QUIZ 9
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/202
Earn XP
Last updated 6:52 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
203 Terms
1
New cards
Glycogen
A highly branched homopolymer of glucose present in all tissues.
2
New cards
The largest stores of glycogen are in the?
Liver and muscle
3
New cards
The liver breaks down _____ and releases _____ to the blood to provide energy for the _____ and the ___ _____ _____.
1) glycogen
2)Glucose
3) brain
4) red blood cells
2)Glucose
3) brain
4) red blood cells
4
New cards
Muscle glycogen stores are mobilized to provide?
Energy for muscle contraction.
5
New cards
what is the Glycogen structure?
the residues at the nonreducing ends are shown in red and the residue that starts a branch is shown in green. The rest of the glycogen molecule is represented by R.
6
New cards
List and describe the steps of glycogen breakdown and identify the enzymes required.
1.Glycogen phosphorylase
2.Phosphoglucomutase.
3.Transferase
4.α-1,6-glucosidase
2.Phosphoglucomutase.
3.Transferase
4.α-1,6-glucosidase
7
New cards
Glycogen phosphorylase degrades glycogen from the
nonreducing ends of the glycogen molecule
8
New cards
The phosphorylase catalyzes a
phosphorolysis reaction that yields glucose 1-phosphate.
9
New cards
Glucose 1-phosphate is converted into glucose 6-phosphate by
phosphoglucomutase
10
New cards
A Debranching Enzyme Also Is Needed for?
the Breakdown of Glycogen
11
New cards
Glycogen phosphorylase cannot cleave near branch points
can only cleave α-1,4-glycosidic bonds.thereby making the glucose moieties accessible to the phosphorylase
12
New cards
A debranching enzyme (α-1,6-glucosidase) then cleaves the α-1,6 bond at the branch point, releasing
a free glucose.
13
New cards
Phosphoglucomutase forms
glucose 6-phosphate from glucose 1-phosphate with the use of a glucose 1,6-bisphosphate intermediate
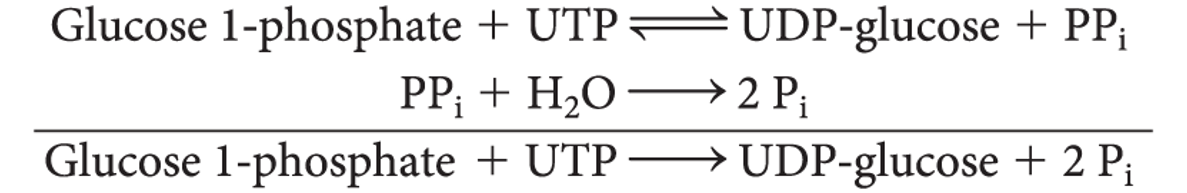
14
New cards
Glucose 6-phosphatase generates
•free glucose from glucose 6-phosphate in liver.
15
New cards
where is Glucose 6-phosphatase
-Found in membrane of the ER, lumen side
16
New cards
The free glucose is released into the blood for use by other tissues such as
the brain and red blood cells.
17
New cards
_____________ is absent in most other tissues
Glucose 6-phosphatase
18
New cards
What enzymes are required for the liver to release glucose into the blood when an organism is asleep and fasting?
Phosphorylase, transferase, glucosidase, phosphoglucomutase, and glucose 6-phosphatase
19
New cards
The Phosphorylase Dimer
Phosphorylase a is phosphorylated on serine 14 of each subunit. This modification favors the structure of the more active R state. One subunit is shown in white, with helices and loops important for regulation shown in blue and red. The other subunit is shown in yellow, with the regulatory structures shown in orange and green. Phosphorylase b is not phosphorylated and exists predominantly in the T state. Notice that the catalytic sites are partly occluded in the T state. [Drawn from 1GPA.pdb and 1NOJ.pdb.]
20
New cards
Phosphorylase Is Regulated by
Allosteric Interactions and Reversible Phosphorylation
21
New cards
Liver Phosphorylase Produces
Glucose for Use by Other Tissues
22
New cards
The key regulatory enzyme for glycogen degradation is
glycogen phosphorylase
23
New cards
Phosphorylase exists in two forms
•a less active b form and a more active a form.
24
New cards
The a form differs from the b form in that
a serine residue is phosphorylated.
25
New cards
Both the a form and b form display _____
RóT equilibrium
26
New cards
In the b form the ________ is favored whereas in the a form, the _______ is favored
1) T state
2) R-state
2) R-state
27
New cards
Phosphorylase Regulation
Both phosphorylase b and phosphorylase a exist in equilibrium between an active R state and a less active T state. Phosphorylase b is usually inactive because the equilibrium favors the T state. Phosphorylase a is usually active because the equilibrium favors the R state. In the T state, the active site is partly blocked by a regulatory structure. The active site is unobstructed in the R state. Regulatory structures are shown in blue and green.
