eukaryotic - gene expression
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
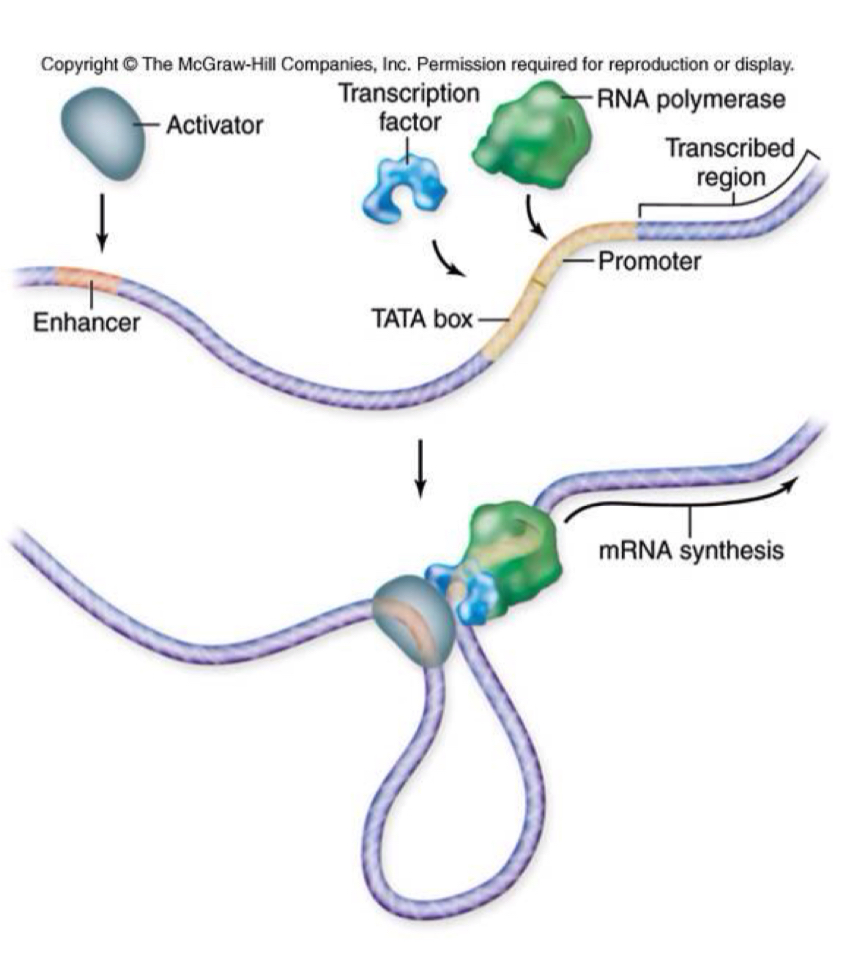
What does eukaryotic gene expression require?
controlling expression requires transcription factors
General transcription factors: needed for transcription initiation
Specific transcription factors/activators: increase transcription by binding to enhancers, certain DNA sequences
Process of eukaryotic gene expression - during transcription
general transcription factors binds to promoter
RNA polymerase II binds to promoter to begin transcription at start site
Enhancers: specific DNA sequences where specific transcription factors bind
Post transcriptional regulation
control of gene expression after transcription using specific mechanisms
RNA interference: degradation or folding
Alternative splicing
Control of gene expression usually involves
Control of transcription initiation
