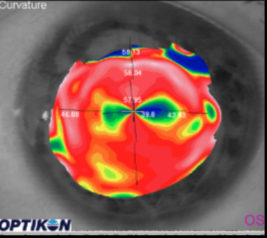
Corneal Topography & Tomography
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
corneal topography
shows the landscape of the cornea
tells us the rate of change of curve across the cornea & whether the eye is optically regular or irregular
Placido Disc Topography
reflects a series of rings off the cornea
measures how the corneal curvature affects the reflection of the rings back
interprets corneal shape based on these reflections
yes
is the placido disc topography tear layer dependent?
large
a ____ cone Placido Disc Topgrapher is more patient friendly but captures a smaller amount of data (8mm)
small
a ____ cone Placido Disc Topographer is not as patient friendly as it must get very close to the eye but provides more data (10mm)
scales
the range by which you are measuring the topography of the cornea
can be in D or mmm for curvature maps
in microns for elevation maps
steeper, higher
hotter colors on a scale mean _____ curvature, ______ elevation
flatter, lower
cooler colors on a scale mean ______ curvature, _______ elevation
normalized, absolute, adjustable
what are the 3 types of scales?
normalized
determines the scale based upon the lowest & highest powers/points on the map & uses them as the low & high ends of the scale
absolute
type of scale that takes the full range of powers into account
not sensitive
apples to apples w/ all other maps
adjustable scale
allows you to choose the high & low end of the scale to suit your needs
can make the top & bottom values anything you want
can allow you to compare apples to apples on a more detailed scale
axial, tangential, elevation
what are the 3 types of maps?
axial curvature
map that gives a global view of the corneal curvature as a whole
tendency to ignore minor variations in curvature
distance along the normal from the corneal surface to the optic axis
reference distance, not a true curvature
running average-excludes extreme values
error increases towards the periphery
spherically biases
may miss abrupt changes
significant smoothing
best for determining K values & understanding corneal refractive power
determining K values & understanding corneal refractive power
what are axial maps best for?
tangential curvature
map that is similar to axial but uses different mathematics to create a more sensitive display
instantaneous rate of curvature based map
based on mathematical formula for local radius at a point along a curve
more sensitive to abrupt changes
less smoothing (more noise)
includes extreme curvature values
localizes exact position of pathology
more detailed
more accurate interpretation of the peripheral cornea
elevation
shows areas of elevation & depression relative to a “reference sphere” generated by the average height of the cornea
corneal tomography
uses a slit beam & Sheimpflug camera to take several cross-sectional images of the anterior segment of the eye
all images go through the central cornea
coverage is nearly limbus to limbus
2D slices are used to create a 3D representation of the object
true measurement, not based on reflections
no
is corneal tomography tear film dependent?
true elevation of anterior & posterior cornea, corneal thickness, corneal curvature
what information can corneal tomography tell you?
curvature, elevation
corneal topography measures ______ & extrapolates _______
elevation, curvature
corneal tomography measures _______ & extrapolates _______
anterior
corneal topography gives you _____ corneal information
anterior & posterior, pachymetry
corneal tomography gives you _________ corneal information, as well as ________
steep/flat
what do curvature maps tell you?
high/low points
what do elevation maps tell you?
tangential map w/ a normalized scale
what map & scale combo will show you the most detail about the cornea?
