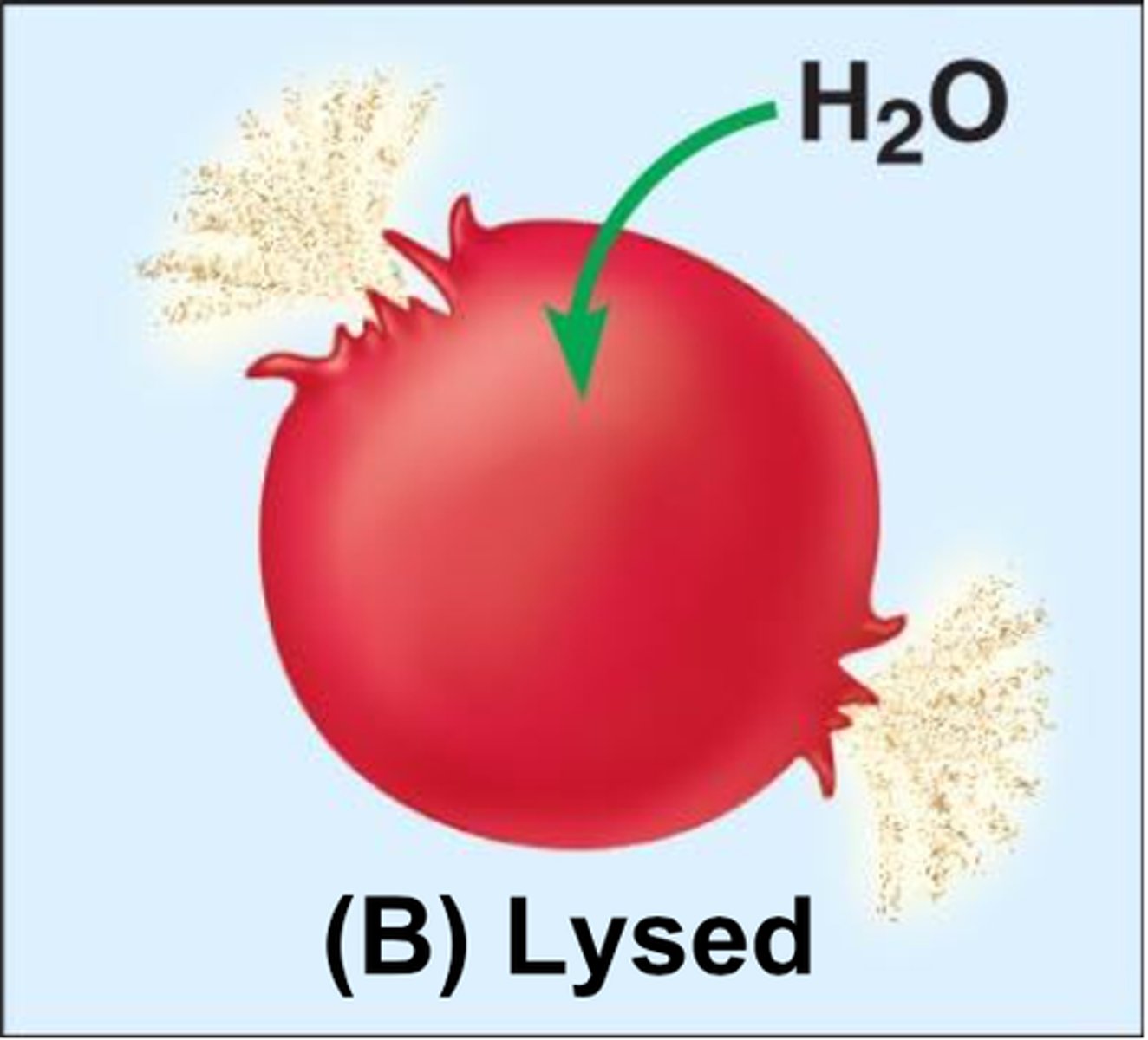
Hypertonic
Solution causing cell shrinkage because water leaves the cell.
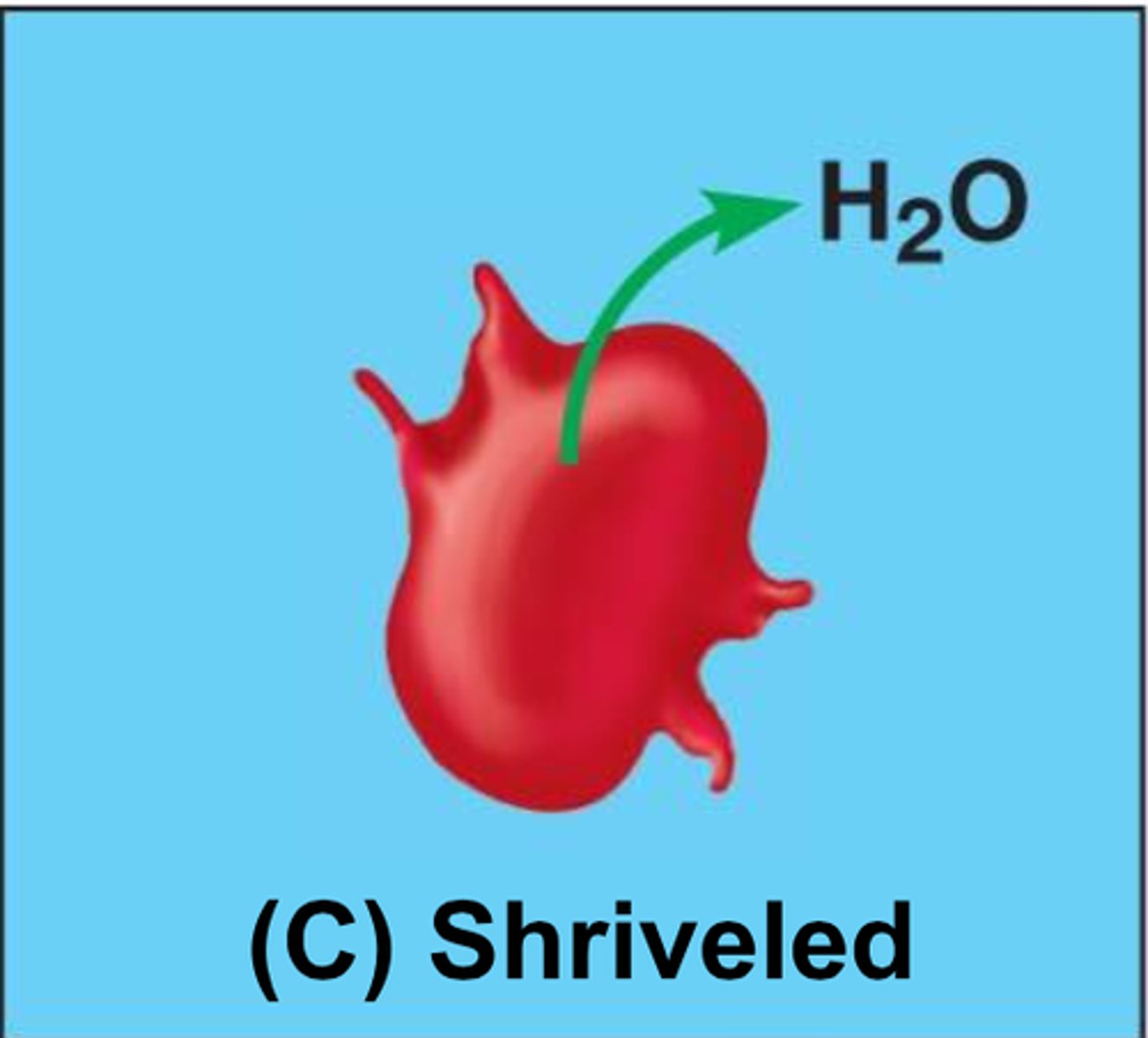
Isotonic
Solution maintaining cell size.
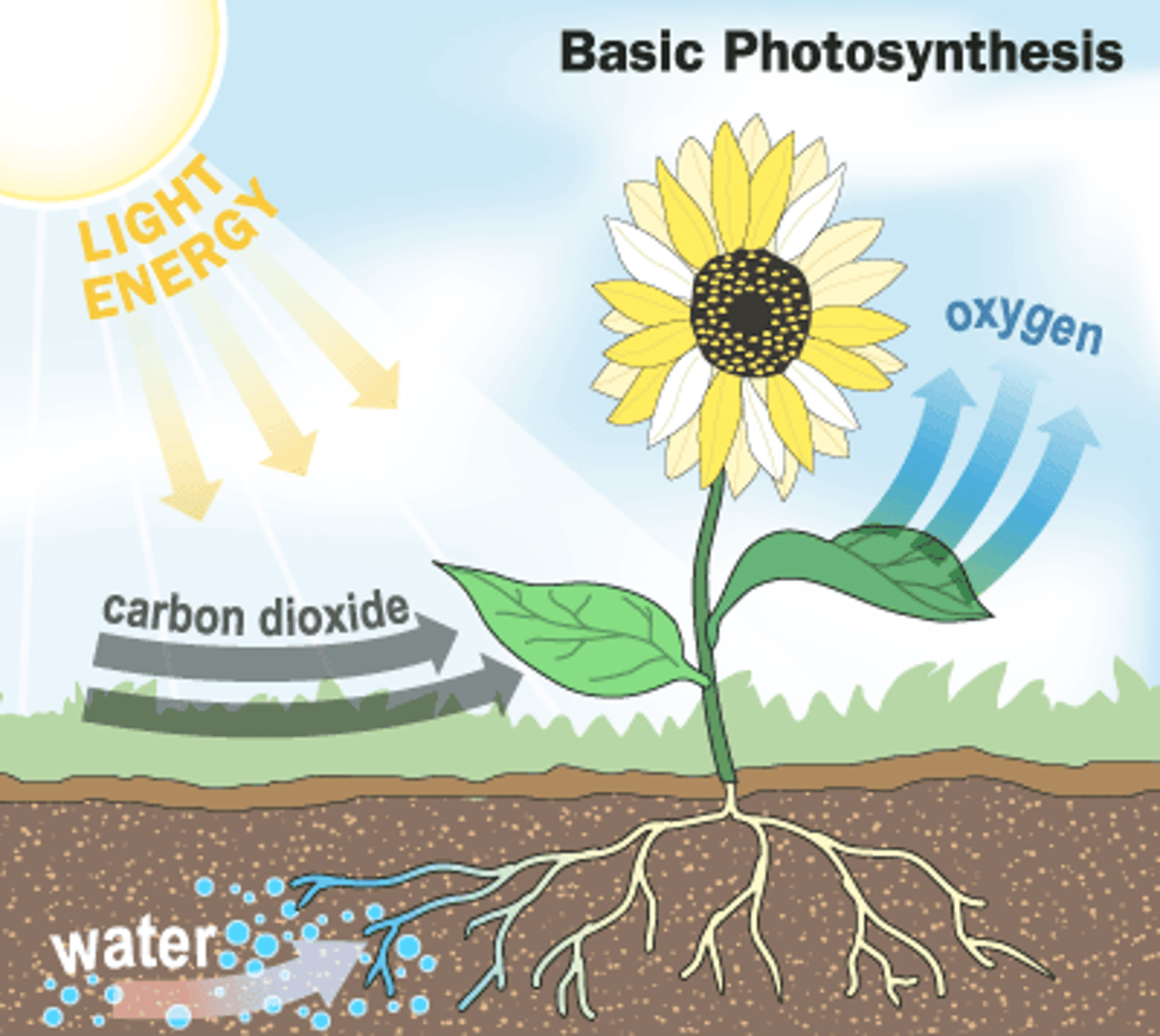
Reactants of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight
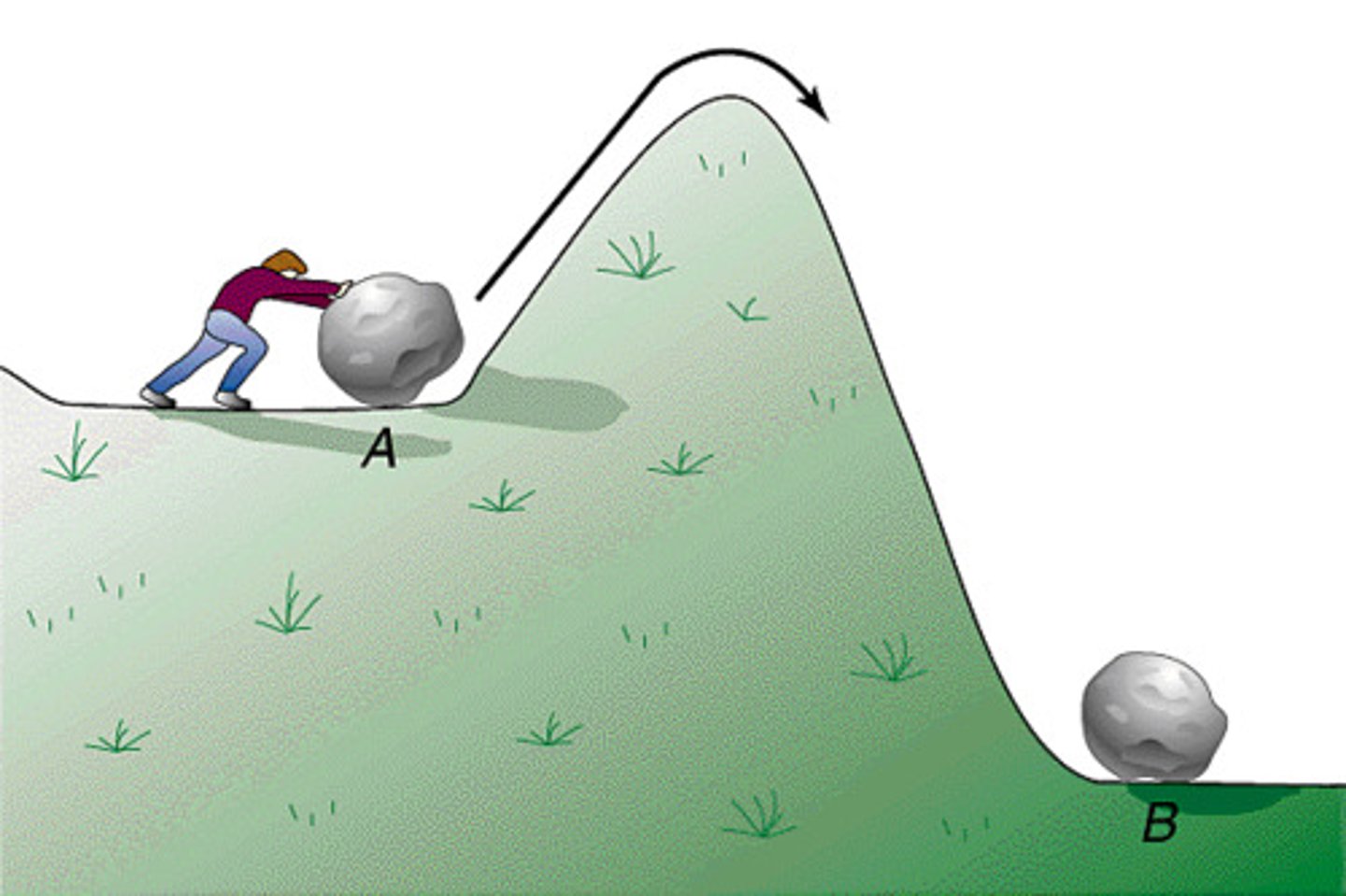
Activation Energy
Energy needed to get a chemical reaction started
Temperature & pH
The two environmental conditions that may cause an enzyme to denature
