Resp structure and Function
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Upper resp tract gross anatomy
nasal cav → nasopharynx
oral cav (hard and soft palate)→ oropharynx
soft palate separates: naso and oropharynx
nasopharynx + oropharynx = pharynx
oesphagus is dorsal to trachea
cartilage rings are ventral
trachealis muscle = dorsal
Horse upper resp tract
soft palate sits ventral to epiglottis
complete separation of naso- and oropharynx
air can only pass to trachea from nasopharynx
no common pharynx
obligate nasal breathers
Larynx (laryngeal cartiages) hangs from skull via hyoid apparatus
Stylohyoid
Epihyoid
Ceratohyoid
Basihyoid
Thyrohyoid
Some elephants can be terrifying (dorsal to ventral)
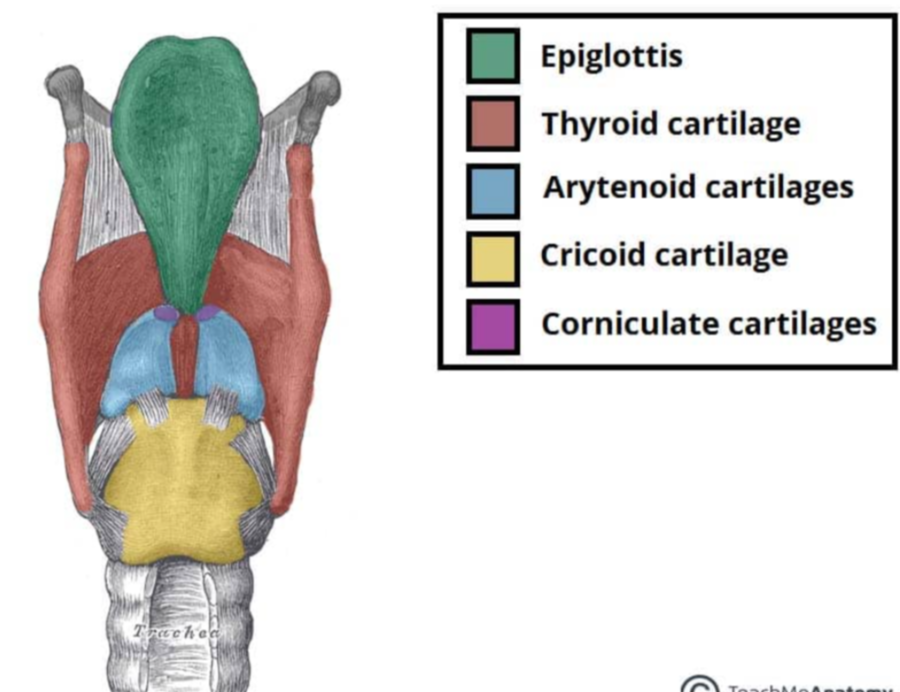
Laryngeal cartilages
Thyroid
Cricoid
Arytenoid
Inspiration
Inspiration:
(diaphragm contract = volume increases BUT neg pressure → draws in air)
Ribcage expands (external intercostals contract)
Diaphragm contracts
Overall size of pleural cavity is bigger
Belly expands because diaphragm is pushing abdominal contents
Often an animal’s abdominal movements will reveal respiratory rate
Diaphragm = primary respiratory muscle
External Intercostal Muscles = accessory respiratory muscles
Horse (and Kangeroo) biphasic ventilation
Locomotor-ventilation coupling
Passive inspiration → active inspiration
Passive expiration → active expiration
Front foot hits the ground → abdominal contents shifts forwards (momentum) → pushes on diaphragm → air forces out of lungs (expiration)
Inspiration - foot moves forward (stride) when cantering and galloping
expansion of thoracic cavity when front feet extend
larger pressure gradient → inspiration
Diffusion Distance
From alveolus → RBC
surfactant → type 1 alveolar epithelial cell → epithelial basal lamina → [connective tissue] → endothelial basal lamona → blood plasma → membrane of RB
Fick’s Law
Rate of transfer of gas through tissue PROPORTIONAL to difference in partial pressure either side of membrane
Rate of transfer INVERSELY P. to tissue thickness
Respiratory Quotient
(typically 0.8)
CO2 / O2 (exchange ratio)
Tissue pp gradients
arterial → tissue cells → venous mmHg
PO2: 95 → 23 → 40
Alveoli partial pressure gradients
arterial → venous (mmHg)
PO2: 40 → 104
PCO2: 45 → 40
Bronchus
Spiral bands of bronchial smooth muscle
Irregular plates of cartilage
BALTs + mast cells
Ciliated columnar epithelium + goblet cells
Bronchioles
Conducting → terminal → respiratory
Gas exchange in respiratory
Cuboidal epithelium + club cells
Alveolar ducts + alveoli
Type 1 pneumocytes → 1 cell thick terminally differentiated blood gas barrier
Type 2 pneumocytes → thicker, make surfactant
Pores of Kohn between alveoli
Pleura
Visceral → attached to lung surface, abundant elastic fibres for inflation
Parietal pleura
Costal
Mediastinal
Diaphragmatic
Pleural fluid
Mediastinum
Continuous with neck, fascia, thoracic inlet, retroperitoneal space
Contains:
Trachea
Thymus
Vagus
Left phrenic nerve
Oesophagus
Heart (pericardium)
Aorta
Cranial vena cava
Thoracic duct
Lymph nodes
Pleural lines of reflection
Vertebral
Costal
Sternal
Within fold of parietal pleura → plica venae cavae
caudal vena cava
right phrenic nerve