Human Bio Chapter 9- DNA
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
What is DNA? And where is it found?
DNA short for deoxyribosenucleic acid
Contains the genetic information that determines the structure of the cells and why it functions
MOLECULE
Most found in nucleus (nuclear DNA), small amount found in mitochondria (mtDNA)
What is the structure of DNA and Nucleotides?
Molecule made up of small repeating units called nucleotides
Each Nucleotide is composed of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose in DNA, ribose in RNA), a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine/uracil in RNA, cytosine, guanine)
How does DNA twist into a double helix?
suagr molecule of one nucleotide bonds to the phosphate group of another one
Forms a long chain of alternating sugars and phosphates with side chains of bases
Two strands join together by specific bases being attracted to one another by weak hydrogen bonds
(A→ T double bond) (G → C triple bond)
What side is the 5’ and 3’? And, which side is the template and new strand?
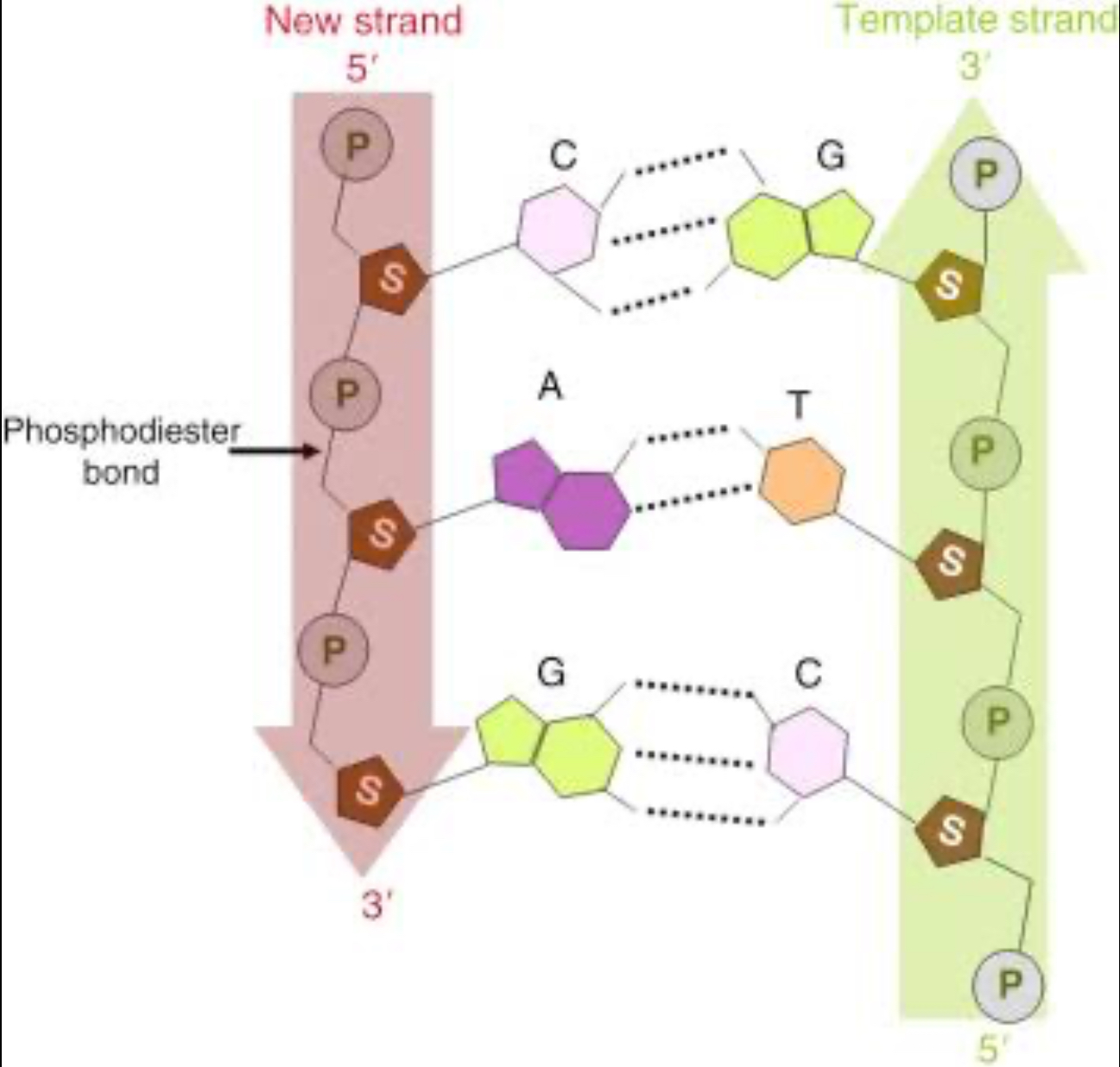
What side of the DNA is the leading and lagging strand?