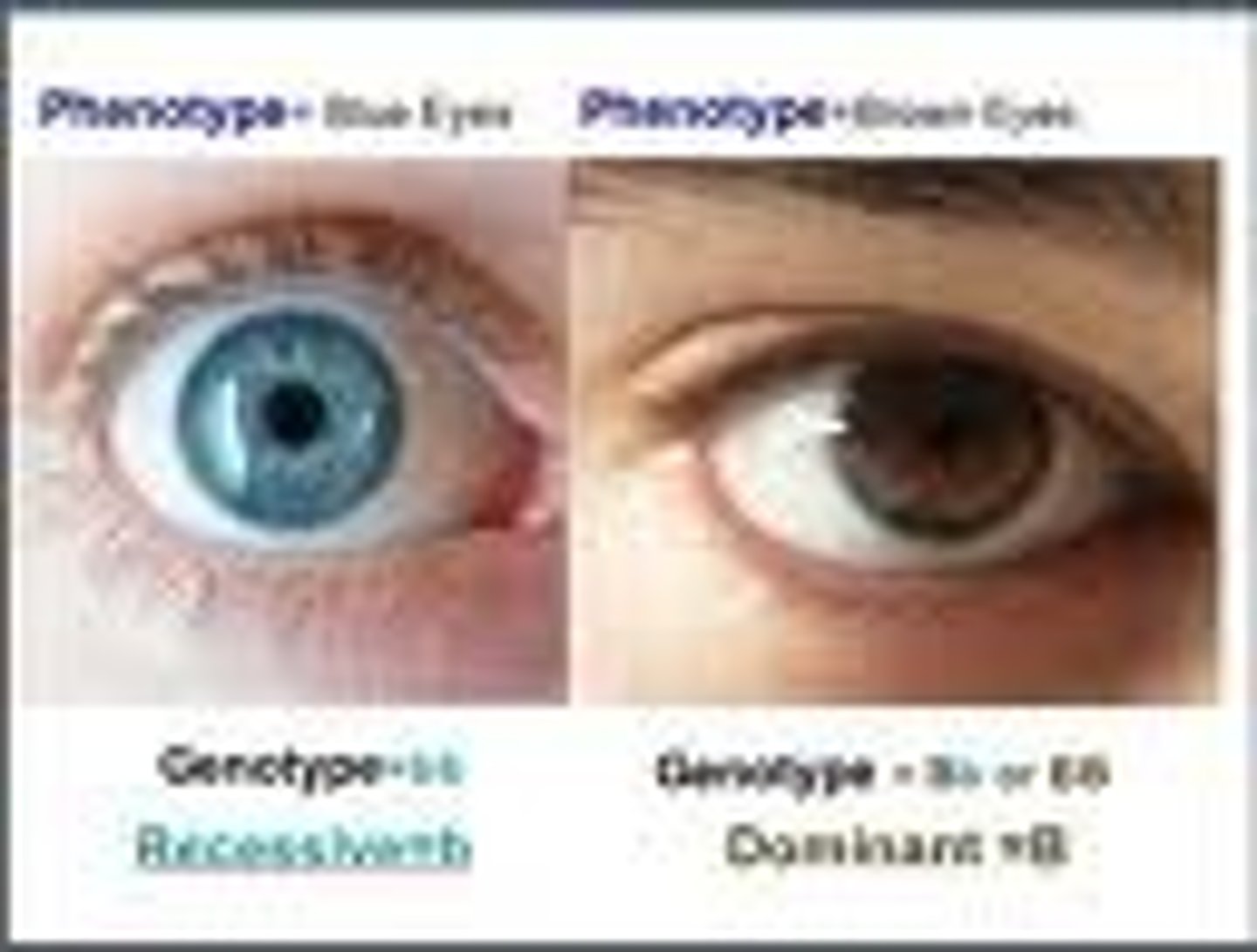
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
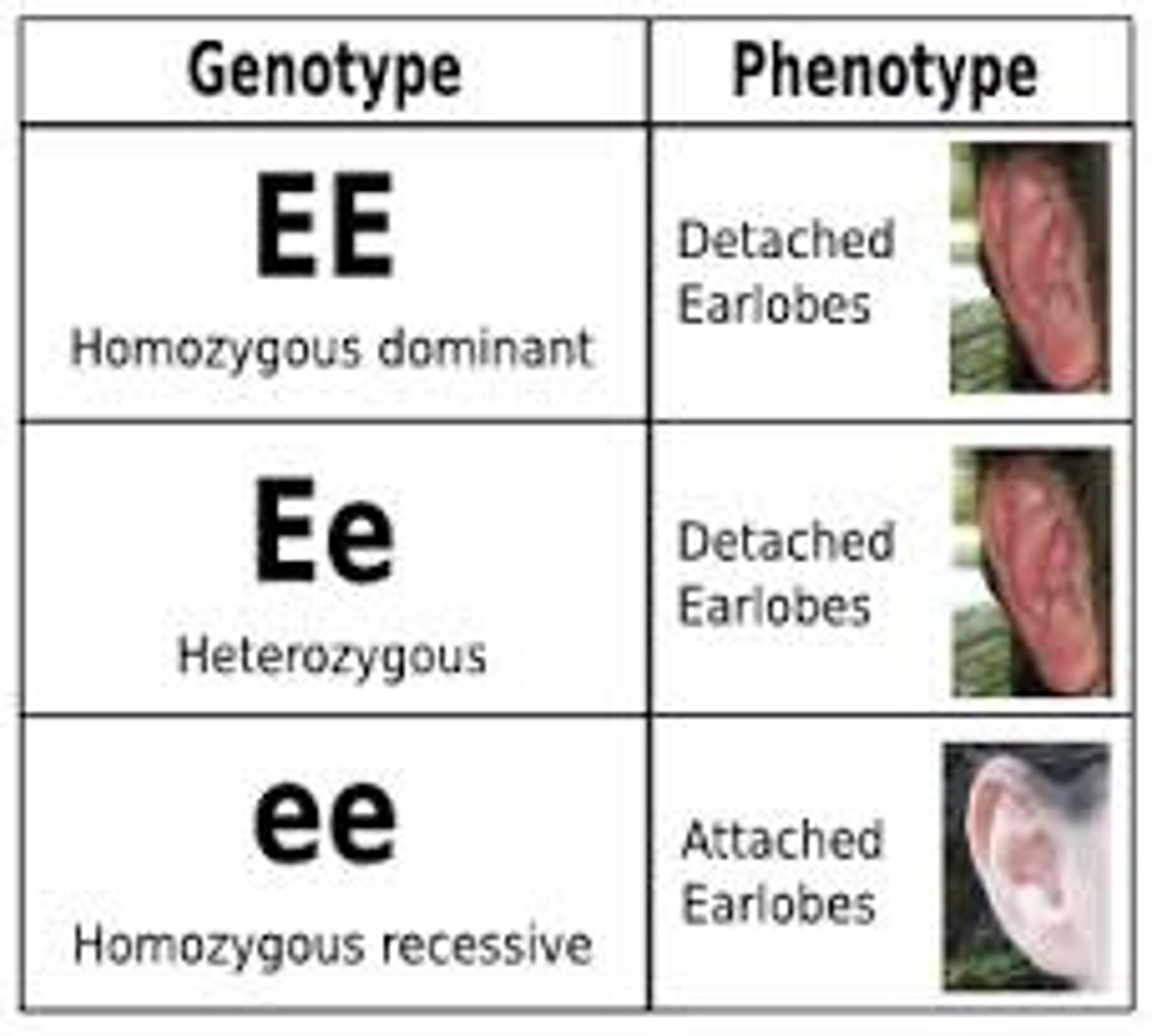
Phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.
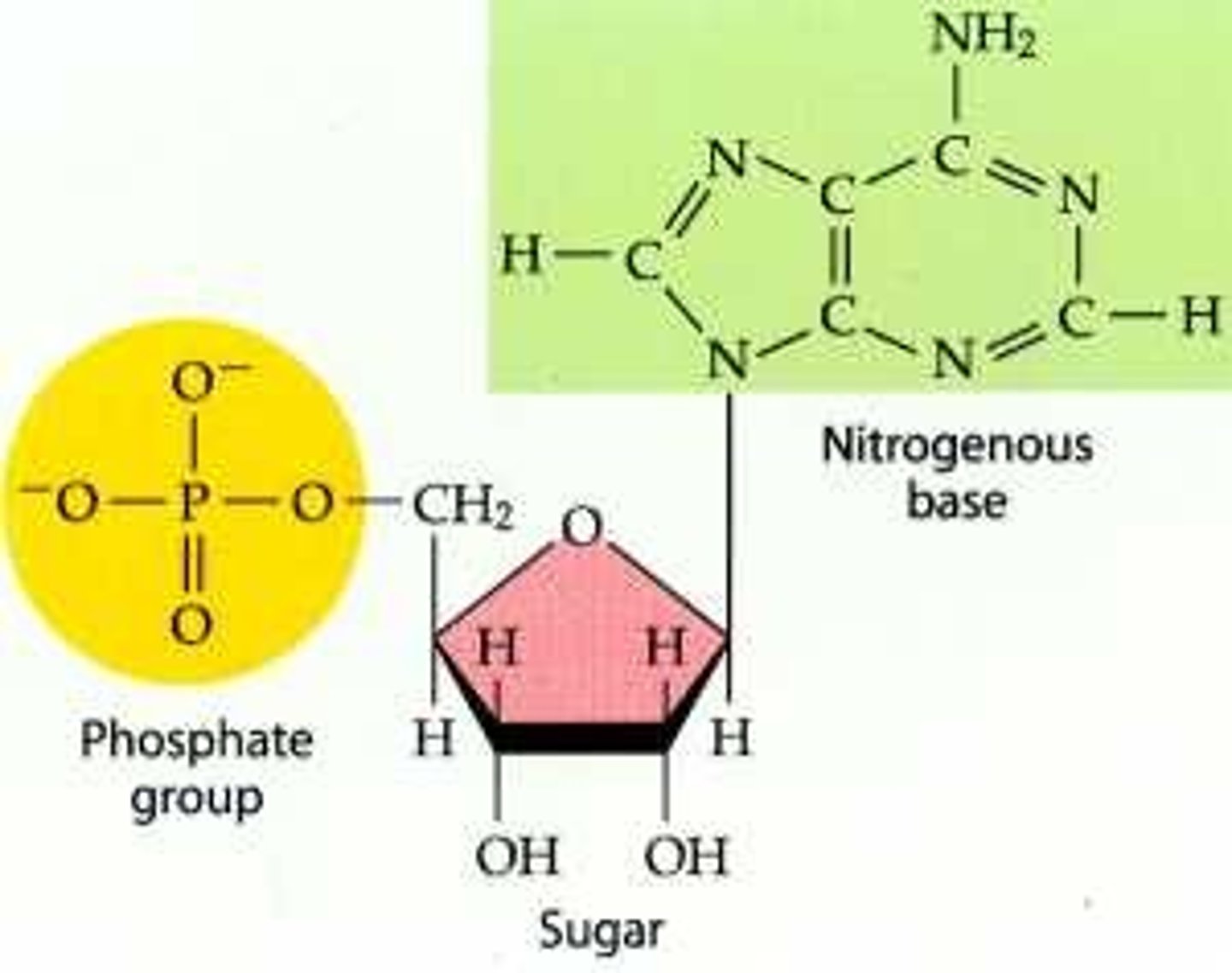
Nucleic Acids
The only biomolecule to contain all 5 CHOPN atoms
Active Site
The location on an enzyme where the substrate binds to
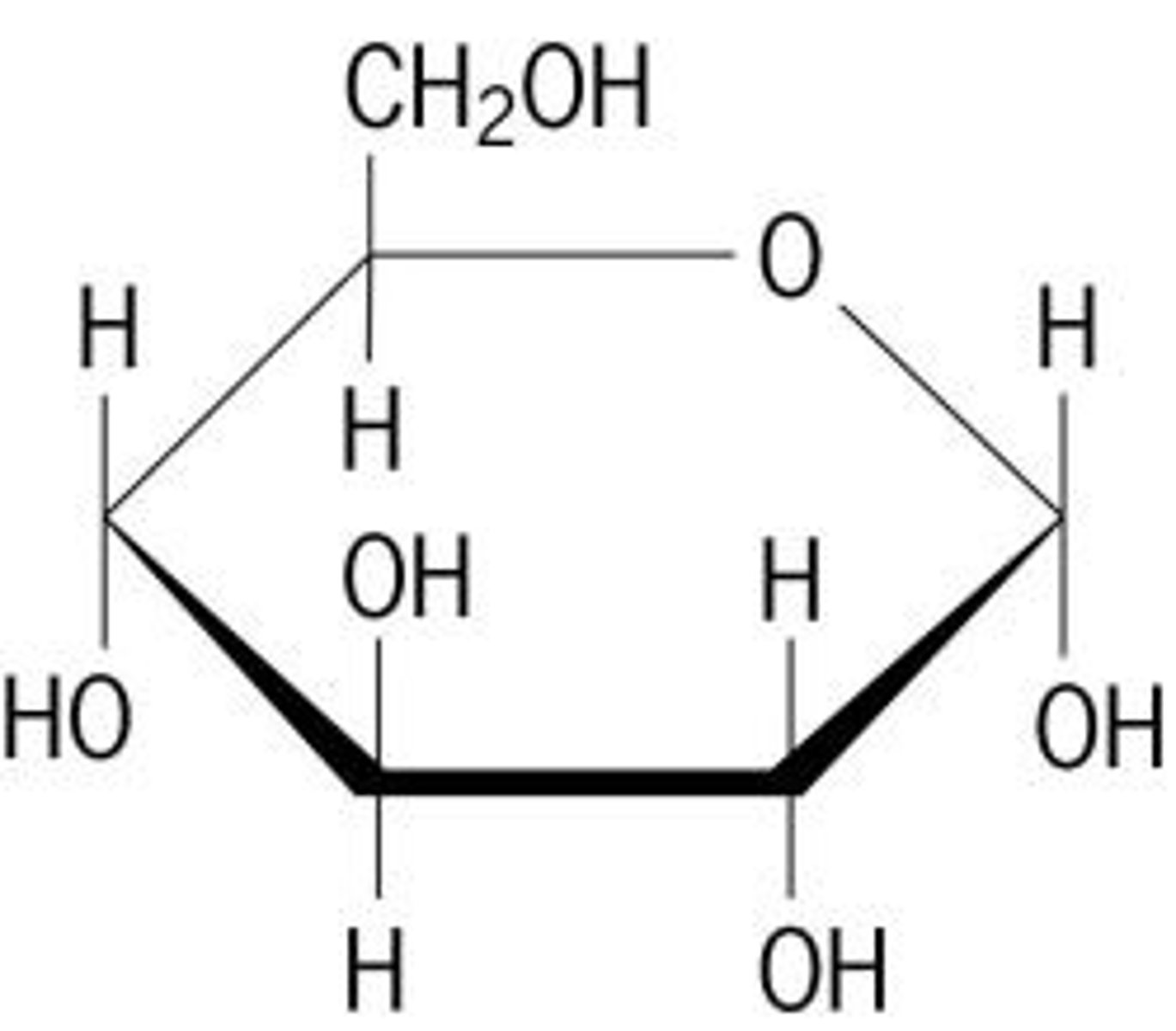
Carbohydrates
