ECON 2020 Exam 2
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Economic growth affects....
human welfare
Why does economic growth matter?
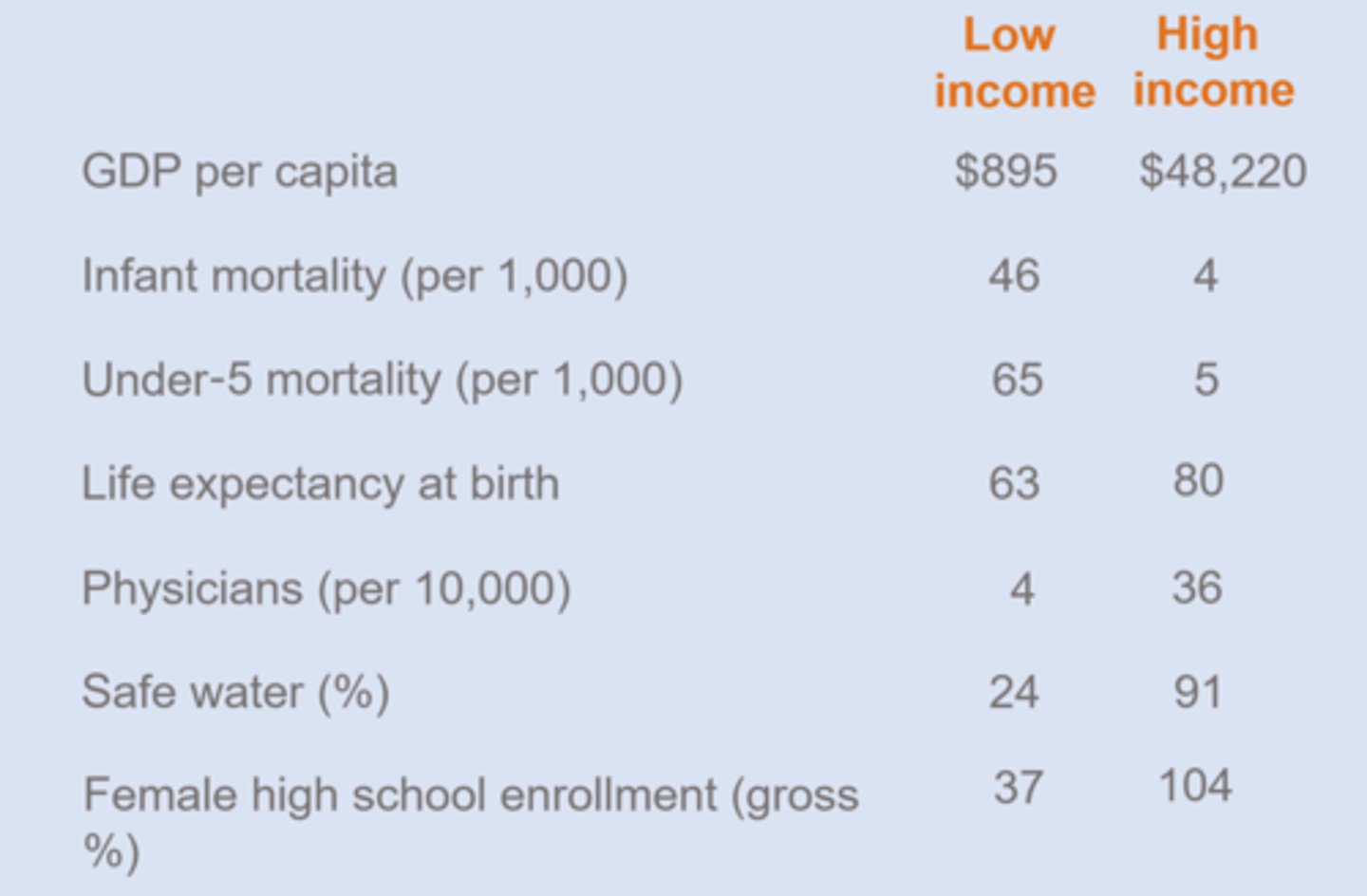
living standards differences: GDP per capita, infant mortality, life expectancy, physicians, access to safe water, female high school enrollment
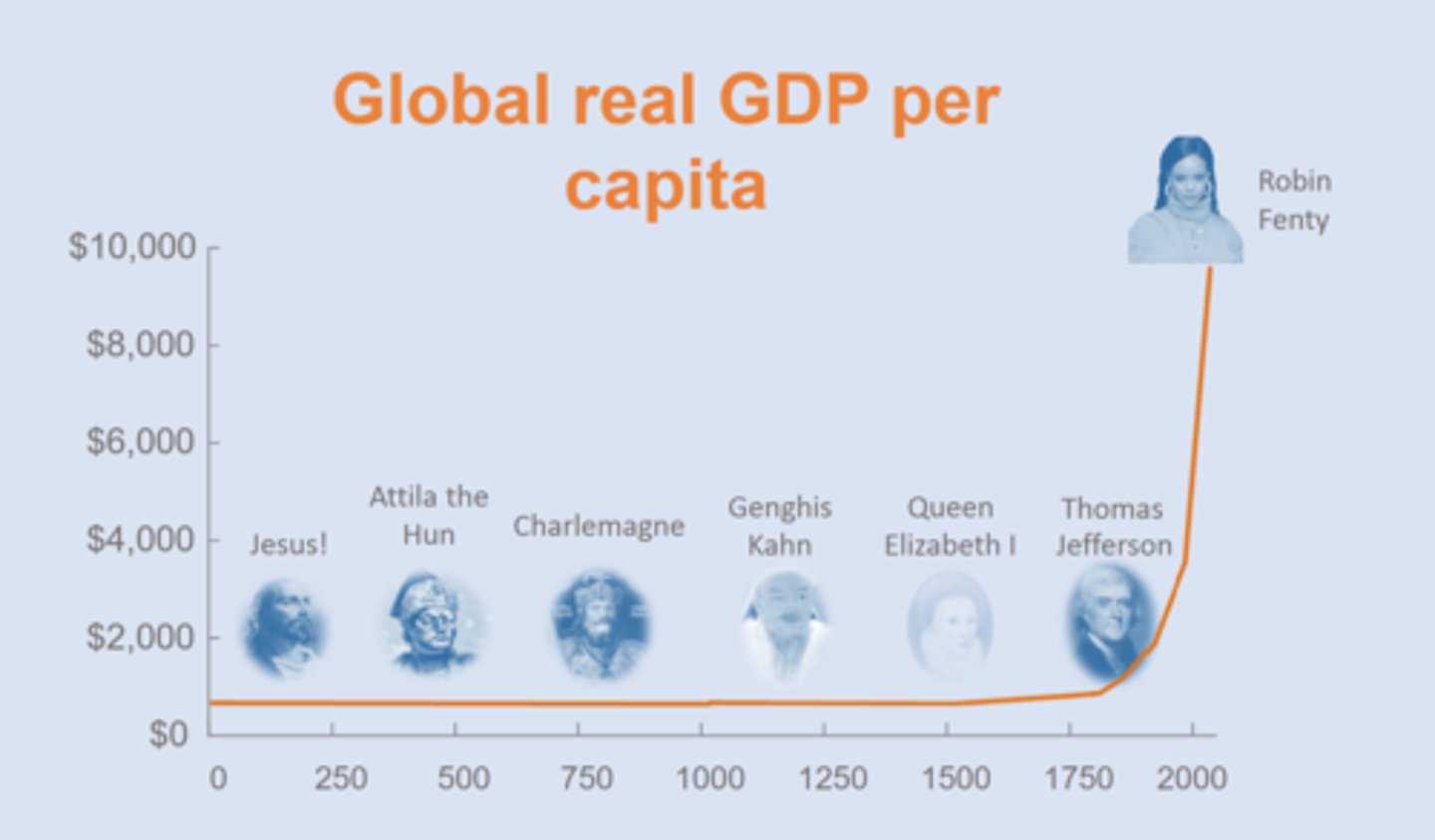
Global real GDP per capita trend historically
exponentially grew globally in 20th & 21st century ==> some countries did stay the same though
Growth Rate of real GDP per capital
nominal GDP growth - inflation - population growth = real PC GDP growth
(% changes)
Rule of 70
With annual growth of x percent, the level of a variable doubles every 70/x years.
With a growth rate of 3% it takes 23.33 years to double? What size is the new value in 70 years relative to the og value?
8x the og
Best Way to Grow an Economy?
consistent long term growth
What contributes to economic growth?
resources, institutions, and technology
resources
land (ex: mountains, oil, water, geography), labor (workers, skills, human capital), capital (tools, public goods, medical tools)
Resources __________, but by themselves _______________________.
aid in economic growth, but by themselves are not sufficient to produce sustained growth
technology
knowledge available for use in production
technological advancements
new techniques/methods to 1. produce more w/ same amount or 2. produce same w/ fewer amount
institution
significant practice/relationship/organizations that officially or unofficially shape society
ex: government, private property, political stability, international trade, taxes, etc.
