Human Eye and the Colourful World
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
Explain the parts of the human eye
Parts of the Human Eye
- outer covering of the eye where most of the refraction takes place , it protects the eye from foreign particles.
Aqueous Humour - water like substance that maintains the pressure balance and moistens the eye.
Iris - controls the size of the pupil
Pupil - hole through which the light enters the eye. It regulates the amount of light entering the eye.
Ciliary Muscles - adjusts the focal length of the eye lens.
Crystalline Lens - a flexible , convex lens that converges the image onto the retina.
Retina - a photosensitive screen that have rods which detect the intensity of light and cones which detect the colour of light.
Vitreous Humour - jelly like substance that maintains the shape of the eye ball
Optic Nerve - carries signals to the brain
Define power of accomodation
The ability for the eye lens to adjust it's focal length to see both near and far away objects is known as power of accomodation.
Explain the difference in the eyes between the changes in the eye between viewing far away objects and nearby objects
Viewing Far Away Object
Light rays are almost parrallel.
Large focal length is enough to converge the rays to form image.
Large focal length means lower power , and can allow the lens to be relaxed or streched out making it thin.
Ciliary muslces expands
Viewing Nearby Object
Light rays from the object are diverging.
Lower focal length is needed to converge the rays to form image.
Lower focal length means higher power , and the lens needs to be contracted becoming thicker.
CIliary muscles contract
A healthy human eye can see from infinity to 25 cm.
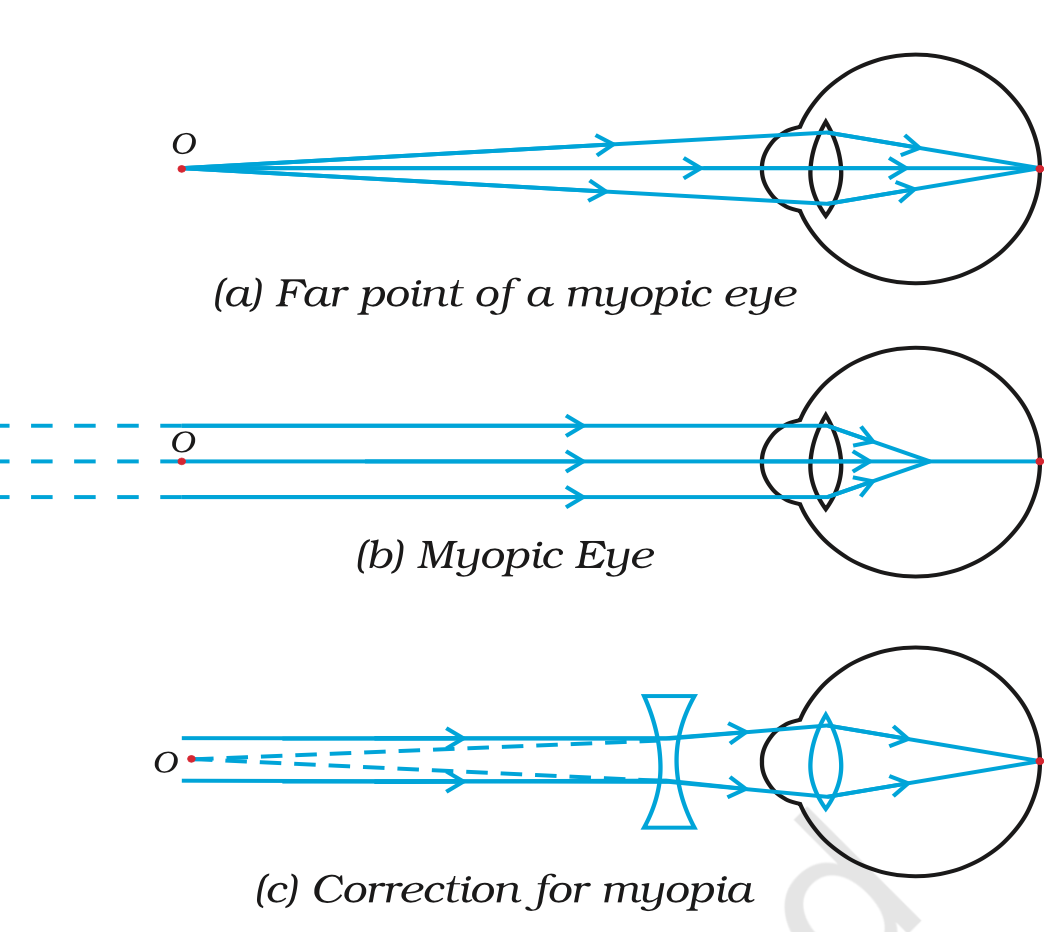
Write a short note on Myopia
Also known as short sightedness or near sightedness. It is when a person cannot see far away objects clearly but can do so for nearby objects.
The image is formed before the retina.
It can be caused by the increase in curvature and power of the lens or the elongation of eyeballs.