Leading = start from the top
Lagging = starting from the “bottom” up
What does the order of the bases determine?
order in which the nitrogenous bases occur in the DNA molecule determines the genetic code.
Each gene consists of up to 2 million pairs of bases therefore number of possible combinations of base pairs is enormous
What is the structure of a chromosome? (Hint: nucleosomes → chromatin →chromatid → chromosome)
DNA strands wrapped around his tones to form NUCELOSOMES
In a cell that is NOT dividing, the coiled DNA forms a tangled network called CHROMATIN
If a cell is undergoing mitosis or meiosis the chromatin may condense and turn into a CHROMATID
Two chromatids make a CHROMOSOME
Chromatins can become chromosomes as well
What is a gene?
a gene is a section of DNA that codes for a particular protein
Each chromosome is made up of these sections/genes
There are 46 chromosomes in a normal human cell
What is the mitochondrial DNA?
Mitochondrial DNA is a circular molecule not bound to histones
Plays an important role in coding for tRNA and enzymes needed for cellular respiration
How does DNA replication work? step 1
1- two strands of DNA is separated by enzyme HELICASE “unzips”
→ this is possible because the hydrogen bonds between the bases are weak
→ each strand has half the original information
→ each strand serves as a template for the nucleotides that will form the new strand
How does DNA replication work? Step 2
2- Because each base can only pair with their complementary base, the new strand formed is identical to the original.
DNA polymerase adds new nucleotides to the new strand
DNA ligase joins short sections of DNA together
What does the genetic code in DNA provide instructions for?
Protein Synthesis
What are proteins produced from?
Amino acids being joined tgt by peptide bonds
What is RNA?
Ribonucleic acid
Composed of a chain of nucleotides
What is the difference between RNA and DNA?
RNA
sugar molecule is ribose (one more oxygen atom than deoxyribose)
Single stranded
Uracil instead of thymine
RNA strand folds onto itself
DNA
sugar molecule os deoxyribese
Double stranded
Thymine not uracil
What is mRNA?
Messenger RNA
Made in the nucleus and takes geneti code into the cytoplasm, allowing the genetic code to be ‘read’ by ribosomes
What is rRNA?
Ribosomal RNA
Makes up ~60% of ribosome’s mass (other 40% protein)
Ensures the correct alignment of mRNA, tRNA, and ribosome
Has enzymatic roles in formation of peptide bonds between amino acids
What is tRNA?
Transfer RNA
Small molecule of RNA (Only 70-90 nucleotides)
Each tRNA molecule is able to carry a specific amino acid and therefore plays a vital roles in protein synthesis
How are proteins made?
Protein synthesis
Through Transcription and Translation
Sequence of bases determine the protein that is produced
What is transcription?
Process by which the genetic instructions are copied (or transcribed) from the DNA to the mrNA molecule
Triggered by chemical messengers that enter the nucleus from the cytosol and bid to the DNA
What is the first step to Transcription?
Occurs in the nucleus
Helicase “unzips”/ makes the double-stranded DNA molecule come apart by breaking the weak hydrogen bonds between the bases
What is the 2nd stage of Transcription?
RNA polymerase transcribes the bases on one strand of the DNA to make complementary molecules of mRNA
* thymine is replaced by uracil when adenine shows up *
Strand that is copied = template strand
Other strand = coding strand
What is the third stage of trancription?