Solow Growth Model 1
Y = F(land, labor, CAPITAL)
==> focus on capital because
1. high income countries have more capital
2. investment and growth are correlated
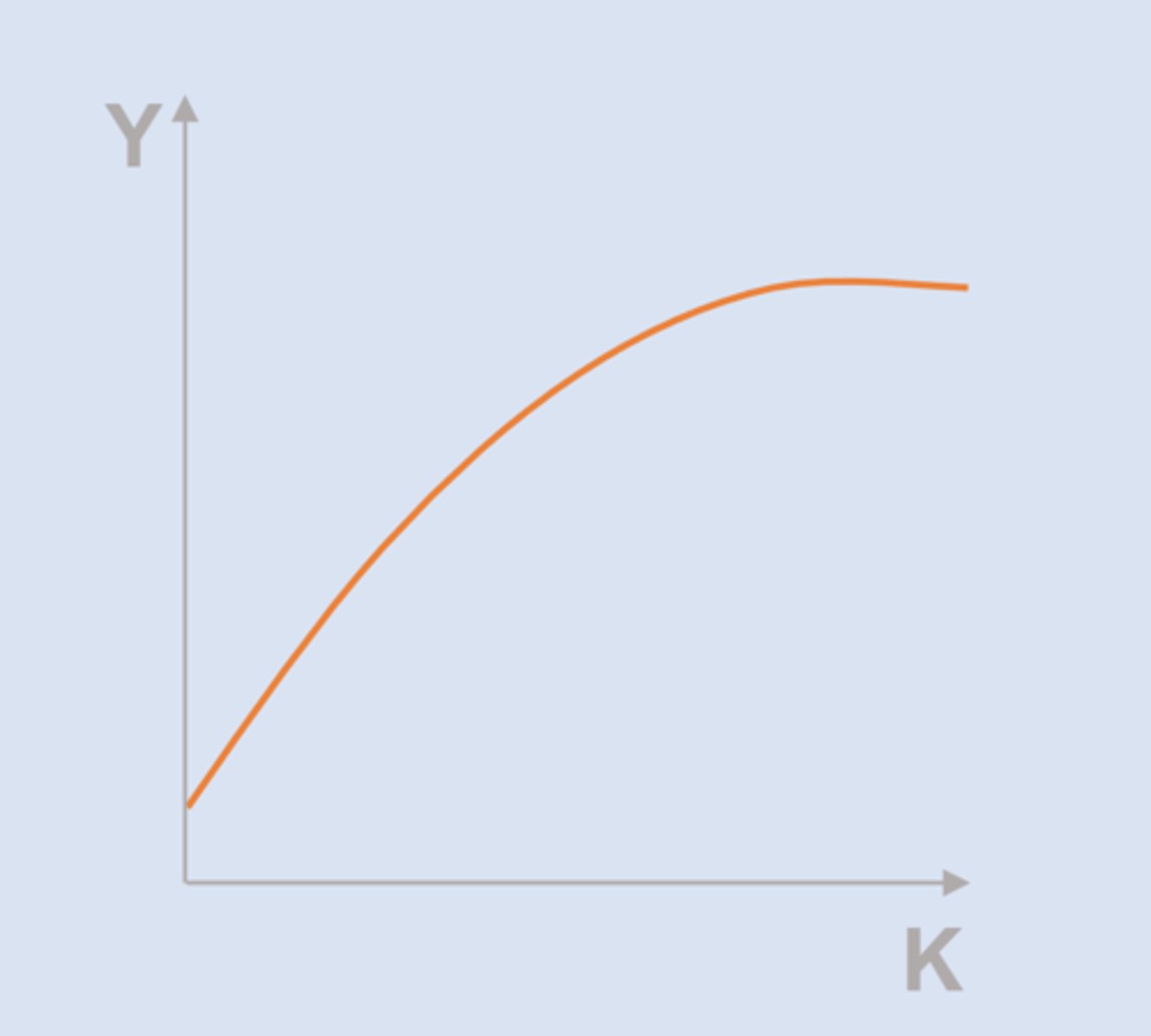
Marginal product
The change in output from a change in an input, everything else held constant
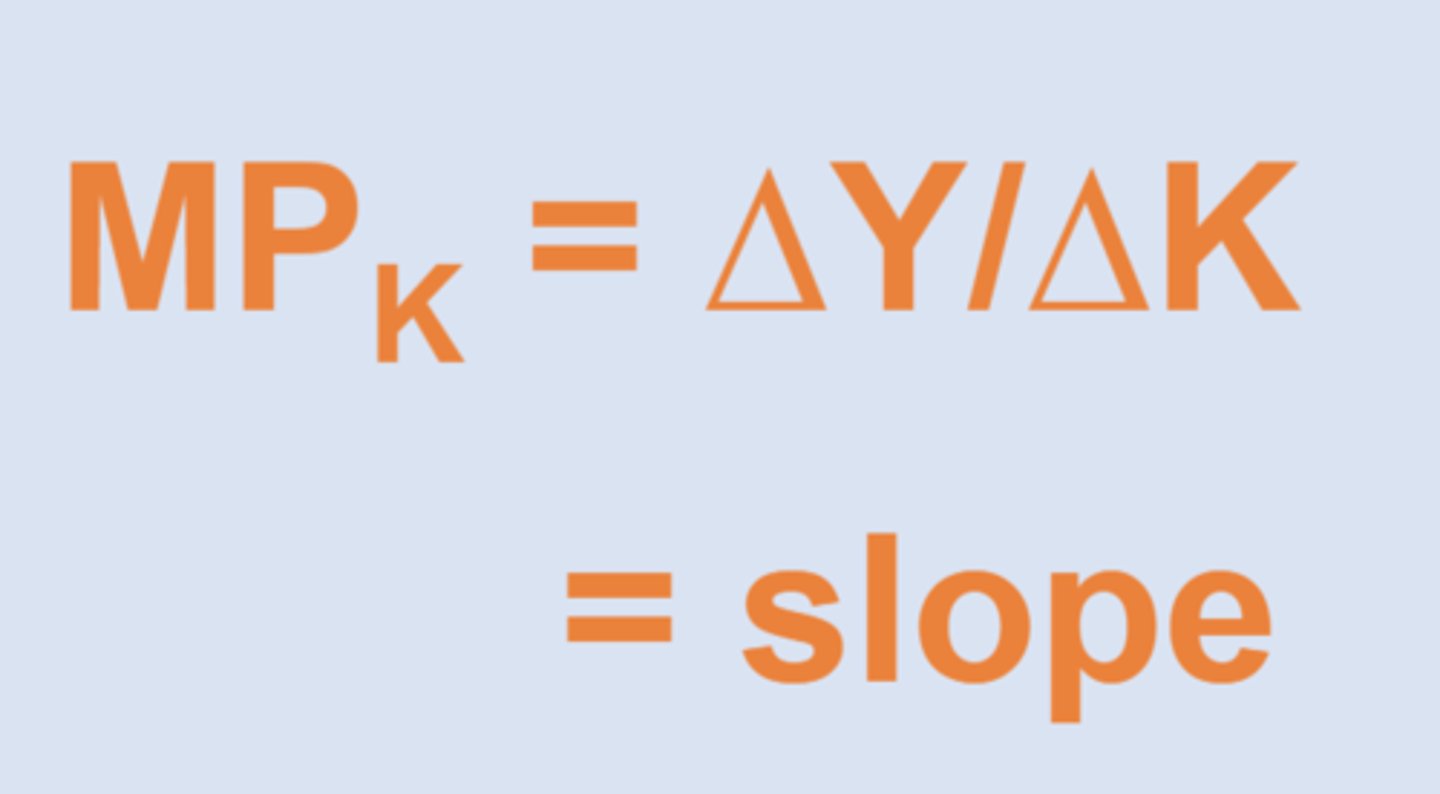
Diminishing Marginal Product
When the marginal product of an input falls as the quantity of the input rises ==> "diminishing returns"
Assumptions of Solow 1
diminishing marginal product
Implications of Solow Model 1
1. steady states ==> condition in econ where there is no net growth ==> "stagnant/sad"
- no net investment
- no changing K
- no growth
2. convergence ==> income levels across nations converge as the approach their SS
- growth in rich countries slows down
- poorer countries enjoy higher returns
Empiricle Problems w/ Solow 1
- wealthy nations keep growing
- many poor nations not growing
Solow Model II
Y = A x F(capital, land, labor)
another growth source is new technology (advancement)
2 Sources of Growth (Solow II)
- technology
- resources
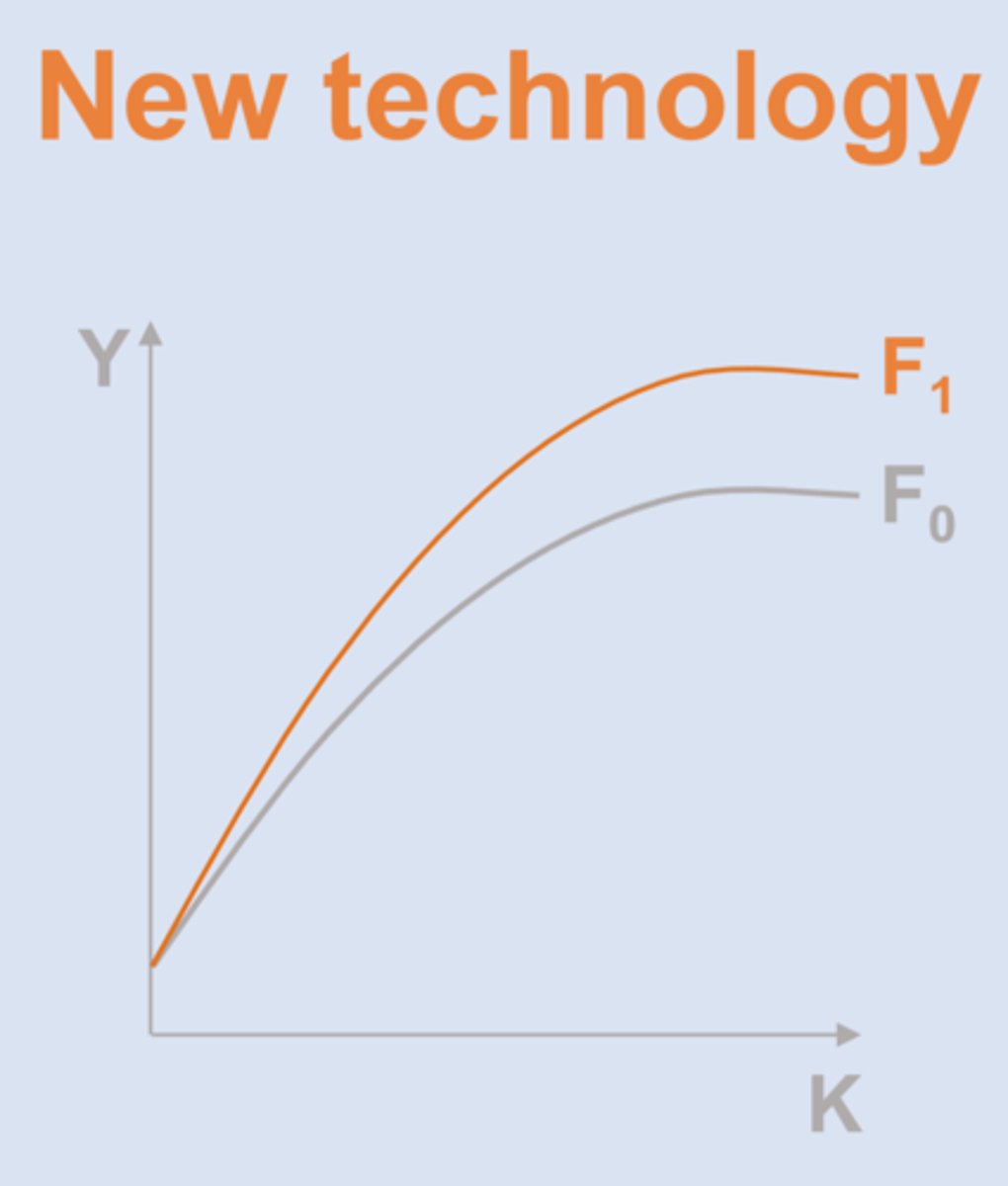
Solow Model II Assumption
technology develops exogenously (randomly) due to external factors
Exogenous technology
When technological advancements are unrelated to conditions or actions inside the economy
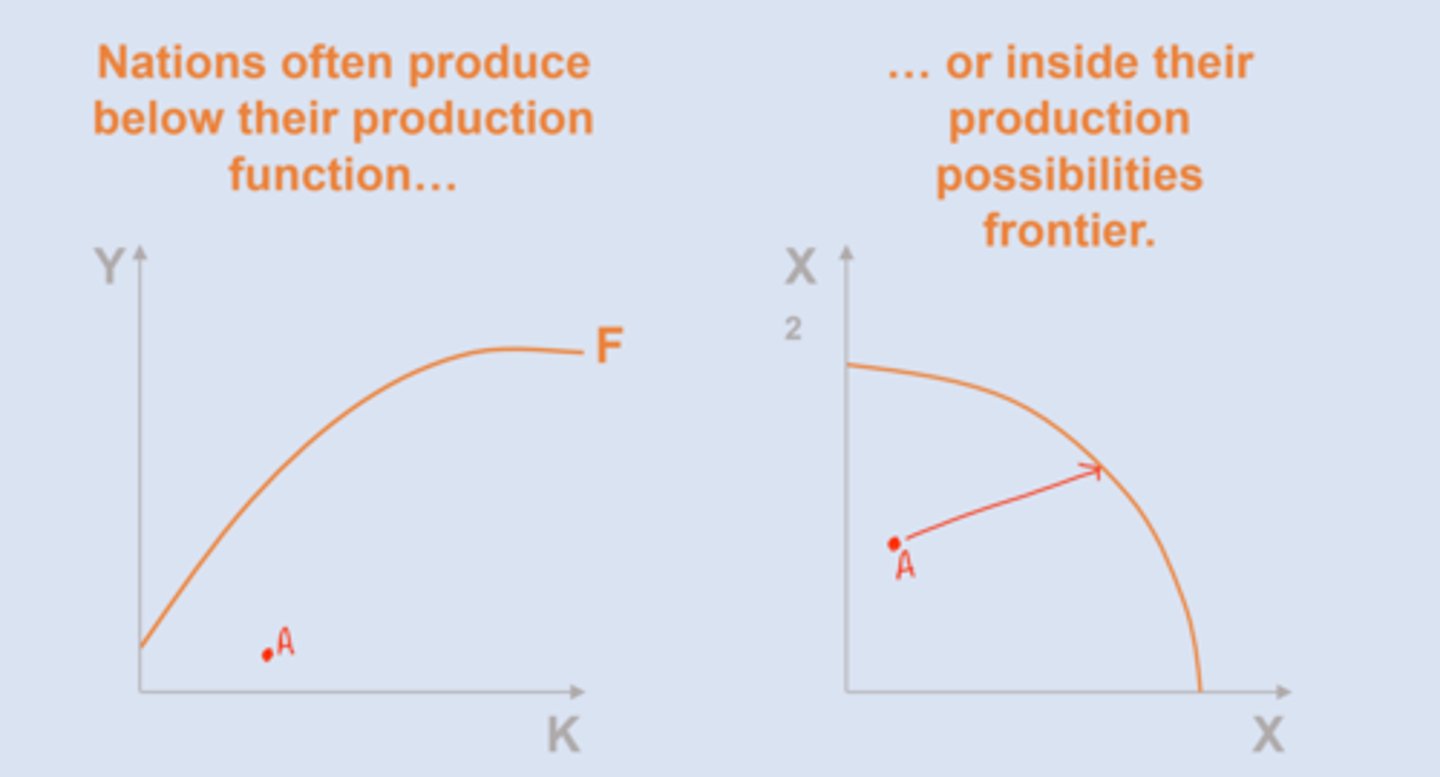
Policy based on SGM
gov & organizations aid supply loans a direct air for infrastructure, healthcare, factories, education ==> FAIL
Modern Growth Theory
Y = A x F(resources & institutions)