Provide quick energy & make up cell walls
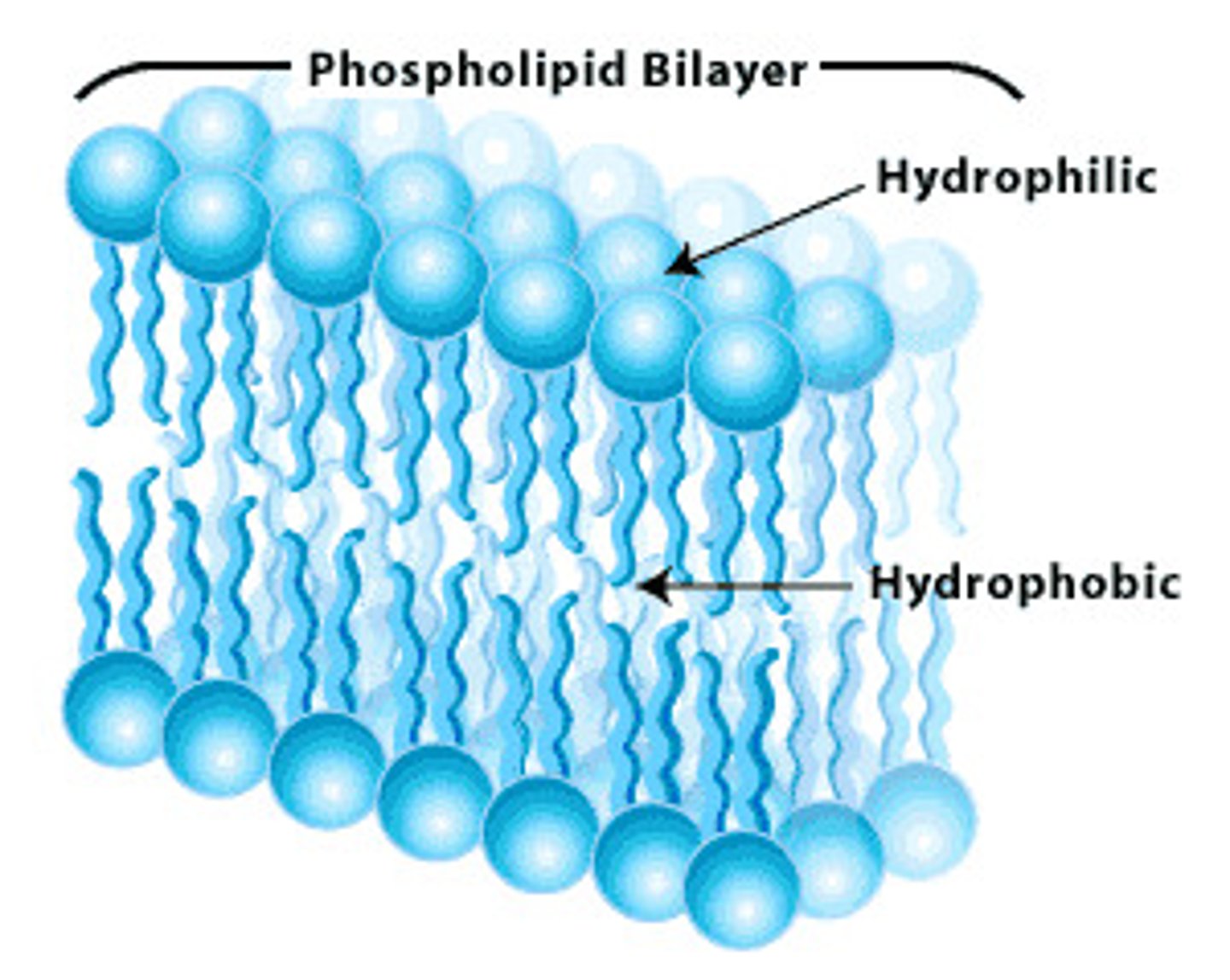
Lipids
Provide long-term energy & make up cell membranes
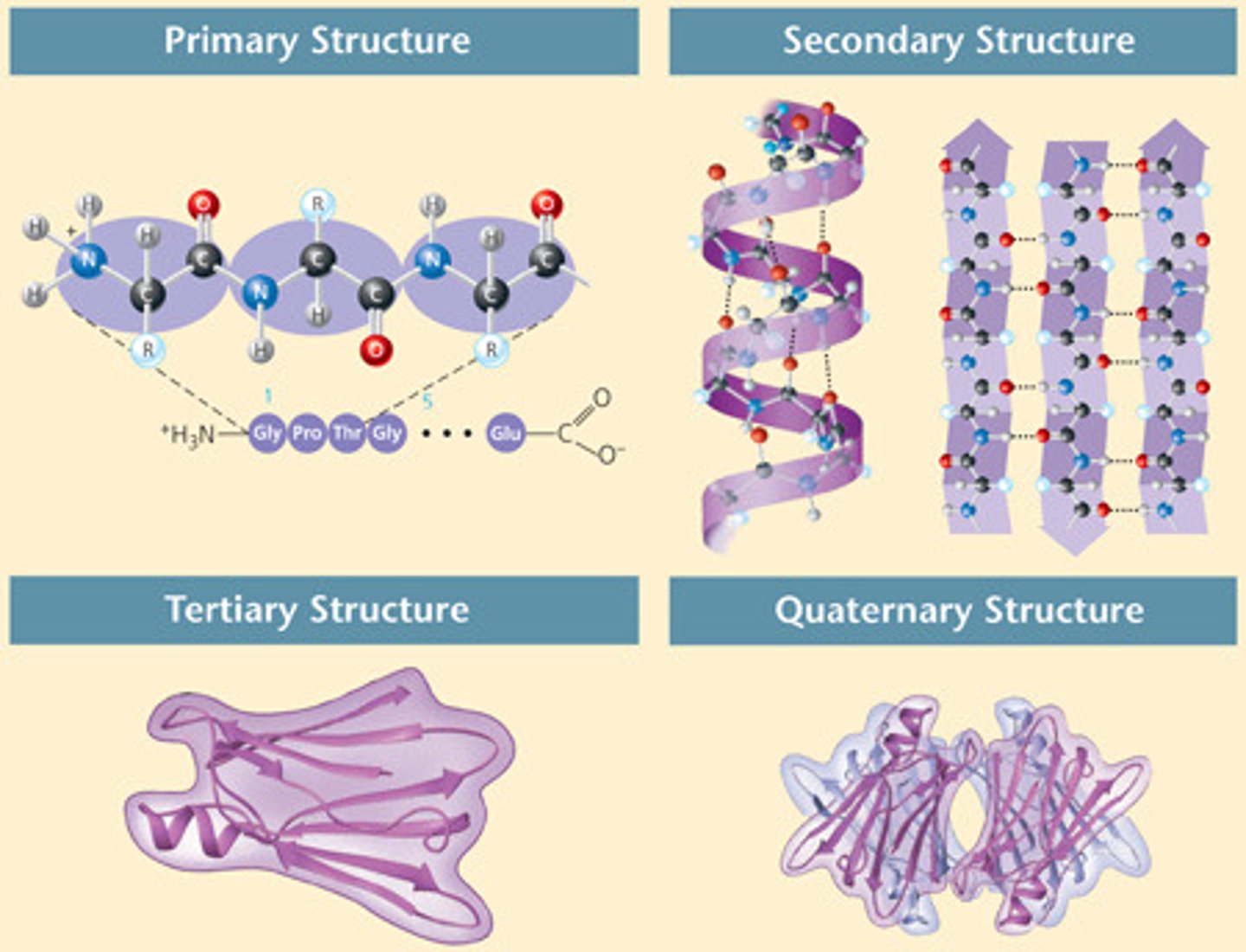
Proteins
Biomolecule that is the main structural component of life
DNA & RNA
Nucleic Acids. Work together to make new proteins.
Gradualism
Slow, gradual change in species over time
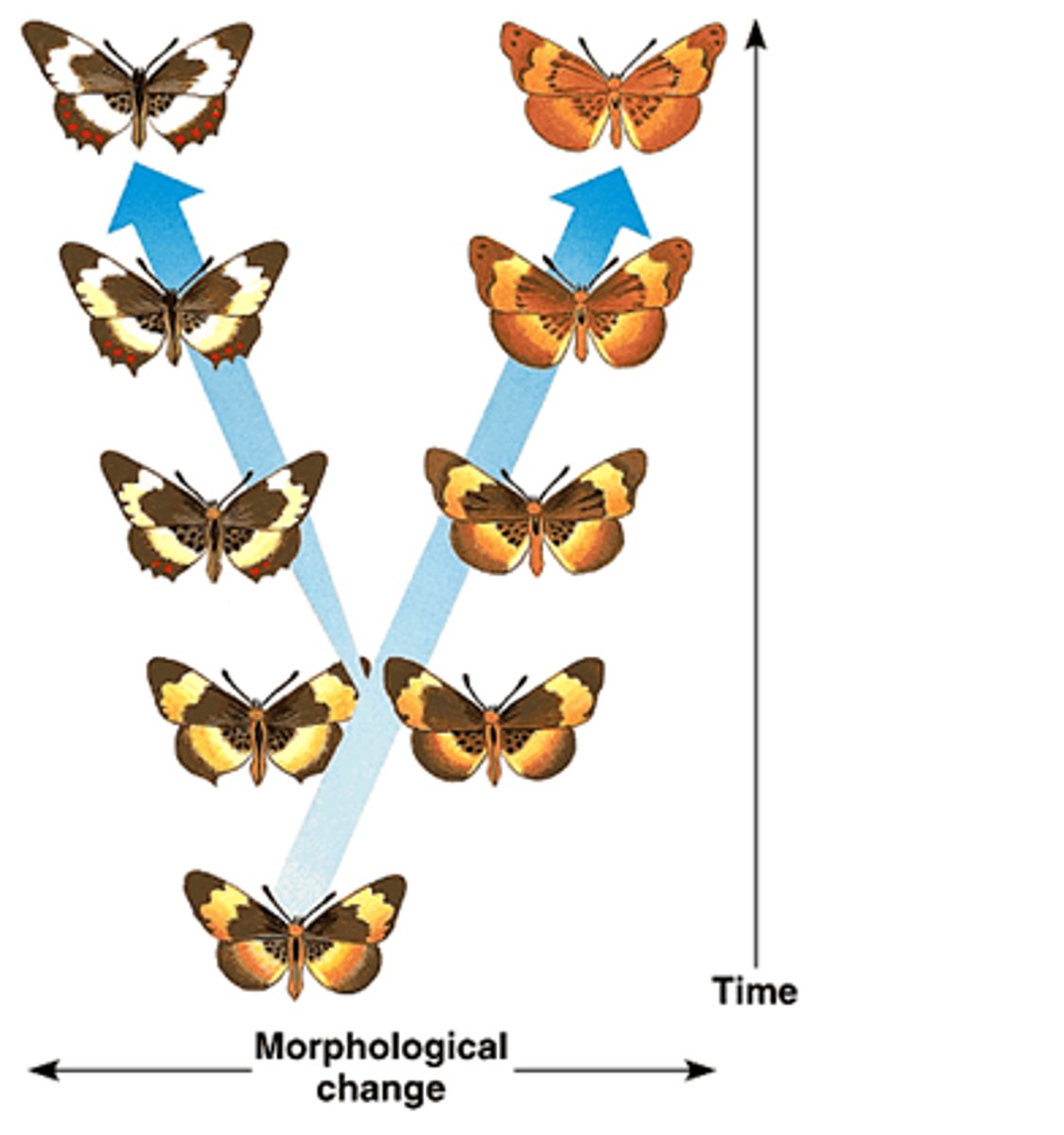
Punctuated Equilibrium
Fast, sudden changes in species. Usually due to a disaster.