RNA interference
post transcriptional regulation
Micro-RNAs bind to mRNA to prevent translation, cause mRNA to fold, blocking ribosome from attaching, cannot make protein
Small interfering RNAs degrade particular mRNA before translation
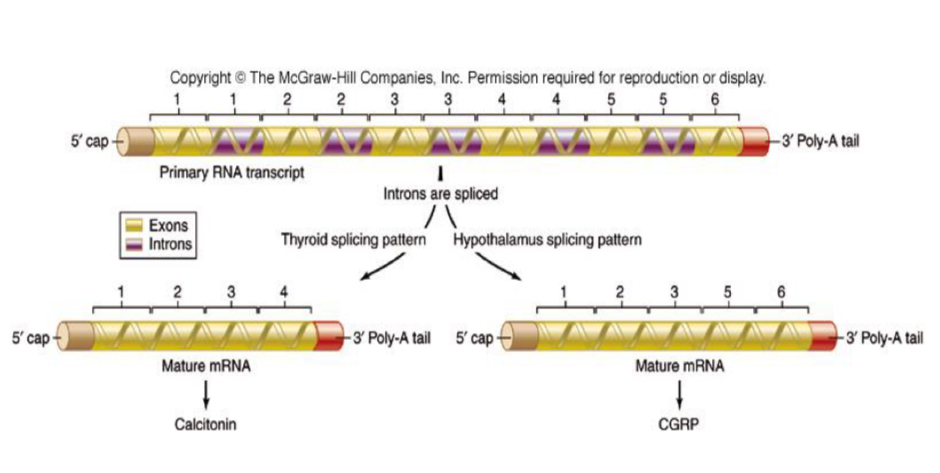
Alternative splicing
Post transcriptional regulation
Splicing: cutting out introns to produce mature mRNA to be translated
Alternative splicing allows multiple proteins to be made from one mRNA
Spliceosome Recognizes different splice sites in different tissue types
Different polypeptides products from same gene
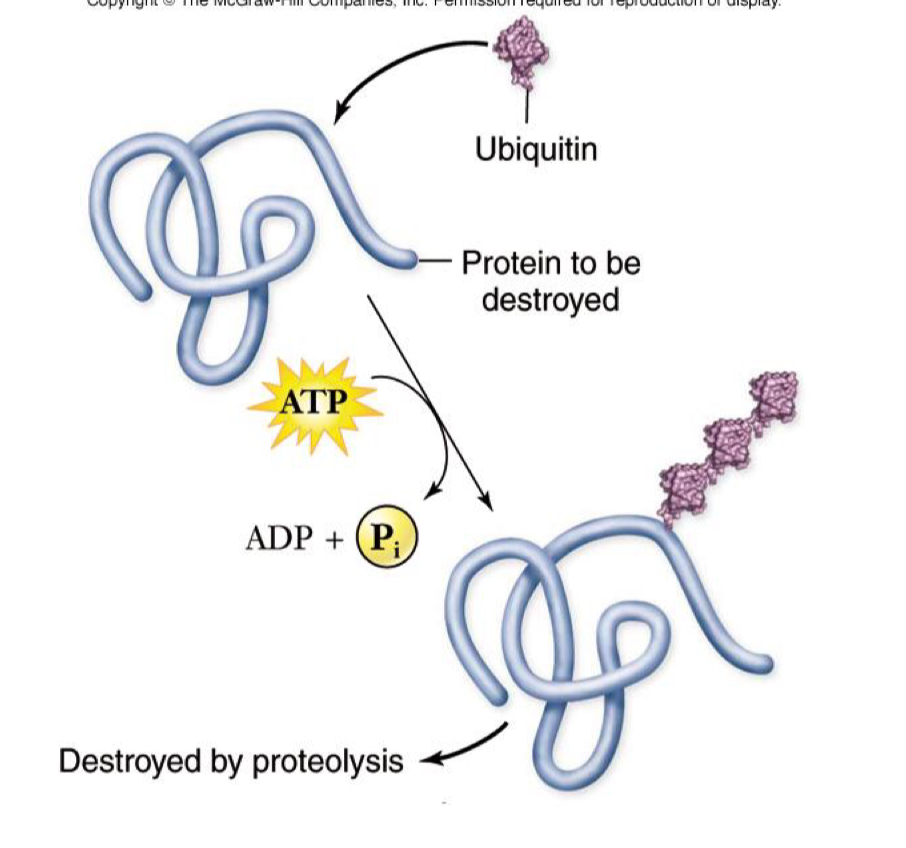
Protein degradation
post translational regulation
Proteins produced and degraded continually in the cell
Not needed protein tagged with ubiquitin
Proteins marked are degraded at proteasome
Allows you to reuse amino acids for something the cell needs