begins w/ idea that growth in endogenous (factors inside an economy)
Harmful Institutions for Economic Growth
Harmful:
- corruption, inflation, high taxes
Growth Fostering Institutions
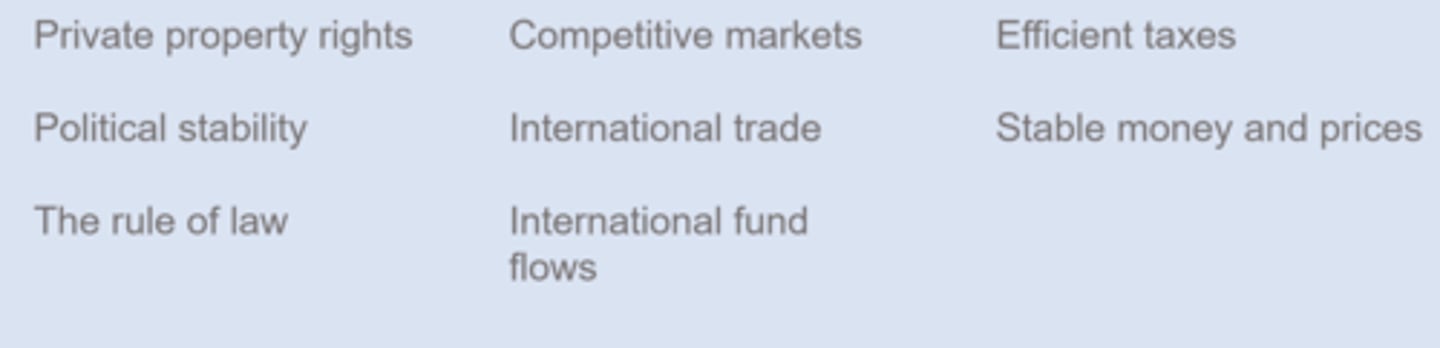
How do institutions affect the production function?
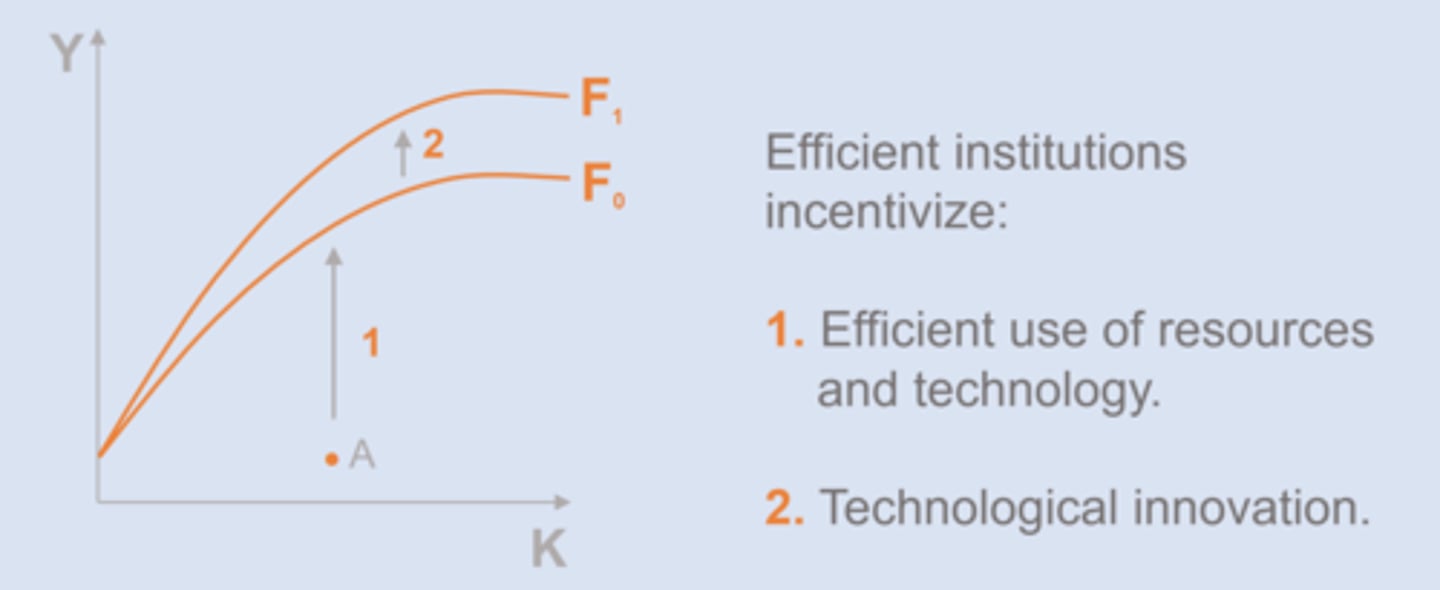
Certain institutions create incentives for __________________.
endogenous growth
Rotunda Principle 3
The three sources of economic growth are resources, technology, and institutions
Short to Long Run Economics
Recessions have _____________ over US history.
decreased substantially
AD-AS Model
The model we use to study short-run fluctuations in the economy.
Aggregate Demand
total demand for all final good & services in an economy (spending side)
Why does AD slope down?
wealth effect, interest rate effect, international trade effect
Changes in P (price level) lead to....
changes in QUANTITY of aggregate demand (movement along the curve)
wealth effect
changes in price level affect people's real wealth and this leads to changes in their quantity of aggregate demand.
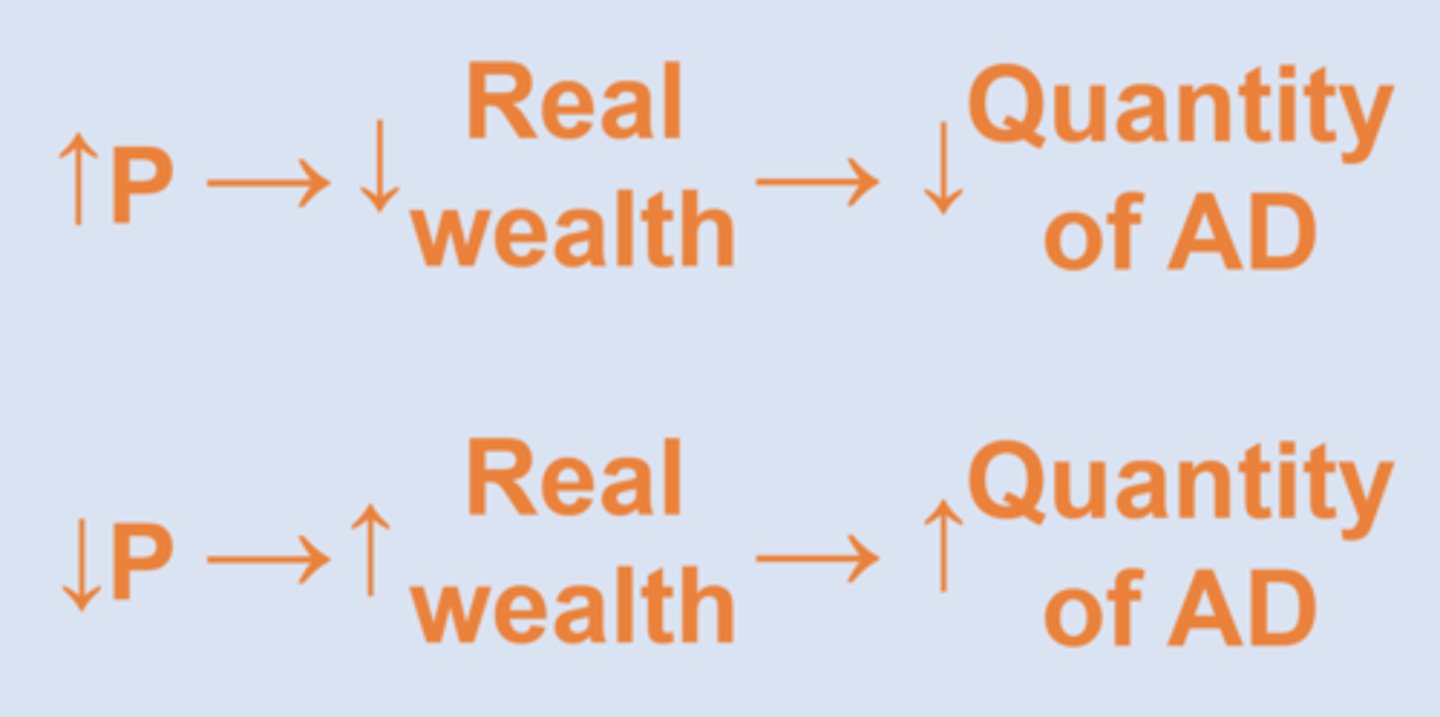
real wealth
market value of all accumulated assets (ex: bank accounts, property, stocks)
interest rate effect
⬆️ P ==> ⬇️real wealth ==> ⬇️savings ==> ⬆️interest rates ==> ⬇️investment ==> ⬇️AD
international trade effect
⬆️ P ==> ⬆️relative price of US goods ==> ⬇️exports ==> ⬆️imports ==> ⬇️NX==> ⬇️AD
Shift Factors of AD (4)
= C + I + NX + G
Movement Along the Demand Curve
results from changes in P
when p ⬆️....