adjacent to
the area of steepest slope on a curvature map is typically ______ the highest point on an elevation map
flatter
the blue arrow represents _____ slope
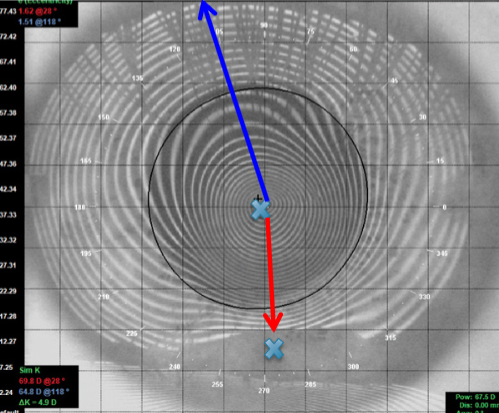
steeper
the red arrow represents _______ slope
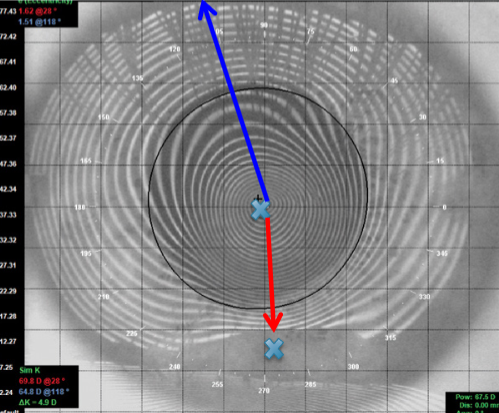
normalized
what type of scale is this?
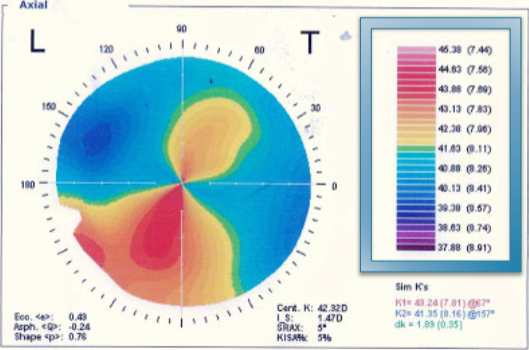
absolute
what type of scale is this?
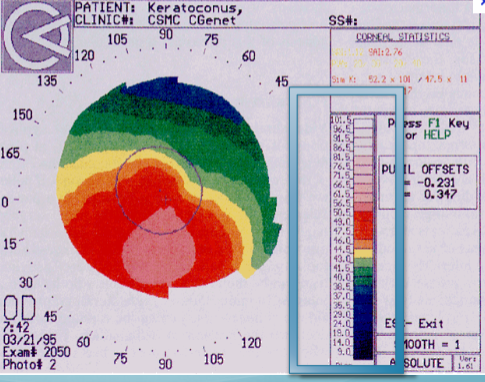
WTR astigmatism
what does this elevation map show?
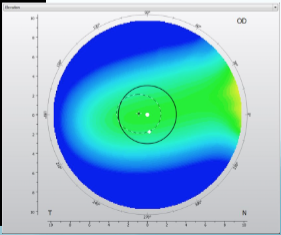
diopters of curvature
what do Placido Disc topographers measure directly?
elevation of anterior & posterior cornea
what do slit-scanning or elevation devices directly measure? (ex: Orbscan, Pentacam, Visante OCT)
patient’s refractive status
what do axial maps allow you to correlate anterior surface shape to?
tangential
_______ maps allow for a clearer view of the size & shape of the cone in a keratoconus patient
tangential
_______ maps define the position of the treatment or effect of corneal reshaping & refractive surgery
positive, red
corneal elevation above the reference sphere is measured in _____ microns & appears as ____ on the elevation map
negative, blue
corneal elevation below the reference sphere is measured in _____ microns & appears as ____ on the elevation map
difference display
shows 2 exams for the same eye & the difference b/t them
helpful when monitoring corneal changes from one exam to the next
symmetric, hourglass
normal astigmatism is ____ & appears as an _____ shape either w/in the pupil margin or extending the entire length of the cornea
horizontal visible iris diameter (white to white measurement)
most topographers are capable of measuring the corneal diameter & label this as the __________
yes
do topographers automatically generate a pupil diameter measurement?
tangential
What type of corneal topographical map tends to accentuate subtle changes in shape?
adjustable
What type of scale is best to use to compare two maps from different dates when you want to look for signs of SUBTLE changes in the map?