28
New cards
Liver Phosphorylase Produces
Glucose for Use by Other Tissues
29
New cards
A key role of the liver is to?
maintain adequate blood levels of glucose.
30
New cards
As a result, the default state of liver phosphorylase is the
a form in the R state.
31
New cards
In essence, liver phosphorylase is prepared to generate?
blood glucose unless signaled otherwise
32
New cards
Glucose is a negative regulator of
liver phosphorylase
33
New cards
Glucose facilitates the transitionfrom ______
the R state to the T state
34
New cards
______ _____ and ______ ______ are isozymes
Liver phosphorylase and muscle phosphorylase
35
New cards
Allosteric Regulation of Muscle Phosphorylase
Binding of glucose to phosphorylase a shifts equilibrium to T state, inactivating the enzyme. Glycogen is not mobilized when glucose is already abundant.
36
New cards
Muscle Phosphorylase Is Regulated by
the Intracellular Energy Charge
37
New cards
In muscle, the default form of the phosphorylase is the
b form in the T state.
38
New cards
When energy is needed, as signaled by an increase in the concentration of AMP, the phosphorylase binds?
AMP, which stabilizes the R state.
39
New cards
The T state of the phosphorylase is stabilized by __ and ___
ATP and glucose 6-phosphate.
40
New cards
phosphorylase b is predominate, and is inactive in
muscle cells
41
New cards
Allosteric Regulation of Liver Phosphorylase
The binding of glucose to phosphorylase a shifts the equilibrium to the T state and inactivates the enzyme. Thus, glycogen is not mobilized when glucose is already abundant. Regulatory structures are shown in blue and green.
42
New cards
Compare the allosteric regulation of phosphorylase in the liver and in muscle and explain the significance of the difference.
In muscle, the b form of phosphorylase is activated by AMP. In the liver, the aform is inhibited by glucose. The difference corresponds to the difference in the metabolic role of glycogen in each tissue. Muscle uses glycogen as a fuel for contraction, whereas the liver uses glycogen to maintain proper blood glucose concentration
43
New cards
Muscle is composed of several fiber types
-Type I, or slow-twitch fibers, rely primarily on cellular respiration as a means of generating ATP.
-Type IIb (type IIx), or fast-twitch fibers, rely primarily on lactic acid fermentation for ATP generation.
-Type IIa fibers have biochemical characteristics intermediate between the other fiber types
-Type IIb (type IIx), or fast-twitch fibers, rely primarily on lactic acid fermentation for ATP generation.
-Type IIa fibers have biochemical characteristics intermediate between the other fiber types
44
New cards
Type IIb fibers are rich in
glycogen phosphorylase
45
New cards
Phosphorylase exists in two forms
a less active b form and a more active a form
46
New cards
The a form differs from the b form in that a ______
a serine residue 14 is phosphorylated.
47
New cards
Phosphorylation is stimulated by the hormones
glucagon and epinephrine (adrenaline).
48
New cards
Phosphorylation alters the active site such that
α helices that partially block the active site in the b form are removed.
49
New cards
phosphorylase kinase
The enzyme responsible for the conversion of glycogen phosphorylation from the unphosphorylated bstate to the a state
50
New cards
Phosphorylase kinase itself is activated by both
phosphorylation and Ca2+ binding
51
New cards
Phosphorylase kinase is phosphorylated by
protein kinase A
52
New cards
calmodulin
The δ (delta) subunit of phosphorylase
53
New cards
Phosphorylase kinase is maximally active when
phosphorylated and bound to calcium
54
New cards
G Proteins Transmit the Signal for
the Initiation of Glycogen Breakdown
55
New cards
Glucagon (in liver) and epinephrine (in muscle) initiate
G-protein cascades that result in the production of cAMP.
56
New cards
Calcium, released in muscle to stimulate contraction, initiates
the activation of phosphorylase kinase.
57
New cards
In liver, Ca2+ release is stimulated by
•epinephrine binding to the α-adrenergic receptor, which activates a G-protein, instigating the phosphoinositidecascade.
58
New cards
Cyclic AMP activates
protein kinase A
59
New cards
Phosphorylase kinase converts
glycogen phosphorylase b to the a form, activating glycogen degradation.
60
New cards
Hormonal Control of Glycogen Breakdown
The left side of the illustration shows the hormonal response to fasting. Glucagon stimulates glycogen breakdown in the liver when blood glucose is low. The right side of the illustration shows the hormonal response to exercise. Epinephrine enhances glycogen breakdown in muscle and the liver to provide fuel for muscle contraction.
61
New cards
regulatory cascade for glycogen breakdown
Glycogen degradation is stimulated by hormone binding to 7TM receptors. Hormone binding initiates a G-protein-dependent signal-transduction pathway that results in the phosphorylation and activation of glycogen phosphorylase.