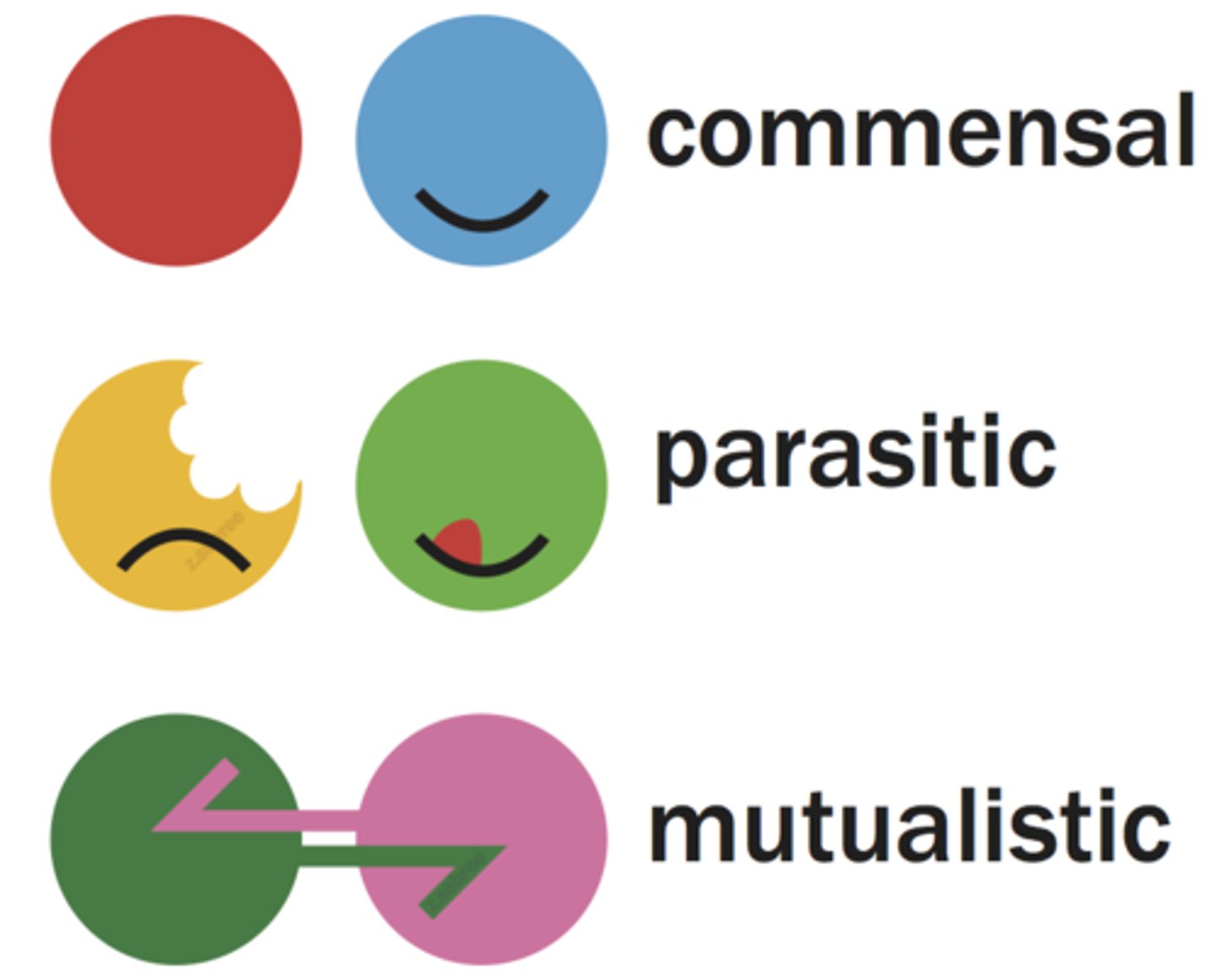
Mutualism
symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit (happy/happy)
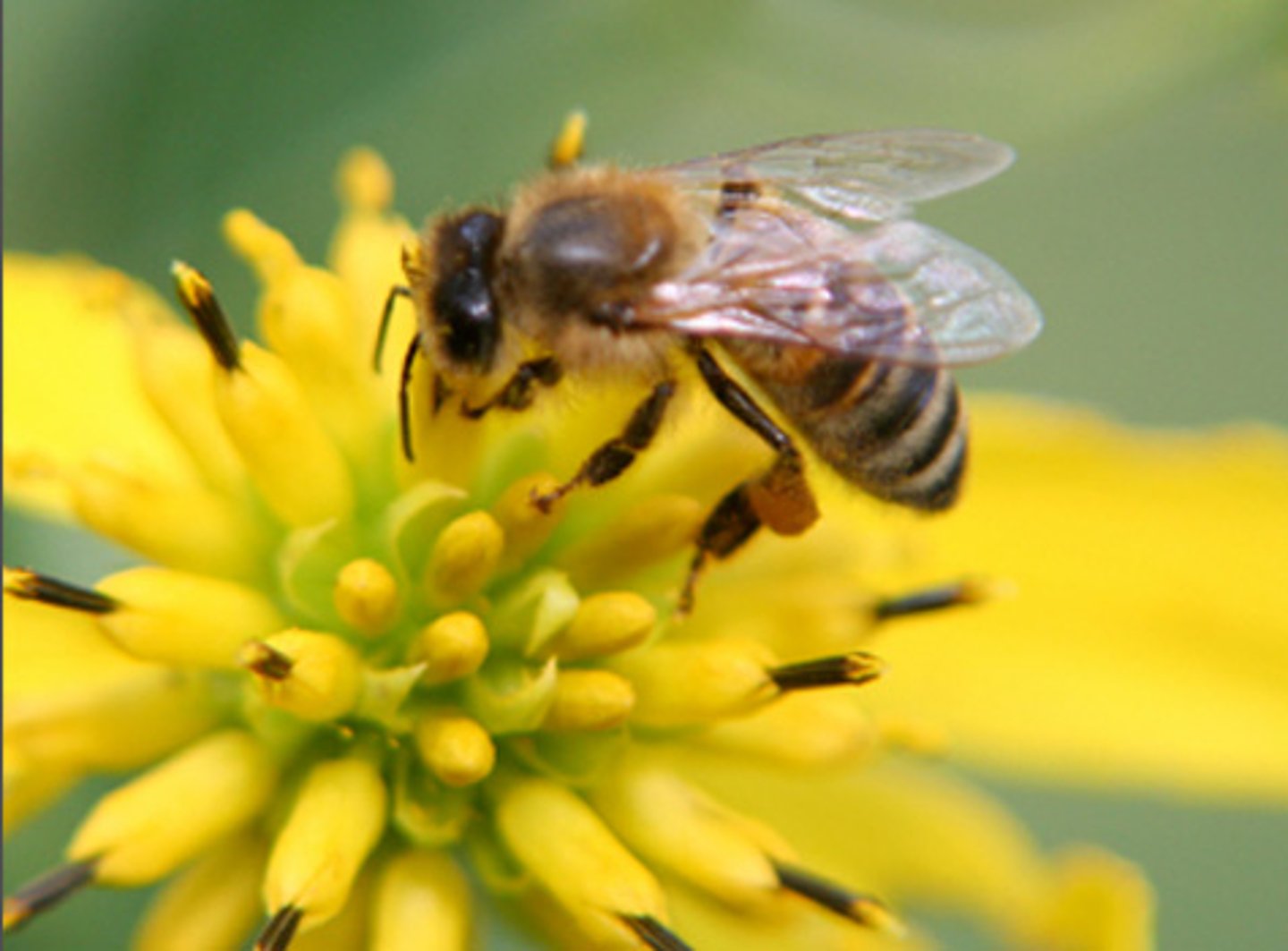

Parasitism
symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits while harming the other (happy/sad)
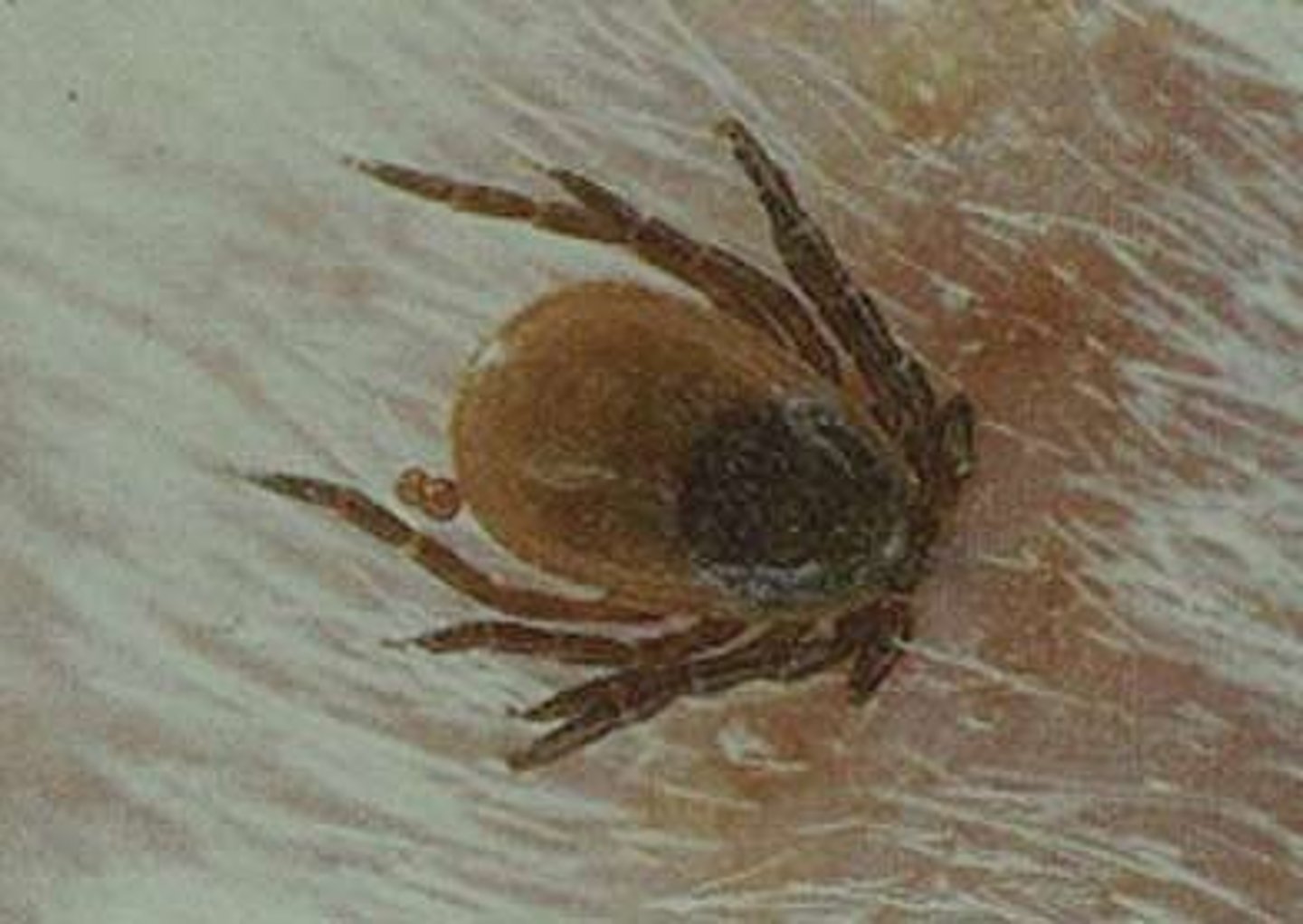

Commensalism
symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits while the other is unaffected (happy/neutral)
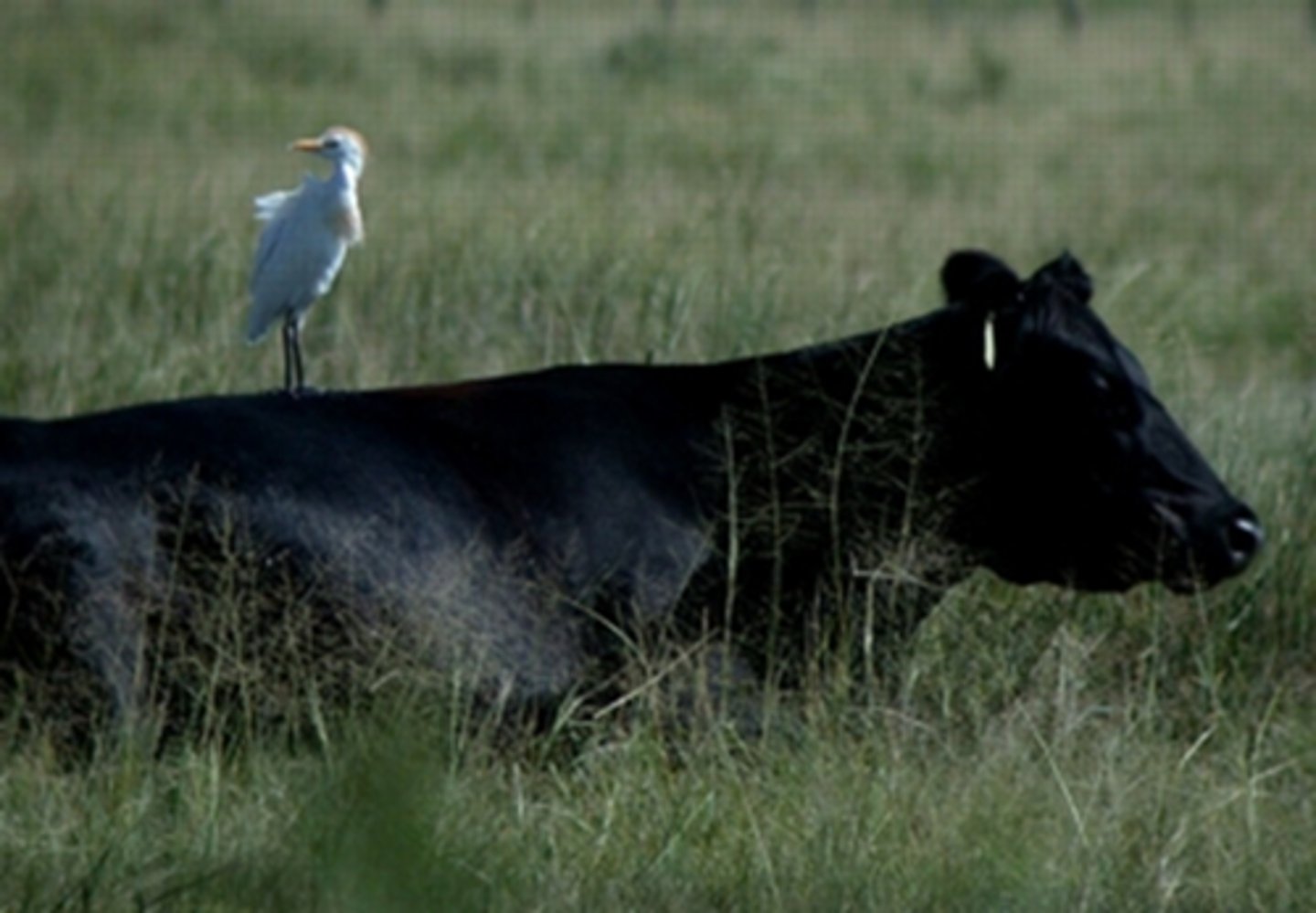

Interphase
G1, S & G2 stages of cell cycle combined.
Cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm to form two separate daughter cells
Prophase
Stage of Mitosis where nucleus disappears & spindles appear
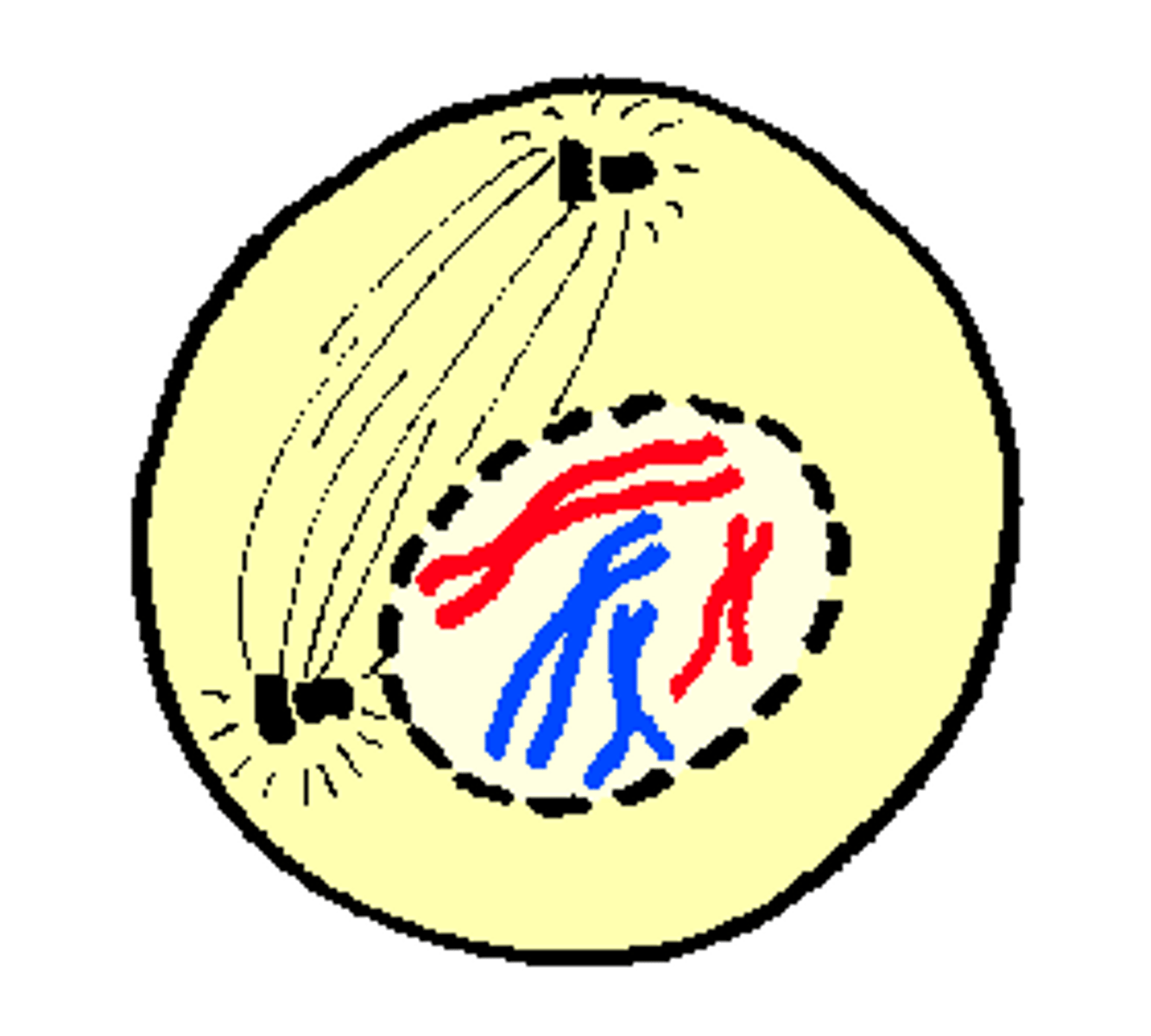
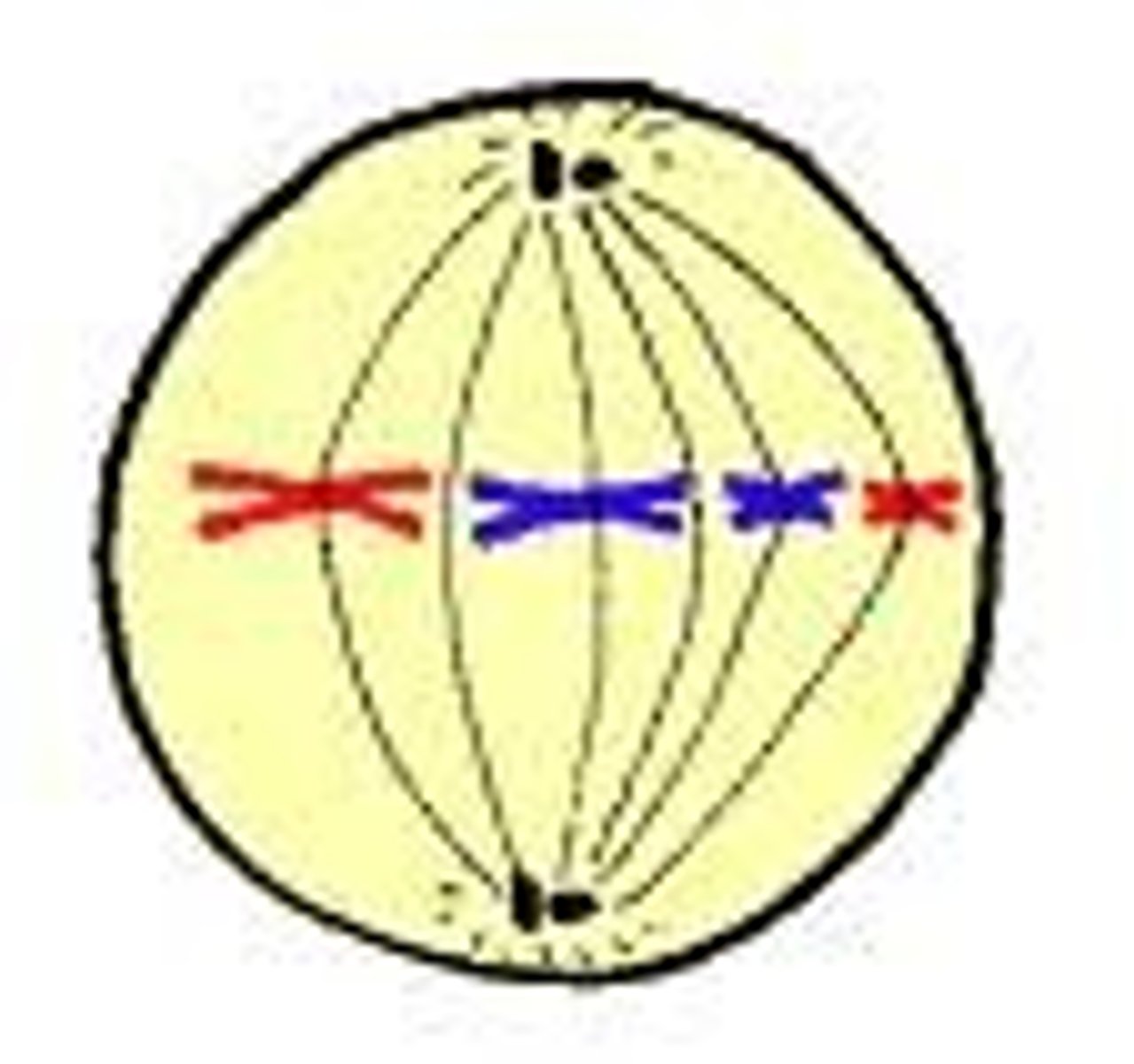
Metaphase
Stage of Mitosis where chromosomes line up in middle of cell
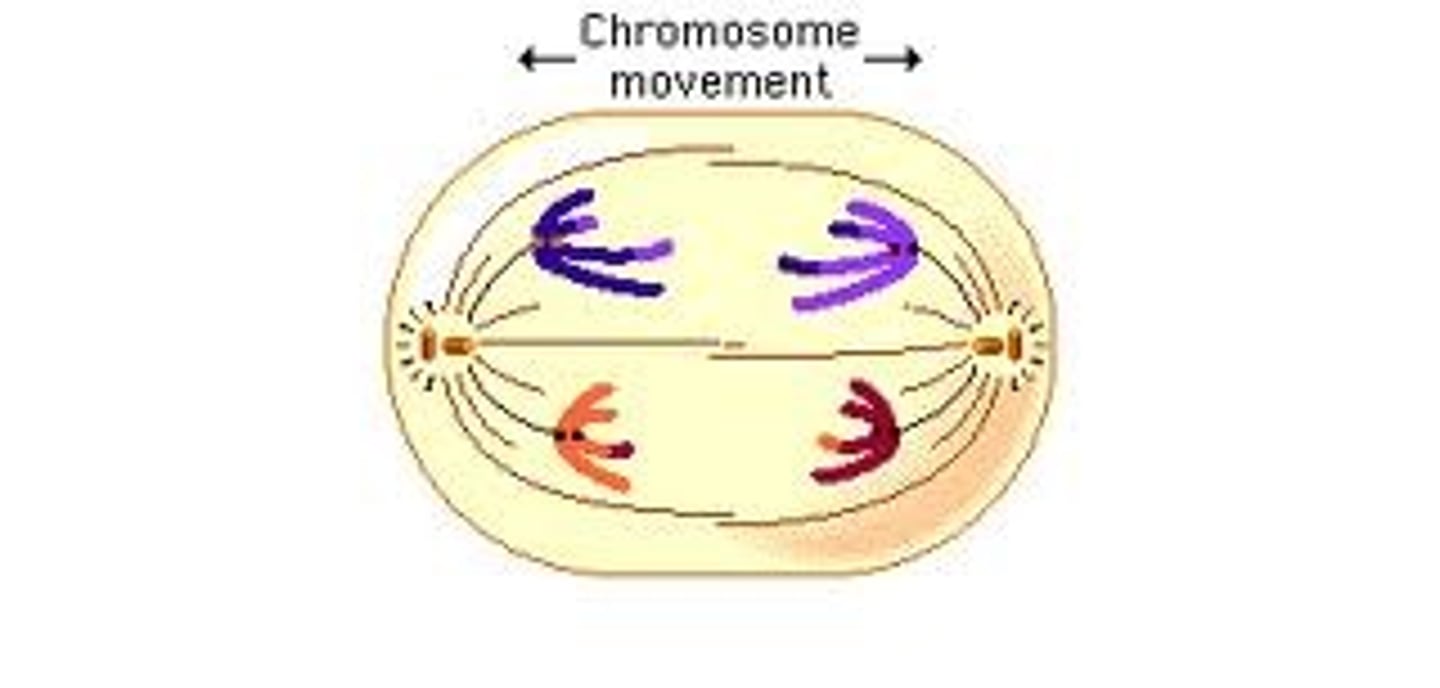
Anaphase
Stage of Mitosis where chromosomes are pulled away to opposite ends of the cell