B
Which of the following statements about Placido Disc Topography is FALSE?
a. Is tear layer dependent
b. Captures true elevation data about the cornea
c. Reflects a series of rings off the cornea
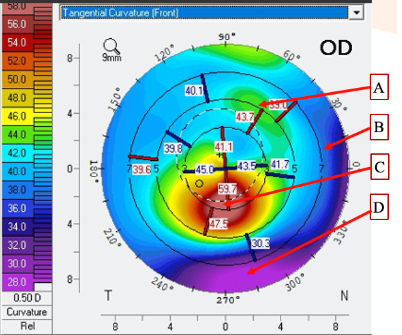
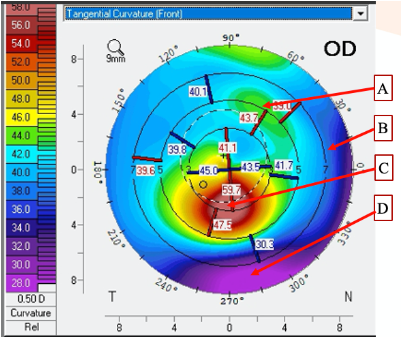
the location of the steepest rate of curvature change/slope
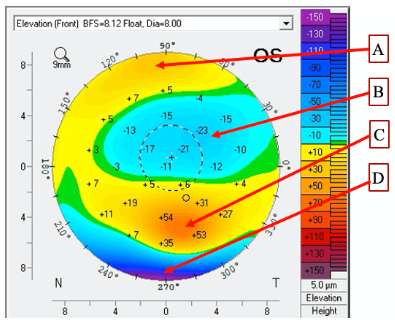
Look at the attached topography. What does point C describe?
D
Look at the attached topography. Which point is the FLATTEST in terms of the slope of the cornea?
the highest spot of elevation on this cornea relative to the reference sphere
Look at the attached topography. What does point C describe?
D
Look at the attached topography. Which point is the in lowest in terms of elevation relative to the reference sphere?
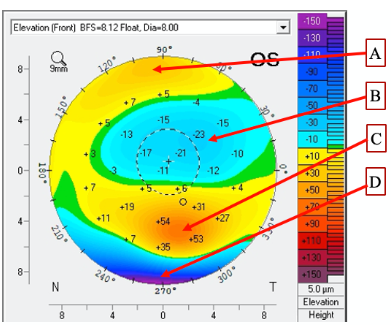
C
Choose the CORRECT answer:
A. Corneal Topography is tear layer independent and measures curvature
B. Corneal Topography is tear layer dependent and measure true elevation
C. Corneal Tomography is tear layer independent and measures true elevation