C⬇️ (wealth effect)
I ⬇️ (interest rate effect)
NX⬇️ (international trade effect)
Consumption Shifts
real weath note**: here it is unrelated to changes in P

consumer confidence
how optimistic consumers are about the economy and their finances ==> measures expected future income how
Investment Shifts

Net Export Shifts
- people wealthier ==> spend more money
- value of the dollar (relative to foreign currencies)
ex: value US dollar up, demand imports up & exports down = lower NX

Bad Vibes (of a recession)
- consumer confidence down
- business confidence down
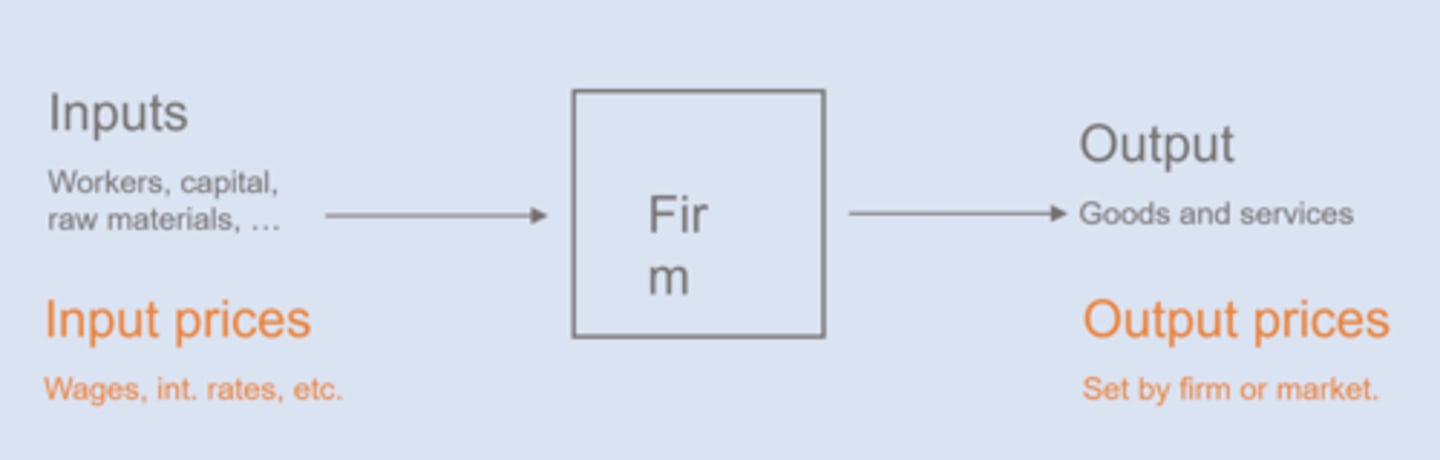
Aggregate Supply
the total supply of all final goods/services
Firm Model
Input prices tend to be stickier than output prices
ex: wage contracts
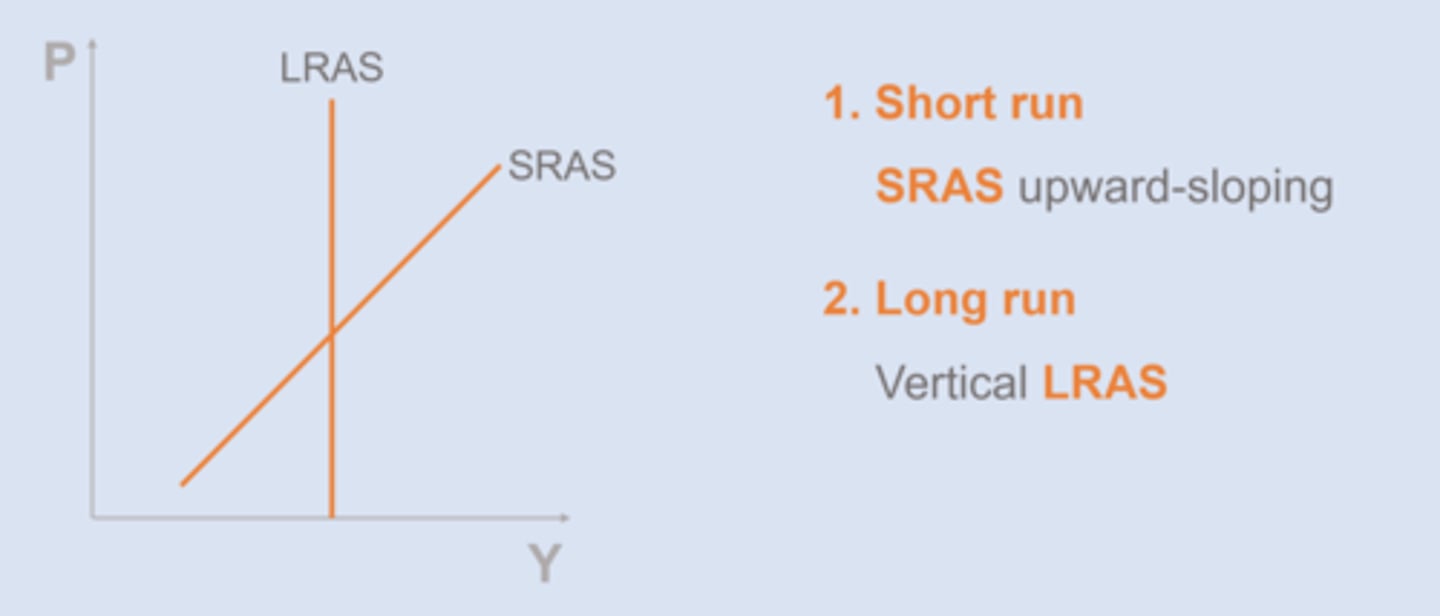
long run
A period of time sufficient for all prices to adjust
short run
A period of time in which some prices have not yet adjusted
Which prices are sticky?
SRAS curve
upward sloping (as p increases, Y increases)
why?
==> inflexible input prices (if P increases, yet input costs stay the same, revenue increases, you increase Y)