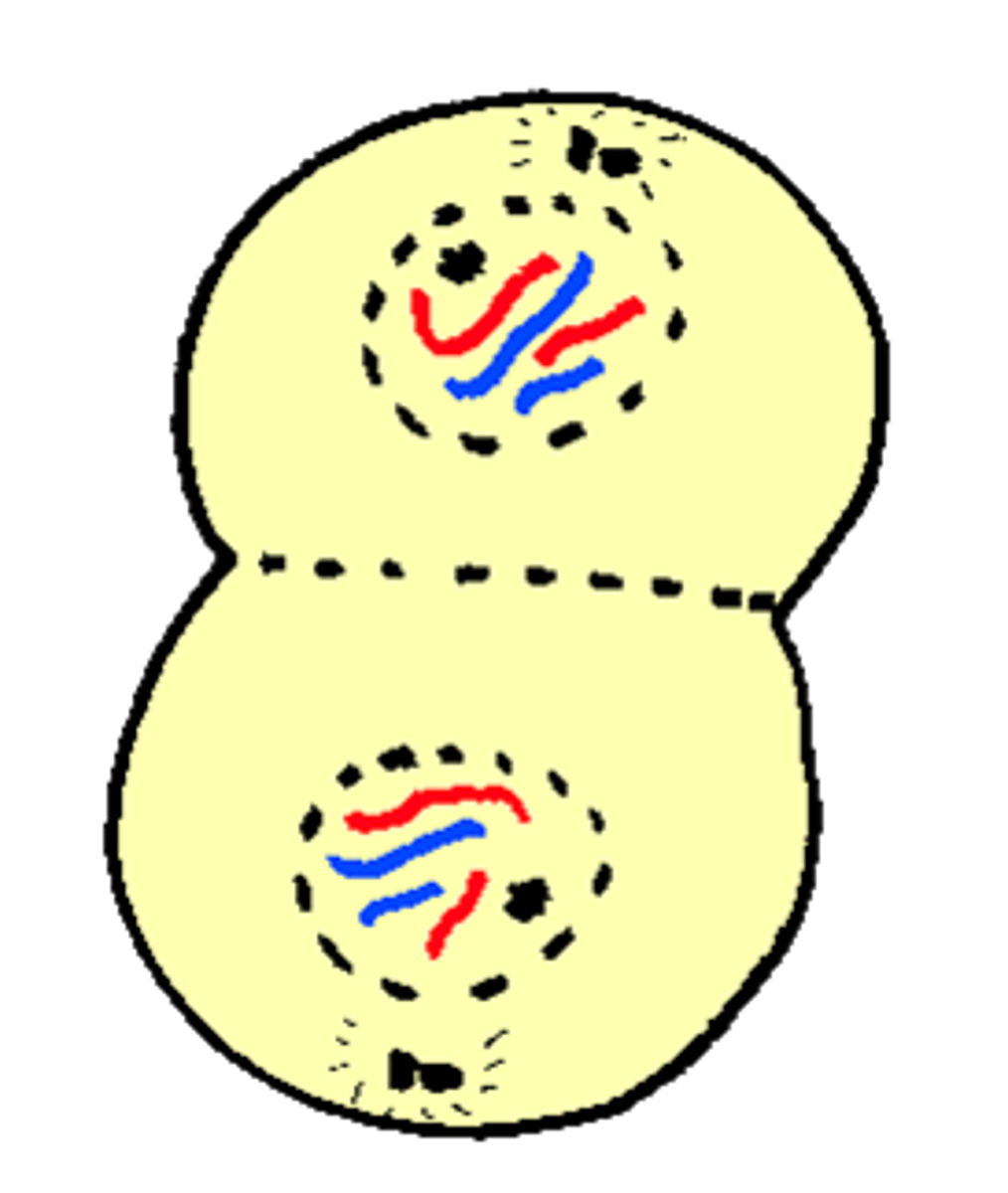
Telophase
Stage of Mitosis where two new nuclei form around each set of chromosomes
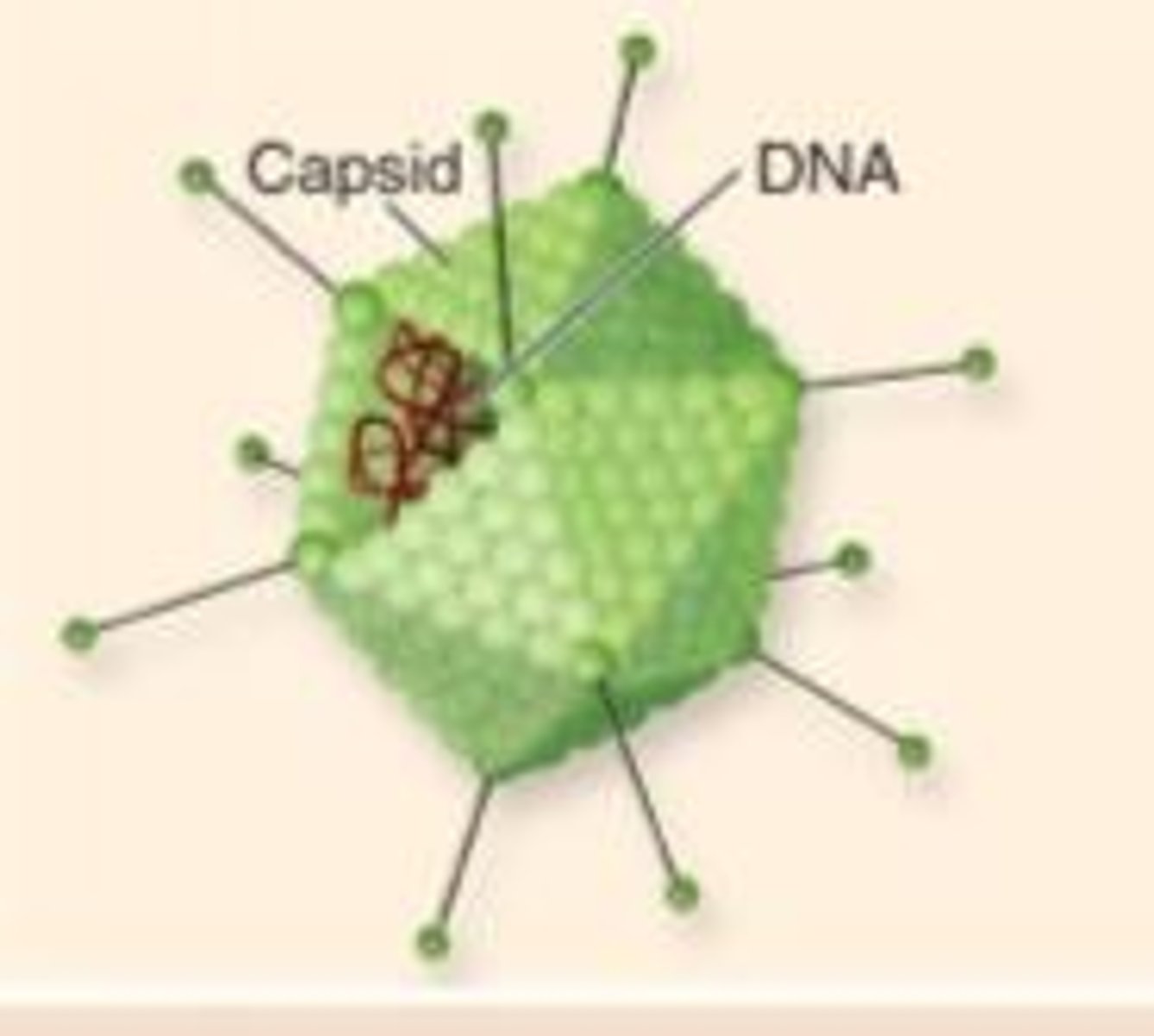
Capsid
Protein coat surrounding viruses
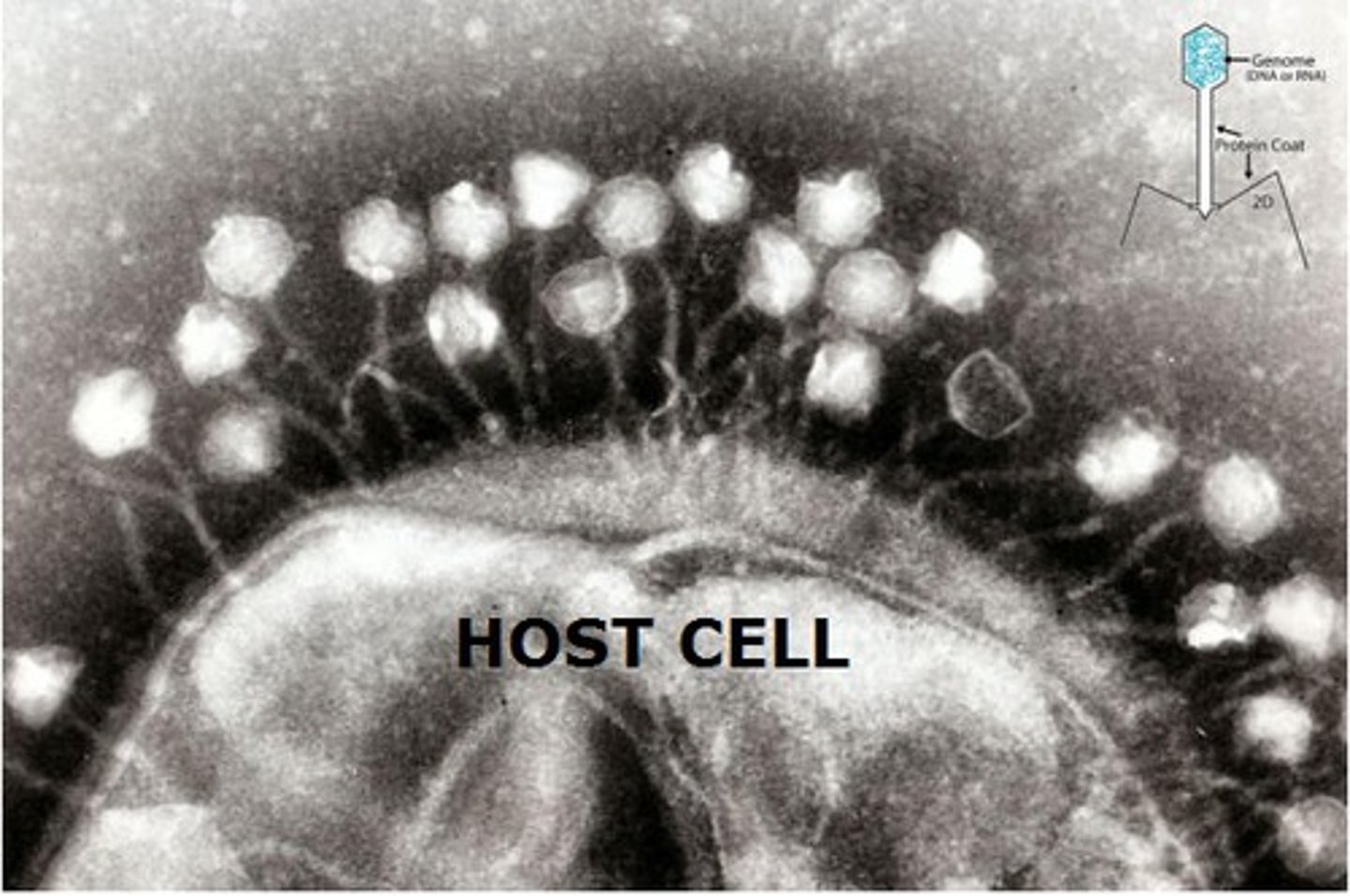
Host cell
What viruses must have to reproduce
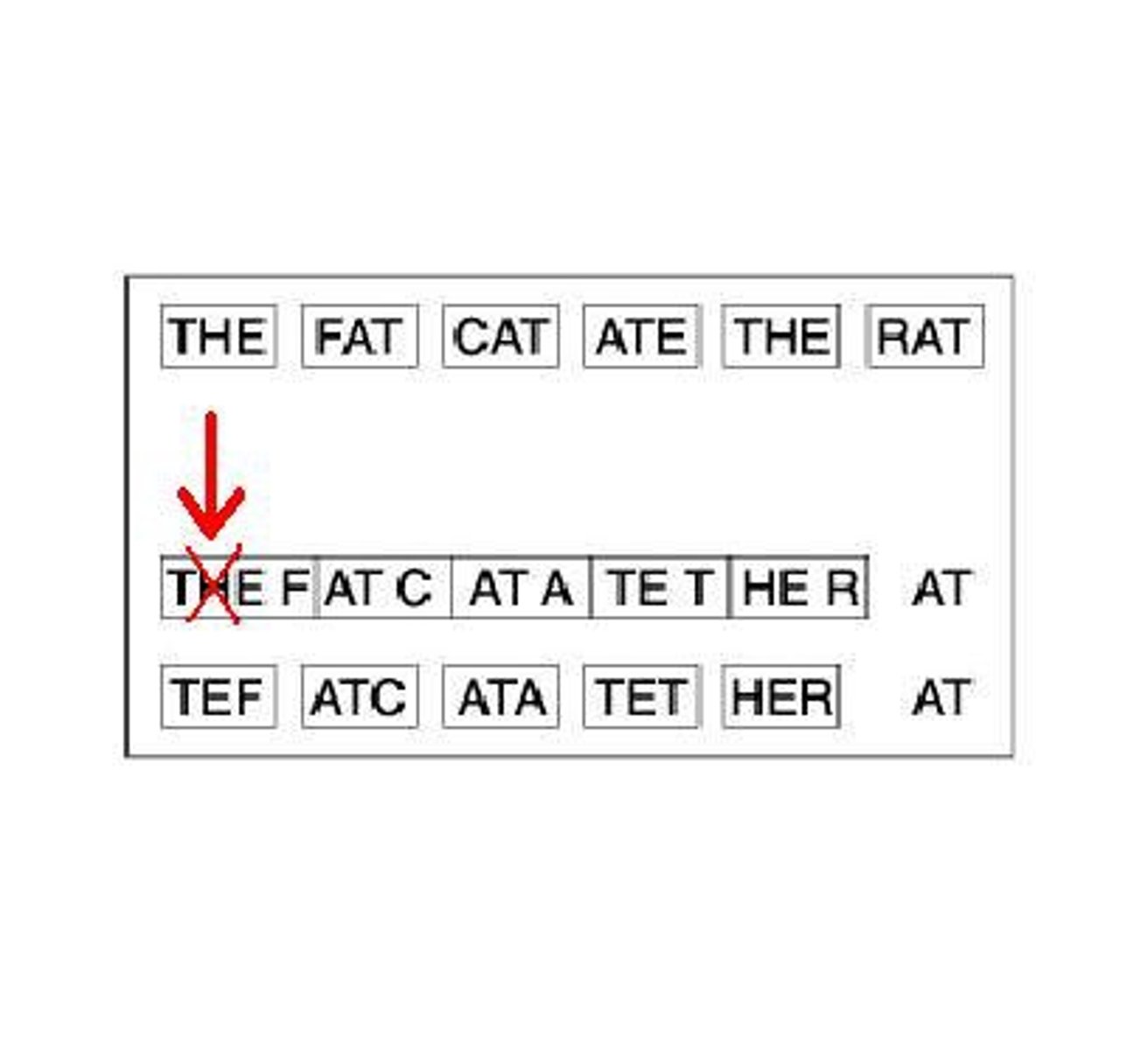
Point Mutation
Substitution mutation, changes only one codon & one amino acid in protein.