D. Corneal Tomography is tear layer dependent and measures curvature
keratoconus
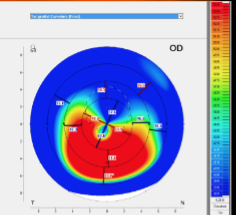
keratoconus
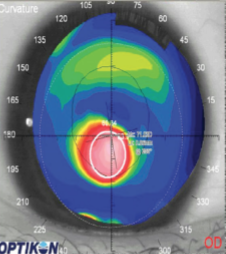
keratoconus
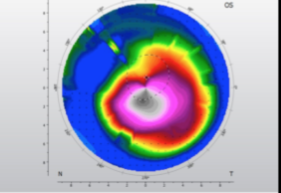
keratoconus
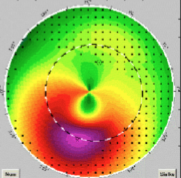
keratoconus (with plastic inlays)
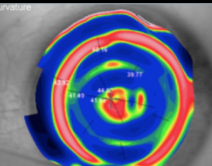
keratoconus (with plastic inlays)
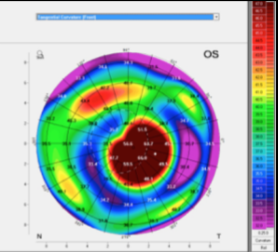
corneal ectasia
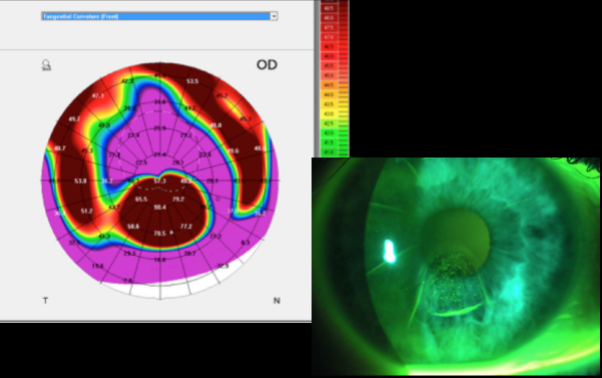
Salzman nodular degeneration
Salzman nodular degeneration
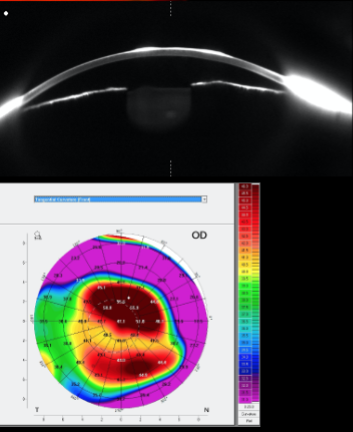
post radial keratotomy
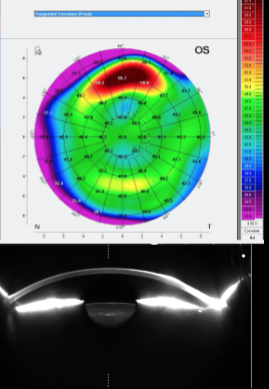
post LASIK
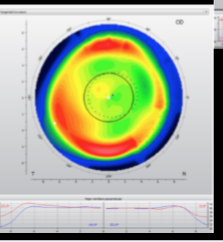
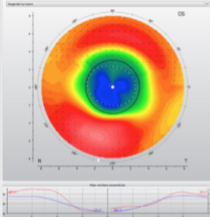
ortho K
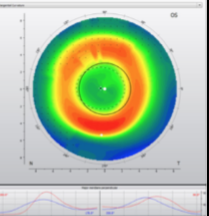
post radial keratotomy
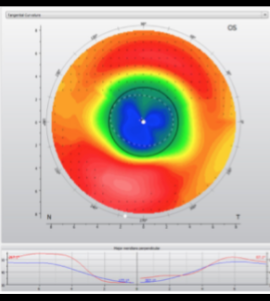
post radial keratotomy
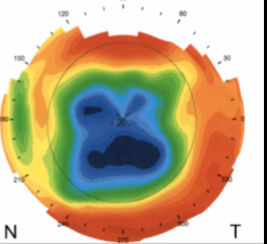
off-center ortho K
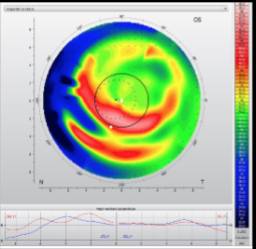
off-center ortho K
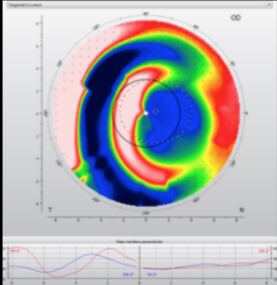
post PK
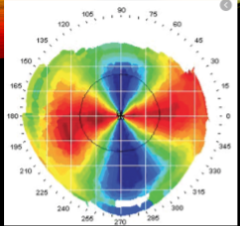
post PK
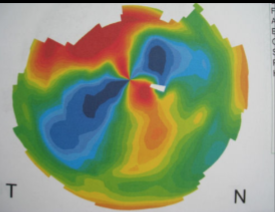
post PK
post PK