A sequence of bases tells RNA polymerase to stop copying
mRNA molecule is released and leaves the nucleus through the pores to the site of protein production (cytosol)
What is translation?
Production of a protein using the information that is coded in the mRNA molecule
What is the first stage of translation?
Occurs in the cytoplasm
Ribosome attaches to one end of the mRNA molecule at the start codon, AUG
This is to ensure the ribosomes attach to the correct end of the mRNA
What is the second stage of translation?
Ribosome moves along the mRNA 3 bases at a time (or 1 codon)
Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid (AUG = methionine)
Therefore every protein beings with methionine, but it can be removed later
What is the third stage of Translation
As the ribosome reads the codons on the mRNA, tRNA molecules join the mRNA with complementary bases. Each bond formed between the amino acids require energy from the breakdown of 1 ATP molecule
Sequence of 3 bases matching the mRNA codon is called an anticodon
Amino acids joined in the correct sequence so the protein is assembled correctly
What is the fourth stage of translation?
Once tRNA has delivered its amino acid, it detaches from the ribosome and can then pick up another amino acid from the cytosol
Creates a chain of amino acids that bind together to become a protein
What is gene expression?
process of copying information from DNA in to mRNA and the translating the message into a series of amino acids to from a protein
What do genes contain?
Instructions for making mRNA
Any given time a cell is making mRNA from only a fraction of its genes
Genes being used to make mRNA said to be “switched on”
Gene not being used = “switched off”
What are the factors that determine wether a gene is being expressed?
Age of the cell
Time of day
Signals from other cells
Environment of the cells
Wether the cel is dividing
What is lipid and carbohydrate synthesis?
There are no genes that carry instructions for the manufacture of lipids or carbohydrates
Synthesis of these substances require enzymes
Enzymes are proteins
DNA in genes carries the code for protein manufacture, therefore genes control synthesis of lipids and carbohydrates indirectly
What are epigenetics?
Factors that make genes more or less likely to be expressed that is inherited
EPI = on top of
Therefore epigenetics refer to changes in gene expression that result from mechanisms other than changes in the genes
Growing list of environmental factors that can cause epigenetic changes that are inherited by offspring
What is the genome?
Hereditary information that is encoded in a person’s DNA
What is the epigenome?
Sum of all the factors that determine: when, where, and which genes are expressed
What does the epigenome do?
Helps control which genes are active in a particular cell, and therefore which proteins are produced
If the epigenome is abnormal, certain cells may be abnormal and disease may result
One way genes are regulated epigenetic all is through changes in chromatin
What do epigenetic factors do?
Tell muscle cells to behave like muscles cells, nerve like nerve cells and so on
Tells each type of cell to behave the way they need to
What is chromatin?
DNA and the histone proteins associated with it
Gene expression may change if the way in which the DNA is wrapped around the histone changes
What happens of the amino acids that are in the histone proteins changes?
Changes the shape of the histone
This modified shape may be copied each time a new DNA molecule os formed
What does this modified histone do?
Ensures that a stem cell that differentiated into a specialised cell remains a specialised cells and doesn’t revert back into a stem cell *like a liver cell*
What is acetylation?
Another way of histone modification
Is the addition of an acetylene group to the histone protein
Reduces the attraction between histones and DNA, relaxing the structure of the chromatin
RROMOTES TRANSCRIPTION by allowing RNA polymerase access, therefore ENHANCES GENE EXPRESSION
What is methylation?
Addition of methyl group to the DNA molecule or histone protein
Occurs at sites on the DNA molecules where a cytosine nucleotide is adjacent to a guanine nucleotide (CpG sites)
INHIBITS gene expression by restricting access to RNA polymerase
Generally decreases transcription of genes, but it depends where the methyl groups attach and how many become attached
If chromatin relaxes, transcription increase
How does ones environment effect their epigenome?
Person’s epigenome can be changed by exposure to certain environmental stimuli
Some environmental agents include (but are not limited to) severe stress, nutritional factors and toxins or drugs that may enter the cell
How does the environmental factors affect?
Does not change DNA, but interferes with transcription and translation process involved in protein production
Epigenetic factors can influence any step in gene expression