It can be corrected by using a concave lens as it has the opposite power and can help cancel out the excessive positive power
Write a short note on Hypermetropia
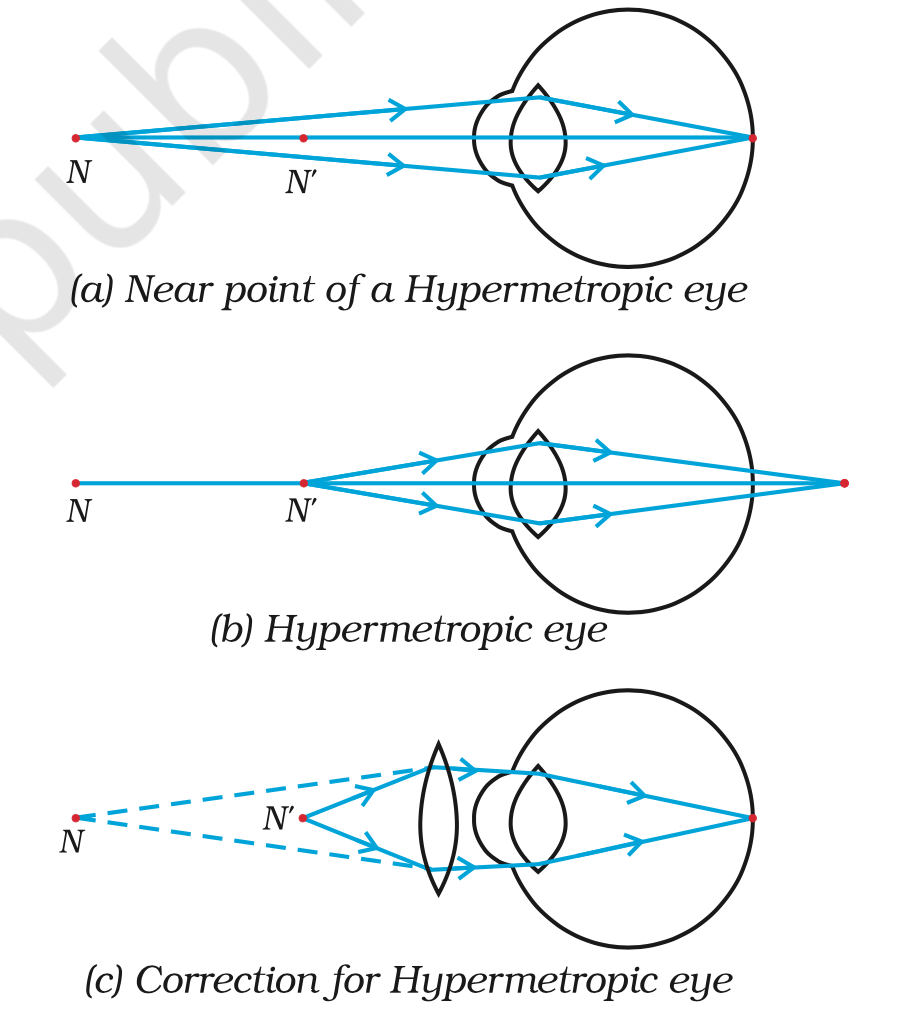
Hypermetropia
Also known as far or long sightedness. It is when one can view far away objects clearly but not the nearby ones.
Mostly occurs due to old age , with decrease in curvature and power of the lens and shortening of eyeballs.
In this case the image is formed behind the retina.
It can be corrected by the use of a convex lens as it acts in the opposite power.
Write a short note on Presbiopia
Presbiopia (Old Age Hypermetropia)
This defect occurs due to old age and both near and far objects become hard to view.
It is caused due to the weakening of the ciliary muscles and reduced flexibility of the eye lens.
It can be corrected by the use of bifocal lens.
Write a short note on Astigmatism
Astigmatism
Person cannot focus on both vertical and horizontal lines at the same time.
Can be corrected using a cylindrical lens.
It is caused by distorted cornea or lens
What is cataract? How can we correct it?
Cataract (Motiabind)
Caused by the deposition of protein on the eye lens gradually making it more opaque
It is corrected using cataract surgery.
What happens when a monochromatic light enters a prism?
In both entry and exit the light bends towards the base of the prism.
The angle of prism is 60 degrees for an equilateral prism
The angle of deviation is the angle between the original path of light and the actual path of light after refracting through a medium
What happens when white light is passed through a prism?
Dispersion of White Light by a Prism
The phenomenon of splitting of white light into it's seven constituent colours while passing through a prism is known as dispersion of light.
The range of seven colours is known as the spectrum of visible light.
Our eyes can only see light of wavelengths between 400 and 700 nm
Violet light deviates the most as it has the shortest wavelength
Red light deviates the least as it has the longest wavelength
Newton placed another prism to try to obtain more colours but that did not occur.
When placing another prism in a inverted way it forms white light again , this is known as recombination of dispersed light.
Explain the formation of rainbow
Water droplets act like small prism , when they are small droplets suspended in the air.
Light refracts and disperses when entering the droplet , then internal reflection occurs with he light undergoing simple refraction again when it exits the water droplet , leading to the formation of the rainbow.
Rainbow is always formed in the direction opposite to the sun
Explain the atomspheric refraction of light.
The refraction of light caused by the Earth's atmosphere is known as atmospheric refraction.
Due to this there is an apparent shift in our perception of the position of the stars.
Twinkling of stars is caused by this , stars are very far away and hence appear to be a point source of light , this is refracted and scattered due to atmospheric conditions changing the apparent position of the stars making it appear like they are twinkling.
Planets do not twinkle as they are much closer to us and hence appear as multiple point sources of light who cancel they are scattering it averages out to appear like a single steady source of light. Like a beam of light rays are coming from the planets.
Due to the apparent shift in the position of the sun there is an advance of 2 minutes for sunrise and 2 minutes delay for sunset.
At noon there is no apparent shift
Explain the tyndall effect
The atmosphere is like a colloidal solution consisting of dust particles , smoke and water droplets.
When light passes through this the beam of light and it's path become visible.
Why is the sky blue?
Colour of the Sky
The small particles in the atmosphere scatter the lights of small wavelength
Blue light has small wavelength and hence gets scattered in all direction making the sky appear blue.
Violet and Indigo are also scattered but our eyes are not so sensitive to them.
The sunlight occurs red during sunrise and sunset as atmosphere is thicker near the horizon , so shorter wavelengths like blue and violet are scattered out before reaching our eyes. The longer wavelengths like orange and red are scattered less and hence reach our eyes.