==> menu costs (if inflation occurs, yet output costs stay the same, they will seem cheaper & sell more)
==> money illusion
LRAS curve
vertical sloping (because P does not affect Y)
shifts in LRAS
related to technology, institutions, and resources (changes in Y) ==> u = u is maintained
Shifts in the LR affect the SR too (lR shift ==> SR shift)
full employment output
output level sustainable for economy in the LR (Y) ==> GDP when u = u, unrelated to P
shifts in the SRAS
1. resource/input prices change (-)
2. SR supply shocks (+/-)
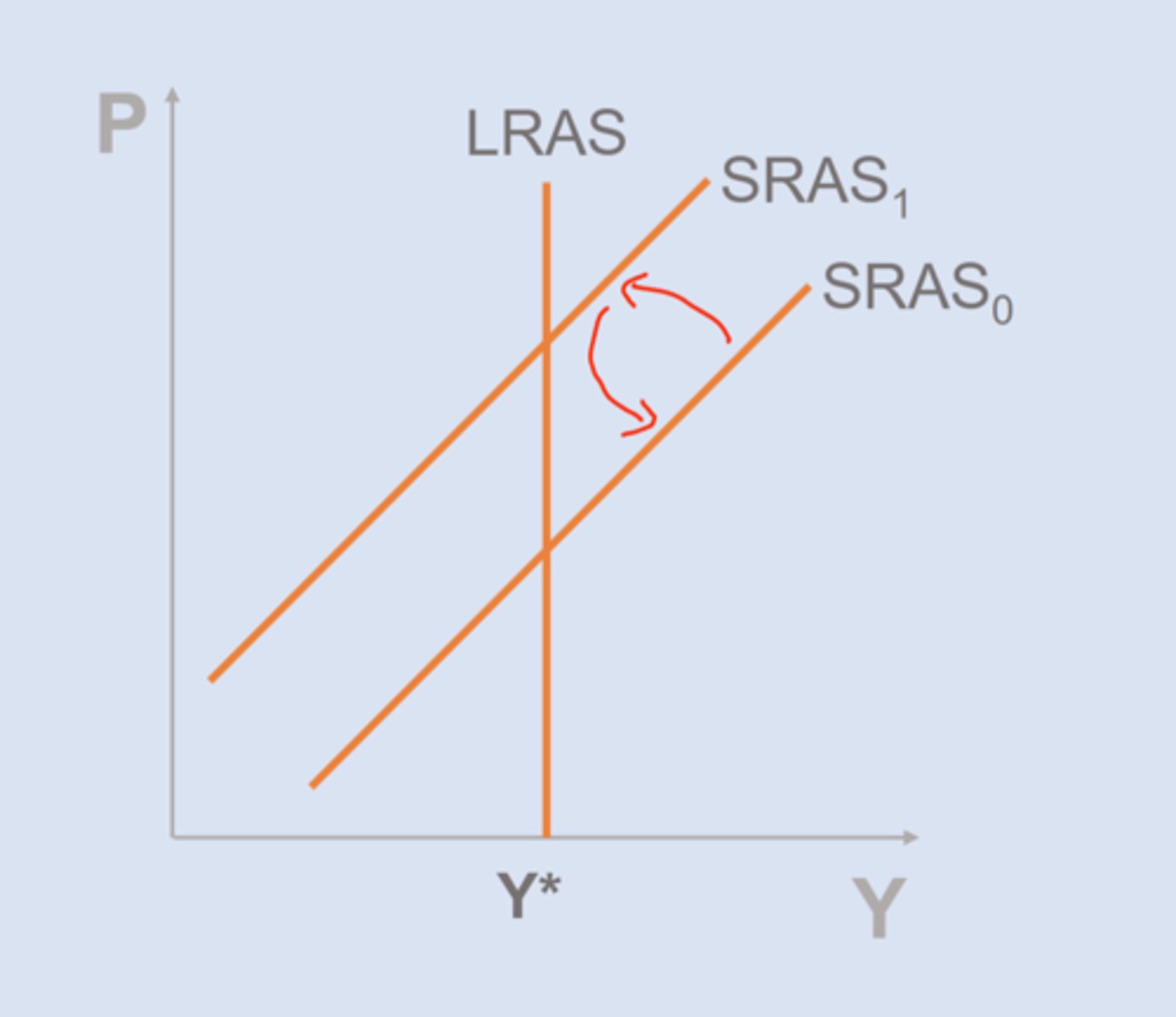
supply shocks
Temporary exogenous events that change production costs
ex: nat disasters, pandemics, droughts
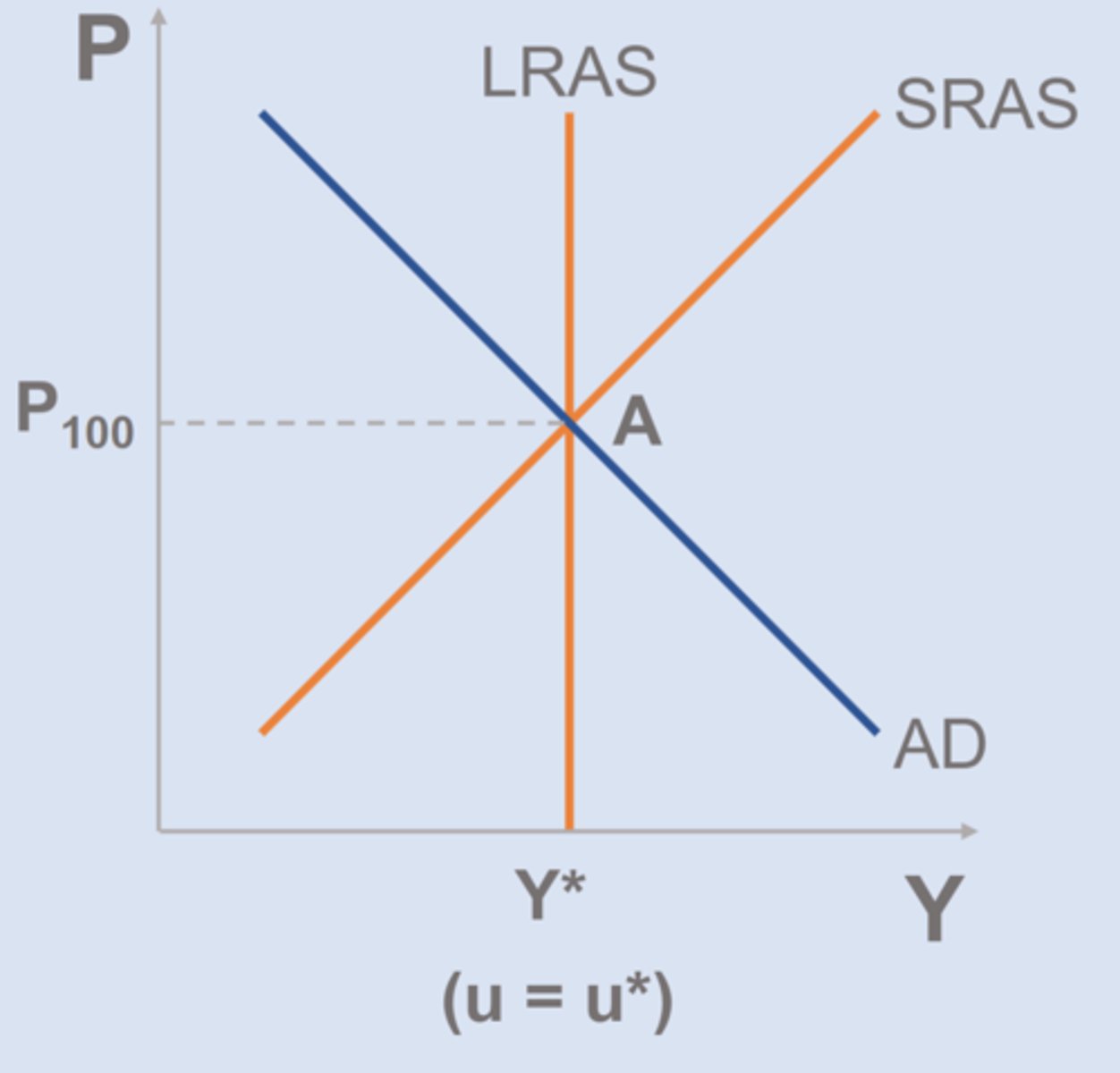
AD-AS Equilibrium
Characteristics of long run equilibrium(A):
LRAS = AD = SRAS
Y = Y*
ex: Increase in AD
1. AD shifts out (SR equilibrium b)
2. SR shifts back (LR equilibrium C)
==> input prices rise to match raise in P
In LR all prices adjust
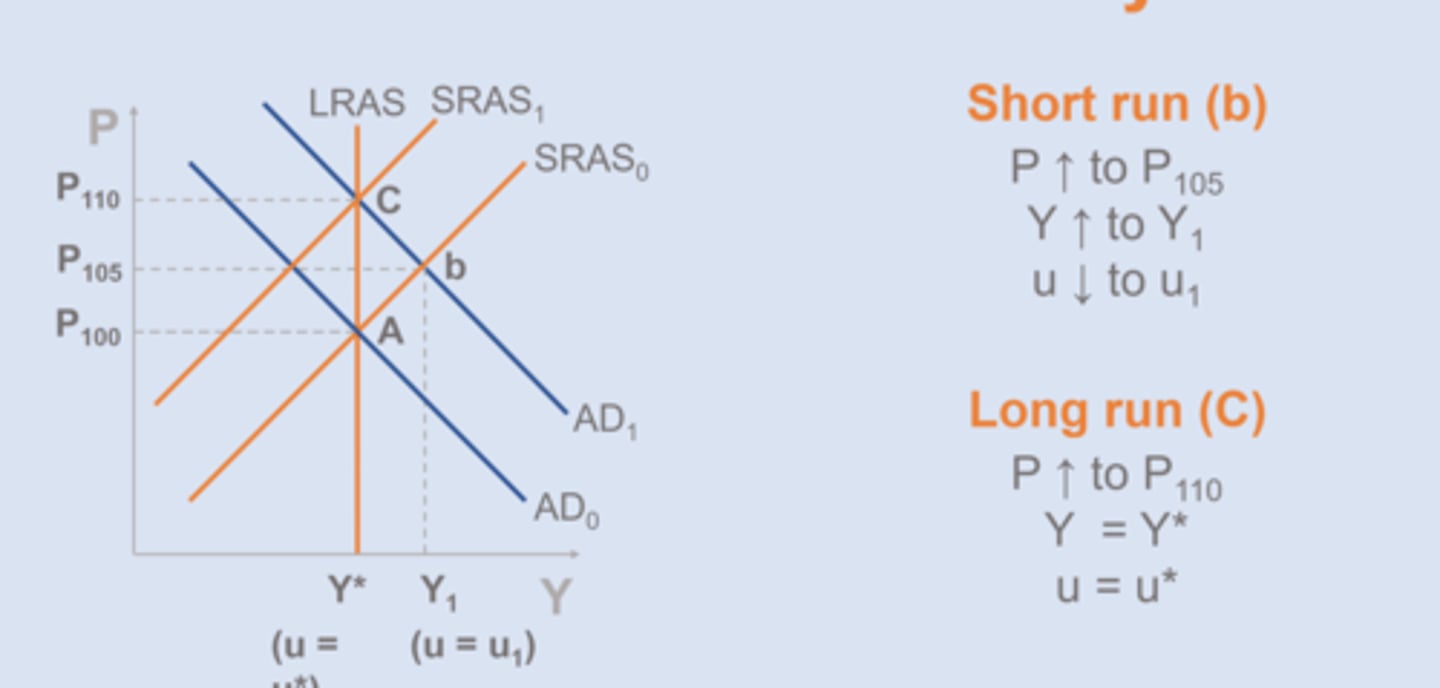
Does spending stimulate the economy?
Yes, in the SR.