62
New cards
Glycogen degradation is turned off by
several mechanisms
63
New cards
The inherent GTPase activity of the G protein renders
proteins inactive
64
New cards
Phosphodiesterase converts
cAMP into AMP, which does not stimulate protein kinase A.
65
New cards
Protein phosphatase 1 removes
phosphoryl groups from phosphorylase kinase and glycogen phosphorylase, thereby inactivating the enzymes.
66
New cards
The onset of fatigue coincides with __________________
the depletion of glycogen reserves.
67
New cards
Depletion as a Result of Exercise
A) Glycogen content of the vastus lateralis decreases as a function of time at 80% effort. (B) The French cyclist Tony Gallopin slumps in exhaustion after winning a stage in the 2014 edition of the Tour de France. [(A) After J. Bergströmand E. Hultman, A study of the glycogen metabolism during exercise in man
68
New cards
25.1 Glycogen Is ___ and _____by Different Pathways
Synthesized
Degraded
Degraded
69
New cards
Glycogen degradation yields
glucose 1-phosphate.
70
New cards
UDP-glucose is the _____that is used to____ the ___
monomer
extend
glycogen chain in synthesis.
extend
glycogen chain in synthesis.
71
New cards
UDP-glucose is an
activated form of glucose.
72
New cards
what is the glucose donor in glycogen synthesis?
Uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glucose)
73
New cards
UDP-glucose is synthesized by
UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase.
74
New cards
UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase reaction is _____under cellular conditions
irreversible
75
New cards
The reaction is subsequently rendered irreversible by the
hydrolysis of pyrophosphate
76
New cards
Glycogen synthase
the key regulatory enzyme in glycogen synthesis
77
New cards
Glycogen synthase transfers a glucose moiety from
UDP-glucose to the C-4 terminal residue of a glycogen chain
78
New cards
what does the transfer of a glucose moiety to the c-4 terminal residue form?
α-1,4-glycosidic bond
79
New cards
Glycogen synthase requires an
oligosaccharide of glucose residues as a primer.
80
New cards
glycogenin
synthesizes a primer and is a dimer of two identical subunits
81
New cards
Each subunit of glycogenin generates an
oligosaccharide of glucose residues 10–20 glucosyl units long.
82
New cards
Glycogen synthase then ____ this primer
extends
83
New cards
Glycogen synthase can only synthesize
α-1,4-linkages.
84
New cards
A branching enzyme generates branches by
cleaving an α-1,4-linkage and taking a block of approximately seven glucoses and synthesizing an α-1,6-linkage.
85
New cards
Glycogen synthase can then extend the
branched polymer.
86
New cards
Glycogen synthase is usually inactive when in the
phosphorylated b form
87
New cards
Glycogen synthase isis usually active when in the
unphosphorylated a form
88
New cards
key regulatory process for glycogen synthase
the conversion of the b form in the T state to the active R state of the b form by binding glucose 6-phosphate.
89
New cards
phosphorylation has ______ effects on glycogen synthase than on glycogen phosphorylase
oposite
90
New cards
Why is the fact that phosphorylation has opposite effects on glycogen synthesis and breakdown advantageous?
Prevents both processes from occurring simultaneously. Prevents wasteful energy expenditure.
91
New cards
Glycogen Is an Efficient Storage Form of
Glucose
92
New cards
Only ____ molecules of ATP are required to incorporate dietary glucose into glycogen
two
93
New cards
The complete oxidation of glucose derived from glycogen yields
31 molecules of ATP.
94
New cards
Coordinate Control of Glycogen Metabolism
Glycogen metabolism is regulated, in part, by hormone-triggered cyclic AMP cascades. The sequence of reactions leading to the activation of protein kinase A ultimately activates glycogen degradation. At the same time, protein kinase A, along with glycogen synthase kinase, inactivates glycogen synthase, shutting down glycogen synthesis.
95
New cards
Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) shifts glycogen metabolism from
the degradation mode to the synthesis mode
96
New cards
PP1 removes phosphoryl groups from glycogen synthase b, converting it into
the more active a form
97
New cards
PP1 also removes phosphoryl groups from
phosphorylase kinase and phosphorylase a, inhibiting glycogen degradation.
98
New cards
Regulation of Glycogen Synthesis by Protein Phosphatase 1
PP1 stimulates glycogen synthesis while inhibiting glycogen breakdown.
99
New cards
Protein phosphatase 1 consists of
a catalytic subunit (PP1) and one of a family of regulatory subunits
100
New cards
A key regulatory subunit is
the G subunit (GL in liver and GM in muscle) that binds glycogen and the catalytic subunit of PP1, localizing the enzyme with its substrates