Frameshift Mutation
Insertion or deletion mutation, changes many codons & many amino acids in protein.
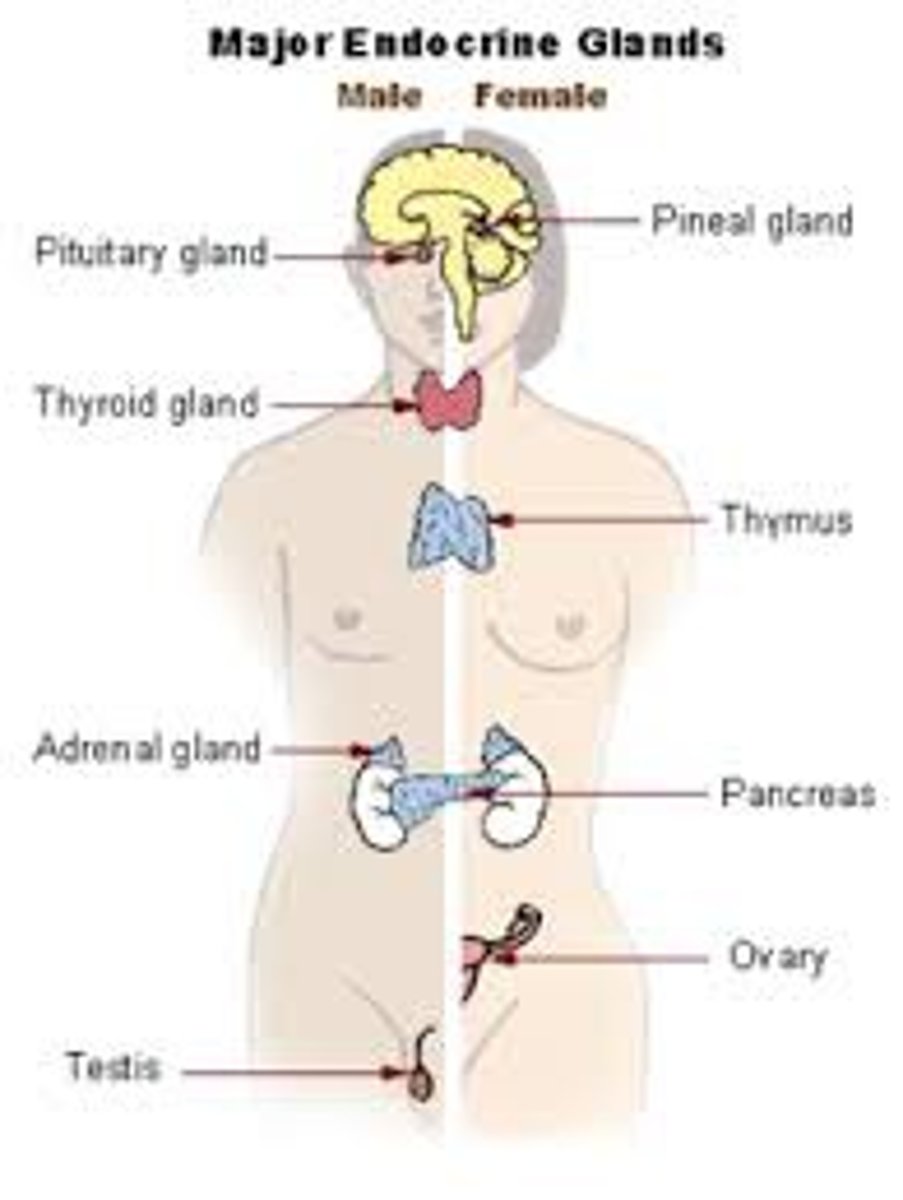
Endocrine System
Animal system containing glands & hormones
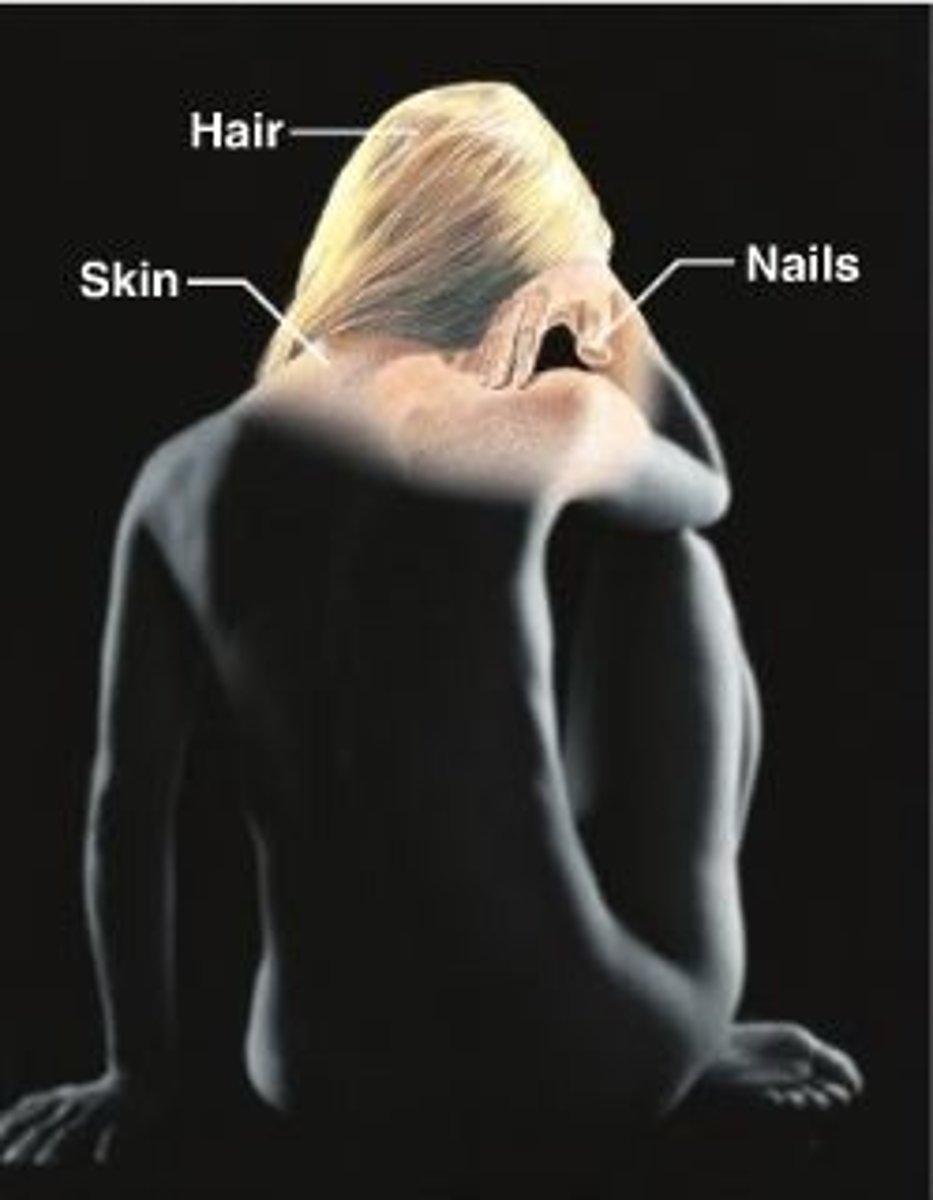
Integumentary System
Animal system containing hair, skin & nails
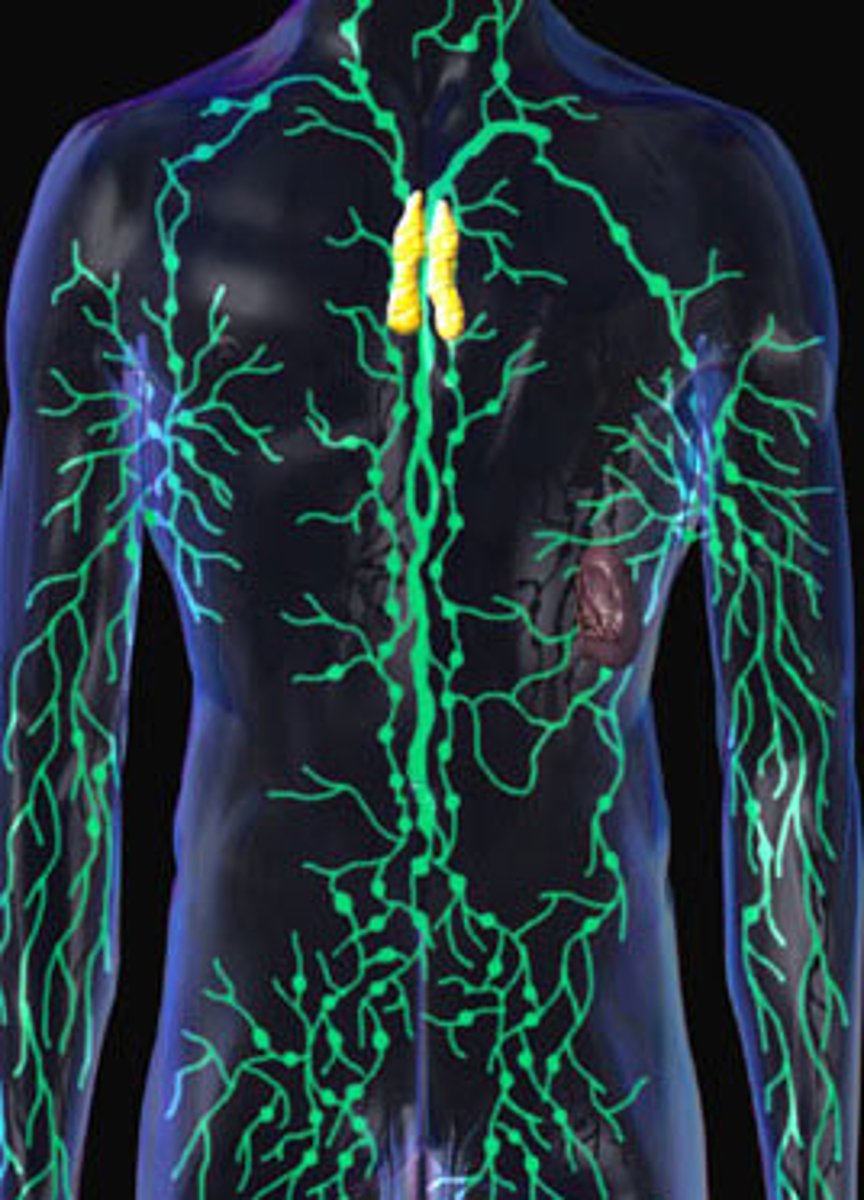
Lymphatic System
Animal System, essentially the same as the immune system, protects you from pathogens
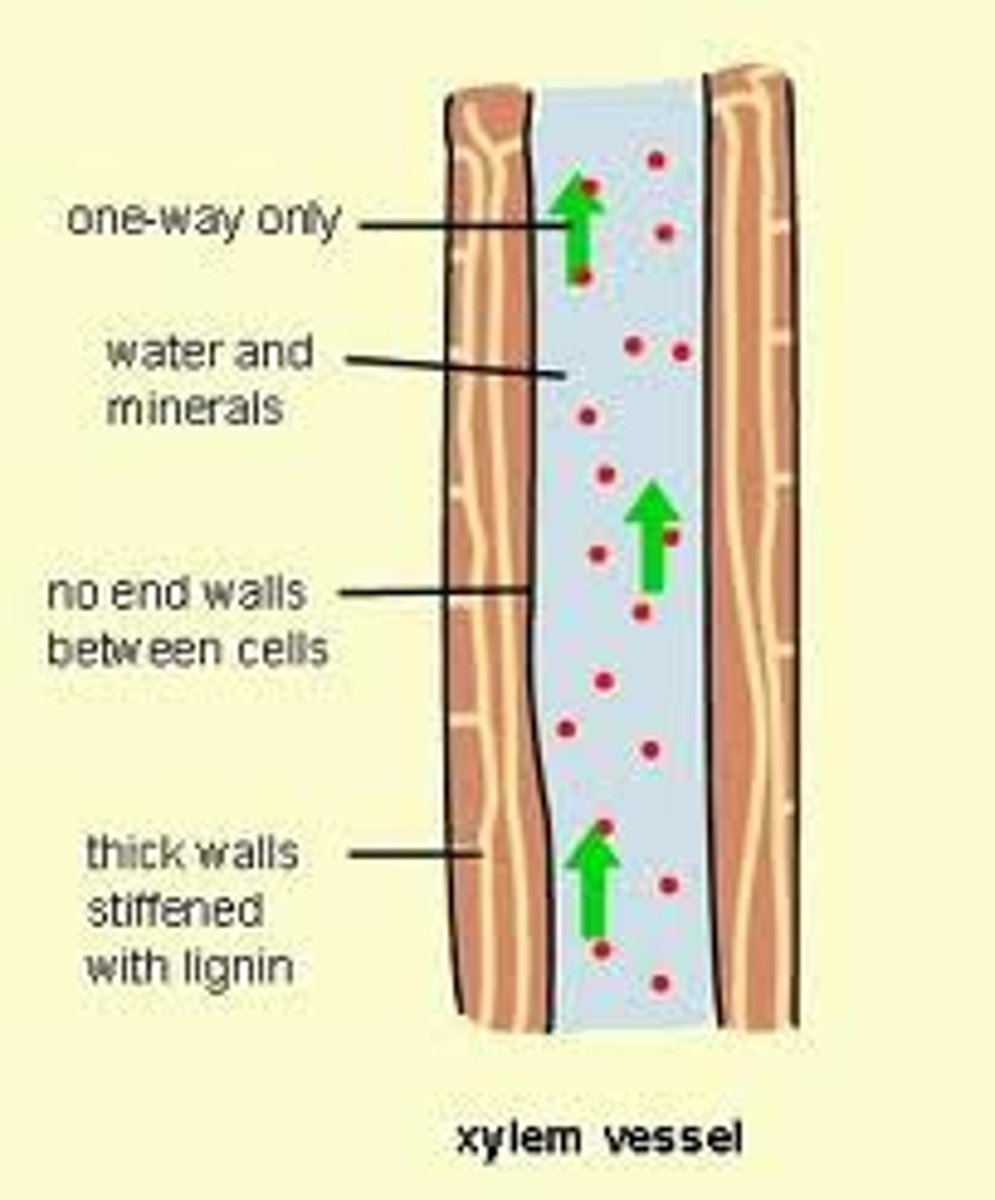