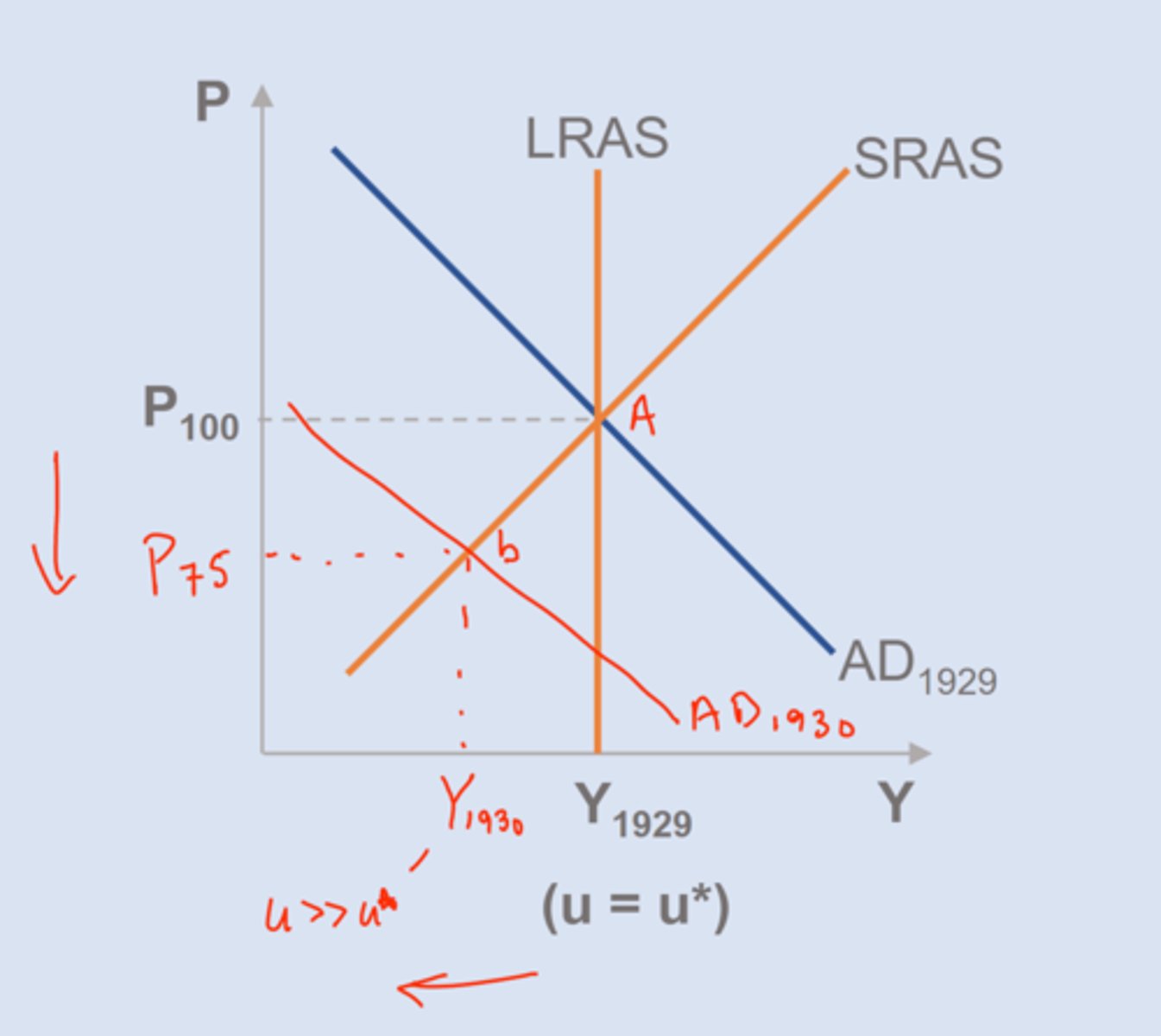
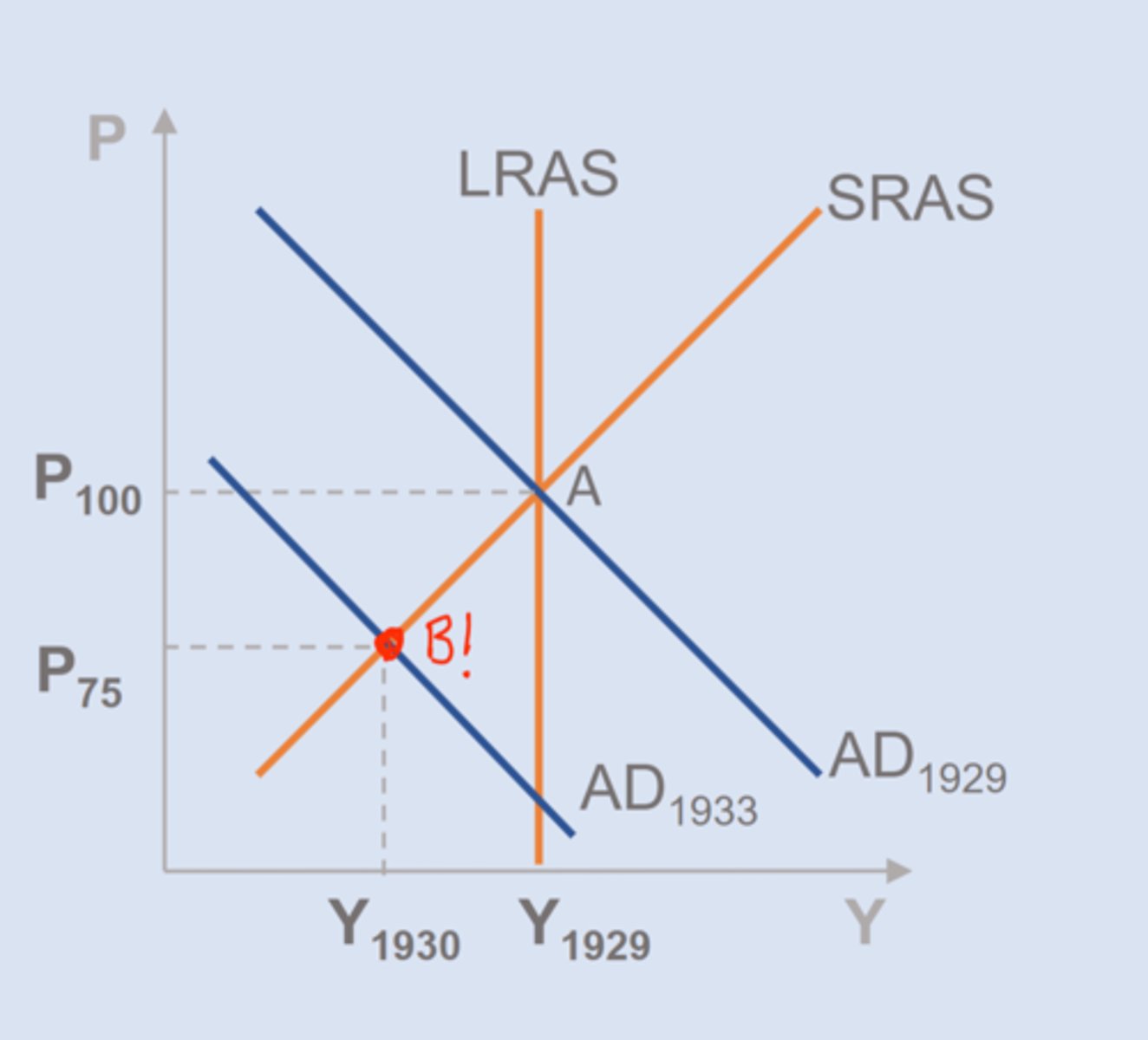
The Great Depression & Cause
AD decline (real GDP down 30%, unemployment > 15%, deflation 25%)
==> decline real wealth
==> decline in expected future income
==> gov. blunders (raise taxes, decrease money supply)
macroeconomic policy
gov acts that influence macroeconomy
fiscal policy
use of gov. budget tools (gov spending & taxes) to influence macroeconomy
monetary policy
change in money supply that influences macroeconomics
Policy during recessions
gov tries to increase AD through spending, tax cuts, expansionary policy
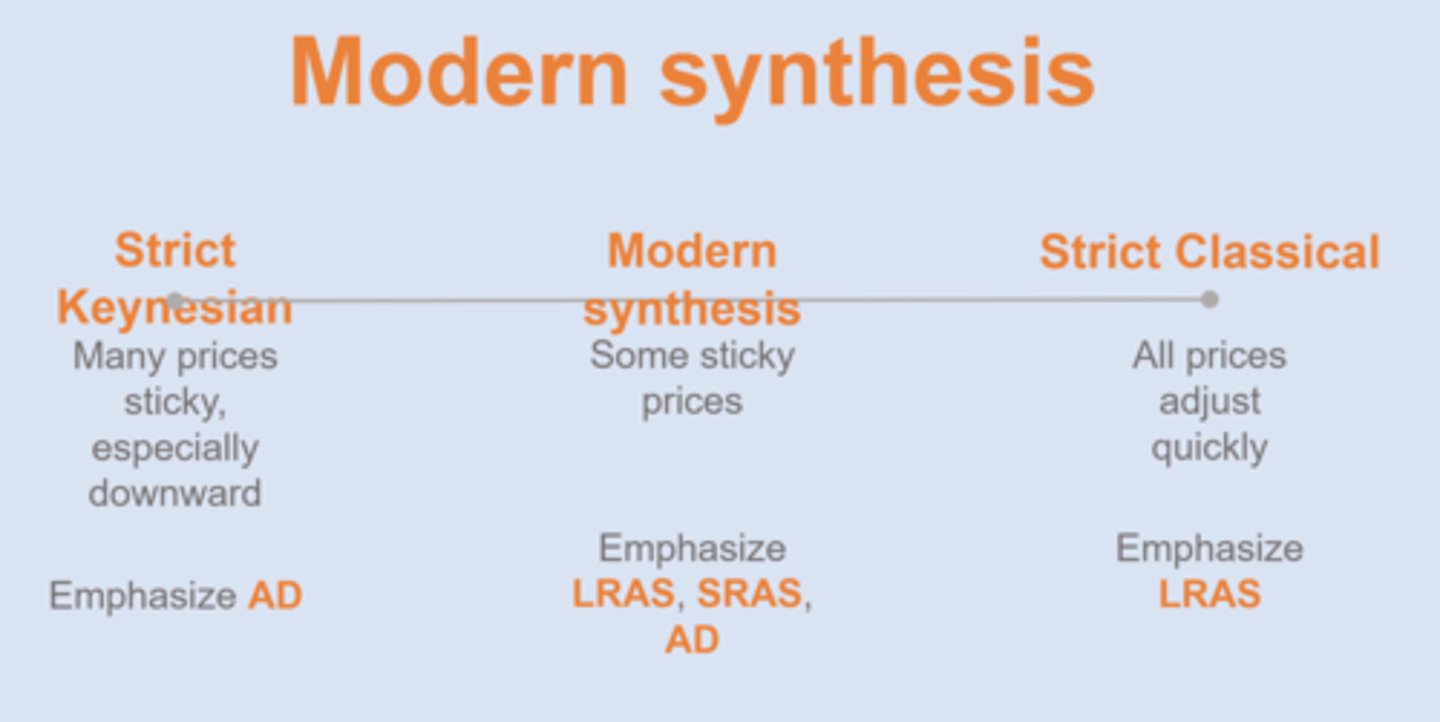
Classical Economics
- focus on spending side
- prices adjust to equilibrium
==> assumption: prices are flexible (no sticky prices)
==> implications:
- no long unemployment
- economy inherently stable
- AS = main focus (only LR)
Keynesian Economics
- focus on demand side
==> assumption: many prices take a while to adjust, especially downward ==> due to money illusion and wage contracts
==> implications:
- GDP adjusts instead ==> "if prices don't adjust, output must"
- focus shifts to AD
- economy in inherently unstable
- government must help!
