Lecture 31 - Climate of the Earth
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ASTR 1210 (Exam 3)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What Factors Can Cause Long-term Climate Change?
Energy in = energy out
When those two things find equilibrium on a planet, that leads to getting the temp of a planet
Sun creates all the energy in the solar system = affects equilibrium temp
Can take a planet and push it closer to the sun = equilibrium temp goes up because energy goes up and vice versa
Can make my star hotter = increase energy even if planet is same distance
What is happening to the Sun
Stars get hotter and hotter as years go on
Solar Brightening
Rate at which sun is fusing at = as it runs out of hydrogen, it has to fuse hydrogen faster
Sun very gradually grows brighter with time, increasing the amount of sunlight warming the planets
In Goldilocks Zone to allow liquid water exist on the Earth
Mars will be pushed into the Goldilocks Zone
Temperature vs Solar Activity
Sunlight is decreasing and relatively stable
Sun is getting colder, Earth is getting hotter
Has to do with the gases around the planet’s atmosphere
Changes in Axis Tilt
Earth’s climate is affected by seasonal temperature changes
Has to do with the axial tilt of the Earth - tilt more extreme = seasons more extreme
Over many years, about 22 to 25 degrees - our tilt is stable because of the Moon
Moon acts as a gravitational sounding board that allows the tilt to stay the same
Mars has had more extreme tilts = more extreme climate change because it doesn’t have a big moon
Changes in Reflectivity
If planet more reflective - energy in going down
Less reflective - energy in is gonna increase
Can change energy of the planet
Changes in Greenhouse Gases
Cause the potential for significant temp change
Greenhouse gases are also vital for the Earth’s life to thrive
Evolution of the Earth’s Atmosphere
When Earth first formed, it was situated in gas and dust that was the solar nebula
Hydrogen and helium made up Earth’s early atmosphere
Earth eventually lost the H and He over time - has to do with Earth’s gravity - can’t hold on to H and He
If planet was bigger, it could retain H and He - gas giants retained it
Ammonia and methane went away and atmosphere dominated by nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and water
Sources of Gas
Impacts — impacts vaporize rock
Outgassing — volcanos can significantly change the amount of gas in our atmosphere
Vaporization — ice or liquid vaporizes
Losses of Gas
Reversible loss
Condensation
Chemical reactions with the surface
Rust removes oxygen from the atmosphere
Permanent loss — losing gas to space
Thermal escape due to planet’s temperature
Escape via the Solar World - particles from Sun smack into planet’s atmosphere and the energy can cause particles to escape the planet’s atmosphere
Thermal Escape from an Atmosphere
Average speed or thermal velocity of particles move at tells you the temperature
Some of those particles travel faster/ some will travel slower
Some will be traveling GREATER than escape velocity - velocity of an object so that it escapes a planet
Thermal Velocity Equation
Particles that have less mass will be moving much faster than the other particle to reach escape velocity

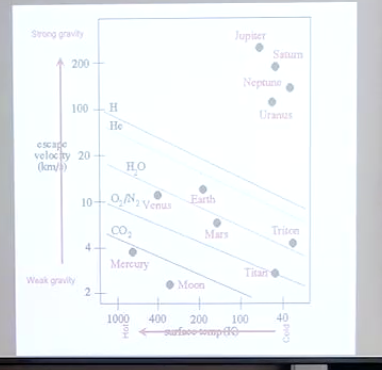
Escape Velocity from Solar System Planets
Low-mass particles will move fastest at any given speed
Further from sun - colder you’re going to be
Gravity affects escape velocity
Exospheres of the Moon and Mercury
Very, very thin atmosphere
Dominated by things smacking into these objects, vaporizing them…
What is Mars like Today?
Thin atmosphere but it has some stuff
Impacts of weather on Mars - seasonally has dust storms
Dust in the Martian atmosphere that’s been blown around as a result of windstorms that has blurred features
Seasonal Ice Caps of Mars
Polar ice cap biggest during winter, smallest during summer - made up of carbon dioxide (dry ice)
Going to increase/decrease CO2 seasonally on Mars
How Has Mars’s Climate Differed in the Past?
Likely had water on the surface
Changing Axis Tilt
layers of ice and rock that Mars goes through freezing and non-freezing periods - these layers were explained by axial tilt from Mars (0 to 60 degrees)
Could’ve cause Mars to lose atmosphere
Why the Climate Change?
Loss of atmospheric gas
Loss of water
Size is a critical factor in the timescale for climate change on a planet
Climate Change on Mars
Magnetic field may have perserved early Martian atmosphere
Solar winds stripped atmosphere after field decreased because of interior cooling
What is Venus like today?
Much thicker than the Earth
Dominated by CO2
90 times thicker atmosphere than Earth
Venus has a very slow rotation. How would the Coriolis effect on Venus compare to the Earth?
Slow rotation —> most spherical planets in the solar system
Coriolis is a byproduct of the speed at which an object is spinning - Venus would have a much weaker Coriolis effect
Probably no hurricanes
No strong weather features
Atmosphere of Venus
Venus has thick CO2 atm with a surface pressure 90 times that of Earth
Little weather - little wind - slate like rocks, no wind erosion
Greenhouse Effect on Venus
Thick CO2 produces strong greenhouse effect
Earth escapes this because most of its carbon and water is in rocks and oceans
Runaway Greenhouse Effect
Venus is super hot because of the runaway greenhouse effect
Result of the fact that gases in Venus are transparent to visible, opaque to infrared
Earth escaped this fate because we have water - water causes rain, taking away CO2 from the atmosphere
What is the main reason why Venus is hotter than Earth?
Because of the greenhouse effect
How Did Earth’s Atmosphere become different?
Water on the surface - Venus is too close to the Sun
Carbon cycle - because Earth is geologically active and because of water
Carbon Dioxide Cycle
Atm CO2 dissolves in rainwater
Rain erodes minerals that flow into ocean - CO2 in minerals
Minerals combine with carbon to make rocks on ocean floor
Subduction carries carbonate rock down into mantle
Rock melts in mantle and CO2 is outgassed back into atmosphere through volcanoes
Earth’s Thermostat
Cooling allows CO2 to build up in atmosphere
Heating causes rain to reduce CO2 in atmosphere