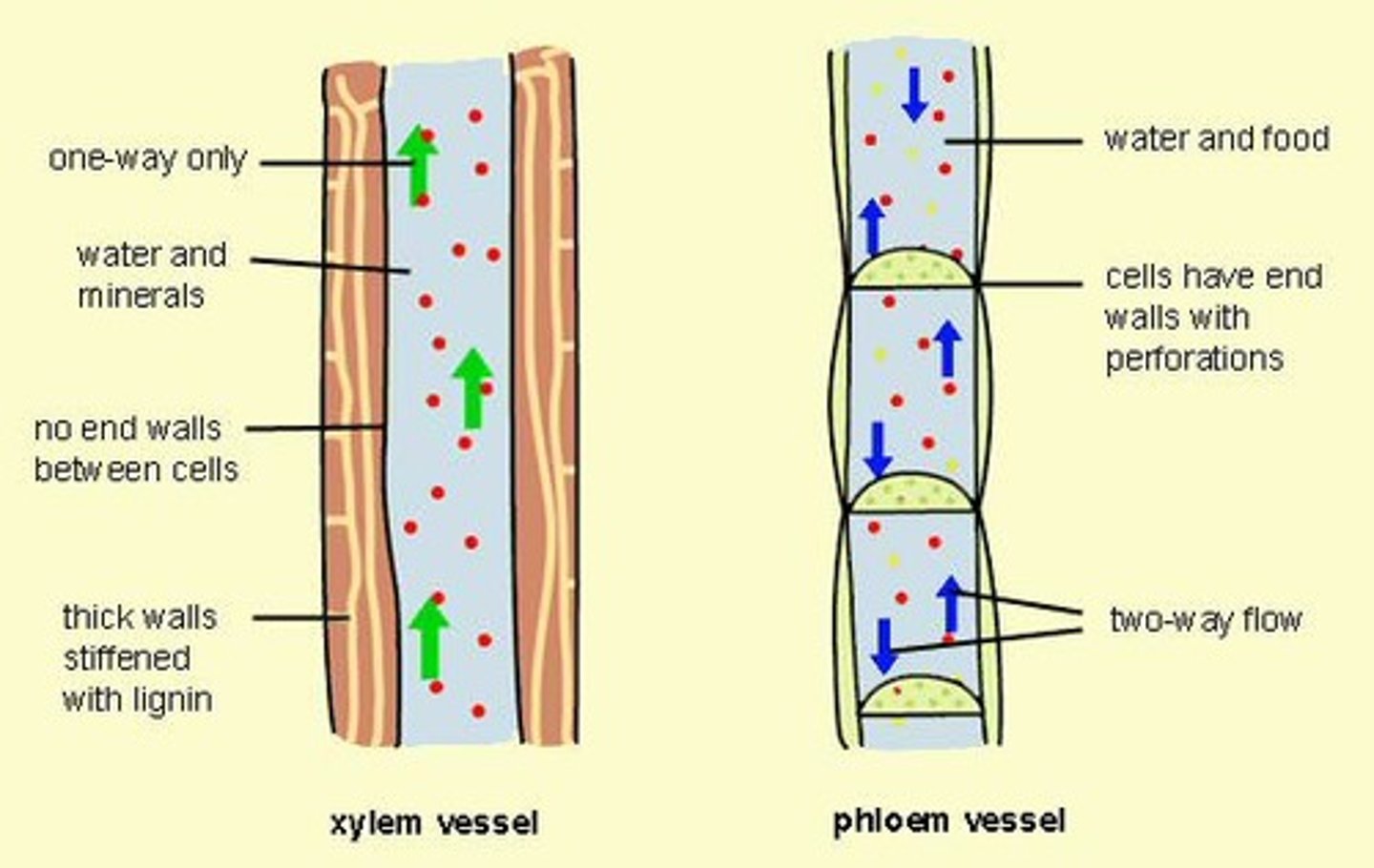
Xylem
Vascular tissue in plants that carry water up from the roots.
Phloem
Vascular tissue in plants that transports food (glucose) throughout the plant.
Pistil
Female reproductive organ of plants. Consists of Stigma, Style & Ovary.
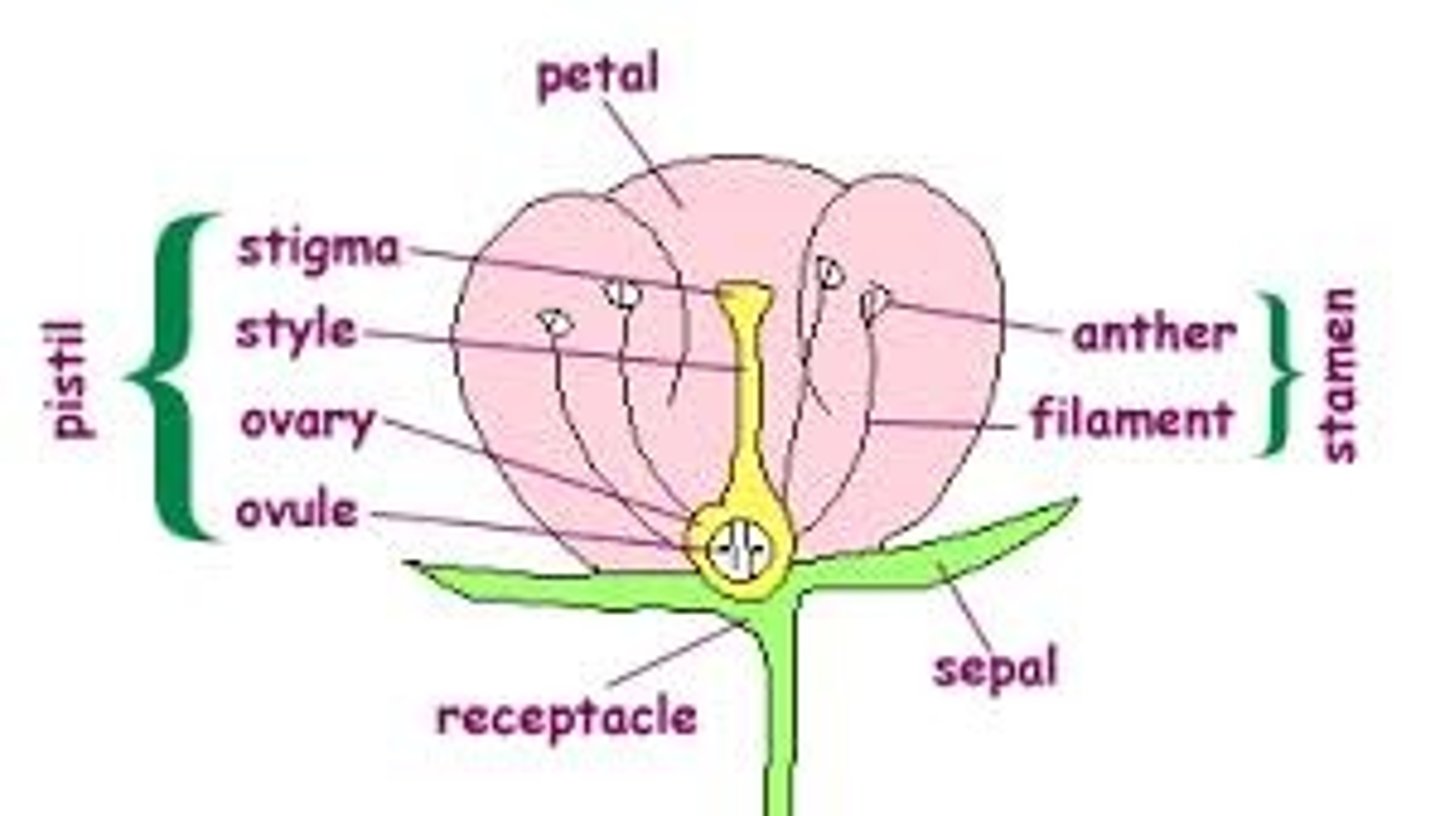
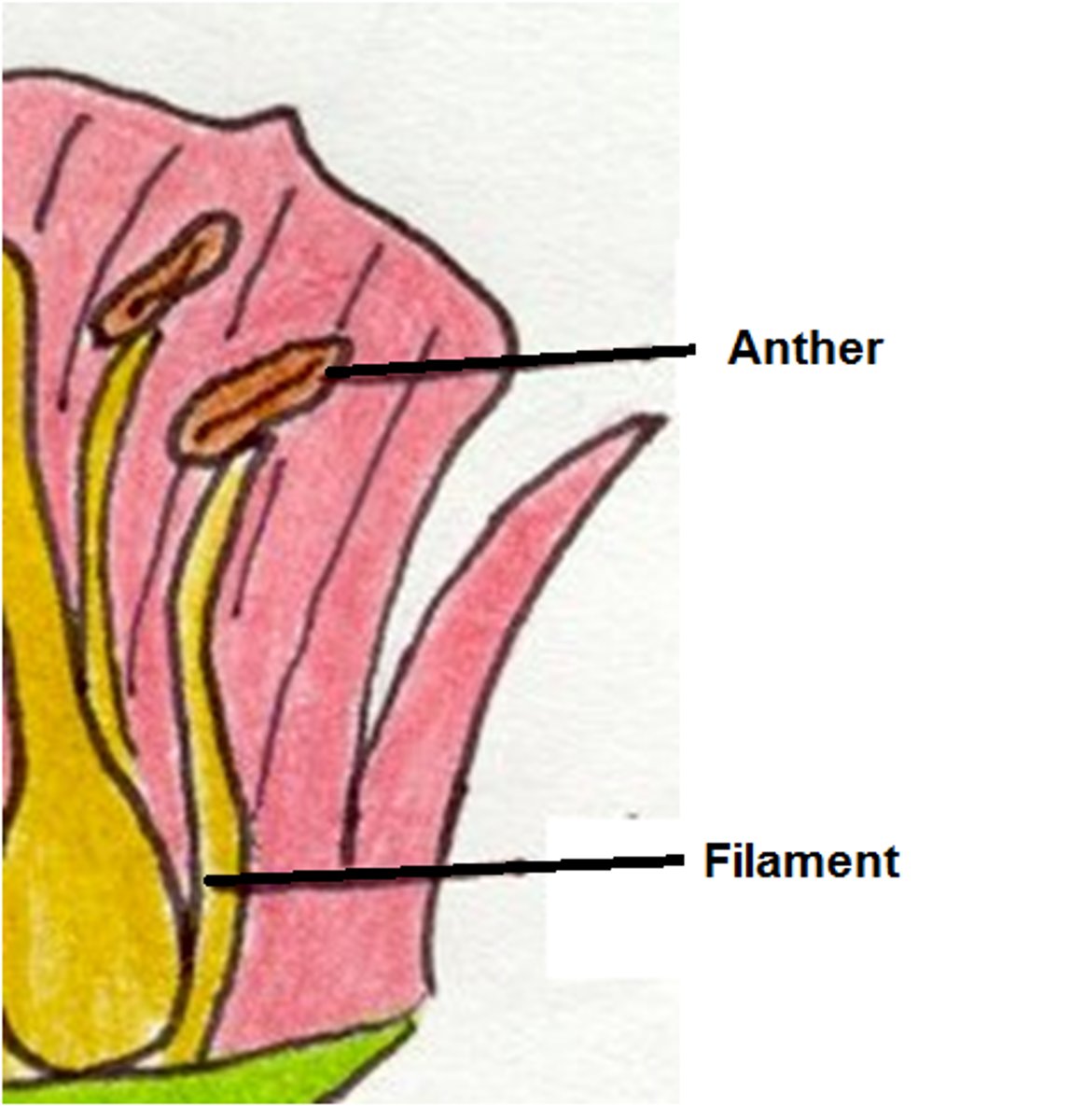
Stamen
Male reproductive organ of plants. Consists of Anther & Filament.
Stigma
Sticky tip of Pistil to catch pollen.