Comparison of Classical, Modern, Keynesian
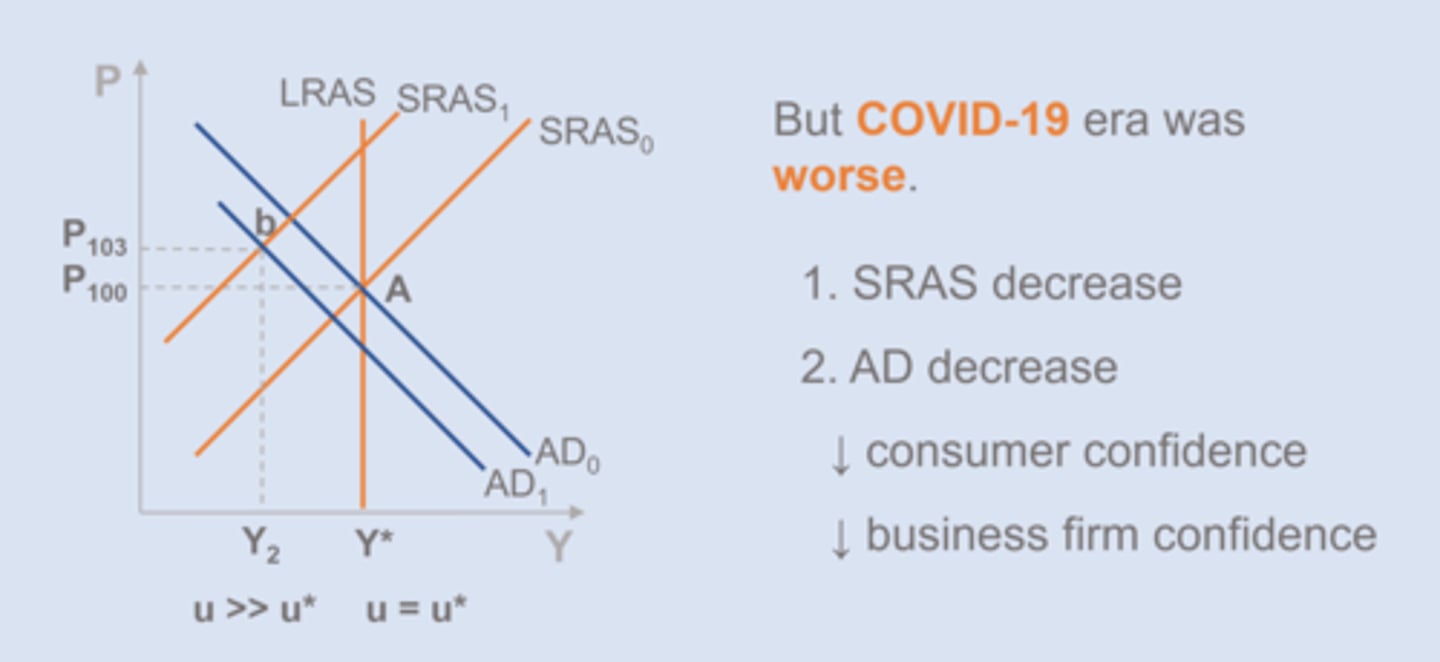
The Great Recession
Dec 2007 - Jun 2009
LOWER AD
- decline in real wealth (housing prices)
- decline in expected future income
SHIFT LEFT IN LRAS
COVID-19 Recession
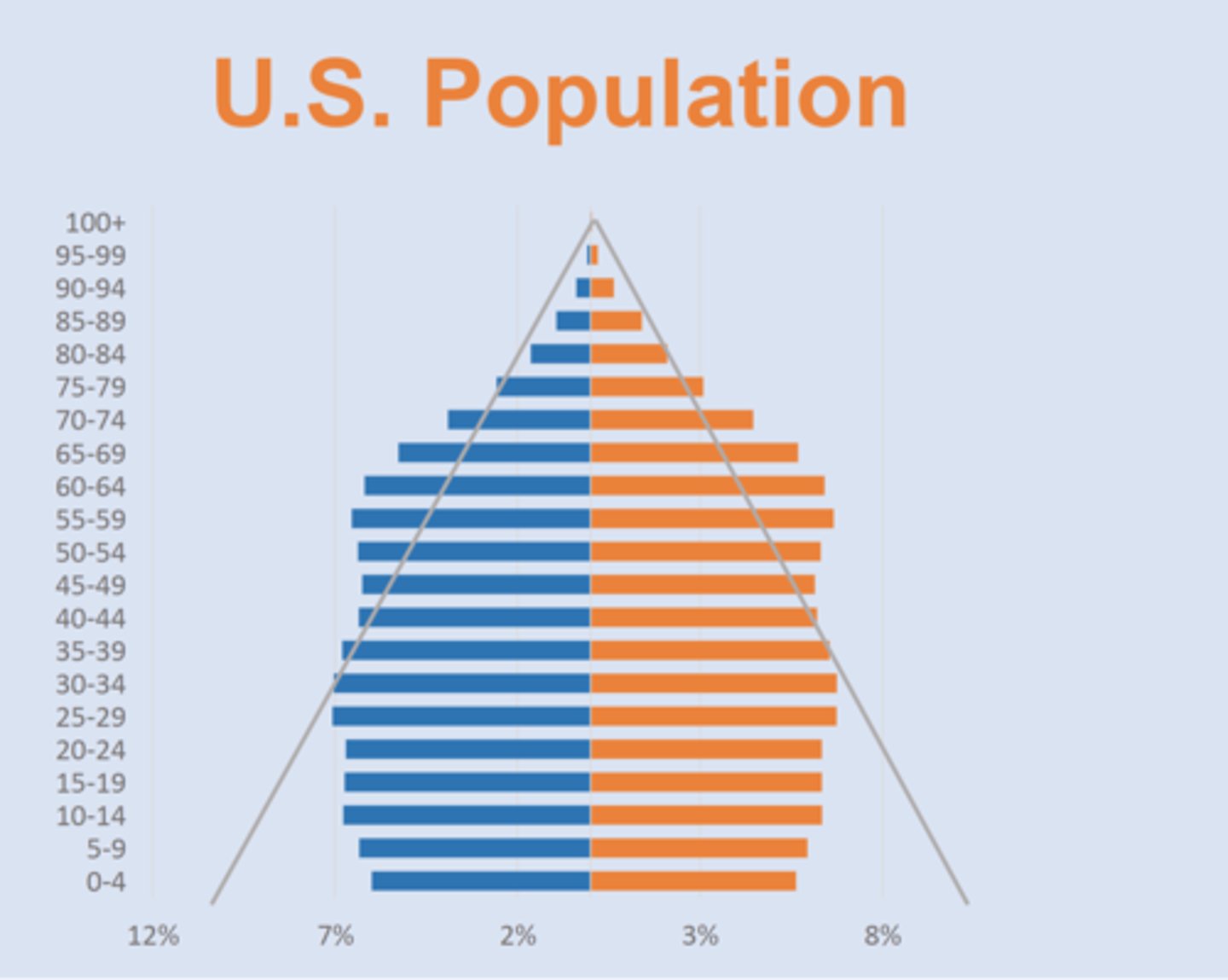
US Population Breakdown
NOT a pyramid
==> so many Boomers, longer lifespans, lower birthrate
==> concerns for fed. budget as population reaching retirement age is larger
Social Security
Retirement program run by the federal government
Medicare
Elderly health insurance program run by the federal government.
Federal Budget
The national government's plan for outlays and revenues
Outlays
The spending side of the budget ==> direct spending plus transfer payments
ex: national defense, education, highways, healthcare, retirement
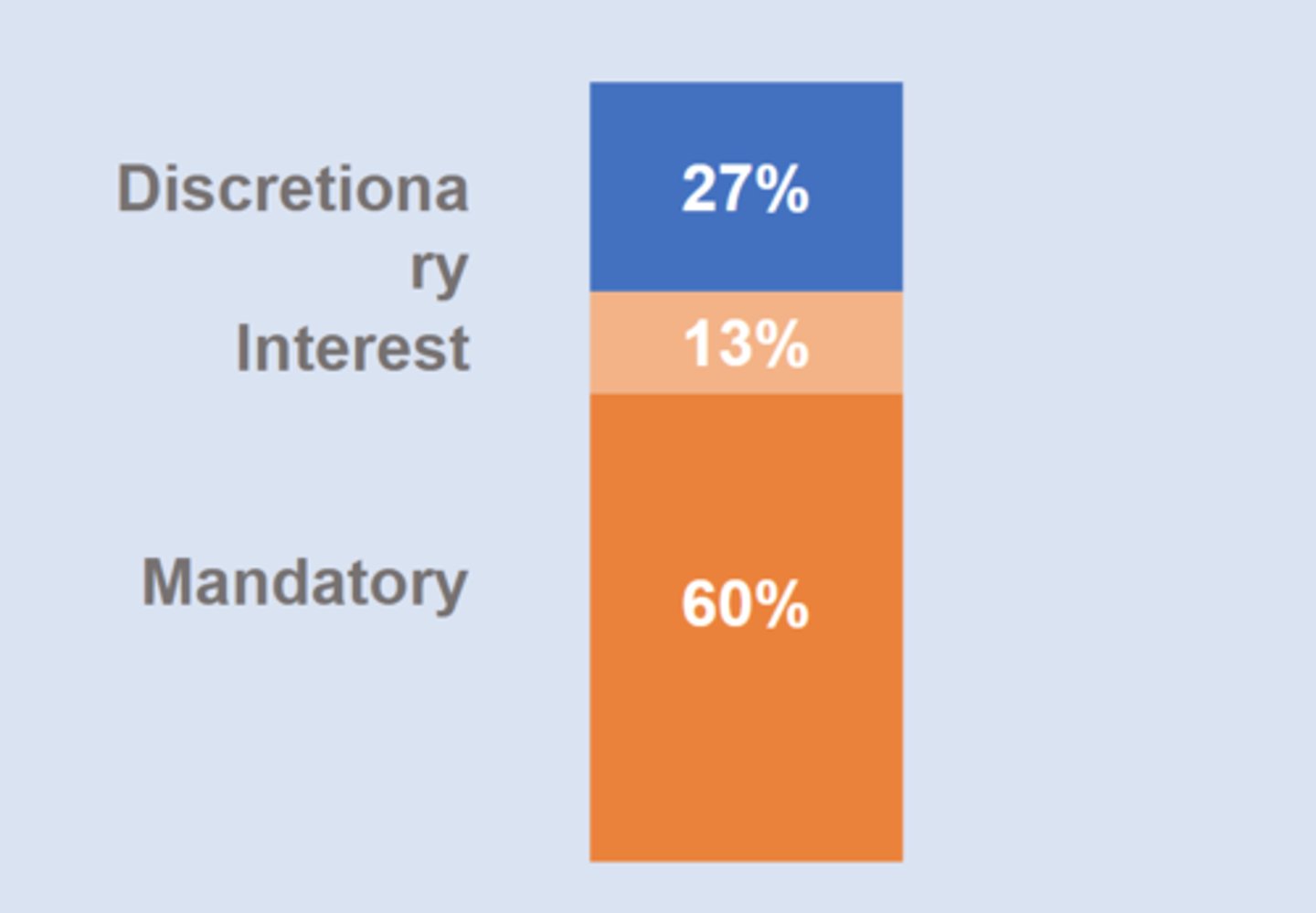
Discretionary Outlays
budget items that are adjustable on a year-to-year basis (flexible) ex: groceries/defense
Mandatory Outlays
budget items that are predetermined each year based on existing obligations
