Forensic science exam
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
DNA
•DNA is a double-stranded molecule, formed from two strands of nucleic acids (i.e., information-carrying molecules) held together by hydrogen bonds.
Where is DNA?
Found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells (e.g., plant and animal cells).
Found in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cell (e.g., bacteria).
Chromosomes
chromosomes are huge lengths of DNA which are coiled and compacted. Humans have 46 chromosomes in total or 23 pairs
Genome
genetic information for an organism
23 pair of chromosomes
sex chromosome (fem XX male XY)
Genes
contain instructions to make proteins
alleles
Different forms of the same gene
phenotype
The physical expression of the alleles/observable characteristics
What influences your phenotype?
your genetics and your environment
Genotype
The two alleles you inherit is called
Categories of crime
Crimes against the state
Crimes against persons (often violent crimes)
Crimes against property
White collar crimes
Public order offences
Drug offences
Traffic offences
Evidence at a crime scene
Trace, impressions, bodily fluids, hair clothing an material fibres, weapons and firearms, documents, CCTV footage, eyewitness testimony
Trace evidence
gunshot residue, paint residue, explosives residue, broken glass, unknown chemicals, drugs, soil, wood, pollen, fibres, hair
impressions
fingerprints, footprints, tool marks, teeth marks
Bodily fluids
blood, semen, saliva, vomit
Weapons and firearms
knives, guns, bullet holes, cartridge casings
Documents
•diaries, suicide note, phone books; also includes electronic documents like answering machines, text messages, receipts, bankcard statements
Direct evidence
first-hand observations.
E.g. Eyewitness accounts, Video surveillance, Voice recordings, forensic lab reports, eyewitness accounts
Circumstantial evidence
•implies a fact but cannot directly prove it.
E.g. DNA, Ballistic evidence, prints (fingerprints, tyre prints, bite marks)
Class evidence
narrows to a group of people
E.g. blood type, Shoe prints, hair (without the follicle)
Individual evidence
narrows to one individual
E.g. DNA, fingerprints, hair (with the follicle)
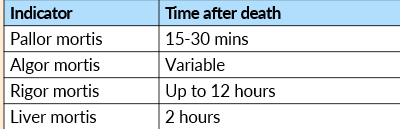
Liver Mortis
The settling of blood in the body due to gravity.
Develops 2-4 hours after death;
Fixed (i.e., non-blanchable) after 8-12 hours after time of death.
Algor mortis
the cooling of the body after death, it goes down by 1.5 c every hour or in cold environments (<37 degrees) it will decrease by 2 c and then the rest will decrease by 1 c. it takes a body approx 18 - 26 hours for a body to become room temperature and algor mortis occurs 1 hour after death
Rigor Mortis
Rigor mortis is the stiffening of the muscles in a body after death.
It becomes fully developed by around 12 hours after death.
It stays for about 24–48 hours.
After that, the muscles start to break down (decompose), and the body becomes loose again.
Pallor mortis
pale or ashen discoloration of the body that occurs shortly after death. (15 - 30 minutes)
yep
yep
ATP
made by cellular respiration