Romans
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Who were patricians in Roman society?
Wealthy landowners. Owned large estates, had slaves and a lot of power
Who were plebeians in Roman society?
Ordinary workers. Some were employed by patricians as teachers or ran businesses
Who were slaves in Roman society?
Slaves were people from conquered places or criminals. They were owned property of patricians. (about 1/3 of the Roman populations were slaves)
What were insulae/an insulage?
Roman apartments where plebeians and freed slaves usually lived
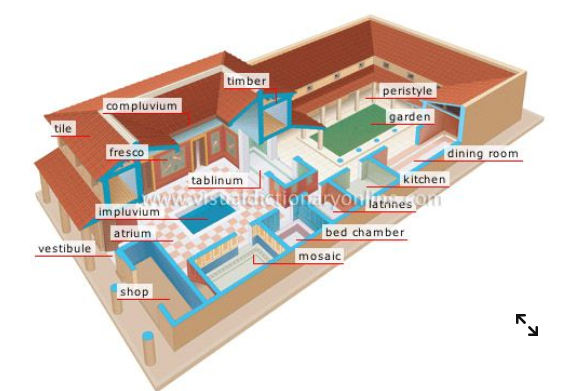
What were the names of patricians houses?
Villa (in the country) and Domus (in the city
What were the names of the restaurants/food shops that lined the streets of Rome?
Thermopolia
What did Romans have to eat?
Bread (sometimes dipped in wine), salad, fruits, nuts, olives, cheese or raisins
What was a Roman main meal called?
Cena
What foods did a patrician dinner party include?
Oysters, raw or uncooked vegetables, roast or boiled meat covered in spicy sauces (cause meat tasted ad), pastries, nuts, fruit and honey
Name some facts about insulae
Water was only piped to the ground floor, the higher up you went in an insular the cheaper the room's rents were. There were no indoor toilets so people went in pots (or used public toilets) and threw the contents out the windows afterward
What was the name given to the handouts of bread from the government given to poor Romans (most depended on it survive)?
Dole
What did Romans wear?
Mostly men wore a knee-length tunic with a belt tied at the waist (togas were uncomfortable) and married women worried a long woollen tunic called a stola. Both men and women wore leather sandals in the house and shoes outside
What rights did Roman women have and not have?
Women were not allowed to become citizens or vote in elections for the senate but they could inherit property and own businesses
What things did a Roman girl learn about?
Greek literature and how to play an instrument
What things did a Roman boy learn about?
Oratory (art of public speaking), reading, writing, arithmetic, Greek and Latin writers and talked about their ideas
What were the gods or guardians spirits that watched over a house called?
The lares
What typically happened when a Roman visited the baths?
A slave would massage the person in olive oil, after you could exercise by weightlifting or wrestling. after you could chat in the warm room or sit in a tub of very hot water in the caldarium. Lastly, you would go to the cold room called a frigidarium that had a cool pool.
Name 3 famous Roman buildings
Circus Maximus (gladiators), Colesseum and Baths of Trajan
How did the Roman Empire influence us?
They were the first people in Euope to make concrete, they learned how to build arches, they were the first to build apartment blocks and shopping centers, they used underfloor heating in their homes, they built aqueducts that are still standing today (brought water to over 130 million people in Rome every day), about 30% of English words come from Latin and they way courts are run in Ireland and the right to inherit property comes from Roman ideas
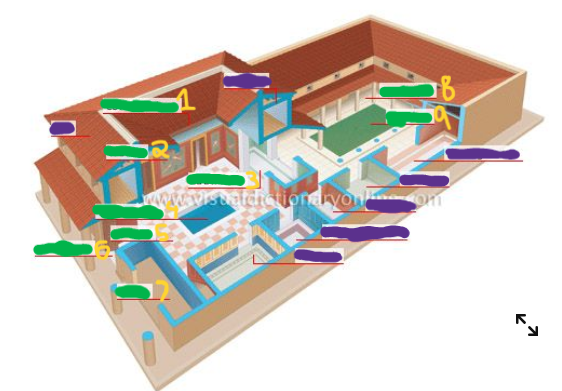
Name the numbered parts of the Roman house from 1-9 in the image shown (write 1: answer, 2: answer…).
1: Compluvium (brings rainwater to impluvium), 2: Fresco, 3: Talinum (office for Roman man), 4: Impluvium (pool!), 5: Atrium (open area), 6: Vestibule (empty place between the door of domus and street), 7: Shop, 8: Peristyle (porch surrounding the courtyard), 9: Garden