ex: rent
==> includes entitlement programs like SS and medicare
Breakdown of Outlays in Fed Budget
mandatory (SS, medicare, income assistance)
discretionary (defense and non-defense)
==> shift over time to more majority mandatory outlays
Revenues & Taxes (types of taxes)
approximately 5 trillion
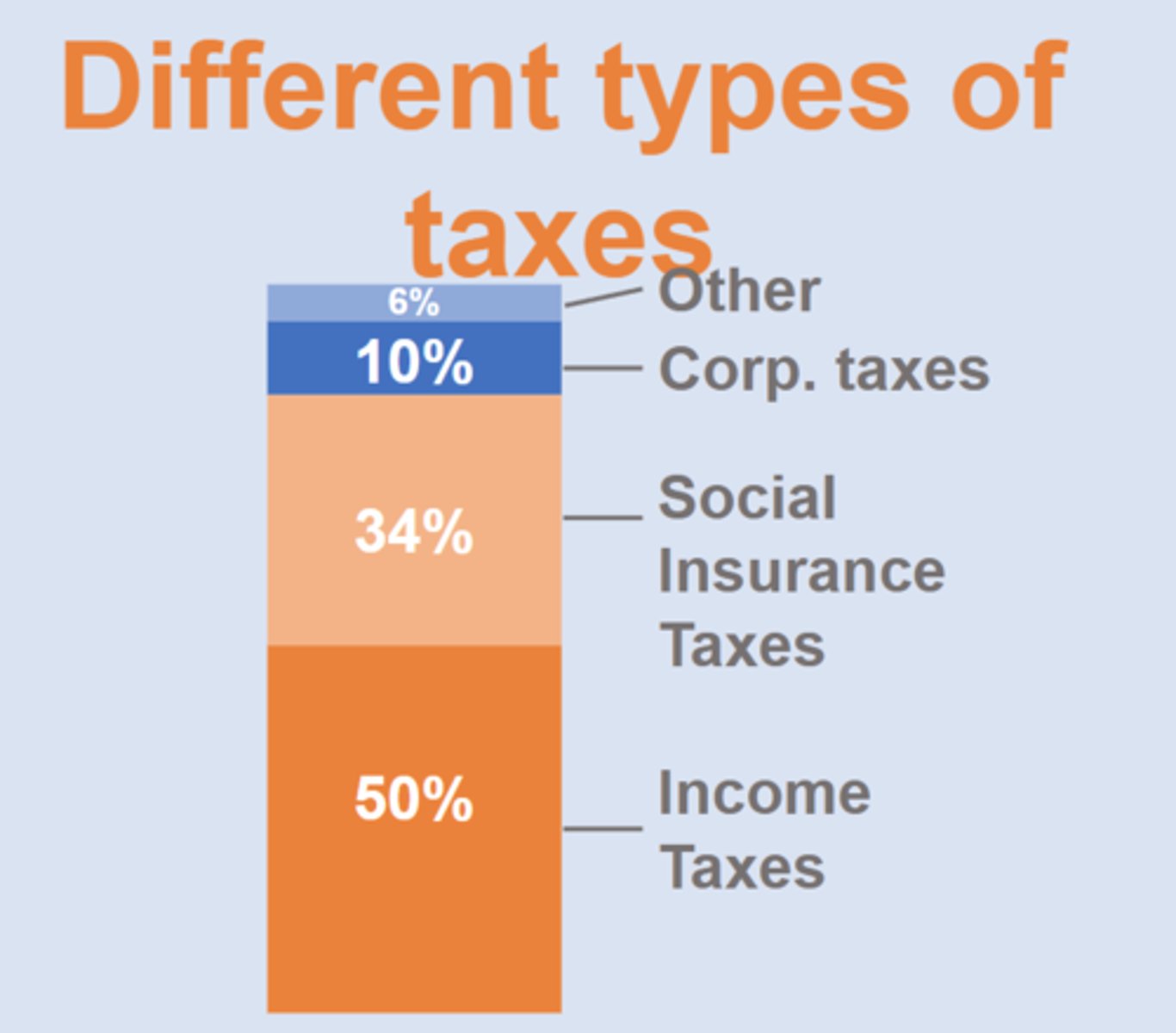
progressive income tax
tax rate increases as person's income rise
marginal tax rate
The tax rate that applies to a person's next dollar of income
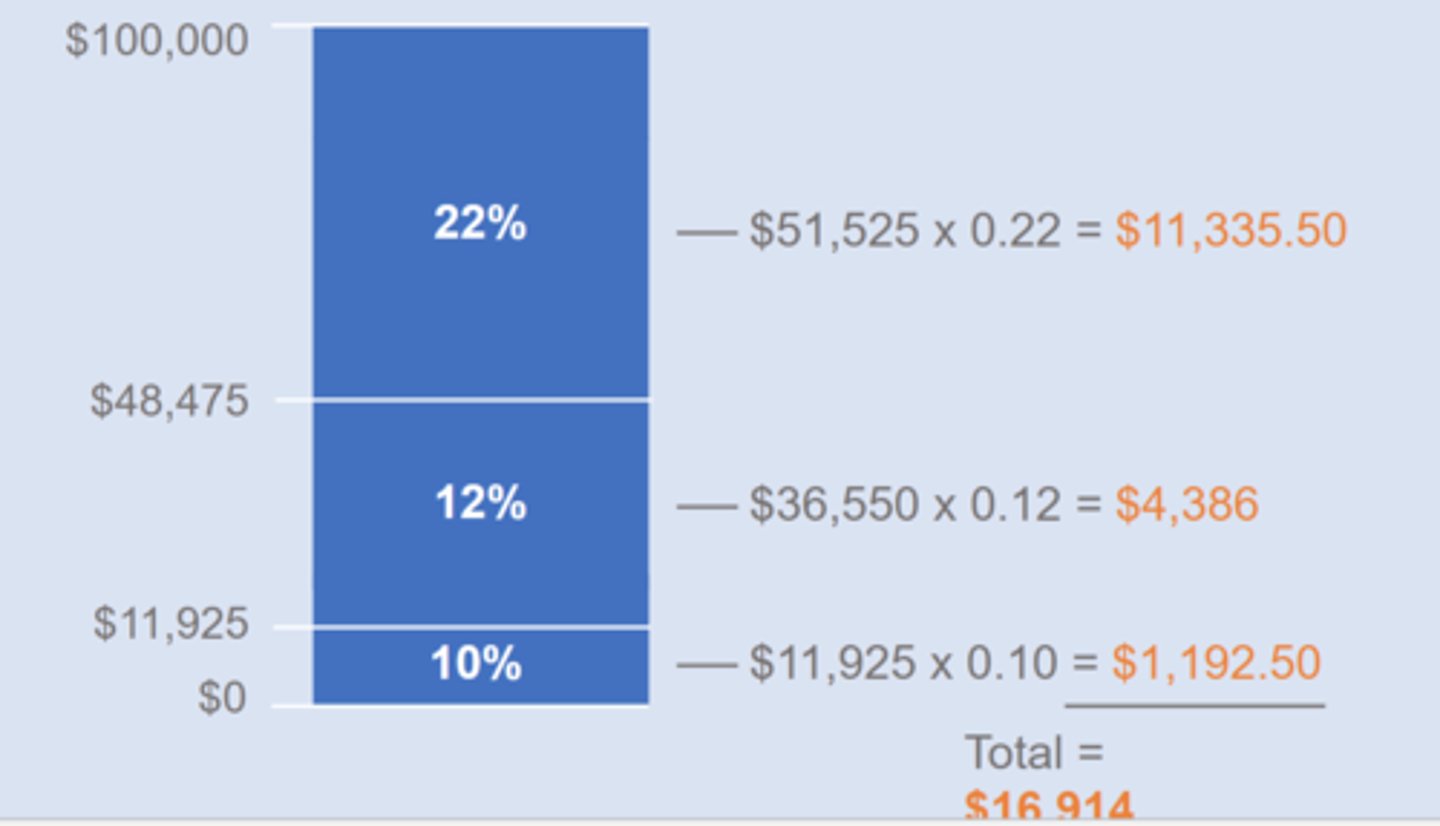
Average tax rate
ATR = T/Y
Budget Deficit
Outlays > revenue
==> applies to a particular time period (a year)
==> must borrow to make up difference
Budget Surplus
tax revenue > total outlays
National Debt
accumulation of all unpaid deficits
==> 36 trillion for US
=> projection to increase as average deficit gap projection increases (4 ==> 6)
Entitlement Reform Ideas
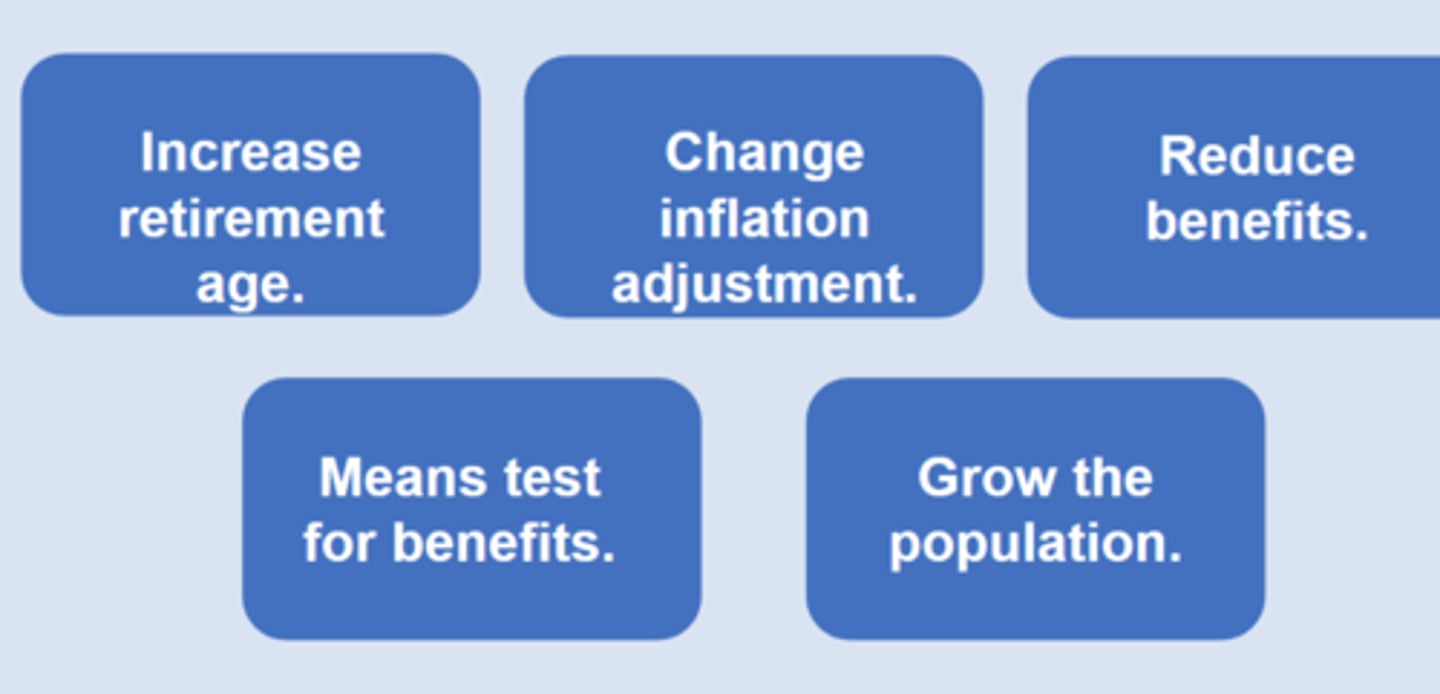
What can DOGE do?
only can control the 27% of outlays (discretionary part)